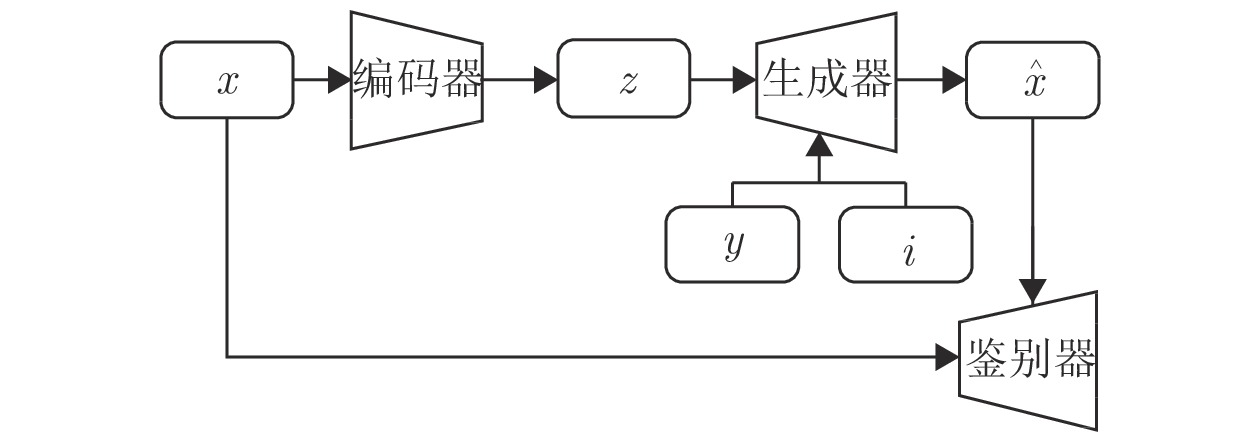
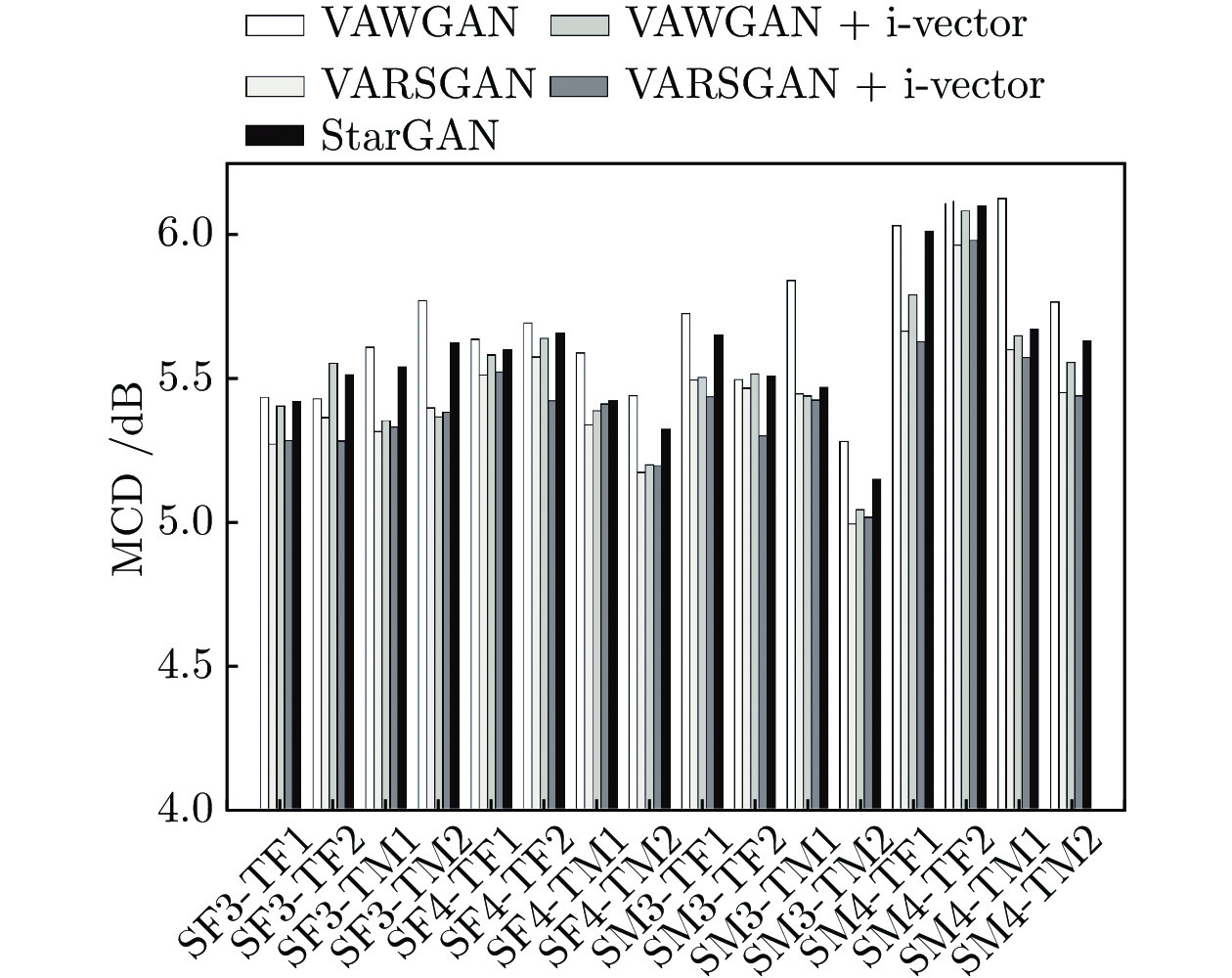
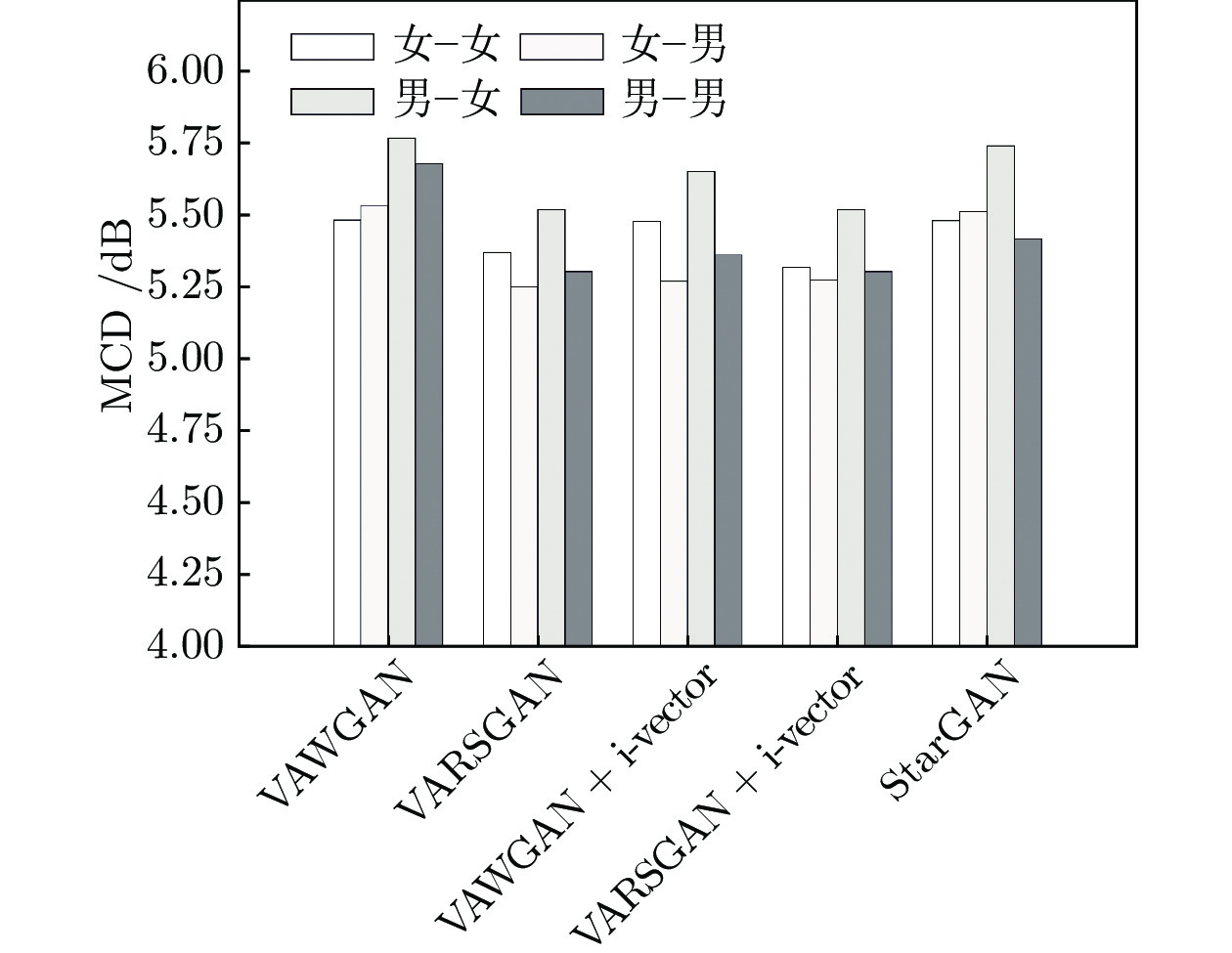
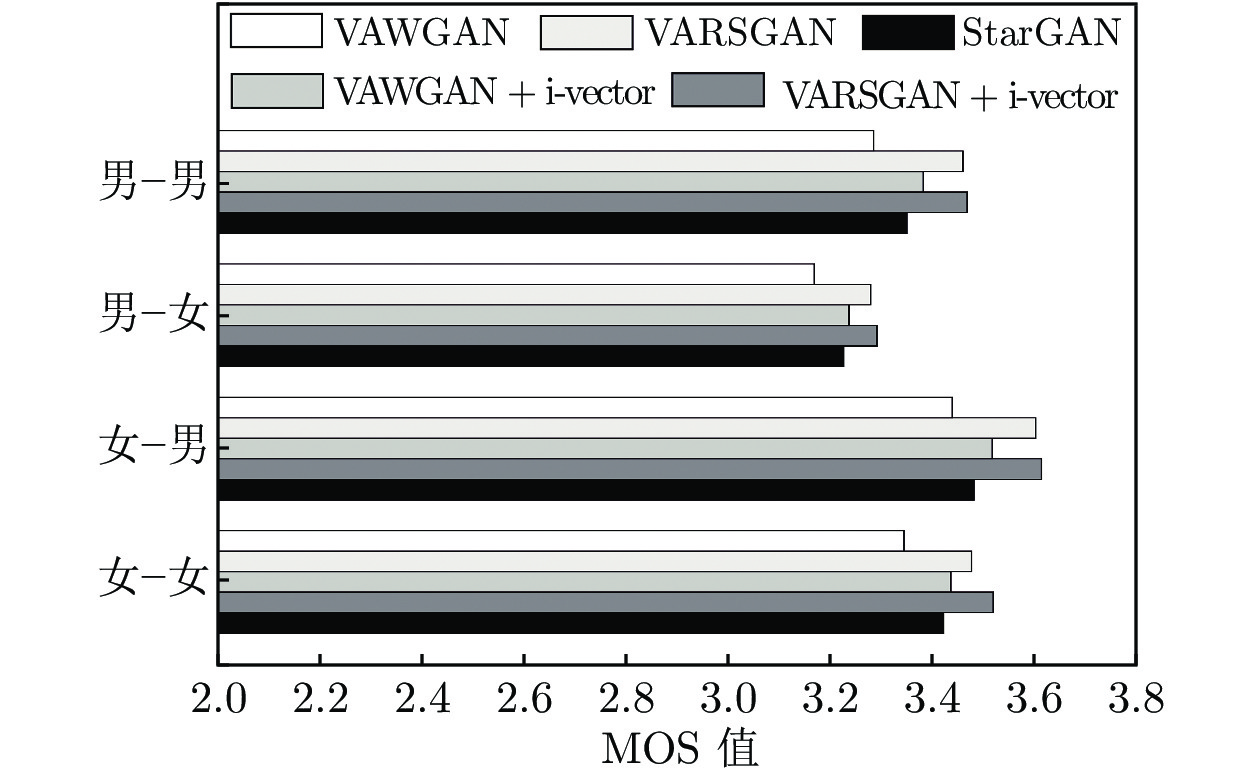
|
[1]
|
Godoy E, Rosec O, Chonavel T. Voice conversion using dynamic frequency warping with amplitude scaling, for parallel or nonparallel corpora. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 2011, 20(4): 1313-1323
|
|
[2]
|
Toda T, Chen L H, Saito D, Villavicencio F, Wester M, Wu Z, et al. The voice conversion challenge 2016. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Interspeech. San Francisco, USA: 2016. 1632−1636
|
|
[3]
|
Dong M, Yang C, Lu Y, Ehnes J W, Huang D, Ming H, et al. Mapping frames with DNN-HMM recognizer for non-parallel voice conversion. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA). Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2015. 488−494
|
|
[4]
|
Zhang M, Tao J, Tian J, Wang X. Text-independent voice conversion based on state mapped codebook. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2008. 4605−4608
|
|
[5]
|
Nakashika T, Takiguchi T, Minami Y. Non-parallel training in voice conversion using an adaptive restricted boltzmann machine. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2016, 24(11): 2032-2045 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2593263
|
|
[6]
|
Mouchtaris A, Van der Spiegel J, Mueller P. Nonparallel training for voice conversion based on a parameter adaptation approach. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2006, 14(3): 952-963 doi: 10.1109/TSA.2005.857790
|
|
[7]
|
Hsu C C, Hwang H T, Wu Y C, Tsaoet Y, Wang H M. Voice conversion from non-parallel corpora using variational auto-encoder. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA). Jeju, South Korea: IEEE, 2016. 1−6
|
|
[8]
|
Hsu C C, Hwang H T, Wu Y C, Tsao Y, Wang H M. Voice conversion from unaligned corpora using variational autoencoding Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Interspeech. Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. 3364−3368
|
|
[9]
|
Kameoka H, Kaneko T, Tanaka K, Hojo N. StarGAN-VC: Non-parallel many-to-many voice conversion using star generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT). Athens, Greece: IEEE, 2018. 266−273
|
|
[10]
|
Fang F, Yamagishi J, Echizen I, Lorenzo-Trueba J. High-quality nonparallel voice conversion based on cycle-consistent adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Calgary, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 5279−5283
|
|
[11]
|
Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: ACM, 2017. 214−223
|
|
[12]
|
王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 林懿伦, 郑心湖, 王飞跃. 生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 321-332Wang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Duan Yan-Jie, Lin Yi-Lun, Zheng Xin-Hu, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative Adversarial Networks: The State of the Art and Beyond. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 321-332.
|
|
[13]
|
Baby D, Verhulst S. Sergan. Speech enhancement using relativistic generative adversarial networks with gradient penalty. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Brighton, United Kingdom: IEEE, 2019. 106−110
|
|
[14]
|
Dehak N, Kenny P J, Dehak R, Dumouchelet P, Ouellet P. Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2010, 19(4): 788-798
|
|
[15]
|
汪海彬, 郭剑毅, 毛存礼, 余正涛. 基于通用背景-联合估计 (UB-JE) 的说话人识别方法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1888-1895Wang Hai-Bin, Guo Jian-Yi, Mao Cun-Li, Yu Zheng-Tao. Speaker recognition based on universal Background-Joint Estimation (UB-JE). Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1888-1895
|
|
[16]
|
Matějka P, Glembek O, Castaldo F, Alam M J, Plchot O, Kenny P, et al. Full-covariance UBM and heavy-tailed PLDA in i-vector speaker verification. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Prague, Czech Republic: IEEE, 2011. 4828−4831
|
|
[17]
|
Kanagasundaram A, Vogt R, Dean D, Sridharan S, Mason M. I-vector based speaker recognition on short utterances. In: Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. International Speech Communication Association (ISCA). Florence, Italy, 2011. 2341−2344
|
|
[18]
|
张一珂, 张鹏远, 颜永红. 基于对抗训练策略的语言模型数据增强技术. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 891-900Zhang Yi-Ke, Zhang Peng-Yuan, Yan Yong-Hong. Data augmentation for language models via adversarial training. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 891-900
|
|
[19]
|
Mao X, Li Q, Xie H, Lau R Y K, Wang Z, Smolley S P. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2794−2802
|
|
[20]
|
Morise M, Yokomori F, Ozawa K. WORLD: a vocoder-based high-quality speech synthesis system for real-time applications. IEICE TRANSACTIONS on Information and Systems, 2016, 99(7): 1877-1884
|
|
[21]
|
Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, Dumoulin V, Courville A C. Improved training of wasserstein gans. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Leicester, United Kingdom: IEEE, 2017. 5767−5777
|
|
[22]
|
Lorenzo-Trueba J, Yamagishi J, Toda T, Satio D, Villavicencio F, Kinnunen T, et al. The voice conversion challenge 2018: Promoting development of parallel and nonparallel methods. In: Proceedings of the Odyssey 2018 The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop. Les Sables d'Olonne, France: ISCA Speaker and Language Characterization Special Interest Group, 2018. 195−202
|
|
[23]
|
Maas A L, Hannun A Y, Ng A Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. Computer Science, 2013, 30(1): 1152-1160
|
|
[24]
|
梁瑞秋, 赵力, 王青云. 语音信号处理(C++版). 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2018.Liang Rui-Qiu, Zhao Li, Wang Qing-Yun. Speech Signal Preprocessing (C++). Beijing: China Machine Press, 2018.
|
|
[25]
|
张雄伟, 陈亮, 杨吉斌. 现代语音处理技术及应用. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2003.Zhang Xiong-Wei, Chen Liang, Yang Ji-Bin. Modern Speech Processing Technology and Application. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2003.
|
|
[26]
|
Chou J C, Lee H Y. One-shot voice conversion by separating speaker and content representations with instance normalization. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Interspeech. Graz, Austria, 2019. 664−668
|




 下载:
下载: