An Improved Video Segmentation Network and Its Global Information Optimization Method
-
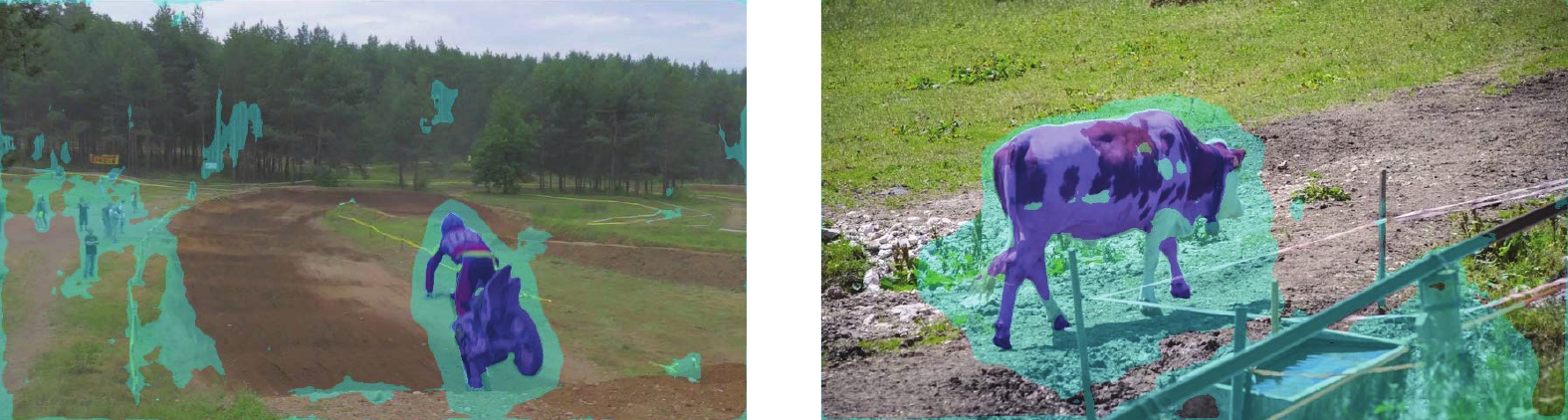
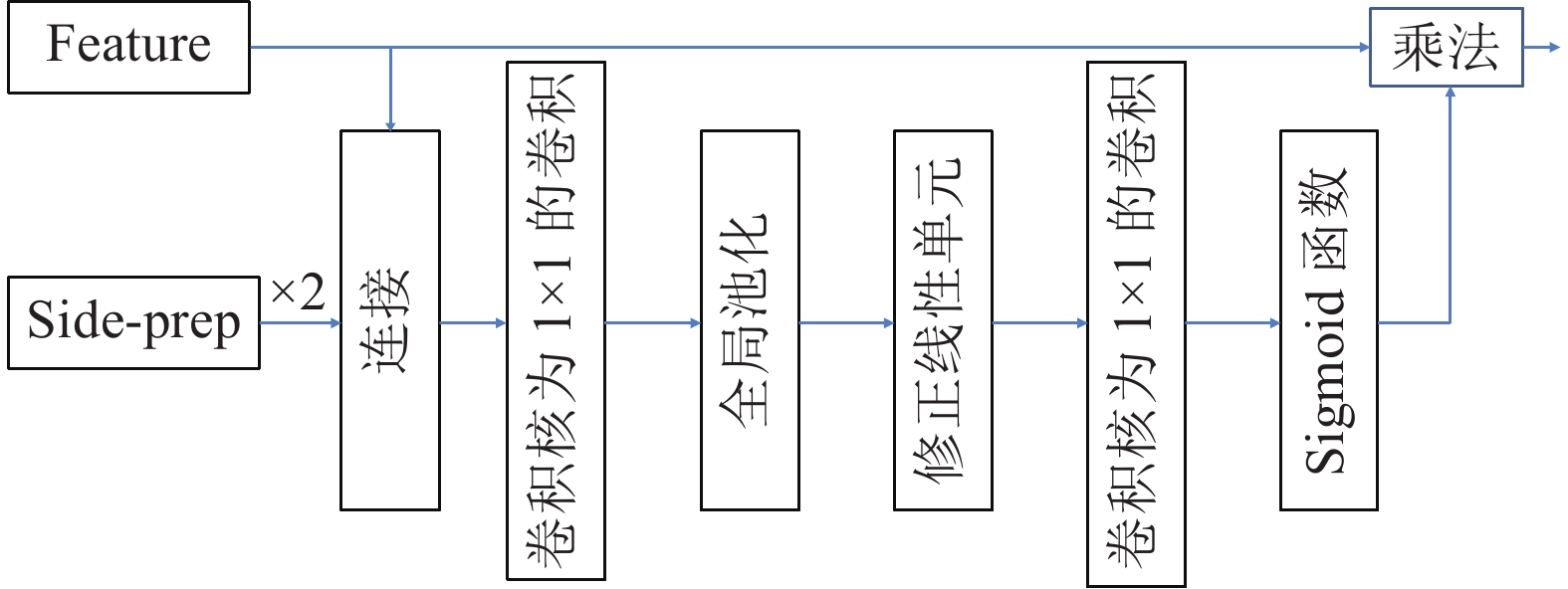
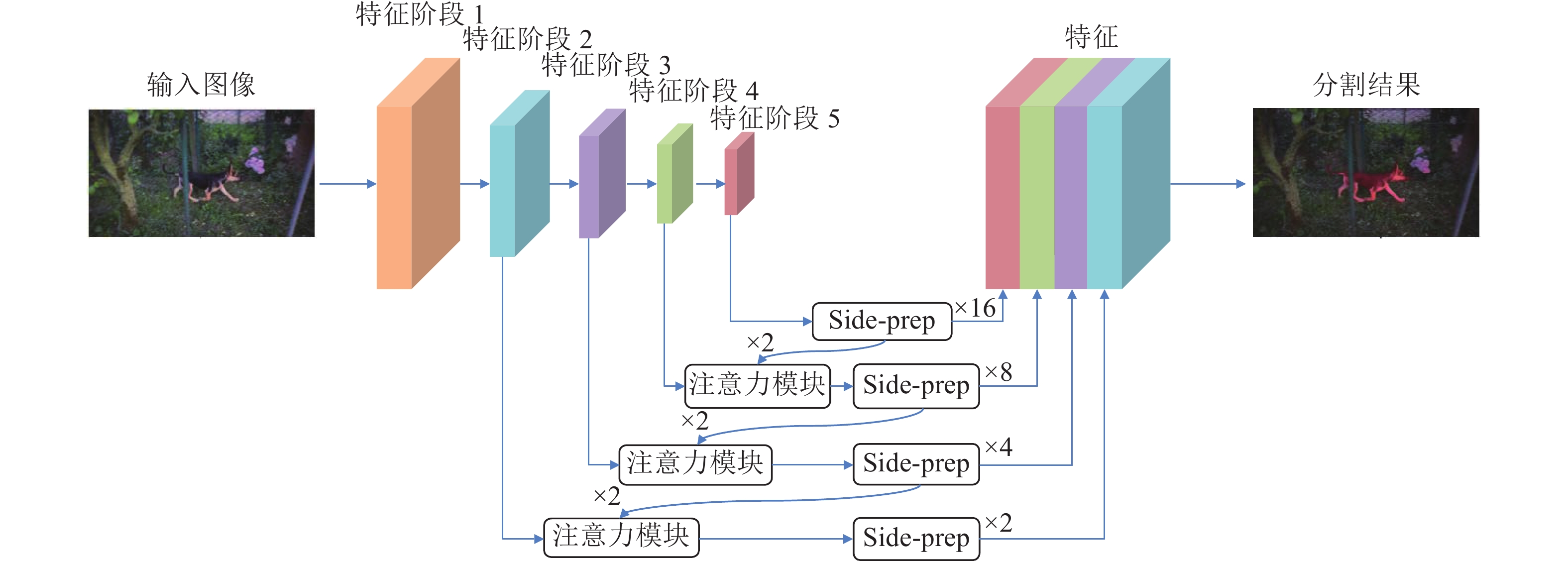
摘要: 提出了一种基于注意力机制的视频分割网络及其全局信息优化训练方法. 该方法包含一个改进的视频分割网络, 在对视频中的物体进行分割后, 利用初步分割的结果作为先验信息对网络优化, 再次分割得到最终结果. 该分割网络是一种双流卷积网络, 以视频图像和光流图像作为输入, 分别提取图像的表观信息和运动信息, 最终融合得到分割掩膜(Segmentation mask). 网络中嵌入了一个新的卷积注意力模块, 应用于卷积网络的高层次特征与相邻低层次特征之间, 使得高层语义特征可以定位低层特征中的重要区域, 提高网络的收敛速度和分割准确度. 在初步分割之后, 本方法提出利用初步结果作为监督信息对表观网络的权值进行微调, 使其辨识前景物体的特征, 进一步提高双流网络的分割效果. 在公开数据集DAVIS上的实验结果表明, 该方法可准确地分割出视频中时空显著的物体, 效果优于同类双流分割方法. 对注意力模块的对比分析实验表明, 该注意力模块可以极大地提高分割网络的效果, 较本方法的基准方法(Baseline)有很大的提高.Abstract: This paper presents an attention-based video segmentation network and its global information optimization training method. We propose an improved segmentation network, and use it to compute initial segmentation masks. Then the initial masks are considered as priors to finetune the network. Finally, the network with the learnt weight generates fine masks. Our two-stream segmentation network includes appearance branch and motion branch. Fed with image and optical flow image separately, the network extracts appearance features and motion features to generate segmentation mask. An attention module is embedded in the network, between the adjacent high level feature and low level feature. Thus the high level features locate the semantic region for the low level feature, speeding up the network convergence and improving segmentation quality. We propose to optimize the initial masks to finetune the original appearance network weights, making the network recognize the object and improving the network performance. Experiments on DAVIS show the effectiveness of the segmentation framework. Our method outperforms the traditional two-stream segmentation algorithms, and achieves comparable results with algorithms on the dataset's leaderboard. Validation experiment illustrates our attention module greatly improves the network performance than the baseline.
-
表 1 有效性对比实验
Table 1 Ablation experiments results
方法 ours_m ours_a Baseline FCN Mean $\cal{M} \uparrow$ 0.595 0.552 0.501 0.519 $\cal{J}$ Recall $\cal{O} \uparrow$ 0.647 0.645 0.558 0.528 Decay $\cal{D} \downarrow$ 0.010 −0.029 −0.046 0.059 Mean $\cal{M} \uparrow$ 0.568 0.493 0.458 0.482 $\cal{F}$ Recall $\cal{O} \uparrow$ 0.648 0.487 0.426 0.448 Decay $\cal{D} \downarrow$ 0.063 −0.035 −0.025 0.054 $\cal{T}$ Mean $\cal{M} \downarrow$ 0.689 0.721 0.679 0.829 表 2 定量实验结果
Table 2 Quantitative experiments results
方法 ours ours_n lmp msg fseg fst tis nlc cvos Mean $\cal{M} \uparrow$ 0.713 0.710 0.700 0.533 0.707 0.558 0.626 0.551 0.482 $\cal{J}$ Recall $\cal{O} \uparrow$ 0.798 0.791 0.850 0.616 0.835 0.649 0.803 0.558 0.540 Decay $\cal{D} \downarrow$ −0.036 −0.007 0.013 0.024 0.015 −0.000 0.071 0.126 0.105 Mean $\cal{M} \uparrow$ 0.684 0.695 0.659 0.508 0.653 0.511 0.596 0.523 0.447 $\cal{F}$ Recall $\cal{O} \uparrow$ 0.772 0.809 0.792 0.600 0.738 0.516 0.745 0.519 0.526 Decay $\cal{D} \downarrow$ −0.009 0.004 0.025 0.051 0.018 0.029 0.064 0.114 0.117 $\cal{T}$ Mean $\cal{M} \downarrow$ 0.534 0.589 0.572 0.301 0.328 0.366 0.336 0.425 0.250 -
[1] 褚一平, 张引, 叶修梓, 张三元. 基于隐条件随机场的自适应视频分割算法. 自动化学报, 2007, 33(12): 1252-1258Chu Yi-Ping, Zhang Yin, Ye Xiu-Zi, Zhang San-Yuan. Adaptive video segmentation algorithm using hidden conditional random fields. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2007, 33(12): 1252-1258 [2] 刘龙, 韩崇昭, 刘丁, 梁盈富. 一种新的基于吉布斯随机场的视频运动对象分割算法. 自动化学报, 2007, 33(6): 608-614Liu Long, Han Chong-Zhao, Liu Ding, Liang Ying-Fu. A new video moving object segmentation algorithm based on Gibbs random field. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2007, 33(6): 608-614 [3] Rother C, Kolmogorov V, Blake A. "GrabCut": Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2004, 23(3): 309-314 doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015720 [4] 胡芝兰, 江帆, 王贵锦, 林行刚, 严洪. 基于运动方向的异常行为检测. 自动化学报, 2008, 34(11): 1348-1357Hu Zhi-Lan, Jiang Fan, Wang Gui-Jin, Lin Xing-Gang, Yan Hong. Anomaly detection based on motion direction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(11): 1348-1357 [5] 鲁志红, 郭丹, 汪萌. 基于加权运动估计和矢量分割的运动补偿内插算法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 1034-1041Lu Zhi-Hong, Guo Dan, Wang Meng. Motion-compensated frame interpolation based on weighted motion estimation and vector segmentation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5): 1034-1041 [6] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2014. 568−576 [7] Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Zisserman A. Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1933−1941 [8] Jain S D, Xiong B, Grauman K. FusionSeg: Learning to combine motion and appearance for fully automatic segmentation of generic objects in videos. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2117−2126 [9] Li X X, Loy C C. Video object segmentation with joint re-identification and attention-aware mask propagation. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 93−110 [10] Zhang P P, Liu W, Wang H Y, Lei Y J, Lu H C. Deep gated attention networks for large-scale street-level scene segmentation. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 88:702-714 [11] Zhao H S, Zhang Y, Liu S, Shi J P, Loy C C, Lin D H, et al. PSANet: Point-wise spatial attention network for scene parsing. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 270−286 [12] Song C F, Huang Y, Ouyang W L, Wang L. Mask-guided contrastive attention model for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1179−1188 [13] Jang W D, Lee C, Kim C S. Primary object segmentation in videos via alternate convex optimization of foreground and background distributions. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 696−704 [14] Tsai Y H, Yang M H, Black M J. Video segmentation via object flow. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3899−3908 [15] Wen L Y, Du D W, Lei Z, Li S Z, Yang M H. JOTS: Joint online tracking and segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2226−2234 [16] Xiao F Y, Lee Y J. Track and segment: An iterative unsupervised approach for video object proposals. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 933−942 [17] Perazzi F, Wang O, Gross M, Sorkine-Hornung A. Fully connected object proposals for video segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 3227−3234 [18] Zhou T F, Lu Y, Di H J, Zhang J. Video object segmentation aggregation. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1−6 [19] Fragkiadaki K, Zhang G, Shi J B. Video segmentation by tracing discontinuities in a trajectory embedding. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1846−1853 [20] Wang W G, Shen J B, Yang R G, Porikli F. Saliency-aware video object segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(1): 20-33 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2662005 [21] Papazoglou A, Ferrari V. Fast object segmentation in unconstrained video. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 1777−1784 [22] Krahenbuhl P, Koltun V. Geodesic object proposals. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 725−739 [23] Perazzi F, Khoreva A, Benenson R, Schiele B, Sorkine-Hornung A. Learning video object segmentation from static images. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3491−3500 [24] Tokmakov P, Alahari K, Schmid C. Learning video object segmentation with visual memory. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4491−4500 [25] Cheng J C, Tsai Y H, Wang S J, Yang M H. SegFlow: Joint learning for video object segmentation and optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 686−695 [26] Song H M, Wang W G, Zhao S Y, Shen J B, Lam K M. Pyramid dilated deeper ConvLSTM for video salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 744−760 [27] Caelles S, Maninis K K, Pont-Tuset J, Leal-Taixe L, Cremers D, Van Gool L. One-shot video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5320−5329 [28] Oh S W, Lee J Y, Sunkavalli K, Kim S J. Fast video object segmentation by reference-guided mask propagation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7376−7385 [29] Cheng J C, Tsai Y H, Hung W C, Wang S J, Yang M H. Fast and accurate online video object segmentation via tracking parts. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7415−7424 [30] Fu J, Liu J, Tian H J, Li Y, Bao Y J, Fang Z W, Lu H Q. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3146−3154 [31] Sun T Z, Zhang W, Wang Z J, Ma L, Jie Z Q. Image-level to pixel-wise labeling: From theory to practice. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm, Sweden: AAAI Press, 2018. 928−934 [32] Chen L C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille A L. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [33] Li K P, Wu Z Y, Peng K C, Ernst J, Fu Y. Tell me where to look: Guided attention inference network. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 9215−9223 [34] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, Kweon I S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 3−19 [35] Corbetta M, Shulman G L. Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nature reviews Neuroscience, 2002, 3(3): 201-215 doi: 10.1038/nrn755 [36] Wang F, Jiang M Q, Qian C, Yang S, Li C, Zhang H G, et al. Residual attention network for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6450−6458 [37] Yu C Q, Wang J B, Peng C, Gao C X, Yu G, Sang N. Learning a discriminative feature network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1857−1866 [38] Li H C, Xiong P F, An J, Wang L X. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 British Machine Vision Conference. Newcastle, UK: BMVA Press, 2018. Article No. 285 [39] Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Ilg E, Hausser P, Hazirbas C, Golkov V, et al. FlowNet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2758−2766 [40] Perazzi F, Pont-Tuset J, McWilliams B, Van Gool L, Gross M, Sorkine-Hornung A. A benchmark dataset and evaluation methodology for video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 724−732 [41] Ochs P, Brox T. Object segmentation in video: A hierarchical variational approach for turning point trajectories into dense regions. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 1583−1590 [42] Tokmakov P, Alahari K, Schmid C. Learning motion patterns in videos. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 531−539 [43] Griffin B, Corso, J. Tukey-inspired video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1723−1733 [44] Faktor A, Irani M. Video segmentation by non-local consensus voting. In: Proceedings of the 2014 British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham, UK: BMVA Press, 2014. [45] Taylor B, Karasev V, Soattoc S. Causal video object segmentation from persistence of occlusions. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 4268−4276 -





 下载:
下载: