-
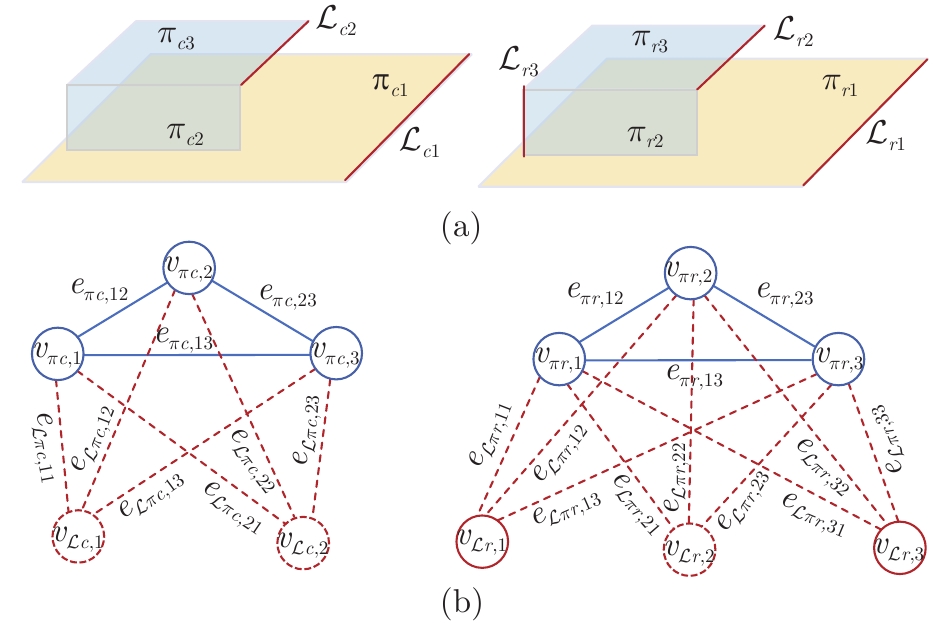
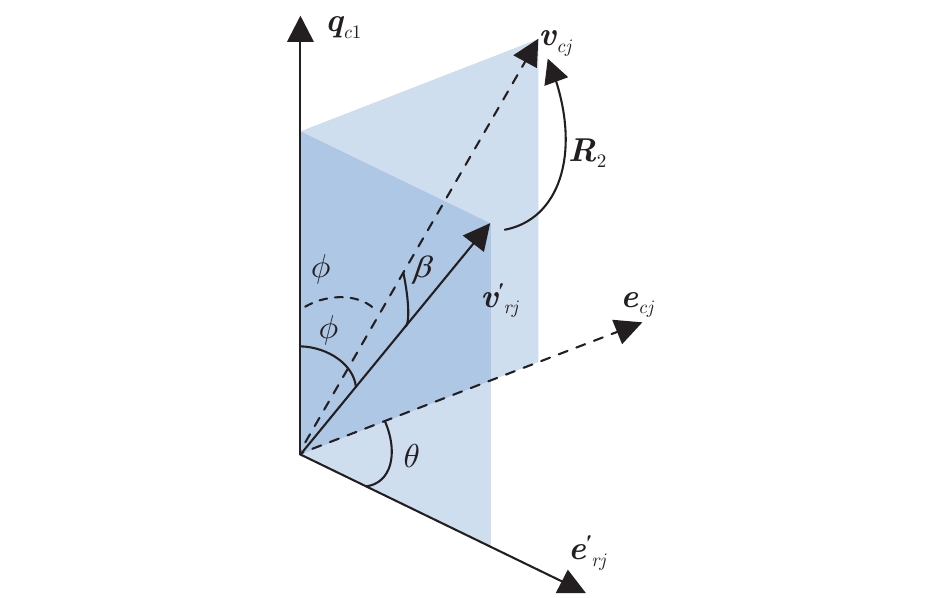
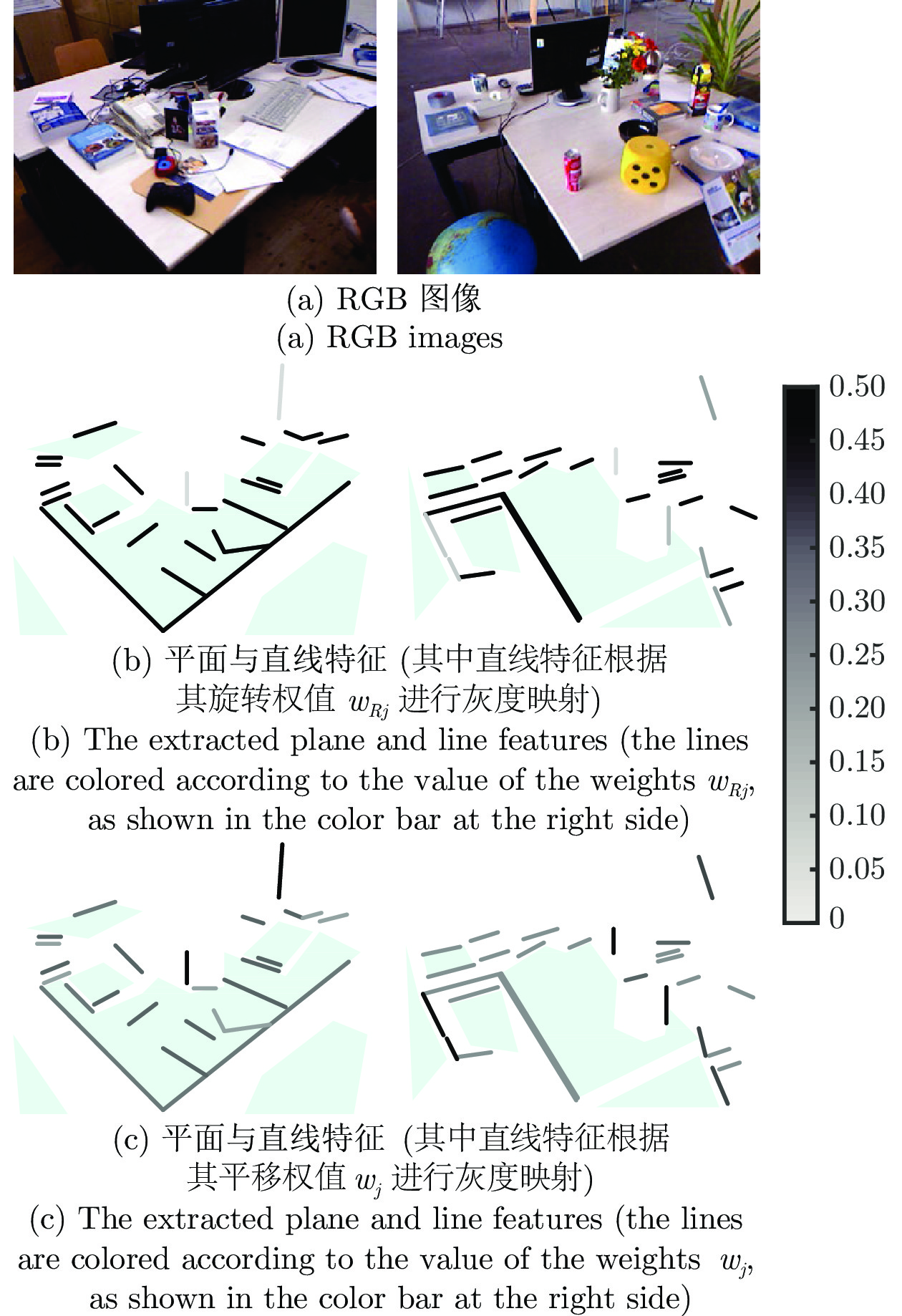
摘要: 针对利用平面特征计算RGB-D相机位姿时的求解退化问题, 提出平面和直线融合的RGB-D视觉里程计(Plane-line-based RGB-D visual odometry, PLVO). 首先, 提出基于平面−直线混合关联图(Plane-line hybrid association graph, PLHAG)的多特征关联方法, 充分考虑平面和平面、平面和直线之间的几何关系, 对平面和直线两类几何特征进行一体化关联. 然后, 提出基于平面和直线主辅相济、自适应融合的RGB-D相机位姿估计方法. 具体来说, 鉴于平面特征通常比直线特征具有更好的准确性和稳定性, 通过自适应加权的方法, 确保平面特征在位姿计算中的主导作用, 而对平面特征无法约束的位姿自由度(Degree of freedom, DoF), 使用直线特征进行补充, 得到相机的6自由度位姿估计结果, 从而实现两类特征的融合, 解决了单纯使用平面特征求解位姿时的退化问题. 最后, 通过公开数据集上的定量实验以及真实室内环境下的机器人实验, 验证了所提出方法的有效性.
-
关键词:
- RGB-D视觉里程计 /
- 平面−直线融合 /
- 机器人定位 /
- 自适应融合 /
- 多特征联合关联
Abstract: A plane-line-based RGB-D visual odometry (PLVO) is proposed to solve the degenerate problem in the pose estimation of an RGB-D camera using plane features. First, the plane-line hybrid association graph (PLHAG) is proposed to associate two types of geometric features. Planes and lines are associated in an integrated framework, which fully exploits the geometric relationships between two planes and between a plane and a line, respectively. Then, the pose of an RGB-D camera is estimated based on the adaptive fusion of planes and lines. Generally speaking, the plane features are more accurately and stably extracted than the line features. As a result, in our method, the planes dominate the calculation of the camera pose through an adaptive weighting algorithm. As for the degrees of freedom (DoFs) of the pose that cannot be constrained by planes, the line features are supplementarily used to obtain the full 6 DoF pose estimation of the camera. Thus, the fusion of two types of features is achieved and the degenerate problem using only plane features is solved. Various experiments on public benchmarks as well as in real-world environments demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed method. -
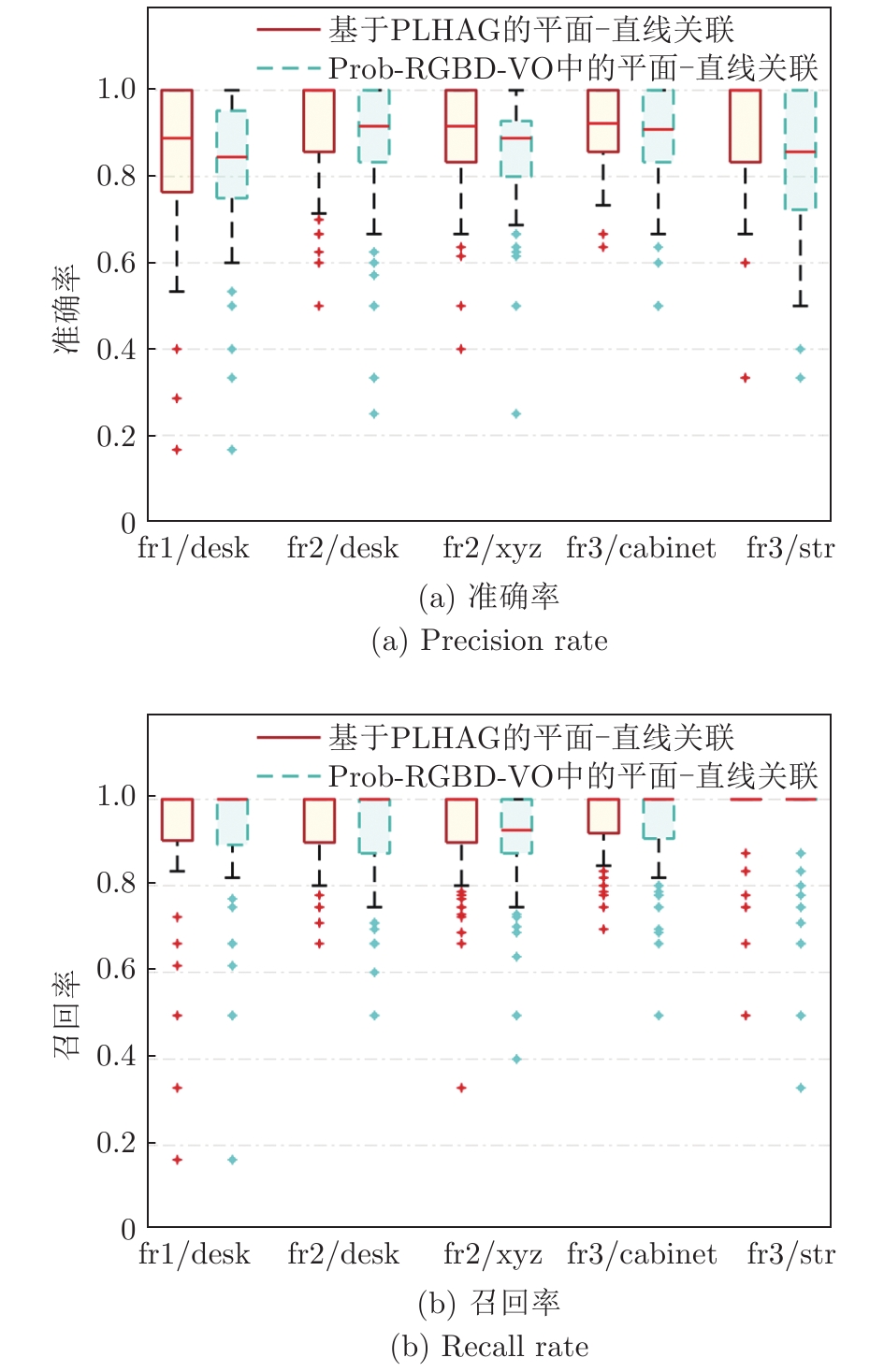
表 1 不同VO算法相对位姿均方根误差对比
Table 1 Comparison of RMSE of RPE for different VO methods
VO 算法 plane-seg-VO Prob-RGBD-VO Canny-VO STING-VO PLVO fr1/desk — 0.023 m/1.70° 0.031 m/1.92° 0.025 m/1.90° 0.021 m/1.37° fr2/desk — — 0.008 m/0.45° 0.048 m/1.75° 0.008 m/0.42° fr2/xyz 0.005 m/0.36° — 0.004 m/0.31° 0.004 m/0.34° 0.004 m/0.30° fr2/360_hemisphere — 0.069 m/1.10° 0.108 m/1.09° 0.092 m/1.47° 0.066 m/0.99° fr3/cabinet 0.034 m/2.04° 0.039 m/1.80° 0.036 m/1.63° 0.011 m/1.02° 0.029 m/1.24° fr3/str_ntex — 0.019 m/0.70° 0.027 m/0.59° 0.014 m/0.83° 0.012 m/0.49° fr3/str_tex — — 0.013 m/0.48° 0.021 m/0.59° 0.013 m/0.45° fr3/office — — 0.010 m/0.50° 0.009 m/0.50° 0.007 m/0.47° 表 2 不同VO算法绝对轨迹均方根误差对比(m)
Table 2 Comparison of RMSE of ATE for different VO methods (m)
VO 算法 Prob-RGBD-VO Canny-VO STING-VO PLVO fr1/desk 0.040 0.044 0.041 0.038 fr2/desk — 0.037 0.098 0.044 fr2/xyz — 0.008 0.010 0.008 fr2/360_hemisphere 0.203 0.079 0.122 0.105 fr3/cabinet 0.200 0.057 0.070 0.052 fr3/str_ntex 0.054 0.031 0.040 0.030 fr3/str_tex — 0.013 0.028 0.013 fr3/office — 0.085 0.089 0.081 表 3 相对位姿均方根误差消融实验结果
Table 3 Results of ablation experiment in term of the RMSE of RPE
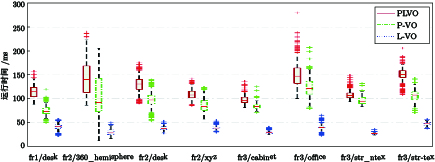
VO 算法 PLVO PLVO (无加权) L-VO P-VO* fr1/desk 0.021 m/1.37° 0.041 m/1.52° 0.039 m/1.56° 0.042 m/1.95° fr2/desk 0.008 m/0.42° 0.011 m/0.42° 0.018 m/0.52° 0.016 m/0.55° fr2/xyz 0.004 m/0.30° 0.005 m/0.34° 0.007 m/0.37° 0.004 m/0.27° fr2/360_hemisphere 0.066 m/0.99° 0.096 m/1.20° 0.162 m/1.22° 0.118 m/1.42° fr3/cabinet 0.029 m/1.24° 0.054 m/1.44° 0.097 m/1.70° 0.029 m/1.71° fr3/str_ntex 0.012 m/0.49° 0.013 m/0.55° 0.015 m/0.48° 0.013 m/0.53° fr3/str_tex 0.013 m/0.45° 0.015 m/0.49° 0.016 m/0.47° 0.023 m/0.75° fr3/office 0.007 m/0.47° 0.012 m/0.57° 0.016 m/0.59° 0.014 m/0.62° * 在P-VO实验中, 出现位姿求解退化情况的位姿估计没有参与RPE的计算. 表 4 P-VO中位姿求解退化情况所占比例
Table 4 Ratio of the degenerate cases in P-VO
fr1/desk fr2/desk fr2/xyz fr2/360_hemisphere fr3/cabinet fr3/str_ntex fr3/str_tex fr3/office Ratio (%) 73.3 60.3 46.3 91.9 83.4 37.9 40.4 17.3 -
[1] 丁文东, 徐德, 刘希龙, 张大朋, 陈天. 移动机器人视觉里程计综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 385-400Ding Wen-Dong, Xu De, Liu Xi-Long, Zhang Da-Peng, Chen Tian. Review on visual odometry for mobile robots. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 385-400 [2] 王楠, 马书根, 李斌, 王明辉, 赵明扬. 震后建筑内部层次化SLAM的地图模型转换方法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(10): 1723-1733Wang Nan, Ma Shu-Gen, Li Bin, Wang Ming-Hui, Zhao Ming-Yang. A model transformation of map representation for hierarchical SLAM that can be used for after-earthquake buildings. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(10): 1723-1733 [3] 杨晶东, 杨敬辉, 洪炳熔. 一种有效的移动机器人里程计误差建模方法. 自动化学报, 2009, 35(2): 168-173 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00168Yang Jing-Dong, Yang Jing-Hui, Hong Bing-Rong. An efficient approach to odometric error modeling for mobile robots. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(2): 168-173 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00168 [4] 季秀才, 郑志强, 张辉. SLAM问题中机器人定位误差分析与控制. 自动化学报, 2008, 34(3): 323-330Ji Xiu-Cai, Zheng Zhi-Qiang, Zhang Hui. Analysis and control of robot position error in SLAM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(3): 323-330 [5] Sun Q X, Yuan J, Zhang X B, Sun F C. RGB-D SLAM in indoor environments with STING-based plane feature extraction. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(3): 1071-1082 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2773576 [6] 韩锐, 李文锋. 一种基于线特征的SLAM算法研究. 自动化学报, 2006, 32(1): 43-46Han Rui, Li Wen-Feng. Line-feature-based SLAM algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 32(1): 43-46 [7] 俞毓锋, 赵卉菁, 崔锦实, 査红彬. 基于道路结构特征的智能车单目视觉定位. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 725-734Yu Yu-Feng, Zhao Hui-Jing, Cui Jin-Shi, Zha Hong-Bin. Road structural feature based monocular visual localization for intelligent vehicle. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 725-734 [8] Lee T, Kim C, Cho D D. A monocular vision sensor-based efficient SLAM method for indoor service robots. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(1): 318-328 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2826471 [9] Li H, Xing Y Z, Zhao J, Bazin J, Liu Z, Liu Y. Leveraging structural regularity of Atlanta world for monocular SLAM. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, QC, Canada: IEEE Press, 2019. 2412−2418 [10] Li H, Yao J, Bazin J, Lu X, Xing Y, Liu K. A monocular SLAM system leveraging structural regularity in Manhattan world. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, QLD, Australia: IEEE, 2018. 2518−2525 [11] 张峻宁, 苏群星, 刘鹏远, 朱庆, 张凯. 一种自适应特征地图匹配的改进VSLAM算法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(3): 553-565Zhang Jun-Ning, Su Qun-Xing, Liu Peng-Yuan, Zhu Qing, Zhang Kai. An improved VSLAM algorithm based on adaptive feature map. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 553-565 [12] Yang S, Song Y, Kaess M, Scherer S. Pop-up SLAM: Semantic monocular plane SLAM for low-texture environments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Daejeon, South Korea: IEEE, 2016. 1222−1229 [13] Lu Y, Song D. Visual navigation using heterogeneous landmarks and unsupervised geometric constraints. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2015, 31(3): 736-749 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2424032 [14] 李磊, 陈细军, 曹志强, 候增广, 谭民. 一处室内轮式自主移动机器人的导航控制研究. 自动化学报, 2003, 29(6): 893-899Li Lei, Chen Xi-Jun Cao Zhi-Qiang, Hou Zeng-Guang, Tan Min. Research on the navigation control of an indoor wheeled autonomous mobile robot. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2003, 29(6): 893-899 [15] 庄严, 陈东, 王伟, 韩建达, 王越超. 移动机器人基于视觉室外自然场景理解的研究与进展. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(1): 1-11 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00001Zhuang Yan, Chen Dong, Wang Wei, Han Jian-Da, Wang Yue-Chao. Status and development of natural scene understanding for vision-based outdoor mobile robot. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(1): 1-11 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00001 [16] Nardi F, Corte B D, Grisetti G. Unified representation and registration of heterogeneous sets of geometric primitives. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(2): 625-632 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2891989 [17] Yang Y, Huang G. Observability analysis of aided INS with heterogeneous features of points, lines, and planes. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(6): 1399-1418 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2927835 [18] Zhang H, Ye C. Plane-aided visual-inertial odometry for 6-DOF pose estimation of a robotic navigation aid. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 90042-90051 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2994299 [19] Taguchi Y, Jian Y D, Ramalingam S, Feng C. Point-plane SLAM for hand-held 3D sensors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 2013. 5182−5189 [20] Cupec R, Nyarko E K, Filko D, Kitanov A. Place recognition based on matching of planar surfaces and line segments. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2015, 34(4-5): 674-704 doi: 10.1177/0278364914548708 [21] Zuo X, Xie X, Liu Y, Huang G. Robust visual SLAM with point and line features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 1775−1782 [22] Gomez-Ojeda R, Moreno F, Zuiga-Nol D, Scaramuzza D, Gonzalez-Jimenez J. PL-SLAM: A stereo SLAM system through the combination of points and line segments. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(3): 734-746 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2899783 [23] Fang B, Zhan Z. A visual SLAM method based on point-line fusion in weak-matching scene. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2020, 17(2): 1-11 [24] Elqursh A, Elgammal A. Line-based relative pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2011. 3049−3056 [25] Proença P F, Gao Y. Probabilistic RGB-D odometry based on points, lines and planes under depth uncertainty. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2018, 104: 25-39 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2018.02.018 [26] Grompone von Gioi R, Jakubowicz J, Morel J, Randall G. LSD: A fast line segment detector with a false detection control. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(4): 722-732 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.300 [27] Dryanovski I, Valenti R G, Xiao J Z. Fast visual odometry and mapping from RGB-D data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 2013. 2305−2310 [28] Sturm J, Engelhard N, Endres F, Burgard W, Cremers D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vilamoura, Portugal: IEEE, 2012. 573−580 [29] Zhang L, Koch R. An efficient and robust line segment matching approach based on LBD descriptor and pairwise geometric consistency. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2013, 24(7): 794-805 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2013.05.006 [30] 董星亮, 苑晶, 黄枢子, 杨少坤, 张雪波, 孙凤池, 黄亚楼. 室内环境下基于平面与线段特征的RGB-D视觉里程计. 机器人, 2018, 40(6): 921-932Dong Xing-Liang, Yuan Jing, Huang Shu-Zi, Yang Shao-Kun, Zhang Xue-Bo, Sun Feng-Chi, Huang Ya-Lou. RGB-D visual odometry based on features of planes and line segments in indoor environments. Robot, 2018, 40(6): 921-932 [31] Zhou Y, Li H, Kneip L. Canny-VO: Visual odometry with RGB-D cameras based on geometric 3-D-2-D edge alignment. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(1): 184-199 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2875382 -





 下载:
下载: