External Generalized Predictive Cascade Control for Main Steam Temperature Based on Weight Factor Self-regulating
-
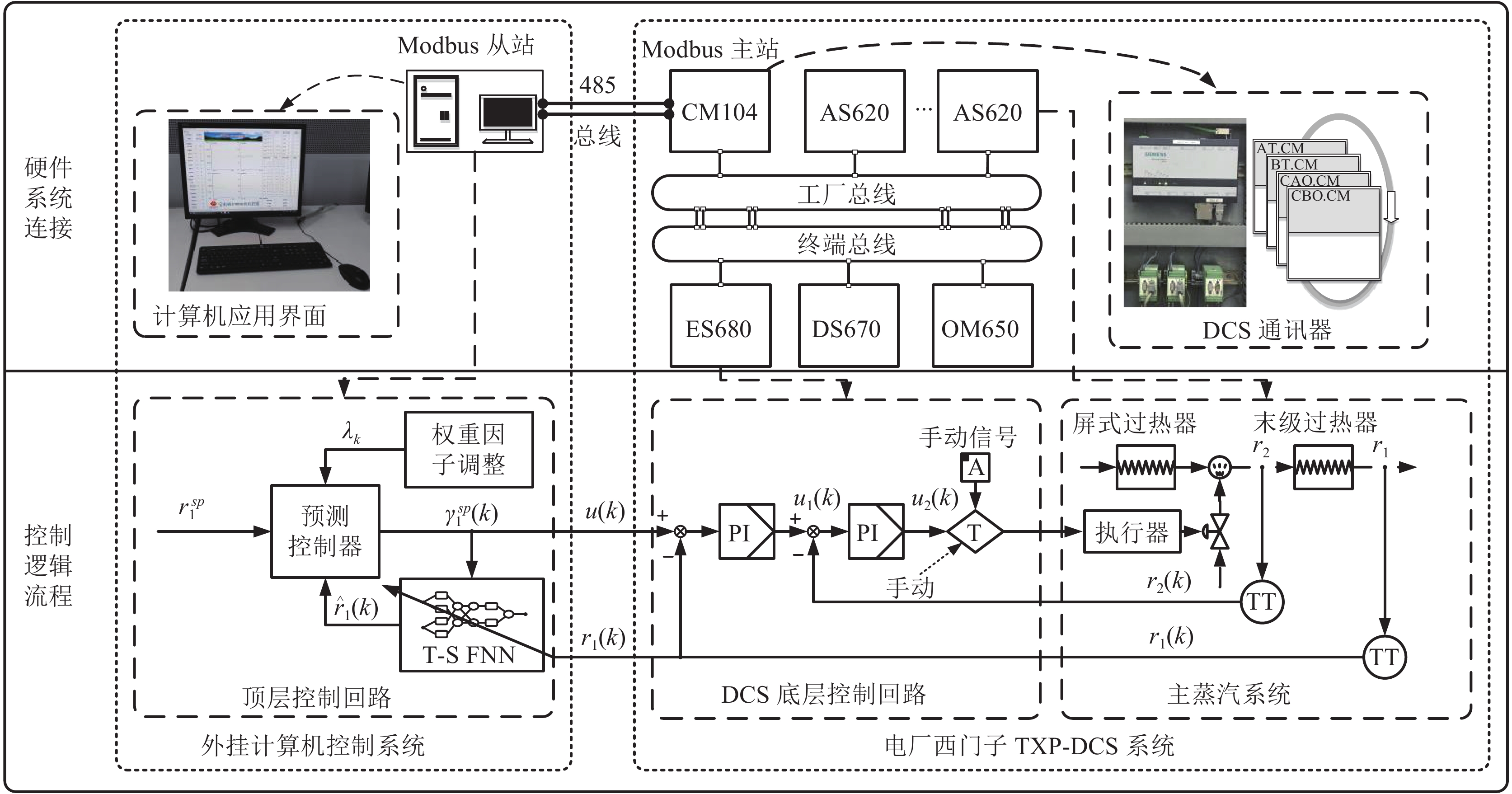
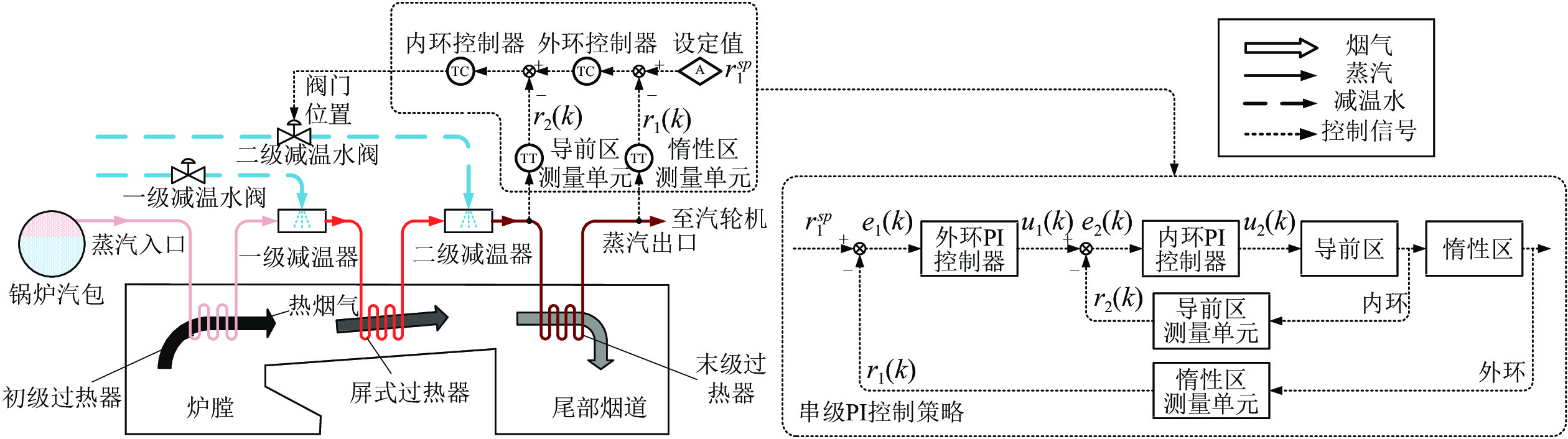
摘要: 针对电厂目前普遍采用PI-PI串级控制器调节锅炉主蒸汽温度系统, 不能有效克服惯性、时滞和参数时变等问题的影响, 本文提出了一种理想GPC (Generalized predictive control)-PI串级控制器. 首先, 该理想串级控制器不仅能抑制一次和二次扰动, 而且外环GPC通过对主蒸汽温度的多步预测, 并结合滚动优化技术能有效克服主蒸汽温度系统的惯性和时滞问题. 另外, 针对主蒸汽温度系统参数时变的特性, 该理想控制器采用了T-S (Takagi-Sugeno)型模糊神经网络(Fuzzy neural network, FNN)作为主蒸汽温度模型, 该模型能够通过反馈校正技术实时更新模型参数. 同时, 为了改善主蒸汽温度系统动态响应品质和稳定性, 对外环GPC中的权重因子进行了模糊自校正设计, 通过理论分析和对比仿真验证了该理想GPC-PI串级控制器优于权重因子固定的GPC-PI和PI-PI串级控制器. 最后, 考虑到直接将电厂集散控制系统(Distributed control system, DCS)中的PI-PI串级控制器升级为理想GPC-PI串级控制器存在安全以及风险责任等问题, 故将电厂的传统PI-PI串级控制器升级成外挂的GPC-PI-PI串级控制器, 既改善了锅炉主蒸汽温度的控制效果又规避了风险责任, 实际应用验证了该方法的有效性.Abstract: The PI-PI cascade controller, which is widely used in power plants for adjusting main steam temperature, cannot effectively overcome the negative effects caused by inertia, time delay and time-varying parameters, therefore an ideal generalized predictive control (GPC)-PI cascade controller is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the GPC-PI cascade controller could attenuate the primary and secondary disturbances. To solve the problems of inertia and time delay in the main steam temperature system, the GPC-PI cascade controller predicts the multi-step main steam temperature integrating with rolling optimization technique. In addition, facing the time-varying parameters of the main steam temperature system, the GPC-PI cascade controller adopts the T-S (Takagi-Sugeno) fuzzy neural networks (FNN) as the main steam temperature model, whose parameters can be identified and updated in real time. Meanwhile, in order to further improve the dynamic response speed and stability of the main steam temperature system, fuzzy self-regulating of weight factor in outer-loop GPC is designed. The theoretical analysis and comparative simulations verify that the ideal GPC-PI cascade controller is superior to the GPC-PI cascade controller with fixed weight factor and the PI-PI cascade controller. Finally, considering the safety and risks due to the substitution of PI-PI cascade controller by the ideal GPC-PI cascade controller in distributed control systems (DCS), the PI-PI cascade controller is upgraded to the GPC-PI-PI controller for power plant, which not only improves the control effects but also avoids liabilities for risks. The practical application demonstrates the effectiveness of the GPC-PI-PI controller.1) 收稿日期 2020-04-08 录用日期 2020-07-12 Manuscript received April 8, 2020; accepted July 12, 2020 国家自然科学基金 (51775103) 资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51775103) 本文责任编委 乔俊飞 Recommended by Associate Editor QIAO Jun-Fei2) 1. 东北大学机械工程与自动化学院 沈阳 110819 2. 东北大学流程工业综合自动化国家重点实验室 沈阳 110819 3. 国家能源投资集团 北京 100011 1. School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, North-eastern University, Shenyang 110819 2. State Key Laboratory of Synthetical Automation for Process Industries, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819 3. China Energy Investment Corporation Limited, Beijing 100011
-
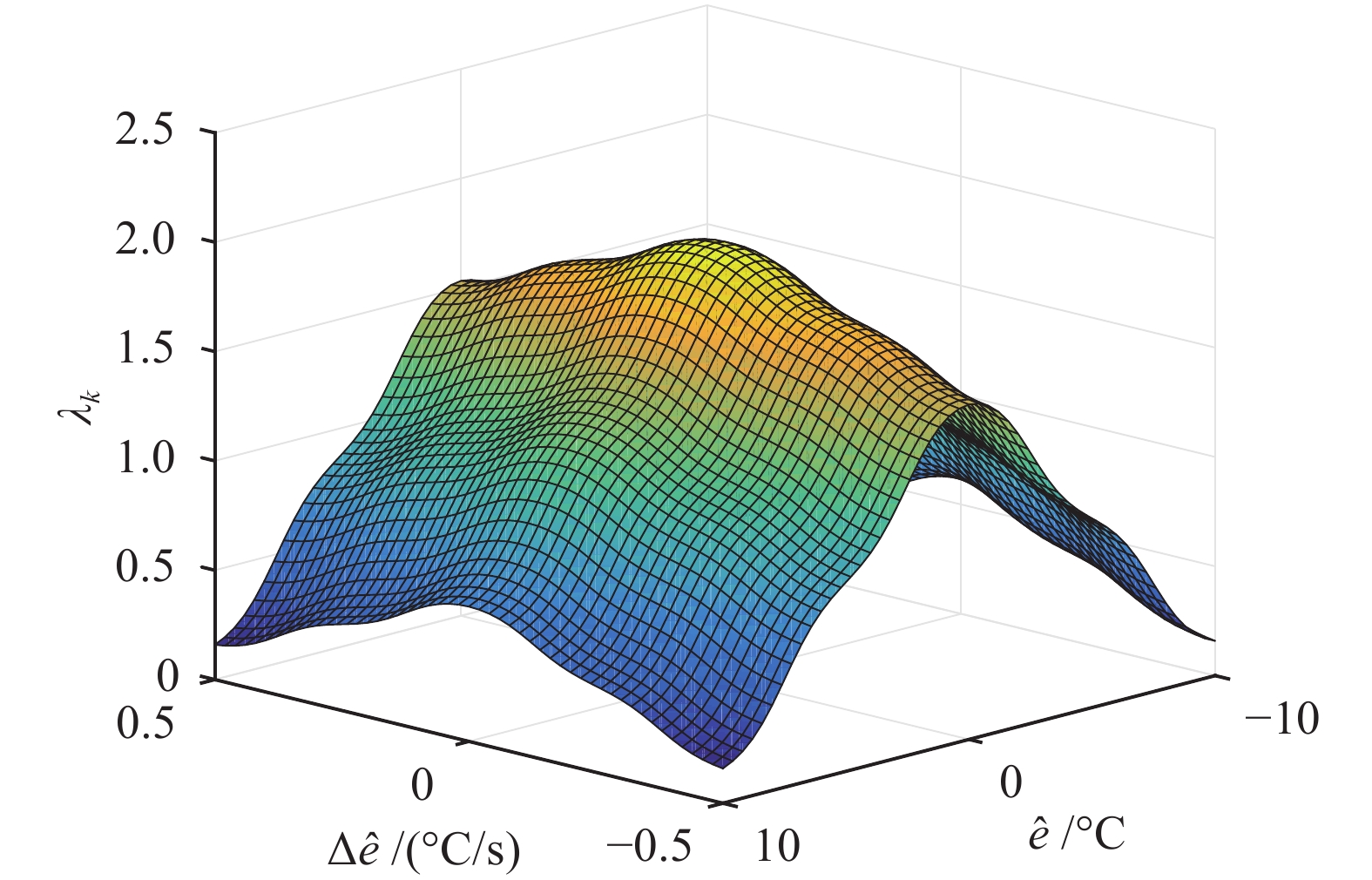
表 1 权重因子
$ \lambda_{k} $ 模糊调节规则Table 1 Fuzzy regulation rules of weight factor
$ \lambda_{k} $ $ \Delta\hat{e} $ $ \hat{e} $ NB NS ZE PS PB NB NL NB NM NB NL NS NS ZE PS ZE NS ZE PM PB PL PB PM PS NS ZE PS ZE NS PB NL NB NM NB NL 表 2 实验结果性能比较
Table 2 Performance comparison of experimental results
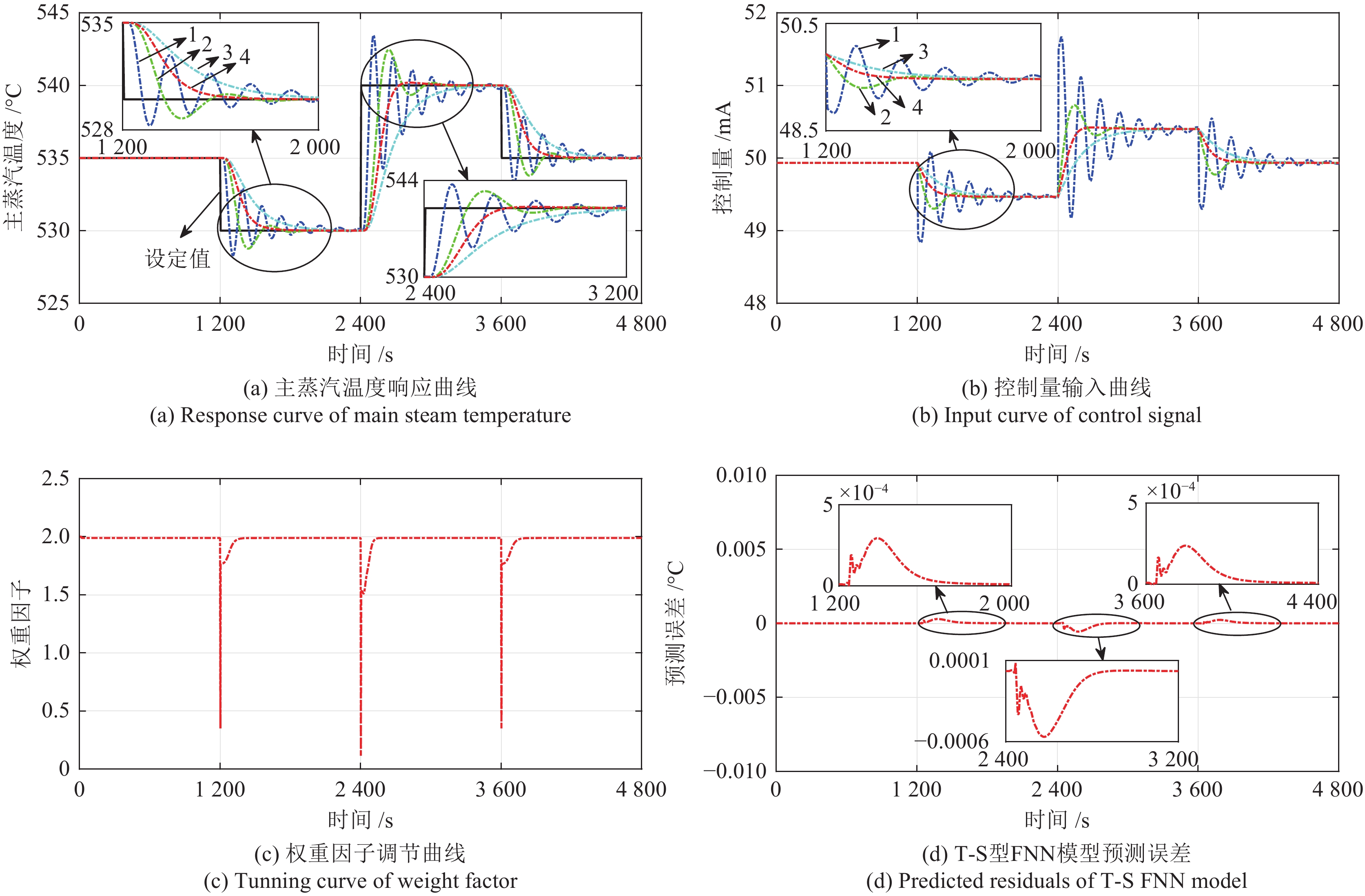
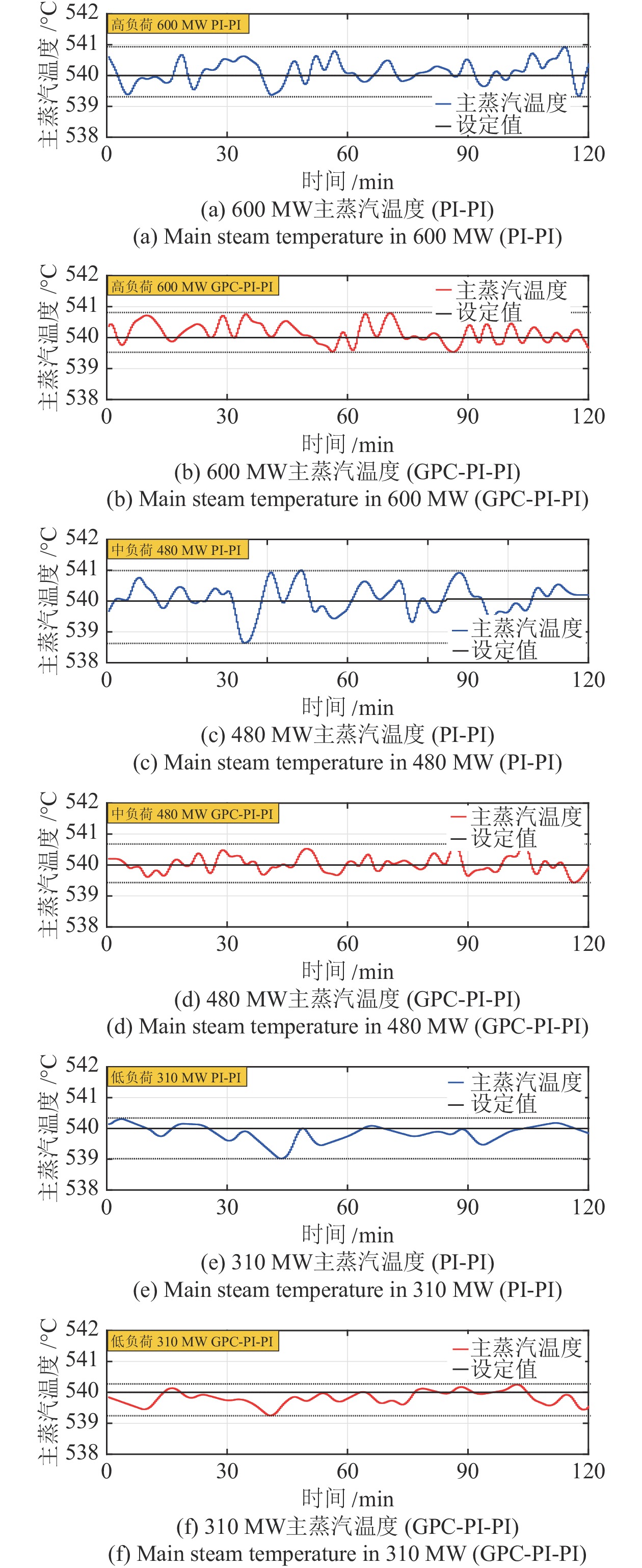
负荷 控制器 指标 $ \epsilon $ RMSE MAE IAE 600 MW 原始 0.9319 0.3677 0.3012 108.7194 外挂 0.7954 0.3372 0.2668 96.3206 480 MW 原始 1.3560 0.4593 0.3635 131.2284 外挂 0.6856 0.2516 0.2011 72.5914 310 MW 原始 0.9791 0.3015 0.2230 80.5173 外挂 0.7458 0.2789 0.2222 80.2247 -
[1] Draganescu M, Guo S, Wojcik J, Wang J H, Liu X J, Hou G L, Xue Y L, Gao Q R. Generalized predictive control for superheated steam temperature regulation in a supercritical coal-fired power plant. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2015, 1(1): 69-77 doi: 10.17775/CSEEJPES.2015.00009 [2] Ma L Y, Ge Y P, Cao X. Superheated steam temperature control based on improved recurrent neural network and simplified PSO algorithm. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2011, 128-129: 1065-1069 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.128-129.1065 [3] Liang G, Li W, Li Z J. Control of superheated steam temperature in large-capacity generation units based on active disturbance rejection method and distributed control system. Control Engineering Practice, 2013, 21: 268-285 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2012.10.002 [4] Huang H P, Yu J A, Su Q, Wang L. 660MW single auxiliary ultra-supercritical unit main stream's temperature control strategy optimization studies. Advanced Materials Research. 2014, 909: 317-322 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.909.317 [5] Zhang J H, Zhang F F, Ren M F, Hou G L, Fang F. Cascade control of superheated steam temperature with neuro-PID controller. ISA Transactions, 2012, 51: 778-785 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2012.06.008 [6] Tian Z D, Ren Y, Wang G. Fuzzy-PID controller based on variable universe for main steam temperature system. Australian Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, 2018, 15(1-2): 21-28 doi: 10.1080/1448837X.2018.1490163 [7] Wang W, Li H-X, Zhang J T. Intelligence-based hybrid control for power plant boiler, IEEE Transaction Control System Technology, 2002, 10(2): 280-287 doi: 10.1109/87.987074 [8] 王东风, 韩璞. 基于免疫遗传算法优化的汽温系统变参数PID控制. 中国电机工程学报, 2003, 23(9): 212-217 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2003.09.044Wang Dong-Feng, Han Pu. Variable arguments PID control for main steam temperature system based on immune genetic optimization. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2003, 23(9): 212-217 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2003.09.044 [9] 刘国宏, 倪桂杰, 孙明, 翟永杰. 基于粒子群优化的汽温系统神经网络自整定PID控制. 华北电力大学学报, 2009, 36(1): 44-49Liu Guo-Hong, Ni Gui-Jie, Sun Ming, Zhai Yong-Jie. Self-tuning of neural networks PID control for main steam temperature system based on particle swarm optimization. Journal of North China Electric Power University, 2009, 36(1): 44-49 [10] Liu X J, Chan C W. Neuro-fuzzy generalized predictive control of boiler steam temperature. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2006, 21(4): 900-908 doi: 10.1109/TEC.2005.853758 [11] Wu X, Shen J, Li Y G, Lee K Y. Fuzzy modeling and stable model predictive tracking control of large-scale power plants. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24: 1609-1626 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.08.007 [12] Zhang Y J, Chai T Y, Wang H, Fu J, Zhang L Y, Wang Y G. An adaptive generalized predictive control method for nonlinear systems based on ANFIS and multiple models. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(6): 1070-1082 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2062524 [13] Escaño J M, Bordons C, Vilas C, García M R, Alonso A A. Neurofuzzy model based predictive control for thermal batch processes. Journal of Process Control, 2009, 19: 1566-1575 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2009.07.016 [14] Cervantes J, Yu W, Salazar S, Chairez I. Takagi–Sugeno dynamic neuro-fuzzy controller of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(6): 1601-1615 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2612697 [15] Zhang R D, Tao J L. A nonlinear fuzzy neural network modeling approach using improved genetic algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(7): 5882-5892 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2777415 [16] 雎刚, 陈来九. 模糊预测控制及其在过热汽温控制中的应用. 中国电机工程学报, 1996, 6(1): 17-21 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.1996.01.004Ju Gang, Chen Lai-Jiu. Fuzzy predictive control and its application study in temperature control system. Proceedings of the CSEE, 1996, 6(1): 17-21 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.1996.01.004 [17] Gao Y, Er M J. NARMAX time series model prediction: feedforward and recurrent fuzzy neural network approaches. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2005, 150: 331-350 doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2004.09.015 [18] 李少远, 王群仙, 李焕芝, 陈增强, 袁著祉. Sugeno模糊模型的辨识与控制. 自动化学报, 1999, 25(4): 488-492Li Shao-Yuan, Wang Qun-Xian, Li Huan-Zhi, Chen Zeng-Qiang, Yuan Zhu-Zhi. Identification and Control Based on Sugeno's Fuzzy Model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 1999, 25(4): 488-492 [19] Johansen T A, Babuška R. Multiobjective identification of Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy models. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2003, 11(6): 847-860 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2003.819824 [20] Liao Q F, Sun D, Cai W J, Li S Y, Wang Y Y. Type-1 and Type-2 effective Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy models for decentralized control of multi-input-multi-output processes. Journal of Process Control, 2017, 52: 26-44 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2017.01.004 [21] 段艳杰, 吕宜生, 张杰, 赵学亮, 王飞跃. 深度学习在控制领域的研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 643-654Duan Yan-Jie, Lv Yi-Sheng, Zhang Jie, Zhao Xue-Liang, Wang Fei-Yue. Deep learning for control: the state of the art and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 643-654 [22] Liu W C, Cheng L, Hou Z G, Yu J Z, Tan M. An inversionfree predictive controller for piezoelectric actuators based on a dynamic linearized neural network model. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016, 21(1): 214-226 [23] Jin Y L, Cao W H, Wu M, Yuan Y. Accurate fuzzy predictive models through complexity reduction based on decision of needed fuzzy rules. Neurocomputing, 2019, 323: 344-351 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.010 [24] Feng S, Chen C. L. Philip. Fuzzy broad learning system: a novel neuro-fuzzy model for regression and classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(2): 414-424 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2857815 [25] Han H G, Wu X L, Liu H X, Qiao J F. An efficient optimization method for improving generalization performance of fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(7): 1347-1361 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2878156 [26] Han H G, Wu X L, Liu H X, Qiao J F. An efficient second-order algorithm for self-organizing fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(1): 14-26 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2762521 [27] Eliasi H, Davilu H, Menhaj M B. Adaptive fuzzy model based predictive control of nuclear steam generators. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2007, 237: 668-676 doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2006.08.007 [28] Peng H, Wu J, Inoussa G, Deng Q L, Nakano K. Nonlinear system modeling and predictive control using the RBF nets-based quasi-linear ARX model. Control Engineering Practice, 2009, 17: 59-66 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2008.05.005 [29] Yeh M F, Tsai C H. Standalone CMAC control system with online learning ability. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man & Cybernetics Part B Cybernetics, 2010, 40(1): 43-53 [30] Zhao J, Lin C M. Wavelet-TSK-type fuzzy cerebellar model neural network for uncertain nonlinear systems.IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(3): 549-558 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2863650 [31] Clarke D W, Mohtadi C, Tuffs P S. Generalized predictive control—Part I. The basic algorithm. Automatica, 1987, 23(2): 137-148 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(87)90087-2 [32] Lu C H, Tsai C C. Adaptive predictive control with recurrent neural network for industrial processes: an application to temperature control of a variable-frequency oil-cooling machine. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2008, 55(3): 1366-1375 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2007.896492 [33] 石宇静, 柴天佑. 基于神经网络与多模型的非线性自适应广义预测控制. 自动化学报, 2007, 33(05): 540-545Shi Yu-Jing, Chai Tian-You. Neural networks and multiple models based nonlinear adaptive generalized predictive control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2007, 33(05): 540-545 [34] 张晓宇, 王天伟, 李燕, 王懋譞, 王永富. 火电机组燃烧系统智能综合优化控制研究. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(9): 2544-2552Zhang Xiao-Yu, Wang Tian-Wei, Li Yan, Wang Mao-Xuan, Wang Yong-Fu. Study of intelligent integrated optimization control of thermal power unit combustion system. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(9): 2544-2552 [35] Xiao H Z, Chen C. L. Philip. Incremental updating multirobot formation using nonlinear model predictive control method with general projection neural network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(6): 4502-4512 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2864707 [36] 代伟, 柴天佑. 数据驱动的复杂磨矿过程运行优化控制方法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 2005-2014Dai Wei, Chai Tian-You. Data-driven optimal operational control of complex grinding processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 2005-2014 [37] 代伟, 陆文捷, 付俊, 马小平. 工业过程多速率分层运行优化控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1946-1959Dai Wei, Lu Wen-Jie, Fu Jun, Ma Xiao-Ping. Multi-rate layered optimal operational control of industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1946-1959 -




 下载:
下载: