Recursive Bilinear Subspace Modeling and Model-free Adaptive Control of Wastewater Treatment
-
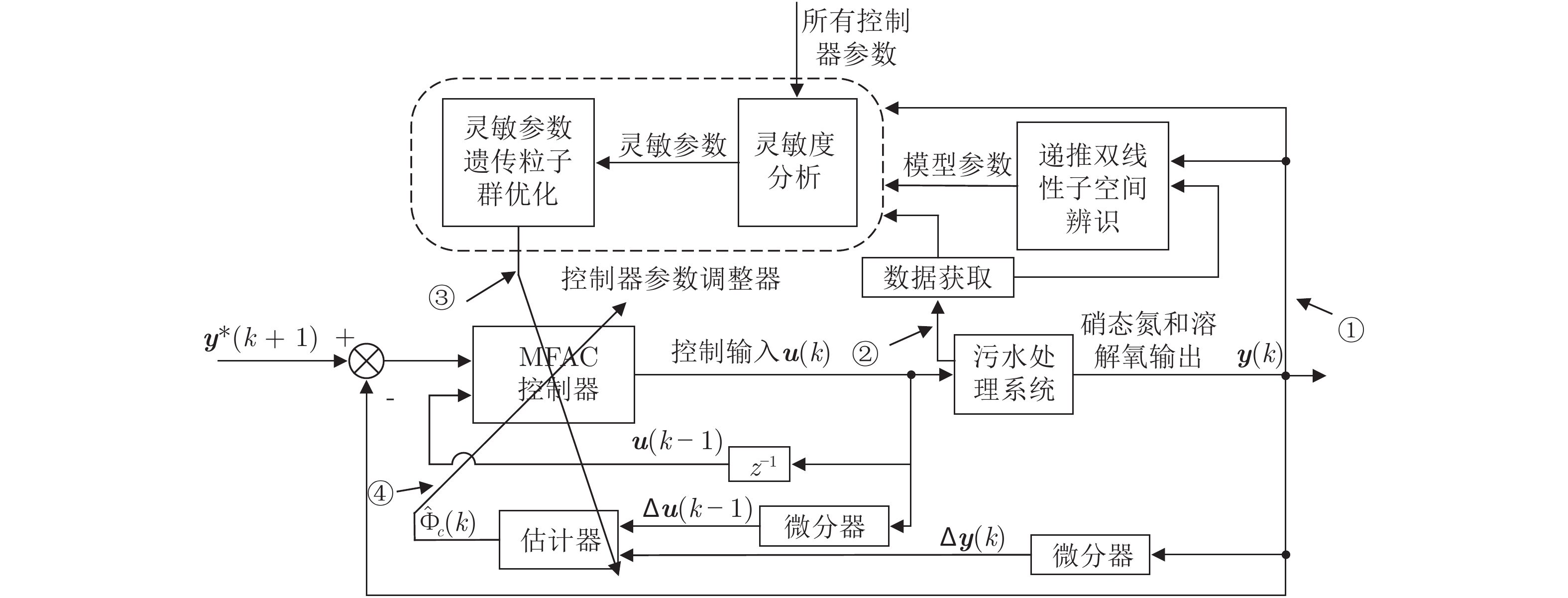
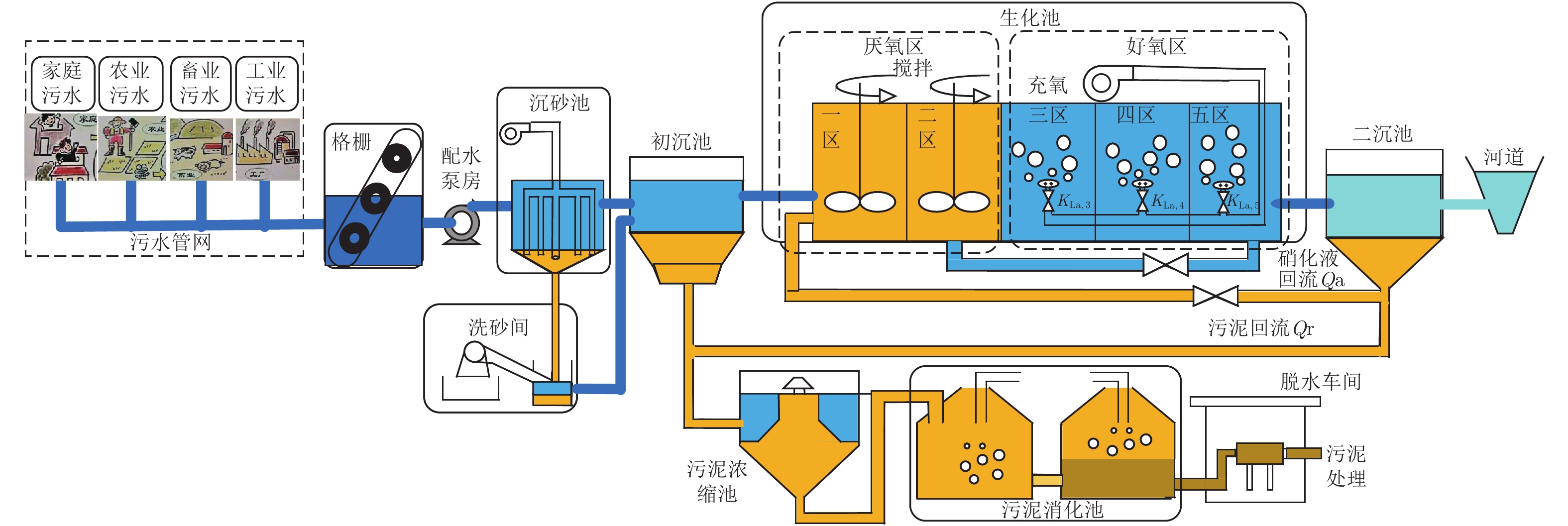
摘要: 污水处理过程中, 生化反应硝态氮浓度和溶解氧浓度是决定出水水质好坏的两个最关键变量, 难以采用常规基于模型的方法进行有效控制. 本文基于数据驱动建模与控制技术, 提出一种污水处理过程递推双线性子空间辨识(Recursive bilinear subspace identification, RBLSI)建模和无模型自适应控制方法. 首先, 针对污水处理过程的非线性时变动态特性, 采用最小二乘递推双线性子空间辨识方法建立污水处理生化反应过程具有参数自适应能力的递推双线性模型; 其次, 基于建立的数据驱动模型, 采用基于多参数灵敏度分析(Multi-parameter sensitivity analysis, MPSA)和遗传粒子群优化(Genetic algorithm-particle swarm optimization, GA-PSO)算法的无模型自适应控制(Model-free adaptive control, MFAC)方法对硝态氮和溶解氧浓度进行直接数据驱动控制; 最后, 数据实验及其比较分析表明了所提方法的有效性和优越性.
-
关键词:
- 污水处理 /
- 递推双线性子空间辨识 /
- 无模型自适应控制 /
- 多参数灵敏度分析
Abstract: Conventional model-based approaches are unable to control the nitrate nitrogen concentration and dissolved oxygen concentration of biochemistry reaction effectively, which are the two most critical variables that determine the quality of effluent in wastewater treatment process. In this paper, a recursive bilinear subspace identification (RBLSI) modeling and model-free adaptive control method for wastewater treatment based on data-driven modeling and control technology was proposed. Firstly, according to the nonlinear time-varying dynamic characteristics of wastewater treatment process, a recursive bilinear model with parameter adaptability for biochemical reaction process of wastewater treatment was established by using the least square recursive bilinear subspace identification method. Secondly, the model-free adaptive control (MFAC) method based on the multi-parameter sensitivity analysis (MPSA) and genetic algorithm−particle swarm optimization (GA-PSO) algorithm was used to directly control the nitrate concentration and dissolved oxygen concentration in a data-driven mode based on the established data-driven model. Finally, data experiments and comparative analysis show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method. -
表 1 不同算法的RMSE比较
Table 1 Comparison of RMSE based on different algorithms
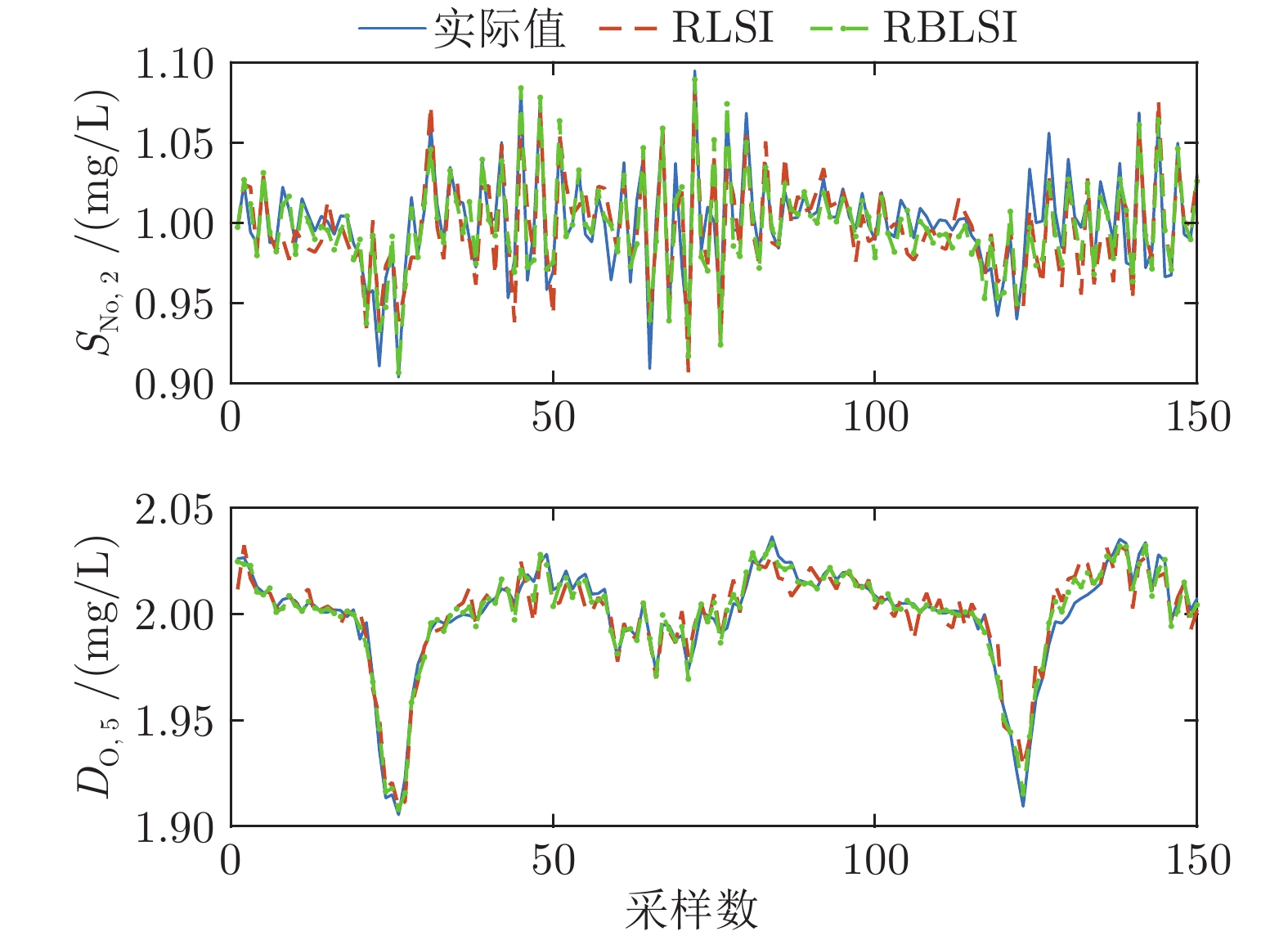
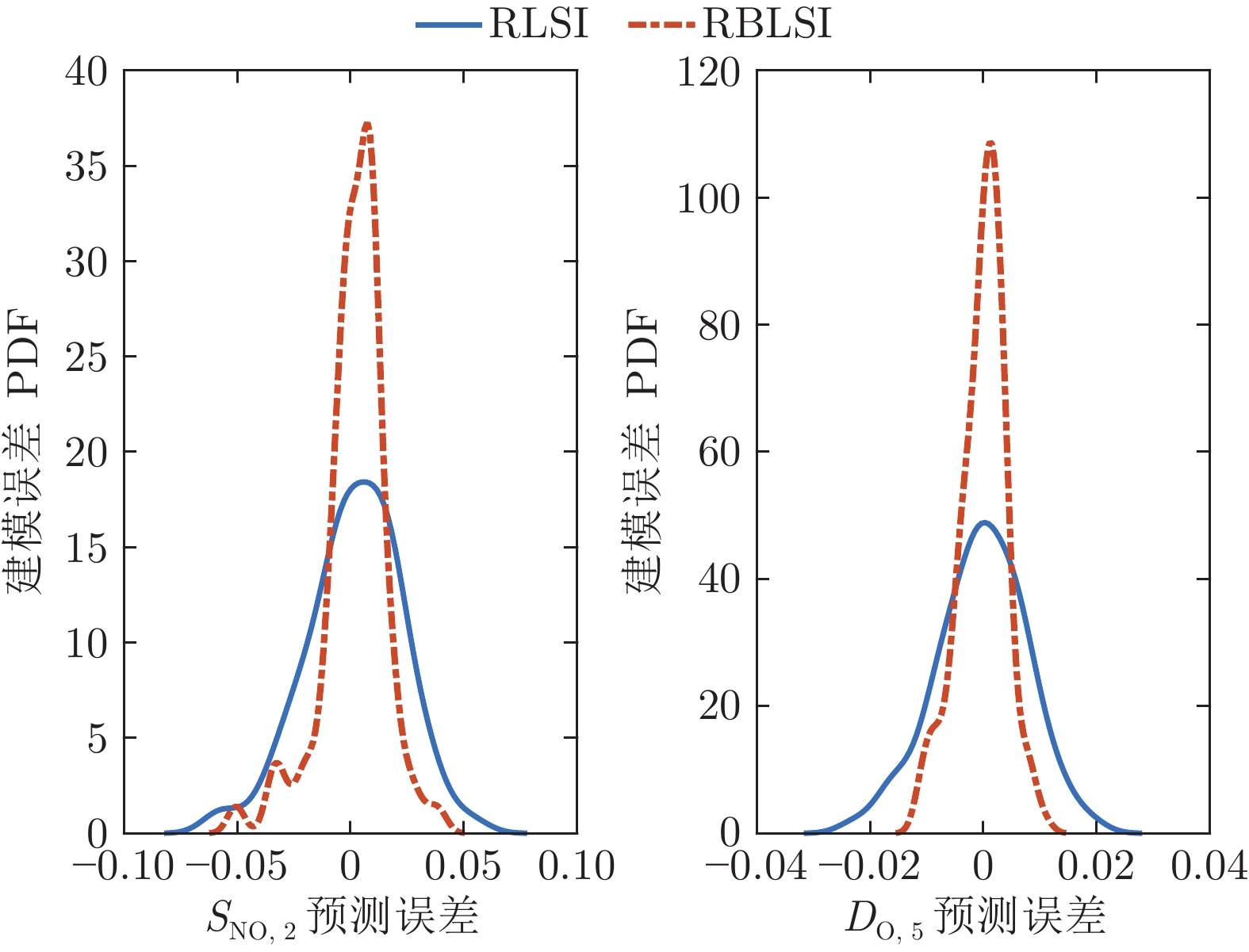
算法 RMSE $(S_{\rm{NO},2 })$ RMSE $(D_{\rm{O},5})$ RBLSI 0.0165 0.0046 RLSI 0.0211 0.0085 表 2 CFDL-MFAC控制器参数灵敏度分析结果
Table 2 Sensitivity analysis results of CFDL-MFAC controller parameters
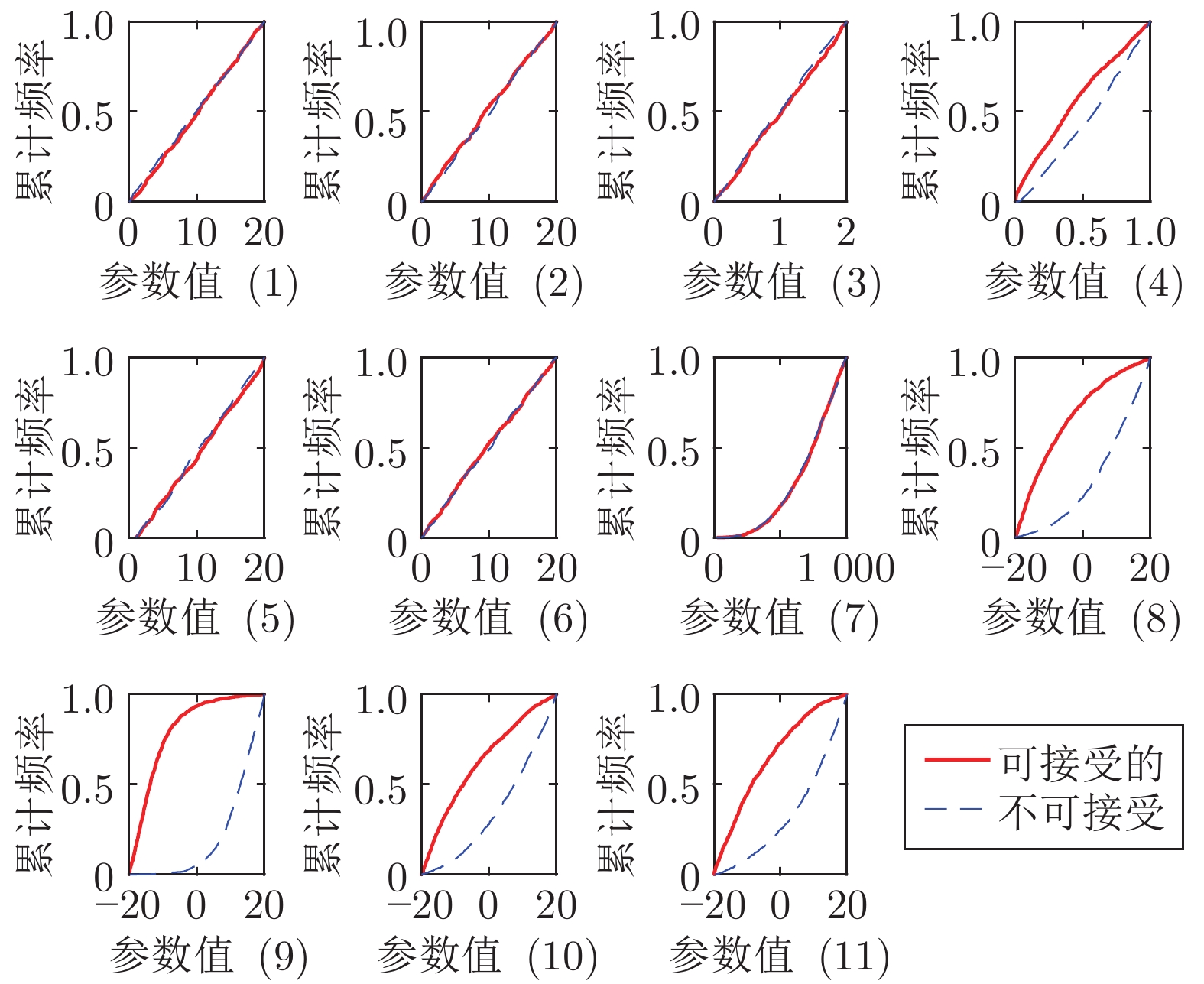
序号 参数 含义 DS 不灵敏参数固定值 1 $\lambda$ 输入权重因子 0.9981 0.5 2 $\mu $ PJM权重因子 0.9985 0.6 3 $\eta $ PJM步长因子 0.9996 0.5 4 $\rho $ 输入步长因子 0.9378 1.0 5 $\alpha $ PJM重置限定参数 0.998 1.5 6 $b_1 $ PJM重置限定参数 0.9991 0.55 7 $b_2 $ PJM重置限定参数 0.9995 0.8 8 $\phi _{11}(0)$ PJM初值 0.5551 − 9 $\phi _{12}(0)$ PJM初值 −0.6339 − 10 $\phi _{21}(0)$ PJM初值 0.7289 − 11 $\phi _{22}(0)$ PJM初值 0.5779 − 表 3 GA-PSO算法参数
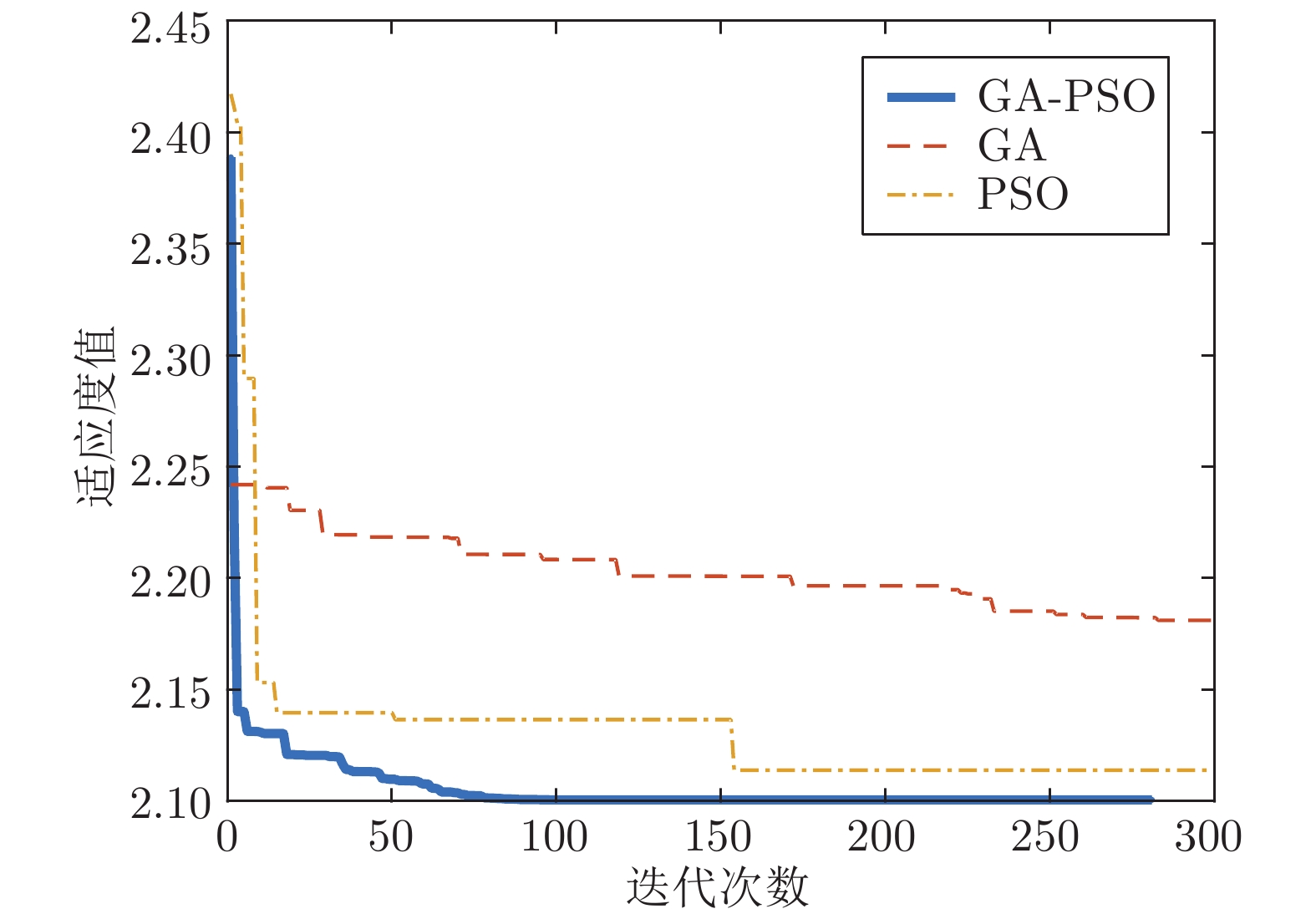
Table 3 GA-PSO algorithm parameters
前期 GA 参数 后期 PSO 参数 种群规模 $M=40$ 种群规模 $M=40$ 指定遗传代数 60 最大迭代次数 240 基因重组概率 0.7 加速系数 ${c_1} = 4,\;{c_2} = 2$ 变异概率 0.25 最大惯性
权重系数$W_{\max } =0.9$ 子代选择系数 T = 1,
${\alpha _T} = 0.5$最小惯性
权重系数$W_{\min } =0.1$ 表 4 不同算法控制性能对比
Table 4 Comparison of control performance based on different algorithms
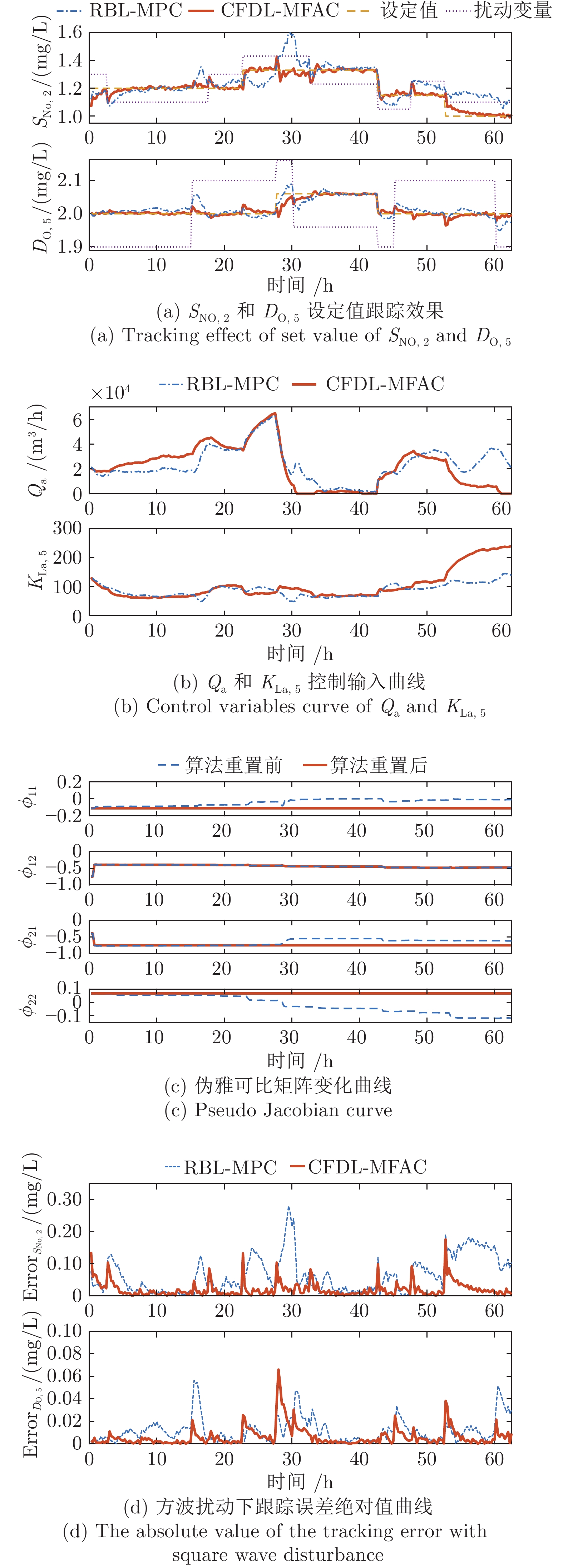
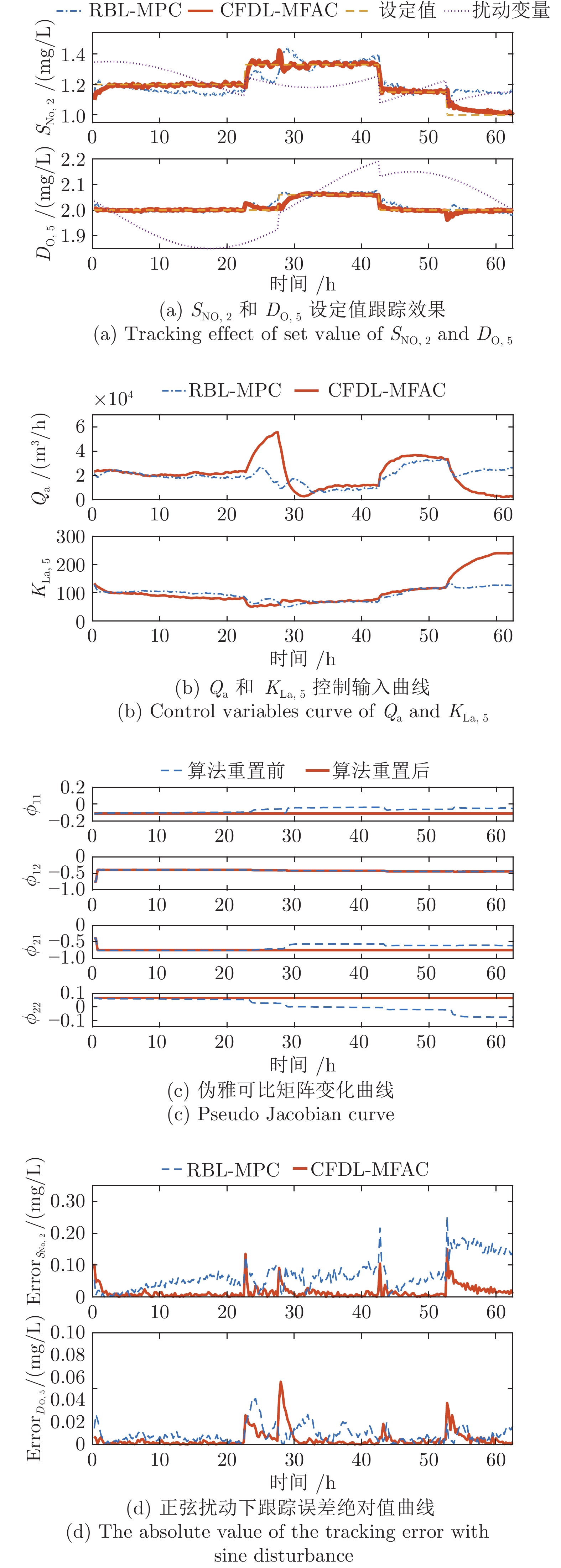
算法 RBL-MPC CFDL-MFAC 控制量平均求解时间 (s) 0.0987 0.00003528 方波扰动 RMSE $S_{\rm{NO},2} $ 0.0865 0.0297 $D_{\mathrm{O},5} $ 0.0158 0.0107 正弦扰动 RMSE $S_{\mathrm{NO},2} $ 0.0859 0.0249 $D_{\mathrm{O},5} $ 0.0099 0.0089 -
[1] 魏伟, 左敏, 李伟, 王小艺, 刘载文. 污水处理过程溶解氧浓度的自抗扰控制. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(1): 24−30 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70229Wei Wei, Zuo Min, Li Wei, Wang Xiao-Yi, Liu Zai-Wen. Control of dissolved oxygen for a wastewater treatment process by active disturbance rejection control approach. Control Theory and Applications, 2018, 35(1): 24−30 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70229 [2] Phuc B D H, You S S, Hung B M, Kim H S. Robust control synthesis for the activated sludge process. Environmental Science Water Research and Technology, 2018, 4: 992−1001 doi: 10.1039/C8EW00032H [3] 栗三一, 乔俊飞, 李文静, 顾锞. 污水处理决策优化控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2198−2209Li San-Yi, Qiao Jun-Fei, Li Wen-Jing, Gu Ke. Advanced decision and optimization control for wastewater treatment plants. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2198−2209 [4] 宋贺达, 周平, 王宏, 柴天佑. 高炉炼铁过程多元铁水质量非线性子空间建模及应用. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(11): 1664−1679Song He-Da, Zhou Ping, Wang Hong, Chai Tian-You. Nonlinear subspace modeling of multivariate molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(11): 1664−1679 [5] Virote B, Tharach J. Data-driven stochastic subspace identification of flutter derivatives of bridge decks. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2010, 98(12): 784−799 doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2010.07.003 [6] Wahab N A Katebi R, Balderud J, Rahmat M F. Datadriven adaptive model-based predictive control with application in wastewater systems. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2011, 5(6): 803−812 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2010.0068 [7] Zhou P Dai P Song H D. Data-driven recursive subspace identification based online modelling for prediction and control of molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 11(14): 2343−2351 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2016.1474 [8] Zhou P, Song He D, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven nonlinear subspace modeling for prediction and control of molten iron quality indices in blast furnace ironmaking. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(5): 1761−1774 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2016.2631124 [9] Gijsvander V, Janwillem W , Bergamasco M, Lovera M, Verhaegen M. Closed-loop subspace identification methods: an overview. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2013, 7(10): 1339−1358 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2012.0653 [10] Qin S. J. An overview of subspace identification. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2006, 30(2006): 1502−1513 [11] Samsudin S I, Rahmat M F, Norhaliza A W, Zulfatman H, Siti N S M, Mashitah C R. Two-time scales matrix decomposition for wastewater treatment plant. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE Eighth International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications. Melaka, Malaysia: IEEE, 2012. 347−351 [12] Dong N, Wu C H, Gao Z K, Chen Z Q, Ip W H. Data-driven control based on simultaneous perturbation stochastic approximation with adaptive weighted gradient estimation. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2016, 10(2): 201−209 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2015.0636 [13] Han H G, Zhang L, Qiao J F, Data-based predictive control for wastewater treatment process. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 1498−1512 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2779175 [14] Qiao J F, Zhou H B. Modeling of energy consumption and effluent quality using density peaks-based adaptive fuzzy neural network. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(5): 968−976 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2018.7511168 [15] Han H G, Qiao J F, Nonlinear model-predictive control for industrial processes: an application to wastewater treatment process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(4): 1970−1982 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2266086 [16] Han H G, Zhang L, Hou Y, Qiao J F. Nonlinear model predictive control based on a self-organizing recurrent neural network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(2): 402−415 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2465174 [17] Wang D, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Self-Learning optimal regulation for discrete-time nonlinear systems under eventdriven formulation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 65(3): 1272−1279 [18] Wang D, He H B, Liu D R. Adaptive critic nonlinear robust control: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3429−3451 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2712188 [19] 侯忠生. 非线性系统参数辨识、自适应控制和无模型学习自适应控制 [博士学位论文]. 东北大学, 中国, 1994.Hou Zhong-Sheng. The Parameter Identification, Adaptive Control and Model Free Learning Adaptive Control for Nonlinear Systems [Ph.D. dissertation], Northeastern University, China, 1994. [20] Hou Z S, Jin S T, Data-driven model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2173−2188 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2176141 [21] Hou Z S, Jin S T. A novel data-driven control approach for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2011, 19(6): 1549−1558 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2010.2093136 [22] Hou Z S, Bu X H. Model-free adaptive control with data dropouts. Express Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(8): 10709−10717 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.01.158 [23] Zhu Y M, Hou Z S. Controller dynamic linearisation-based model-free adaptive control framework for a class of nonlinear system. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 9(7): 1162−1172 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2014.0743 [24] Bu X H, Qiao Y X, Hou Z S, Yang J Q. Model free adaptive control for a class of nonlinear systems using quantized information. Asian Journal of Control, 2018, 20(2): 962−968 doi: 10.1002/asjc.1610 [25] 侯忠生, 金尚泰. 无模型自适应控制: 理论与应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. 34−122Hou Zhong-Sheng, Jin Shang-Tai. Model Free Adaptive Control: Theory and Application. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. 34−122 [26] Hou Z S, Chi R H, Gao H J. An overview of dynamiclinearization-based data-driven control and applications. IEEE Transactions on Industral Electronics, 2017, 64(5): 4076−4090 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2636126 [27] 乔俊飞, 薄迎春, 韩广. 基于ESN 的多指标DHP控制策略在污水处理过程中的应用. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(7): 1146−1151Qiao Jun-Fei, Bo Ying-Chun, Han Guang. Application of ESN-based multi indices dual heuristic dynamic programming on wastewater treatment process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(7): 1146−1151 [28] Vincent V, Verhaegenz M. Identification of multivariable bilinear state space systems based on subspace techniques and separable least squares optimization. International Journal of Control, 2010, 74(18): 1824−1836 [29] Francesco V, Minh Q P, Raimondo B, Longman R W. Linear state representations for identification of bilinear discretetime models by interaction matrices. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2014, 77(4): 1561−1576 doi: 10.1007/s11071-014-1399-9 [30] Van B H. Theory of adjoint structures. AIAA Journal, 1976, 14(7): 977−979 doi: 10.2514/3.7174 [31] Wang D Y, Zeng P, Li L W, Wang K. A novel particle swarm optimization algorithm. In: Processings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Sciences. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2010. 408−411 [32] Eberhart R C, Shi Y H. Particle swarm optimization: developments, applications and resources. In: Proceedings of the 2001 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2001. 81−86 [33] 吉根林. 遗传算法研究综述. 计算机应用与软件, 2004, 21(2): 69−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386X.2004.02.032Ji Gen-Lin. Survey on genetic algorithm. Computer Applications and Software, 2004, 21(2): 69−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386X.2004.02.032 [34] Tang K S, Man K F, Kwong S, He Q H. Genetic algorithms and their applications. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 1996, 13(6): 22−37 doi: 10.1109/79.543973 -




 下载:
下载: