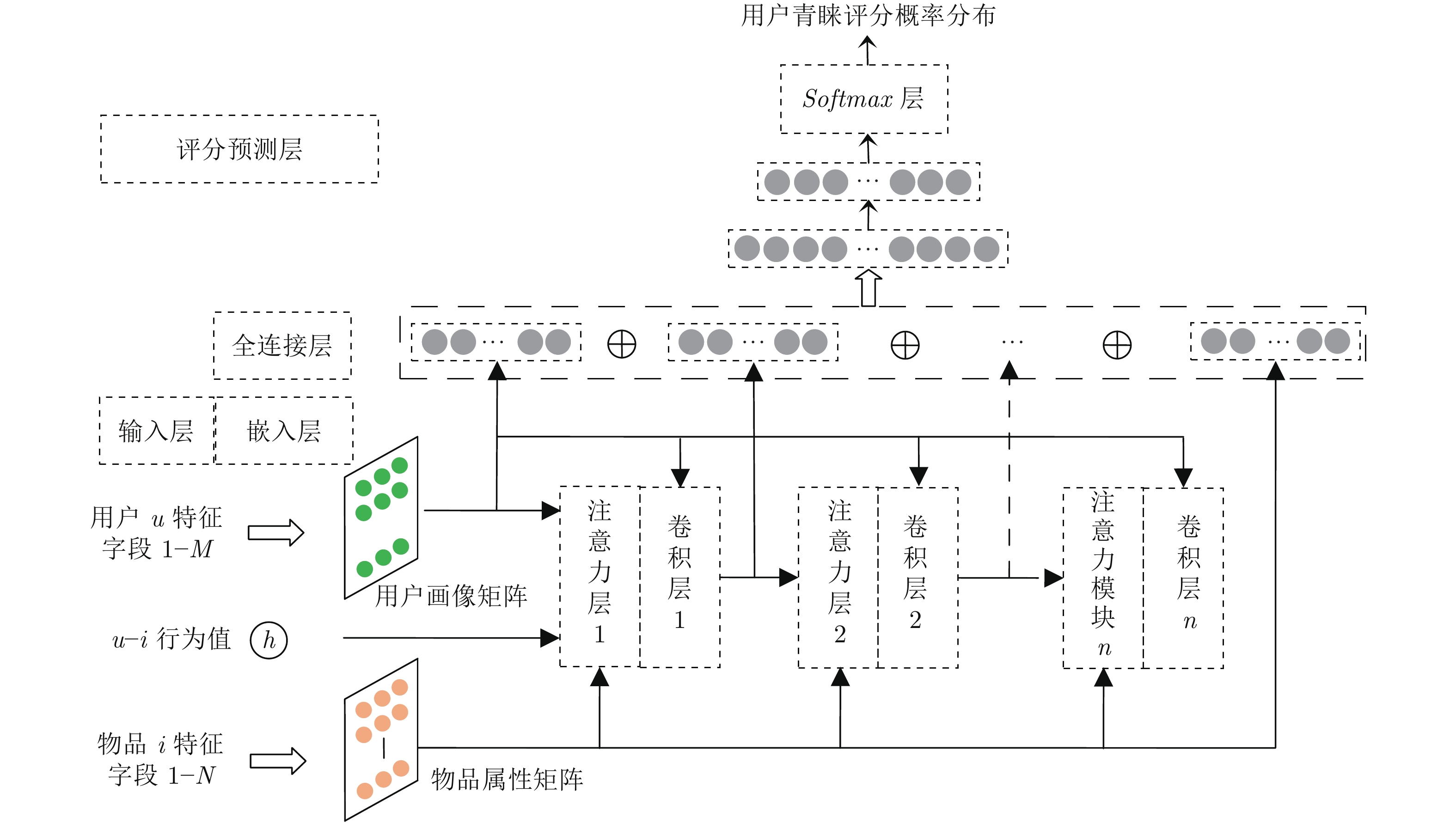
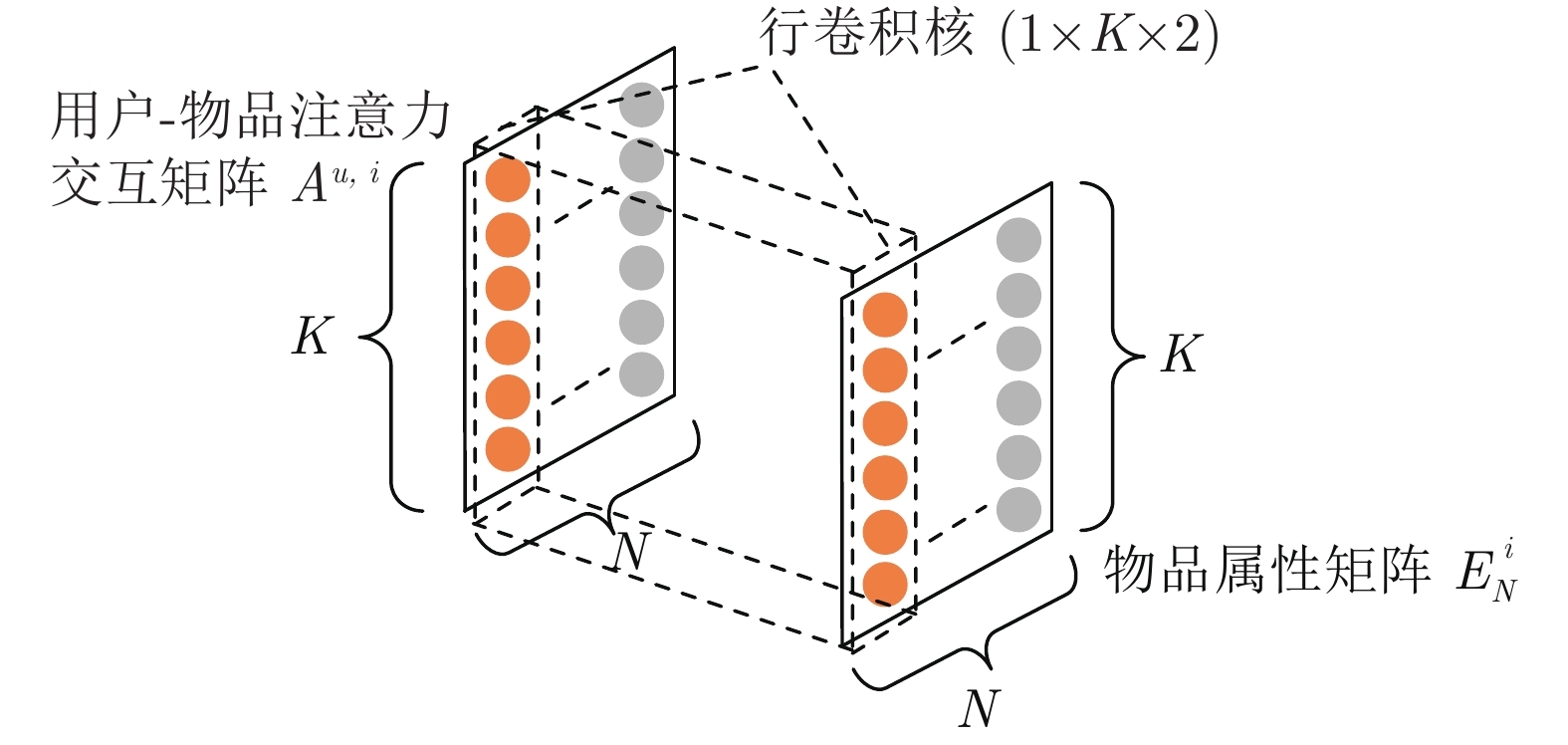
-
摘要: 一直以来, 各种推荐系统关注于如何挖掘用户与物品特征间的潜在关联, 特征信息的充分利用有利于用户到物品的精准匹配. 基于矩阵分解和分解机的推荐算法是该领域的主流, 前者学习用户历史行为而后者分析对象特征关系, 但都难以兼顾用户行为与个体特征. 而近年来, 深度神经网络凭借其强大的特征学习能力和灵活可变的结构被应用到了推荐系统领域. 鉴于此, 本文提出了一种基于注意力机制的协同卷积动态推荐网络(Attentionbased collaborative convolutional dynamic network, ACCDN), 它通过注意力机制实现用户历史行为、用户画像与物品属性的多重交互, 再通过卷积网络逐层捕捉更高阶的特征交互. 网络同时接受不同组块输出的低阶至高阶信息, 最后给出用户对指定物品青睐评分概率的预估. 而且本文还提出了一种基于无参时间衰减的用户兴趣标签来量化用户关注的变化. 通过比较若干先进模型在两个现实数据集的表现, 本文设计的动态推荐模型不但能够缓解推荐时滞性, 还能明显提高推荐质量, 为用户带来更好的个性化服务体验.Abstract: A variety of recommender systems focus on connecting users′ and item′s features, and the full use of the potential information presented by features contributes to the accurate user-item matching. Recommendation algorithms based on matrix factorization and factorization machine have risen to the backbone in this field, with the former learning the users′ behavior in history and the latter analyzing the individual features, but neither of them are taken into account by algorithms. Recently, deep neural networks are widely applied to recommendation because of their powerful representation learning and flexible structures. Thus, this paper proposes a novel attention-based collaborative convolutional dynamic network (ACCDN) for recommendation, which realizes the multiple interactions of the user behavior, user profiles and item attributes through attention mechanism and models higher-order interactions by convolution layers. And it absorbs all the low-to-high-order interaction features to predict the user preferable rating probability given an item. In addition, this paper puts forward the unique user interest label based on non-parametric time decay, as an auxiliary tool, to quantify the change of user focus. We conduct extensive experiments on two real-world datasets, which justifies that our proposed ACCDN not only alleviates the recommendation lag, but also improves the quality of recommendation significantly, bringing a better personalized service experience.
-
表 1 数据集概述表
Table 1 Statistics of the evaluation datasets
数据集 用户 物品 字段 样本 稀疏度 MovieLens-1M 6040 3883 5 1000 K 95.74% Niconico 20566 13195 7 1045 K 99.62% 表 2 超参对 ACCDN Top -30 推荐效果的影响 (Niconico数据集)
Table 2 ACCDN′s hyper-parameters′ infulence on the Top-30 recommendation for Niconico
固定参数 调节参数 预测准确率 (%) HR@30 NDCG@30 K=16,
T=32L=1 71.85 0.1659 0.0685 L=2 82.54 0.2545 0.0872 L=3 88.67 0.3001 0.0971 L=3,
T=32K=8 84.91 0.2683 0.0905 K=16 88.67 0.3001 0.0971 K= 24 89.02 0.3089 0.0972 L=3,
K=16T=8 80.22 0.2244 0.0868 T=16 84.58 0.2696 0.0919 T=32 88.67 0.3001 0.0971 表 3 推荐列表评析结果
Table 3 The evaluation results of recommendation lists between baselines and ACCDN
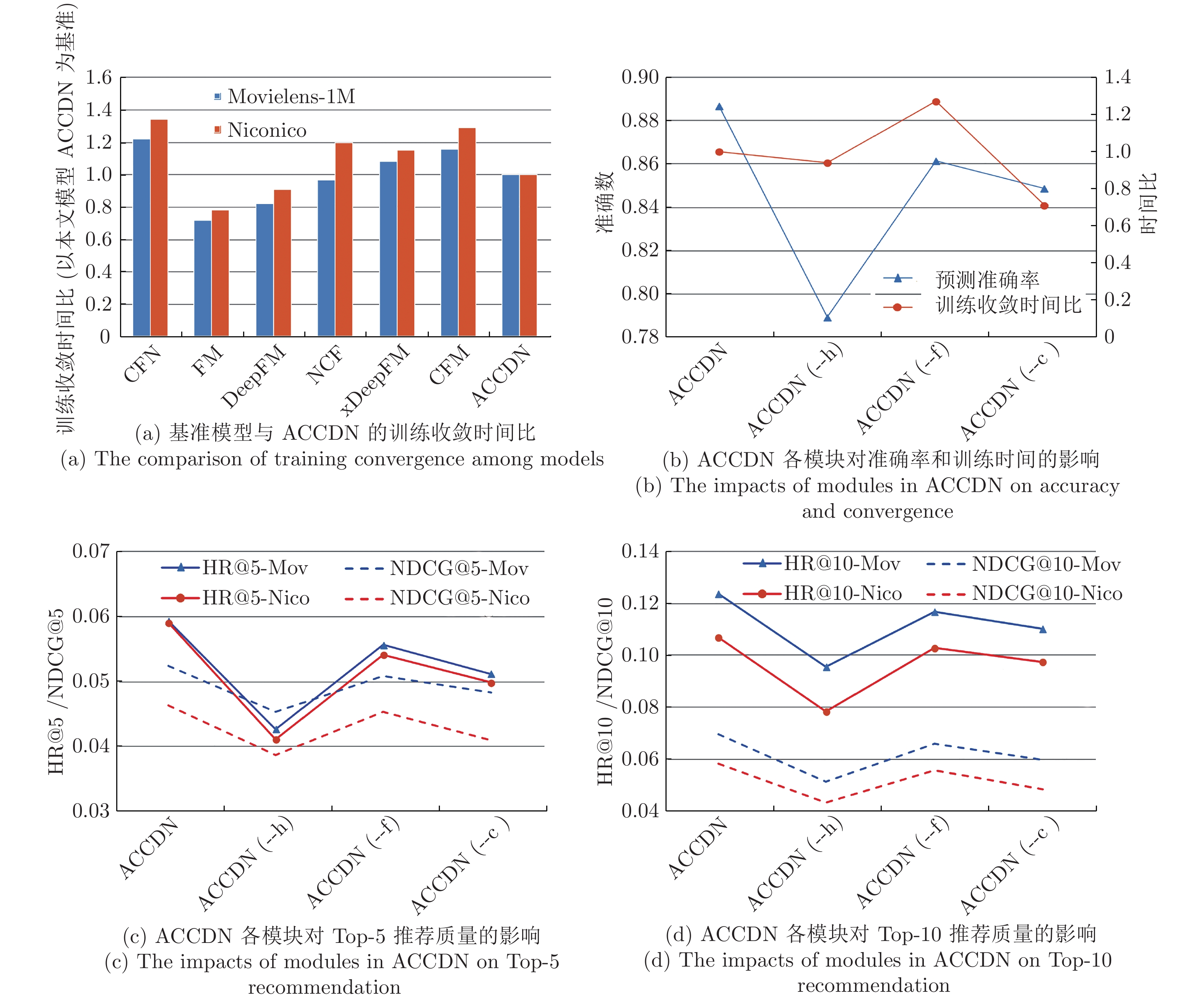
HR MovieLens-1 M Niconico HR@5 HR@10 HR@20 HR@30 HR@5 HR@10 HR@20 HR@30 CFN 0.0395 0.0788 0.1480 0.1923 0.0358 0.0676 0.1205 0.1747 FM 0.0498 0.0953 0.1899 0.2785 0.0471 0.0902 0.1659 0.2580 DeepFM 0.0577 0.1168 0.2101 0.3043 0.0543 0.1013 0.1928 0.2773 NCF 0.0543 0.1175 0.2081 0.2976 0.0485 0.0964 0.1799 0.2618 xDeepFM 0.0584 0.1250 0.2113 0.3109 0.0594 0.1032 0.2038 0.2843 CFM 0.0612 0.1233 0.2198 0.3177 0.0589 0.1054 0.2077 0.2917 ACCDN 0.0593 0.1237 0.2254 0.3253 0.0590 0.1069 0.2136 0.3001 NDCG MovieLens-1 MM Niconico NG@5 NG@10 NG@20 NG@30 NG@5 NG@10 NG@20 NG@30 CFN 0.0326 0.0475 0.0610 0.0738 0.0308 0.0425 0.0535 0.0694 FM 0.0382 0.0504 0.0658 0.0790 0.0339 0.0492 0.0617 0.0760 DeepFM 0.0415 0.0549 0.0720 0.0853 0.0403 0.0544 0.0689 0.0832 NCF 0.0444 0.0612 0.0779 0.0901 0.0420 0.0535 0.0712 0.0859 xDeepFM 0.0493 0.0684 0.0852 0.0940 0.0448 0.0565 0.0723 0.0901 CFM 0.0470 0.0649 0.0815 0.0921 0.0487 0.0566 0.0728 0.0914 ACCDN 0.0524 0.0697 0.0862 0.1027 0.0463 0.0583 0.0750 0.0971 注: ACCDN(--h) 表示本文模型在注意力机制模块不加人用户行为值进行交互. 表 4 Top-5动态推荐对比示例
Table 4 The examples of the dynamic Top-5 recommendation
用户1 喜欢类型 1) 动作 2) 冒险 3) 超凡 4) 运动 原Top-5推荐 xDeepFM 1. Tengen Toppa Gurren Lagann 动作/冒险/机甲 2. Mononoke Hime 动作/冒险/魔幻 3.Fate/Zero2 动作/超凡/魔幻
4. Fullmetal Alchemis 动作/冒险/魔幻 5. Hunter x Hunter 动作/冒险/超凡CFM 1. One Piece 动作/冒险/超凡/喜剧 2.Fate/Zero2 动作/超凡/魔幻 3. JoJo no Kimyou na Bouken 动作/超凡/冒险/青春
4. Kizumonogatari II 动作/悬疑/超凡 5. Hellsing Ultimate 动作/惊悚/超凡本文模型 1. Hunter x Hunter 动作/冒险/超凡 2. JoJo no Kimyou na Bouken 动作/超凡/冒险/青春 3. Fate/Zero 动作/超凡/魔幻
4. Fate/Zero2 动作/超凡/魔幻 5. One Piece 动作/冒险/超凡/喜剧增加三次用户行为: 1. Tonari no Totoro 动作/喜剧/超凡 2. Kuroko no Basket 校园/运动/青春 3. Redline 动作/赛车/科幻/运动 新Top-5推荐 xDeepFM 无变化 CFM 无变化 本文模型 1. JoJo no Kimyou na Bouken 动作/超凡/冒险/青春 2. One Piece 动作/冒险/超凡/喜剧 3. Fate/Zero 动作/超凡/魔幻
4. Fairy Tail 动作/冒险/喜剧/青春 5. Hunter x Hunter 动作/冒险/超凡用户2 喜欢类型 1) 惊悚 2) 超凡 3) 动作 原Top-5推荐 xDeepFM 1. Hellsing Ultimate 动作/惊悚/超凡 2. Akira 冒险/惊悚/超凡/科幻 3. Paprika 魔幻/惊悚/神秘
4. Vampire Hunter D 动作/魔幻/惊悚 5. Another 惊悚/恐怖/超凡CFM 1. Hellsing Ultimate 动作/惊悚/超凡 2. Ajin Part 1: Shoudou 动作/惊悚/神秘 3. Ajin 动作/惊悚/神秘
4. Change!! Getter Robo 动作/冒险/惊悚/科幻 5. Memories 惊悚/科幻本文模型 1. Higurashi no Naku Koro ni 惊悚/神秘/恐怖 2.Tokyo Ghoul 惊悚/超凡/动作/青春 3. Change!! Getter Robo 动作/冒险/
惊悚/科幻 4. Jigoku Shoujo 惊悚/神秘/超凡 5. Gakkou no Kaidan 惊悚/超凡增加三次用户行为: 1. Ano Natsu de Matteru 喜剧/生活 2. Ling Qi 动作/喜剧/超凡 3. One Piece 动作/冒险/超凡/喜剧 新Top-5推荐 xDeepFM 无变化 CFM 无变化 本文模型 1.Tokyo Ghoul 惊悚/超凡/动作/青春 2. Change!! Getter Robo 动作/冒险/惊悚/科幻 3. One Piece 动作/冒险/超凡/喜剧
4. Sankarea 喜剧/超凡/生活 5. Kemonozume 动作/惊悚/超凡 -
[1] Adomavicius G, Tuzhilin A. Toward the next generation of recommender systems: a survey of the state-of-the-art and possible extensions. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 17(6): 734-749. [2] Zhang S, Yao L, Sun A, Tay Y. Deep learning based recommender system: A survey and new perspectives. ACM Computing Surveys, 2017. [3] Rendle S. Factorization machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2011. 995−1000 [4] Blondel M, Fujino A, Ueda N, Ishihata M. Higher-order factorization machines. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. New York, USA: Curran Associates Inc, 2016. 3359−3367 [5] Koren Y. Factorization meets the neighborhood: A multifaceted collaborative fifiltering model. In: Proceedings of 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Las Vegas Nevada, USA: SIGKDD, 2008. 426-434 [6] Koren Y, Bell R, Volinsky C. Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer, 2009, 42(8): 30-37. doi: 10.1109/MC.2009.263 [7] Bharat K, Kamba T, Albers M. Personalized, interactive news on the Web. Multimedia Systems, 1998, 6(5): 349-358. doi: 10.1007/s005300050098 [8] Herlocker J L, Konstan J A, Borchers A, Riedl J. An algorithmic framework for performing collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. New York, USA: ACM, 1999. 230−237 [9] Salakhutdinov R, Mnih A. Probabilistic matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. New York, USA: NIPS, 2008. 1257–1264 [10] Lee J, Kim S, Lebanon G, Singer Y. Local low-rank matrix: approximation. In: Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. Atlanta, USA: ICML, 2013. 741−749 [11] Sedhain S, Menon A K, Sanner S, Xie L. Autorec: autoencoders meet collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web. Florence, Italy: WWW, 2015. 111−112 [12] Strub F, Mary J. Collaborative filtering with stacked denoising autoencoders and sparse inputs. NIPS Workshop, 2015. [13] Wu Y, DuBois C, Zheng A X, Ester M. Collaborative denoising auto-encoders for top-n recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. San Francisco, USA: WSDM, 2016. 153−162 [14] Salakhutdinov R, Mnih A, Hinton G. Restricted Boltzmann machines for collaborativeffltering. In: Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Machine Learning. Corvallis, USA: ICML, 2007. 791−798 [15] Jia X, Li X, Li K, Gopalakrishnan V, et al. Collaborative restricted Boltzmann machine for social event recommendation. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2016. 402−405 [16] 李金忠, 刘关俊, 闫春钢, 蒋昌俊. 排序学习研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(8): 1345-1369.Li Jin-Zhong, Liu Guan-Jun, Yan Chun-Gang, Jiang Chang-Jun. Research advances and prospects of learning to rank. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(8): 1345-1369. [17] Strub F, Gaudel R, Mary J. Hybrid recommender system based on autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Deep Learning for Recommender Systems. Boston, USA: ICPS, 2016. 11−16 [18] Dong X, Yu L, Wu Z, et al. A hybrid Collaborative filtering model with deep structure for recommender systems. In: Proceeding of 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, USA: AAAI, 2017. 1309−1315 [19] Liang D, Krishnan R G, Hoffman M D, Jebara T. Variational autoencoders for collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Web Conference. Lyon, France: IEEE, 2018. [20] He X, Liao L, Zhang H, Nie L, Hu X, Chua T. Neural collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web. Perth, Australia: ACM, 2017. 173−182 [21] Cheng H T, Koc L, Harmsen J, et al. Wide & deep learning for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on the Deep Learning for Recommender Systems. Boston, USA: ICPS, 2016. 7−10 [22] Guo H, Tang R, Ye Y, Li Z, He X. A factorization-machine based neural network for CTR prediction. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1703.04247, 2017. [23] Lian J, Zhou X, Zhang F, Chen Z, Xie X, Sun G. xDeepFM: Combining explicit and implicit feature interactions for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. London, UK: SIGKDD, 2018. [24] Zheng L, Noroozi V, Yu P S. Joint deep modeling of users and items using reviews for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. Cambridge, UK: ACM WSDM, 2017. 425−434 [25] Kim D, Park C, Oh J, Lee S, Yu H. Convolutional matrix factorization for document context-aware recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems. Boston, USA: RecSys, 2016. 233−240 [26] Covington P, Adams J, Sargin E. Deep neural networks for YouTube recommendations. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems. Boston, USA: RecSys, 2016. 191−198 [27] Soh H, Sanner S, White M, Jamieson G. Deep sequential recommendation for personalized adaptive user interfaces. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces. Limassol, Cyprus: ACM, 2017. 589–593 [28] Suglia A, Greco C, Musto C, Gemmis M, Lops P, Semeraro G. A deep architecture for content-based recommendations exploiting recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th Conference on User Modeling Adaptation and Personalization. Bratislava, Slovakia: UMAP, 2017. 202−211 [29] Li Z, Zhao H, Liu Q, Huang Z, Mei T, Chen E. Learning from history and present: Next-item recommendation via discriminatively exploiting user behaviors. arXiv, preprint, arXiv: 1808.01075, 2018. [30] Xin X, Chen B, He X, Wang D, Ding Y, Jose H M. CFM: Convolutional factorization machines for context-aware recommendation. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Macao, China: IJCAI, 2019. 3926−3932 [31] Jiang J, Yang D, Xiao Y, Shen C. Convolutional Gaussian embeddings for personalized recommendation with uncertainty. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Macao, China: IJCAI, 2019. 2642−2648 [32] Christakopoulou E, Karypis G. Local latent space models for top-n recommendation. In: Proceedings of 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. London, UK: SIGKDD, 2018. 1235−1243 [33] Zhou X, Liu D, Lian J, Xie X. Collaborative metric learning with memory network for multi-relational recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Macao, China: IJCAI, 2019. [34] Chae D, Kang J, Kim S, Lee J. CFGAN: A generic collaborative filtering framework based on generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Torino, Italy: CIKM, 2018. 137−146 [35] 李慧, 马小平, 施珺, 李存华, 仲兆满, 蔡虹. 复杂网络环境下基于信任传递的推荐模型研究. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(2): 363-376.Li Hui, Ma Xiao-Ping, Shi Jun, Li Cun-Hua, Zhong Zhao-Man, Cai Hong. A recommendation model by means of trust transition in complex network environment. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2018, 44(2): 363-376. [36] Chen J, Zhang H, He X, Nie L, Liu W, Chua T. Attentive collaborative filtering: Multimedia recommendation with item- and component-level attention. In: Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference. Tokyo, Japan: SIGIR, 2017. 335−344 [37] 冯永, 陈以刚, 强保华. 融合社交因素和评论文本卷积网络模型的汽车推荐研究. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(3): 518-529.Feng Yong, Chen Yi-Gang, Qiang Bao-Hua. Social and comment text CNN model based automobile recommendation. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2019, 45(3): 518-529. [38] Xu Z, Chen C, Lukasiewicz O, Miao Y, Meng X. Tag-aware personalized recommendation using a deep-semantic similarity model with negative sampling. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Indianapolis, USA: CIKM, 2016. 1921–1924 [39] Rawat Y S, Kankanhalli M S. ConTagNet: Exploiting user context for image tag recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on Multimedia Conference. Amsterdam, Netherland: ACM, 2016. 1102−1106 [40] Luong M, Pham H, Manning C D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1508.04025v5, 2015. [41] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1706.03762v5, 2017. [42] Jarvelin K, Kekalainen J. Cumulated gain-based evaluation of IR techniques. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2002, 20(4): 422-446. doi: 10.1145/582415.582418 -




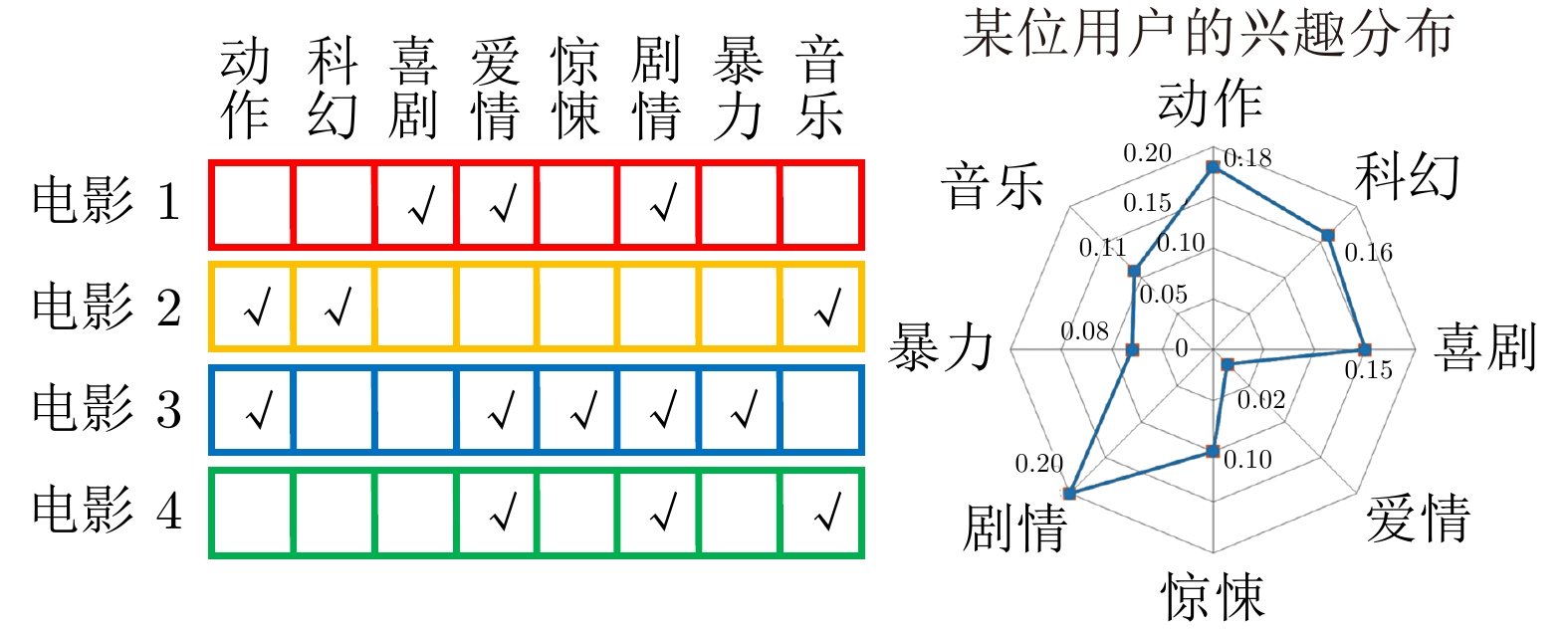
 下载:
下载: