|
[1]
|
Maciejowski J M. Predictive Control With Constraints. London: Prentice Hall, 2001.
|
|
[2]
|
Qin S J, Badgwell T A. A survey of industrial model predictive control technology. Control Engineering Practice, 2003, 11(7):733-764. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00186-7
|
|
[3]
|
Grüne L, Pannek J. Nonlinear Model Predictive Control: Theory and Algorithms. New York: Springer, 2011.
|
|
[4]
|
席玉庚. 预测控制. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013.Xi Yu-Geng. Predictive Control. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013.
|
|
[5]
|
陈虹. 模型预测控制. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.Chen Hong. Model Predictive Control. Beijing: China Science Press, 2013.
|
|
[6]
|
Rawlings J B, Mayne D Q, Diehl M. Model Predictive Control: Theory, Computation, and Design (2nd Edition). Madison, Wisconsin: Nob Hill Publishing, LLC, 2017.
|
|
[7]
|
Yu S, Reble M, Chen H, Allgower F. Inherent robustness properties of quasi-infinite horizon nonlinear model predictive control. Automatica, 2014, 50(9):2269-2280. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.07.014
|
|
[8]
|
Allan D A, Bates C N, Risbeck M J, Rawlings J B. On the inherent robustness of optimal and suboptimal nonlinear MPC. Systems & Control Letters, 2017, 106:68–78.
|
|
[9]
|
Grüne L. Analysis and design of unconstrained nonlinear MPC schemes for finite and infinite dimensional systems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2010, 48: 1206–1228
|
|
[10]
|
Chen H, Allgower F. A quasi-infinite horizon nonlinear model predictive control scheme with guaranteed stability. Automatica, 1998, 34(10):1205–1217. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(98)00073-9
|
|
[11]
|
Mayne D Q, Rawlings J B. Constrained model predictive control: stability and optimality.Automatica, 2000, 36(6):789–814. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00214-9
|
|
[12]
|
Mayne D Q. An apologia for stabilising terminal conditions in model predictive control. International Journal of Control, 2013, 86(11):2090–2095. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2013.813647
|
|
[13]
|
Yu S, Qu T, Xu F, Chen H. Stability of finite horizon model predictive control with incremental input constraints. Automatica, 2017, 79:265–272. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.01.040
|
|
[14]
|
Rajhans C, Patwardhan S C, Pillai H K. Discrete time formulation of quasi infinite horizon nonlinear model predictive control scheme with guaranteed stability. In IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2017, 50(1):7181–7186. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.602
|
|
[15]
|
于树友, 陈虹, 张鹏, 李学军. 一种基于LMI的非线性模型预测控制终端域优化方法.自动化学报, 2008, 34(7):798-804.Yu S, Chen H, Zhang P, Li X J. An LMI optimization approach for enlarging the terminal region of NMPC, Acta Automatica Sinca, 2008, 34, (7):798–804.
|
|
[16]
|
Cannon M, Deshmukh V, Kouvaritakis B. Nonlinear model predictive control with polytopic invariant sets. Automatica, 2003, 39:1487–1494. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(03)00128-6
|
|
[17]
|
Pluymers B, Roobrouck L, Buijs J, Suykens J, Moor B. Constrianed linear MPC with time-varying terminal cost unsing convex combinations. Automatica, 2005, 41(5):831-837. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.11.023
|
|
[18]
|
Fitri I R, Kim J S, Yu S, Lee Y I. Computation of feasible and invariant sets for interpolationbased MPC. International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems,
|
|
[19]
|
Mircea L, Spinu V. Finite-step terminal ingredients for stabilizing model predictive control. In IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2015, 48(23):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.11.256
|
|
[20]
|
Lazar M, Tetteroo M. Computataion of terminal sets and sets for discrete time nonlinear mpc. IFAC-Papers OnLine 2018, 51(20):141–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.11.006
|
|
[21]
|
Rajhans C, Griffith D, Patwardhan S C, Biegler L T, Pillai H K. Two approaches for terminal region characterization in discrete time quasi-infinite horizon NMPC. In: Proceedings of the 6th IFAC Conference on Nonlinear Model Predictive Control. Madison, WL, USA: IFAC, 2018. 19−22
|
|
[22]
|
Rajhans C, Griffith D, Patwardhan S C, Biegler L T, Pillai H K. Terminal region characterization and stability anslysis of discrete time quasi-infinite horizon nonlinear model predictive control.Journal of Process Control, 2019, 83:30–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2019.08.002
|
|
[23]
|
Boyd S, Ghaoui L E, Feron E, Balakishnan V. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory. Philadelphia: SIAM, 1994.
|
|
[24]
|
Kothare M V, Balakrishnan V, Morari M. Robust constrained model predictive control using linear matrix inequalities. Automatica, 1996, 32(10):1361–1379. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(96)00063-5
|
|
[25]
|
Oliveira M, Bernussou J, Geromel J C. A new discrete-time robust stability condition. Systems & Control Letters, 1999, 37(4):261-265.
|
|
[26]
|
Cuzzola F, Geromel J C, Morari M. An improved approach for constrained robust model predictive control. Automatica, 2002, 38(7):1183–1189. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(02)00012-2
|
|
[27]
|
Vandenberghe L, Boyd S, Wu S P. Determinant Maximization with Linear Matrix Inequality Constraints. Siam Journal on Matrix Analysis & Applications, 1998, 19(2):499-533.
|
|
[28]
|
Nesterov Y, Nemirovsky A. Interior Point Polynomial Methods in Convex Programming. Philadelphia, USA: SIAM Publications, 1994.
|
|
[29]
|
Bohm C, Raff T, Findeisen R, Allgower F. Calculating the terminal region of NMPC for Lure systems via LMIs. In: Proceedings of the 2008 American Control Conference. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1127−1132
|
|
[30]
|
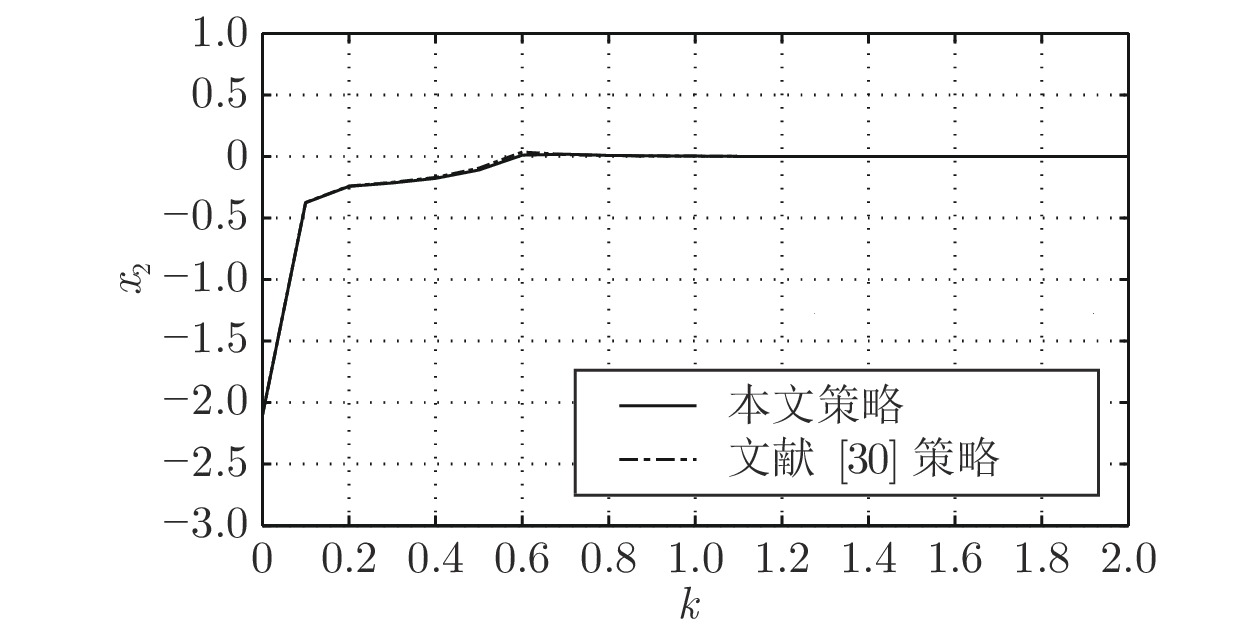
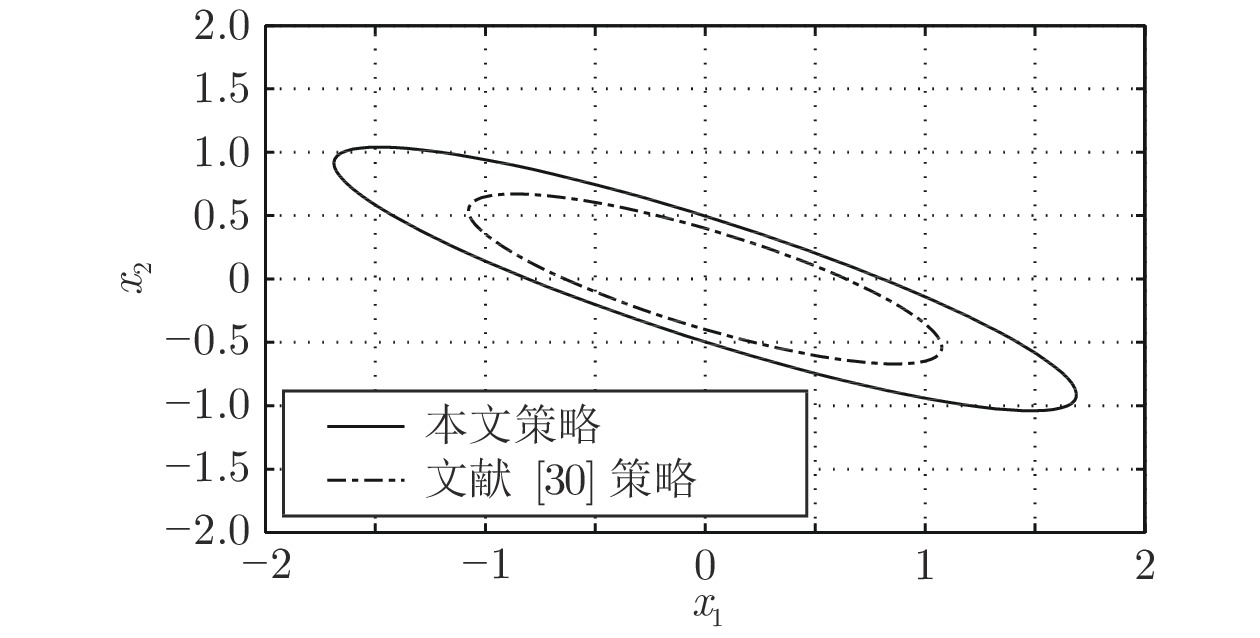
Bohm C, Yu S, Allgower F. Predictive control for constrained discrete-time periodic systems using a time-varying terminal region. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2009, 42(13):537-542. doi: 10.3182/20090819-3-PL-3002.00093
|




 下载:
下载: