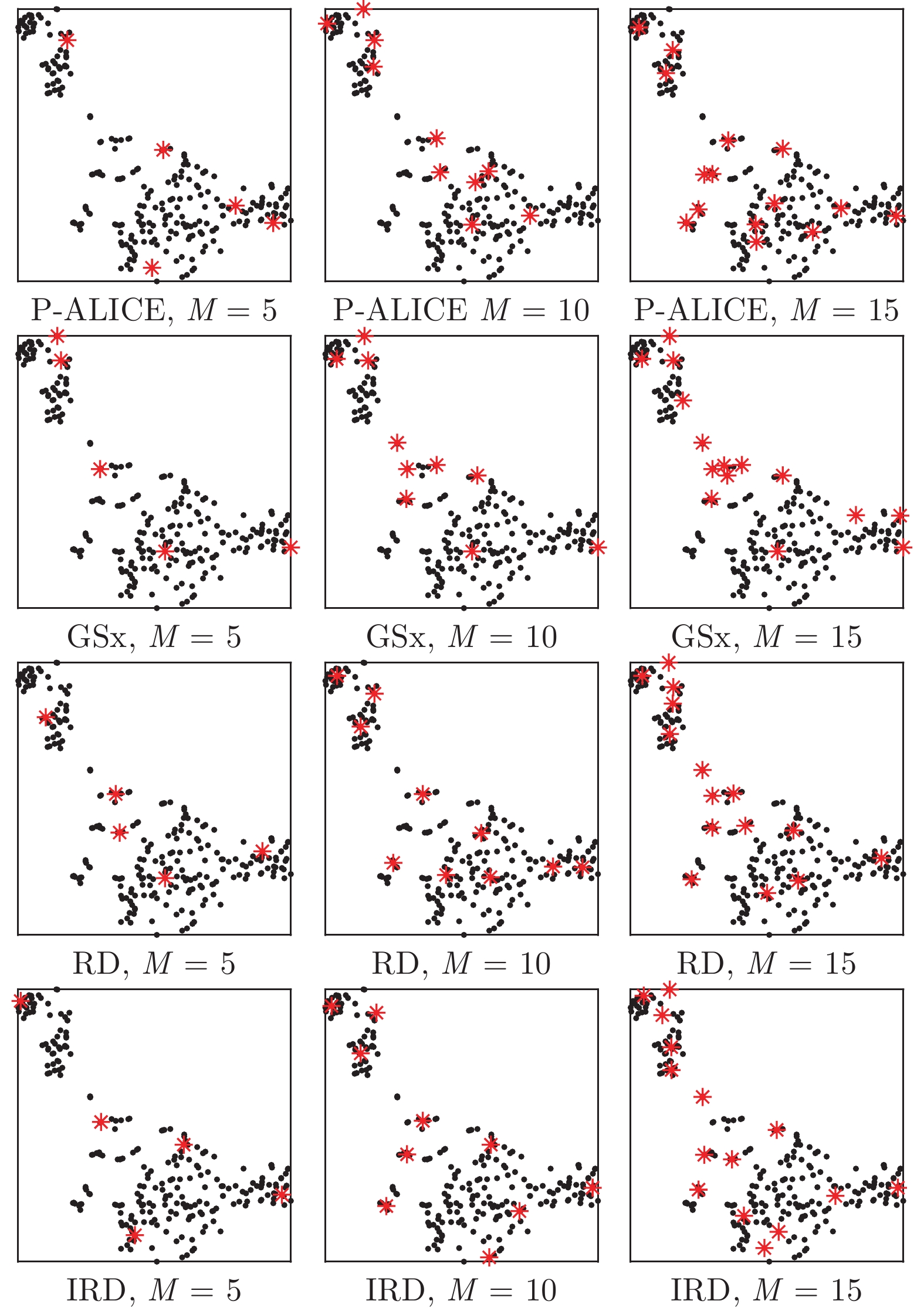
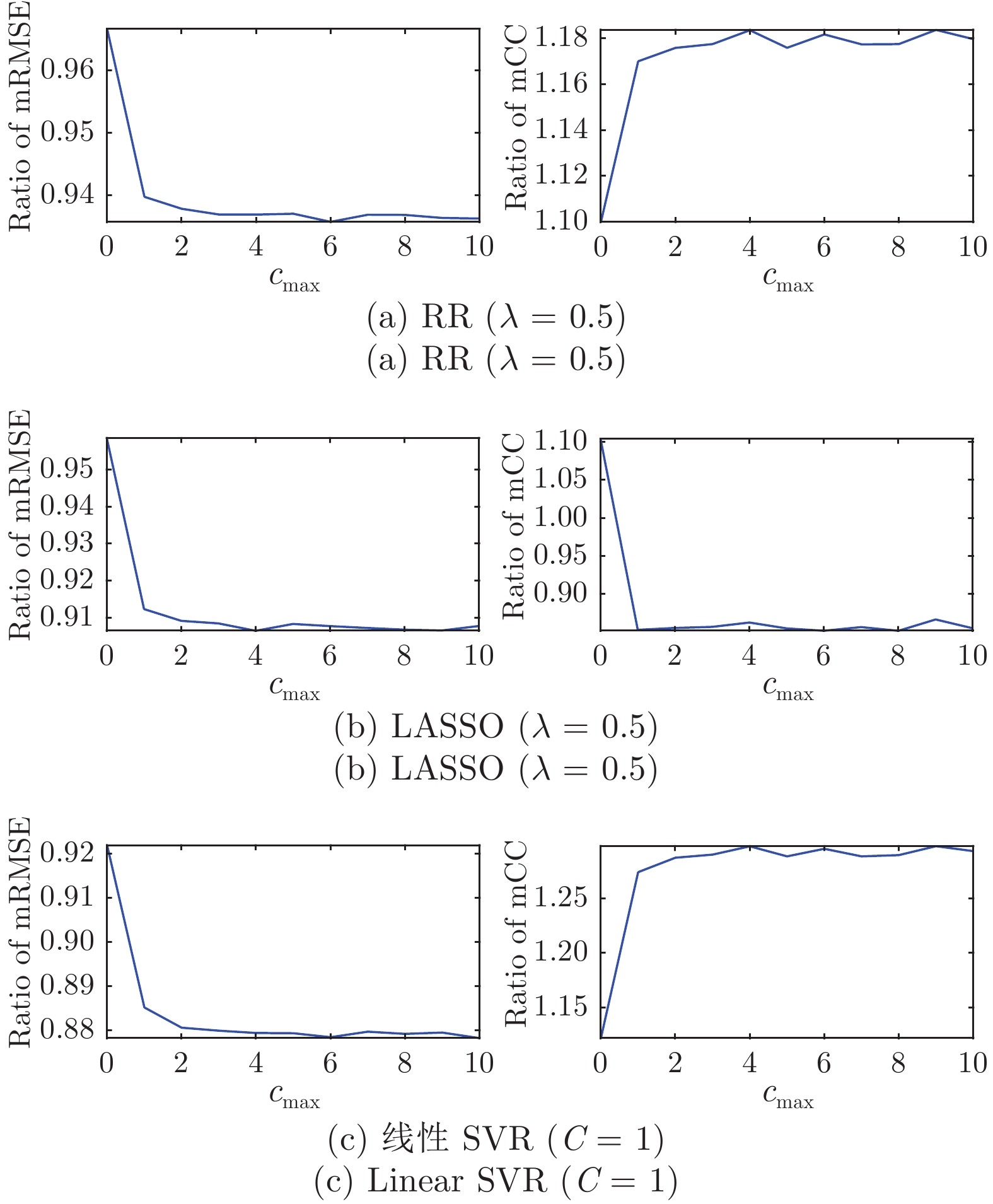
-
摘要: 在许多现实的机器学习应用场景中, 获取大量未标注的数据是很容易的, 但标注过程需要花费大量的时间和经济成本. 因此, 在这种情况下, 需要选择一些最有价值的样本进行标注, 从而只利用较少的标注数据就能训练出较好的机器学习模型. 目前, 主动学习(Active learning)已广泛应用于解决这种场景下的问题. 但是, 大多数现有的主动学习方法都是基于有监督场景: 能够从少量带标签的样本中训练初始模型, 基于模型查询新的样本, 然后迭代更新模型. 无监督情况下的主动学习却很少有人考虑, 即在不知道任何标签信息的情况下最佳地选择要标注的初始训练样本. 这种场景下, 主动学习问题变得更加困难, 因为无法利用任何标签信息. 针对这一场景, 本文研究了基于池的无监督线性回归问题, 提出了一种新的主动学习方法, 该方法同时考虑了信息性、代表性和多样性这三个标准. 本文在3个不同的线性回归模型(岭回归、LASSO (Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator)和线性支持向量回归)和来自不同应用领域的12个数据集上进行了广泛的实验, 验证了其有效性.Abstract: In many real-world machine learning applications, unlabeled data can be easily obtained, but it is very time-consuming and/or expensive to label them. So, it is desirable to be able to select the optimal samples to label, so that a good machine learning model can be trained from a minimum number of labeled data. Active learning (AL) has been widely used for this purpose. However, most existing AL approaches are supervised: they train an initial model from a small number of labeled samples, query new samples based on the model, and then update the model iteratively. Few of them have considered the completely unsupervised AL problem, i.e., starting from zero, how to optimally select the very first few samples to label, without knowing any label information at all. This problem is very challenging, as no label information can be utilized. This paper studies unsupervised pool-based AL for linear regression problems. We propose a novel AL approach that considers simultaneously the informativeness, representativeness, and diversity, three essential criteria in AL. Extensive experiments on 12 datasets from various application domains, using three different linear regression models (ridge regression, LASSO (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator), and linear support vector regression), demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed approach.1) 1
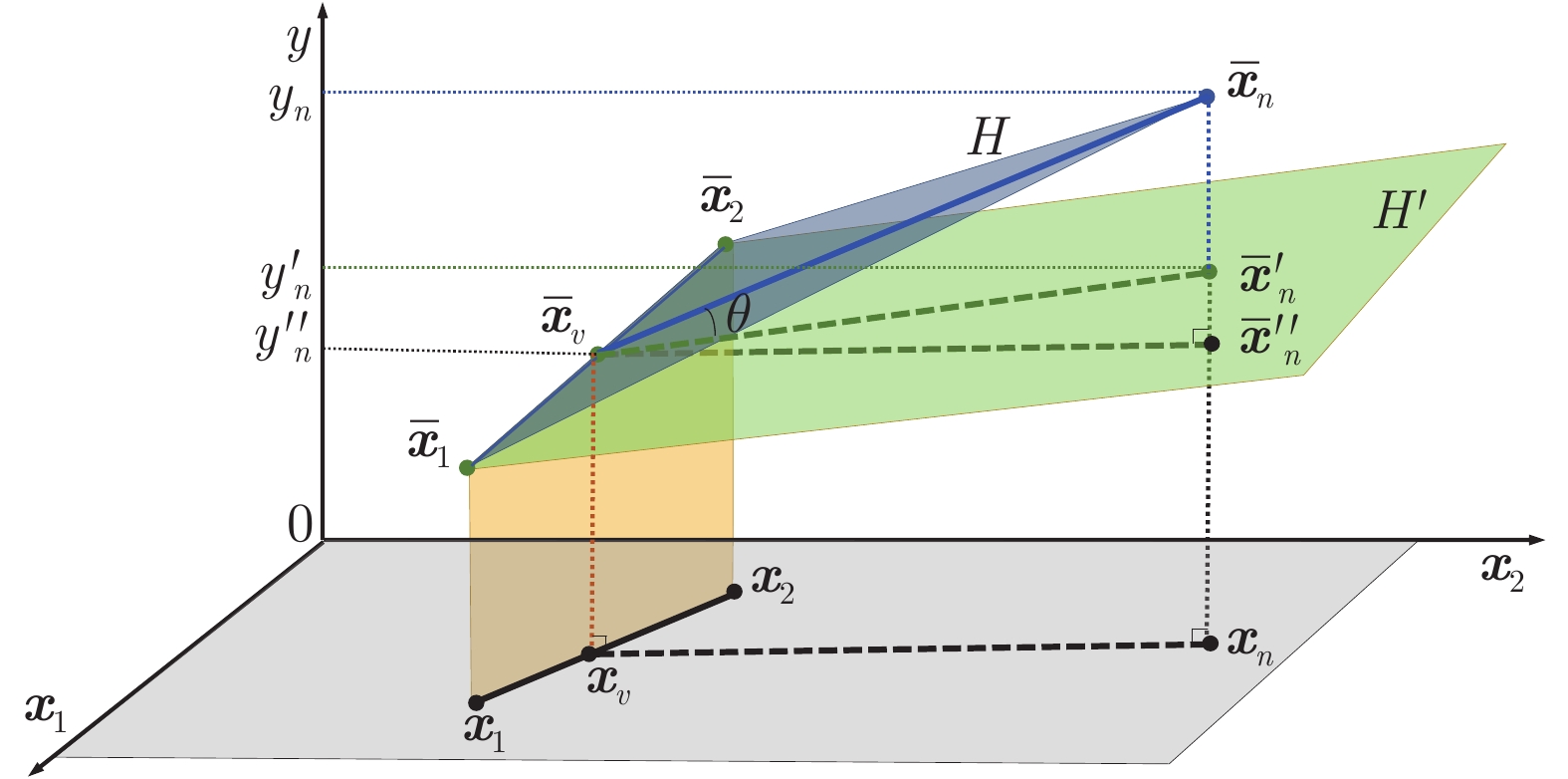
$ \theta $ 并不是$ H $ 和$ H' $ 之间的真实角度, 当满足$ \overrightarrow{\bar{{\boldsymbol{x}}} _v\bar{{\boldsymbol{x}}}_n'}\perp\overrightarrow{\bar{{\boldsymbol{x}}}_1\bar{{\boldsymbol{x}}}_2} $ 时,$ \theta $ 才是$ H $ 和$ H' $ 间的夹角, 通常$ \bar{{\boldsymbol{x}}}_n' $ 并不满足这一条件. 然而, 如同$ H $ 和$ H' $ 之间的真实角度,$ \theta $ 会随着$ H' $ 和$ H $ 越来越接近而单调递减, 因此可以用它来度量$ H' $ 和$ H $ 之间的接近程度. 我们使用这样的$ \theta ,$ 而不是$ H $ 和$ H' $ 之间的真实角度来进行计算, 将会使得推导更加容易. 2我们还考虑了其他兼顾代表性、信息性和多样性的方法, 例如$ {\boldsymbol{x}} _n^* = $ $ \arg\min_{{\boldsymbol{x}}_n}(\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i = 1}^N|{\boldsymbol{x}}_i-{\boldsymbol{x}}_n|^2)^{1/2}+\lambda\cdot |{\boldsymbol{x}}_v-{\boldsymbol{x}}_n| $ , 但这种方法会引入超参数$ \lambda $ , 并且我们的实验表明, 从最佳的$ \lambda $ 获得的性能要比式(11)差. 因此, 由于其简单性和准确性, 我们最终使用式(11)作为选择准则.2) 收稿日期 2020-02-17 录用日期 2020-08-14 Manuscript received February 17, 2020; accepted August 14,2020 湖北省技术创新专项基金 (2019AEA171), 国家自然科学基金 (61873321), NSFC-深圳机器人基础研究中心重点项目基金 (U1913207), 科技部政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项基金 (2017YFE0128300) 资助 Supported by Technology Innovation Project of Hubei Province of China (2019AEA171), National Natural Science Foundation of China (61873321), NSFC-Shenzhen Robotics Basic Research Center (U1913207), and International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (2017YFE0128300) 本文责任编委 王立威 Recommended by Associate Editor WANG Li-Wei 1. 华中科技大学人工智能与自动化学院图像信息处理与智能控制教育部重点实验室 武汉 4300743) 3http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/index.php4http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/4) 1. Ministry of Education Key Laboratory on Image Information Processing and Intelligent Control, School of Artificial Intelligence and Automation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 4300745) 5对普通最小二乘法(Ordinary least squares, OLS)回归也进行了尝试, IRD依然取得了最佳表现. 但当训练样本较少时, OLS非常不稳定, 因此在实际中不是一个合理的选择, 本文不讨论其结果.6) 6由于页面限制, 只展示了RR的详细结果, 因为它通常表现更稳定. 其他两个回归模型上的结果类似. -
表 1 基于池的无监督ALR方法中考虑的标准
Table 1 Criteria considered in the three existing and the proposed unsupervised pool-based ALR approaches
方法 信息性 代表性 多样性 现有方法 P-ALICE $\checkmark$ $-$ $-$ GSx $-$ $-$ $\checkmark$ RD $-$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 本文方法 IRD $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 表 2 12个数据集的总结
Table 2 Summary of the 12 regression datasets
数据集 来源 样本个数 原始特征个数 数字型特征个数 类别型特征个数 总的特征个数 Concrete-CSa UCI 103 7 7 0 7 Yachtb UCI 308 6 6 0 6 autoMPGc UCI 392 7 6 1 9 NO2d StatLib 500 7 7 0 7 Housinge UCI 506 13 13 0 13 CPSf StatLib 534 10 7 3 19 EE-Coolingg UCI 768 7 7 0 7 VAM-Arousalh ICME 947 46 46 0 46 Concretei UCI 1030 8 8 0 8 Airfoilj UCI 1503 5 5 0 5 Wine-Redk UCI 1599 11 11 0 11 Wine-Whitel UCI 4898 11 11 0 11 a https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Concrete+Slump+Test
b https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Yacht+Hydrodynamics
c https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/auto+mpg
d http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/
e https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/housing/
f http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/CPS_85_Wagesg http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/energy+efficiency
h https://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/conf/icmcs/icme2008.html
i https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Concrete+Compressive+ Strength
j https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Airfoil+Self-Noise
k https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Wine+Quality表 3 AUC-mRMSE/sRMSE和AUC-mCC/sCC的提升百分比
Table 3 Percentage improvements of the AUCs of the mean/std RMSEs and the mean/std CCs
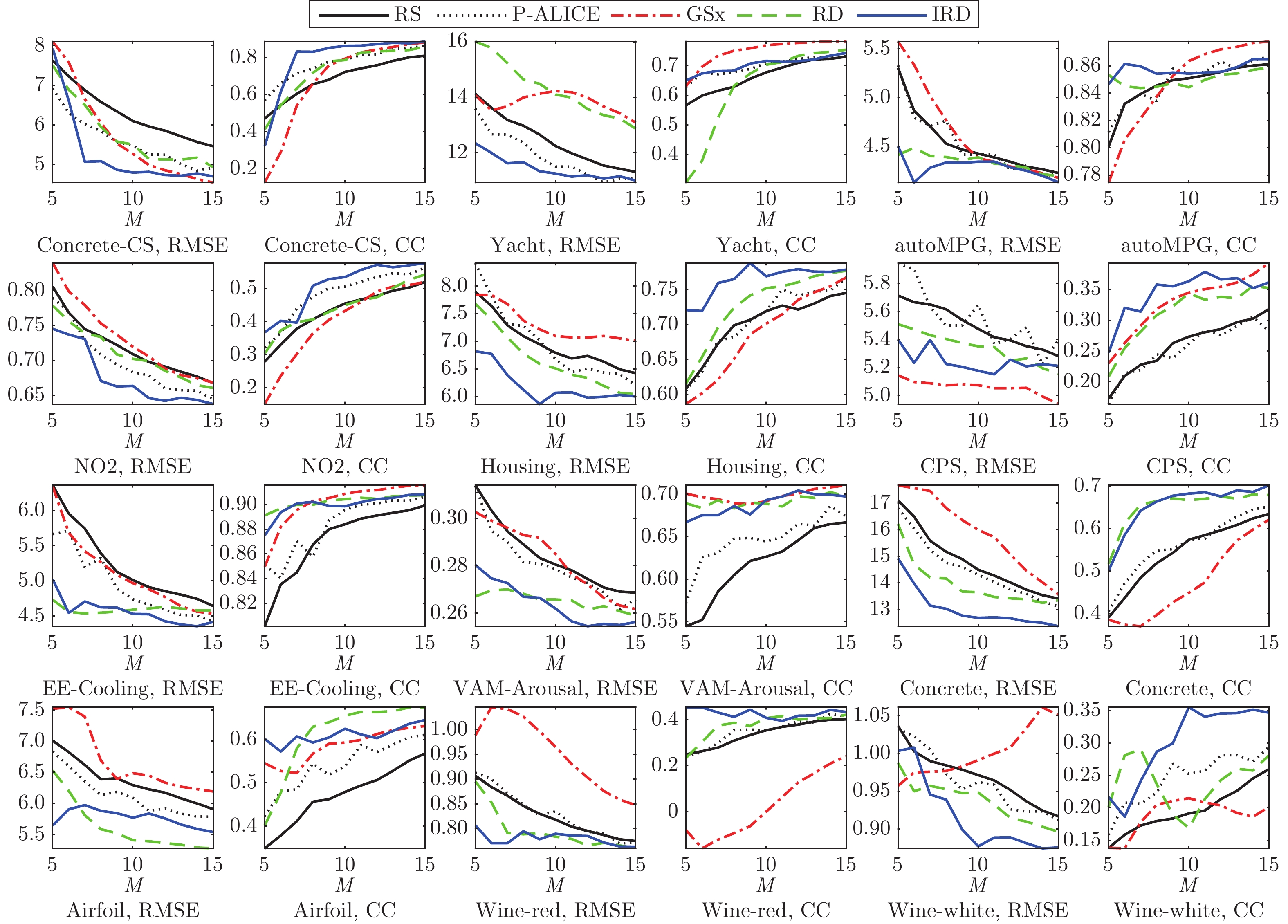
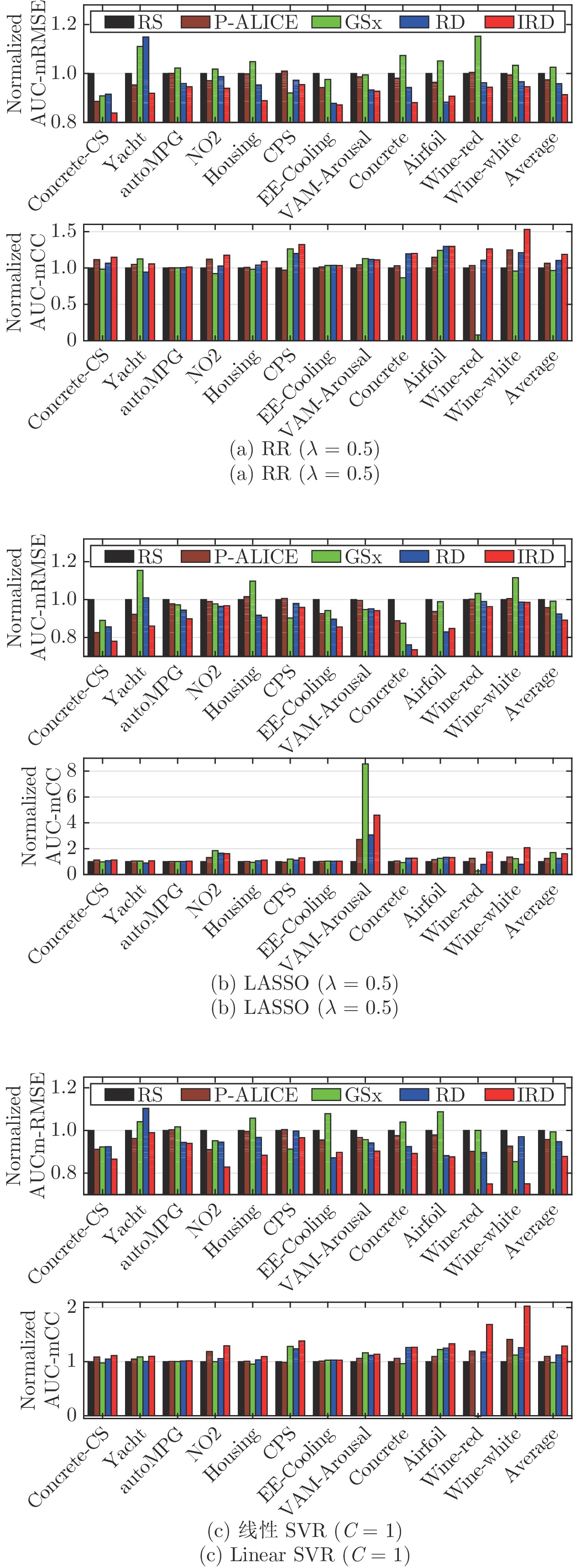
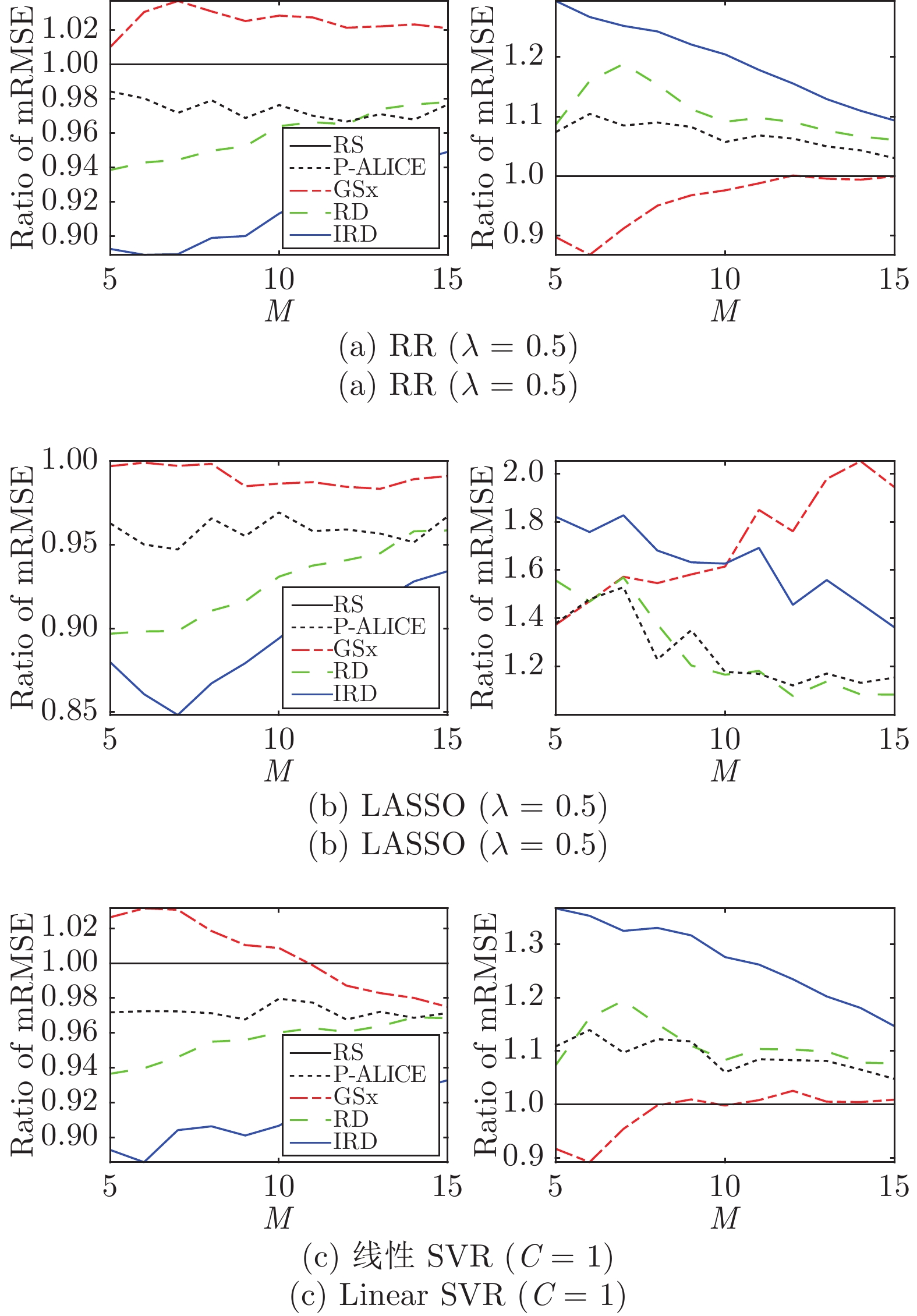
回归模型 性能指标 相对于 RS 的提升百分比 P-ALICE GSx RD IRD RR RMSE Mean 2.58 −2.57 4.15 8.63 std 2.75 3.98 36.60 34.84 CC Mean 6.54 −3.43 10.39 18.70 std 12.74 29.47 35.03 42.97 LASSO RMSE Mean 4.22 0.84 7.58 10.81 std 6.77 0.85 43.45 39.84 CC Mean 25.06 69.41 25.67 60.63 std 6.39 31.05 22.46 29.82 SVR RMSE Mean 4.21 0.66 5.23 12.12 std 6.62 −0.19 33.99 38.69 CC Mean 9.71 −1.65 12.46 28.99 std 11.10 25.78 34.97 43.25 表 4 非参数多重检验的
$p$ 值($\alpha=0.05$ ; 如果$p<\alpha/2$ 拒绝$H_0$ ).Table 4
$p$ -values of non-parametric multiple comparisons ($\alpha=0.05$ ; reject$H_0$ if$p<\alpha/2$ )回归模型 性能指标 IRD versus RS P-ALICE GSx RD RR RMSE 0.0000 0.0003 0.0000 0.0284 CC 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0005 LASSO RMSE 0.0000 0.0004 0.0000 0.0596 CC 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 SVR RMSE 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0018 CC 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 -
[1] Mehrabian A. Basic Dimensions for a General Psychological Theory: Implications for Personality, Social, Environmental, and Developmental Studies. Cambridge: Oelgeschlager, Gunn & Hain, 1980. [2] Grimm M, Kroschel K, Narayanan S. The Vera am Mittag German audio-visual emotional speech database. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Hannover, Germany: IEEE, 2008. 865−868 [3] Bradley M M, Lang P J. The International Affective Digitized Sounds: Affective Ratings of Sounds and Instruction Manual, Technical Report No. B-3, University of Florida, USA, 2007. [4] Joo J I, Wu D R, Mendel J M, Bugacov A. Forecasting the post fracturing response of oil wells in a tight reservoir. In: Proceedings of the 2009 SPE Western Regional Meeting. San Jose, USA: SPE, 2009. [5] Settles B. Active Learning Literature Survey, Computer Sciences Technical Report 1648, University of Wisconsin, USA, 2009. [6] Burbidge R, Rowland J J, King R D. Active learning for regression based on query by committee. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning. Birmingham, UK: Springer, 2007. 209−218 [7] Cai W B, Zhang M H, Zhang Y. Batch mode active learning for regression with expected model change. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(7): 1668-1681 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2542184 [8] Cai W B, Zhang Y, Zhou J. Maximizing expected model change for active learning in regression. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Data Mining. Dallas, USA: IEEE, 2013. 51−60 [9] Cohn D A, Ghahramani Z, Jordan M I. Active learning with statistical models. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 1996, 4(1): 129-145 [10] Freund Y, Seung H S, Shamir E, Tishby N. Selective sampling using the query by committee algorithm. Machine Learning, 1997, 28(2-3): 133-168 [11] MacKay D J C. Information-based objective functions for active data selection. Neural Computation, 1992, 4(4): 590-604 doi: 10.1162/neco.1992.4.4.590 [12] Sugiyama M. Active learning in approximately linear regression based on conditional expectation of generalization error. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2006, 7: 141-166 [13] Sugiyama M, Nakajima S. Pool-based active learning in approximate linear regression. Machine Learning, 2009, 75(3): 249-274 doi: 10.1007/s10994-009-5100-3 [14] Castro R, Willett R, Nowak R. Faster rates in regression via active learning. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2005. 179−186 [15] Wu D R, Lawhern V J, Gordon S, Lance B J, Lin C T. Offline EEG-based driver drowsiness estimation using enhanced batch-mode active learning (EBMAL) for regression. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2016. 730−736 [16] Yu H, Kim S. Passive sampling for regression. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2010. 1151−1156 [17] Wu D R. Pool-based sequential active learning for regression. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(5): 1348-1359 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2868649 [18] Wu D R, Lin C T, Huang J. Active learning for regression using greedy sampling. Information Sciences, 2019, 474: 90-105 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.09.060 [19] Liu Z, Wu D R. Integrating informativeness, representativeness and diversity in pool-based sequential active learning for regression. In: Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Glasgow, UK: IEEE, 2020. 1−7 [20] Wu D R, Huang J. Affect estimation in 3D space using multi-task active learning for regression. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2019, DOI: 10.1109/TAFFC.2019.2916040 [21] Tong S, Koller D. Support vector machine active learning with applications to text classification. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 2: 45-66 [22] Lewis D D, Catlett J. Heterogeneous uncertainty sampling for supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). New Brunswick, Canada: Elsevier, 1994. 148−156 [23] Lewis D D, Gale W A. A sequential algorithm for training text classifiers. In: Proceedings of the 17th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Dublin, Ireland: Springer, 1994. 3−12 [24] Grimm M, Kroschel K. Emotion Estimation in Speech Using a 3D Emotion Space Concept. Austria: I-Tech, 2007. 281−300 [25] Grimm M, Kroschel K, Mower E, Narayanan S. Primitives-based evaluation and estimation of emotions in speech. Speech Communication, 2007, 49(10-11): 787-800 doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2007.01.010 [26] Wu D R, Parsons T D, Mower E, Narayanan S. Speech emotion estimation in 3D space. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Singapore, Singapore: IEEE, 2010. 737−742 [27] Wu D R, Parsons T D, Narayanan S S. Acoustic feature analysis in speech emotion primitives estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2010 InterSpeech. Makuhari, Japan: ISCA, 2010. 785−788 [28] Dunn O J. Multiple comparisons among means. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1961, 56(293): 52-64 doi: 10.1080/01621459.1961.10482090 [29] Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 1995, 57(1): 289-300 doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x [30] van der Maaten L, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9: 2579-2605 -













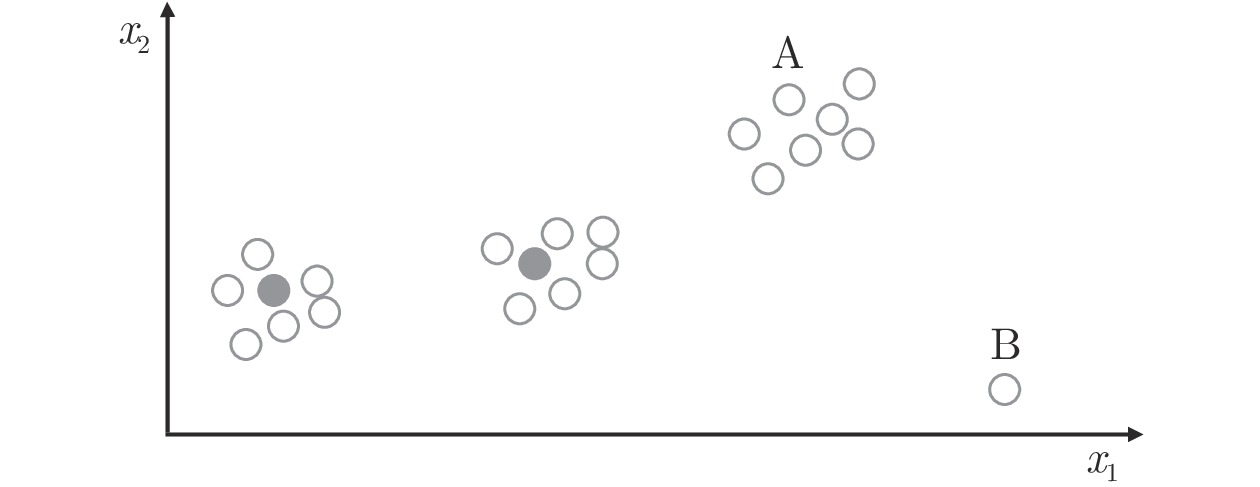
 下载:
下载: