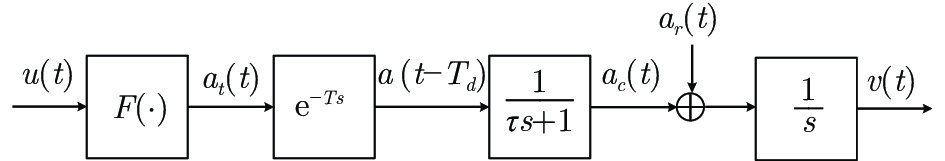
Robust Self-triggered Model Predictive Control for Accurate Stopping of High-speed Trains
-
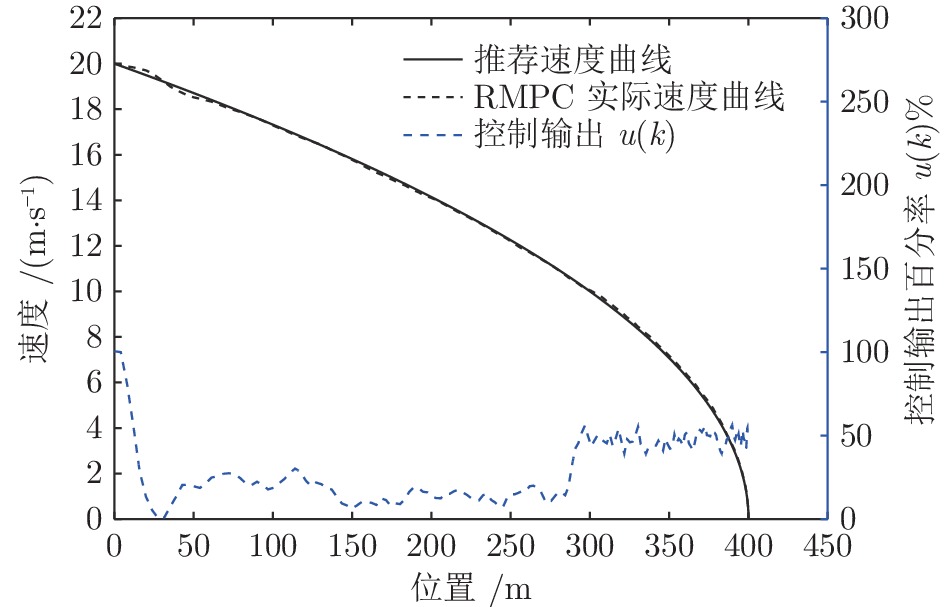
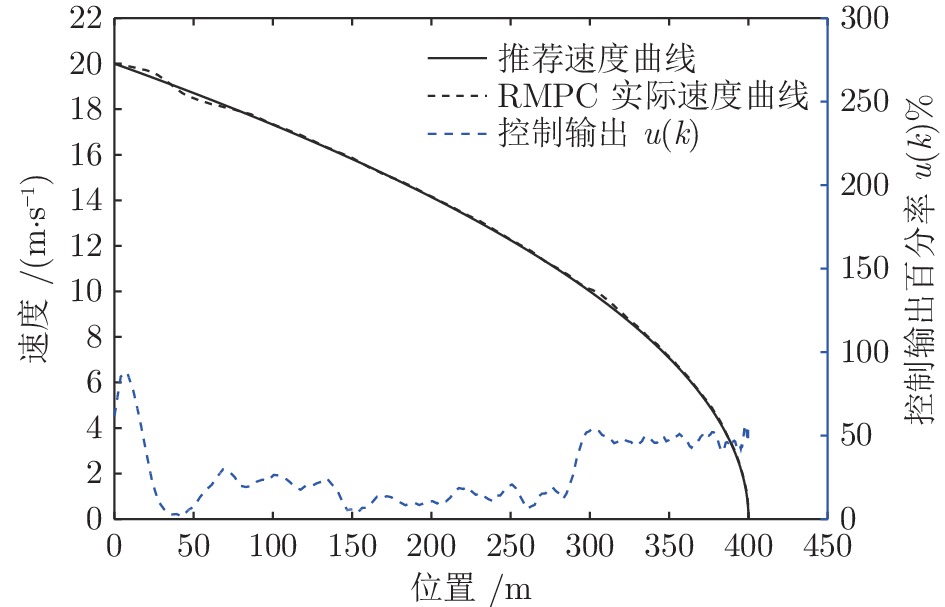
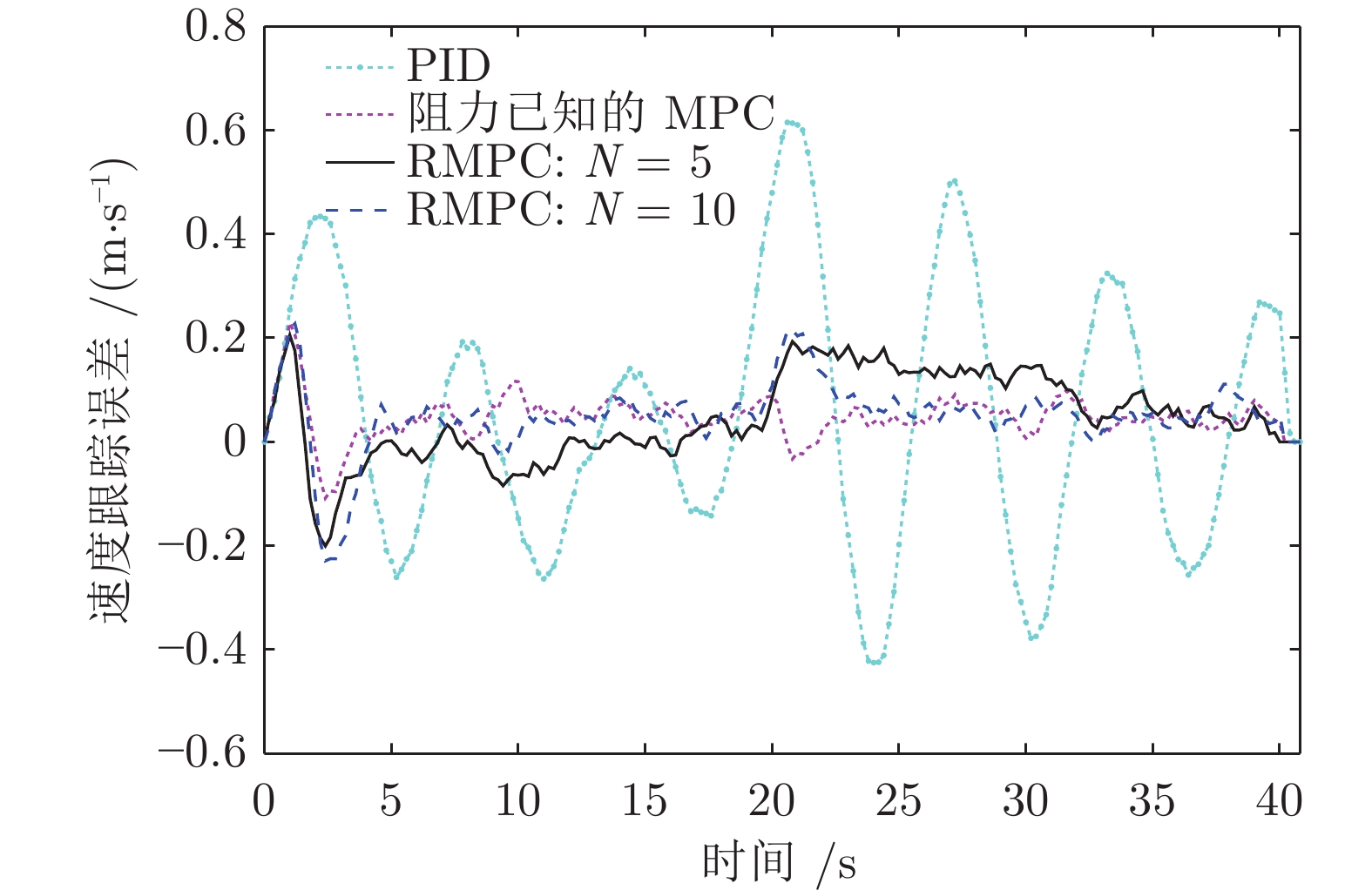
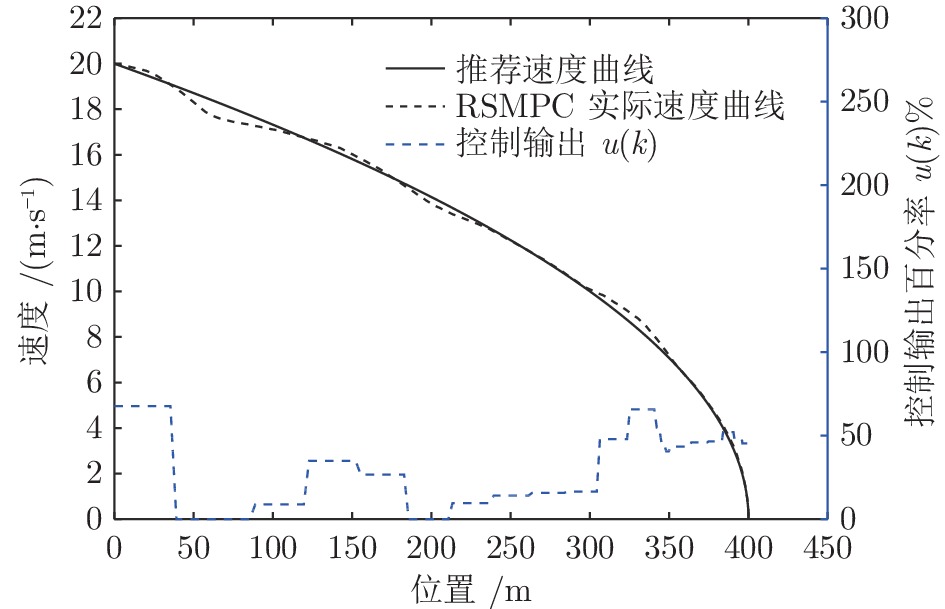
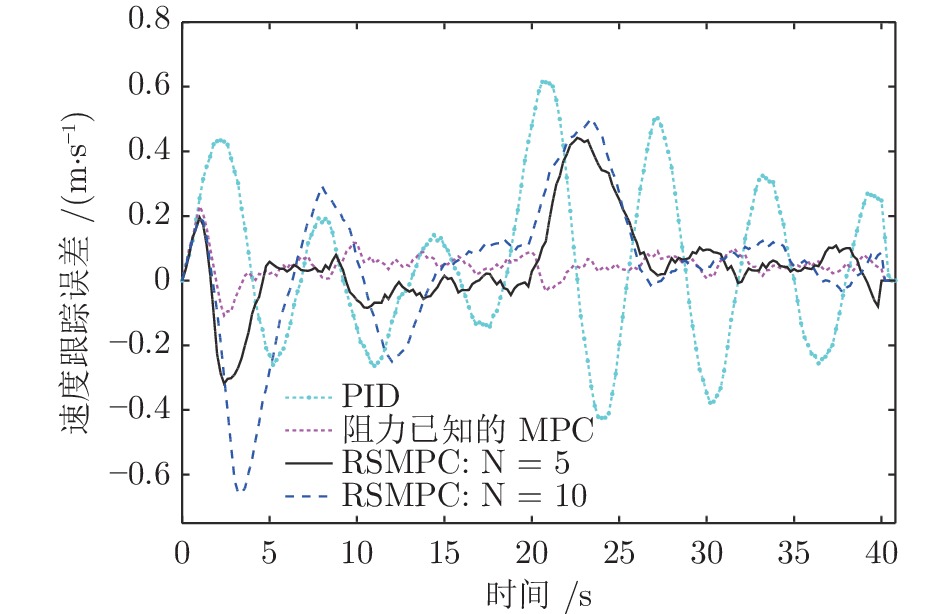
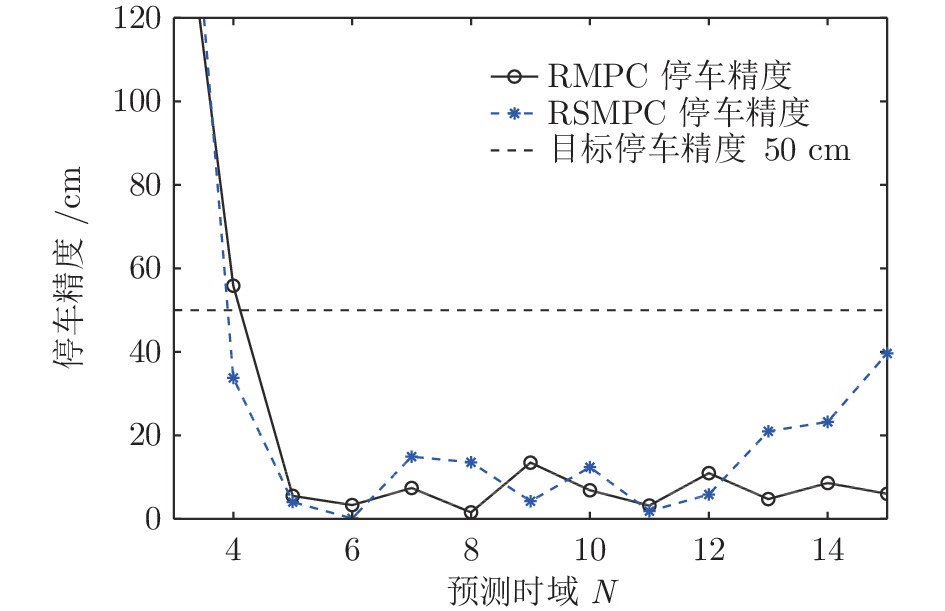
摘要: 列车精确停车作为列车自动运行(Automatic train operation, ATO)系统的一项核心功能, 对高速列车的安全和高效运行至关重要. 本文针对高速列车停车过程的特点, 考虑在避免控制输出频繁切换的前提下实现高精度的停车曲线跟踪, 提出了基于模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)的精确停车算法. 针对列车停车过程中外部不确定性阻力干扰, 采用鲁棒模型预测控制方法, 提高对外部干扰的鲁棒性. 引入自触发控制策略, 以进一步减少控制输出的频繁切换, 提高停车过程的舒适度. 该方法不需要每个采样时间都求解线性约束二次规划问题, 降低了对系统采样和通信能力的要求, 提高了算法的实用性. 分析结果表明, 高速列车精确停车控制方法的稳定性和性能指标的次优性可以得到保证. 基于高速列车实际运行数据的仿真结果验证了算法的有效性.Abstract: Accurate stopping is a key technology of the automatic train operation (ATO) system and plays an important role in safe and efficient train operations. This paper presents a model predictive control (MPC) based train stop control method according to the characteristics of train stopping processes, which can realize high-precision speed tracking and avoid frequent switching of control output. Considering the uncertain disturbance from the external environment, a robust MPC method is adopted to improve the robustness for external disturbances. Then, a self-triggered control scheme is introduced to reduce the frequent switches of the control output. Furthermore, the control scheme does not require calculating the linear constraints quadratic programming problem at all times resulting in lower sampling and communication requirements. The stability and sub-optimality of the approach can be guaranteed. The simulation results based on the real-life operation data verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1 The simulation parameters
参数 取值 最大制动加速度 −1.07 m/s2 列车重量 490 t 基本阻力 5.4 + 0.0098 v + 0.00163 v2 采样间隔T 0.2 s 制动模型时延Td 1.0 s 制动模型时间常数$\tau$ 0.4 s 制动起始点速度 20 m/s 制动起始点位置 0 m 停车点位置 400 m 限速 20 m/s 参考制动加速度 −0.5 m/s2 -
[1] 宁滨, 董海荣, 郑伟, 荀径, 高士根, 王洪伟, 孟令云, 李浥东. 高速铁路运行控制与动态调度一体化的现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2208-2217Ning Bin, Dong Hai-Rong, Zheng Wei, Xun Jing, Gao Shi-Gen, Wang Hong-Wei, Meng Ling-Yun, Li Yi-Dong. Integration of train control and online rescheduling for high-speed railways: challenges and future. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2208-2217 [2] Dong H, Ning B, Cai B, Hou Z. Automatic train control system development and simulation for high-speed railways. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 2010, 10(2): 6-8 doi: 10.1109/MCAS.2010.936782 [3] Hou Z, Wang Y, Yin C, Tang T. Terminal iterative learning control based station stop control of a train. International Journal of Control, 2011, 84(7): 1263-1274 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2011.569030 [4] Jin S, Hou Z, Chi R. Optimal terminal iterative learning control for the automatic train stop system. Asian Journal of Control, 2015, 17(5): 1992-1999 doi: 10.1002/asjc.1065 [5] Guo G, Wang Q. Fuel-Efficient En Route Speed Planning and Tracking Control of Truck Platoons. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(8): 3091-3103 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2872607 [6] Guo G, Li D. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control of Vehicular Platoons With Prescribed Tracking Performance. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 7511-7520 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2921816 [7] 佘守宪, 赵雁. 加加速度(加速度的时间变化率)——冲击、乘座舒适性、缓和曲线. 物理与工程, 2001, 11(3): 7-12, 22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7104.2001.03.002She Shou-Xian, Zhao Yan. Jerk (the time rate of change of acceleration) - impact, passenger's comfortability, transition curve. Physics and Engineering, 2001, 11(3): 7-12, 22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7104.2001.03.002 [8] Chen D, Chen R, Li Y, Tang T. Online learning algorithms for train automatic stop control using precise location data of balises. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(3): 1526-1535 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2265171 [9] Yasunobu S, Miyamoto S, Ihara H. A fuzzy control for train automatic stop control. Transactions of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, 1983, 19(11): 873-880 doi: 10.9746/sicetr1965.19.873 [10] Yasunobu S, Murai Y. Predictive fuzzy control and parking control. In: Proceedings of 1995 American Control Conference. Washington, USA: IEEE, 1995. 2277−2281 [11] Chen D, Gao C. Soft computing methods applied to train station parking in urban rail transit. Applied Soft Computing, 2012, 12(2): 759-767 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2011.10.016 [12] 于振宇, 陈德旺. 城轨列车制动模型及参数辨识. 铁道学报, 2011, 33(10): 37-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.10.007Yu Zhen-Yu, Chen De-Wang. Modeling and system identification of the braking system of urban rail vehicles. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(10): 37-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.10.007 [13] Wu P, Wang Q. Research of the automatic train stop control based on adaptive generalized predictive control. In: Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control Conference. Nanjing, China: IEEE, 2014. 3399-3404 [14] 罗仁士, 王义惠, 于振宇, 唐涛. 城轨列车自适应精确停车控制算法研究. 铁道学报, 2012, 30(4): 64-68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.04.011Luo Ren-Shi, Wang Yi-Hui, Yu Zhen-Yu, Tang Tao. Adaptive stopping control of urban rail vehicle, Journal of the China Railway Society. 2012, 30(4): 64-68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.04.011 [15] 王青元, 吴鹏, 冯晓云, 张彦栋. 基于自适应终端滑模控制的城轨列车精确停车算法. 铁道学报, 2016, 38(2): 56-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.02.008Wang Qing-Yuan, Wu Peng, Feng Xiao-Yun, Zhang Yan-Dong, Precise automatic train stop control algoritm based on adaptive terminal sliding mode control. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38(2): 56-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.02.008 [16] Qin S J, Badgwell T A. A survey of industrial model predictive control technology. Control Engineering Practice, 2003, 11(7): 733-764 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00186-7 [17] 席裕庚, 李德伟, 林姝. 模型预测控制——现状与挑战. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(3): 222-236 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60024-5Xi Yu-Geng, Li De-Wei, Lin Shu. Model Predictive Control - Status and Challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(3): 222-236 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60024-5 [18] Wang X, Tang T. Optimal operation of high-speed train based on fuzzy model predictive control. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 9(3): 1-14 [19] 汪仁智, 李德伟, 席裕庚. 采用预测控制的地铁节能优化控制算法. 控制理论与应用, 2017, 34(9): 1129-1135 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.60861Wang Ren-Zhi, Li De-Wei, Xi Yu-Geng. Metro energy saving optimization algorithm by using model predictive control. Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 34(9): 1129-1135 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.60861 [20] Farooqi H, Fagiano L, Colaneri P, Barlini D. Shrinking horizon parametrized predictive control with application to energy-efficient train operation. Automatica, 2020, 112(2020), 108635 [21] Liu X, Xun J, Ning B, Yuan L. An approach for accurate stopping of high-speed train by using model predictive control. In: Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference. Auckland, NZ: IEEE, 2019. 846−851 [22] Mayne D Q, Rawlings J B, Rao C V, Scokaert P O. Constrained model predictive control: Stability and optimality. Automatica, 2000, 36(6): 789-814 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00214-9 [23] 席裕庚. 预测控制 (第2版). 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013Xi Yu-Geng. Predictive control, 2nd ed. Beijing: Nationnal Defence Industry Press, 2013 [24] 陈虹. 模型预测控制. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013Chen Hong. Model Predictive control. Beijing: Science Press, 2013 [25] Chisci L, Rossiter J A, Zappa G. Systems with persistent disturbances: predictive control with restricted constraints. Automatica, 2001, 37(7): 1019-1028 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(01)00051-6 [26] Mayne D Q, Seron M M, Rakovi S V. Robust model predictive control of constrained linear systems with bounded disturbances. Automatica, 2005, 41(2): 219-224 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.08.019 [27] Velasco M, Fuertes J, Marti P. The self triggered task model for real-time control systems. In: Proceedings of the 24th IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Washington, USA: IEEE, 1995. 67-70 [28] Berglind J B, Gommans T M P, Heemels W P M H. Self-triggered MPC for constrained linear systems and quadratic costs. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2012, 45(17): 342-348 doi: 10.3182/20120823-5-NL-3013.00058 [29] Xun J, Yin J, Liu R, Liu F, Zhou Y, Tang T. Cooperative control of high-speed trains for headway regulation: A self-triggered model predictive control based approach. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 102(2019): 106-120 [30] Brunner F D, Heemels W P M H, Allgower F. Robust self-triggered MPC for constrained linear systems. In: Proceedings of 2014 European Control Conference. Strasbourg, FR: IEEE, 2014. 472−477 [31] Aydiner E, Brunner F D, Heemels W P M H, Allgower F. Robust self-triggered model predictive control for discrete-time linear systems based on homothetic tubes. In: Proceedings of 2015 European Control Conference. Linz, AT: IEEE, 2015. 1587−1593 [32] Brunner F D, Heemels W P M H, Allgower F. Robust self-triggered MPC for constrained linear systems: A tube-based approach. Automatica, 2016, 72(2016): 73-83 [33] Yin J, Tang T, Yang L, Xun J, Huang Y, Gao Z. Research and development of automatic train operation for railway transportation systems: A survey. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2017, 85(2017): 548-572 [34] 王呈, 陈晶, 荀径, 李开成. 基于混合滤波最大期望算法的高速列车建模. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2260-2267Wang Cheng, Chen Jing, Xun Jing, Li Kai-Cheng. Hybrid filter based expectation maximization algorithm for high-speed train modeling. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2260-2267 [35] 谢国, 金永泽, 黑新宏, 姬文江, 高士根, 高桥圣, 望月宽. 列车动力学模型时变环境参数自适应辨识. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2268-2280Xie Guo, Jin Yong-Ze, Hei Xin-Hong, Ji Wen-Jiang, Gao Shi-Gen, Takahashi Sei, Mochizuki Hiroshi. Adaptive identification of time-varying environmental parameters in train dynamics model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2268-2280 [36] Davis W J. The tractive resistance of electric locomotives and cars. General Electr. Rev., 1926, 29(10): 685-708 [37] Liu X, Ning B, Xun J, Wang C, Xiao X, Liu T. Parameter identification of train basic resistance using multi-innovation theory. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(18): 637-642 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.09.352 [38] Rakovic S V, Kerrigan E C, Kouramas K I, Mayne D Q. Invariant approximations of the minimal robust positively invariant set. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(3): 406-410 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.843854 [39] Kolmanovsky I, Gilbert E G. Maximal output admissible sets for discrete-time systems with disturbance inputs. In: Proceedings of 1995 American Control Conference. Seattle, US: IEEE, 1995. 1995−1999 [40] Chen H, Allgower F. A quasi-infinite horizon nonlinear model predictive control scheme with guaranteed stability. Automatica, 1998, 34(10): 1205-1217 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(98)00073-9 -




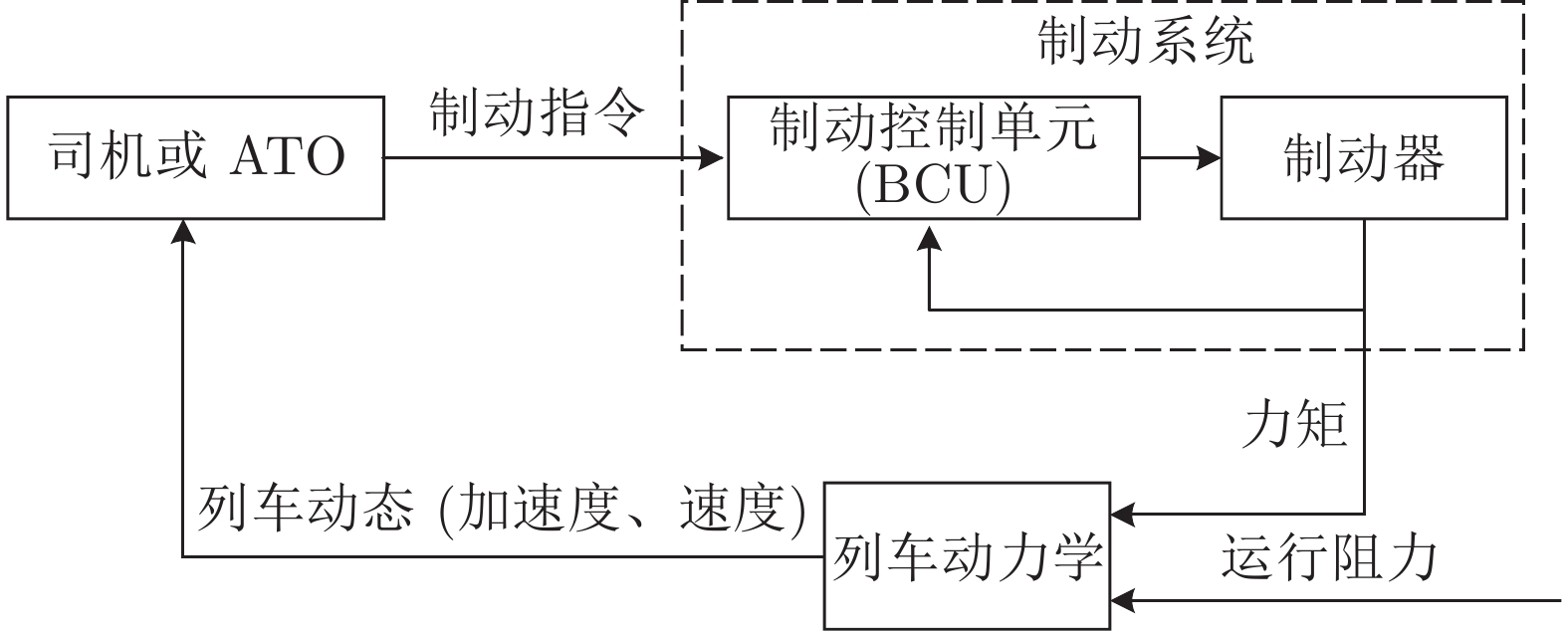
 下载:
下载: