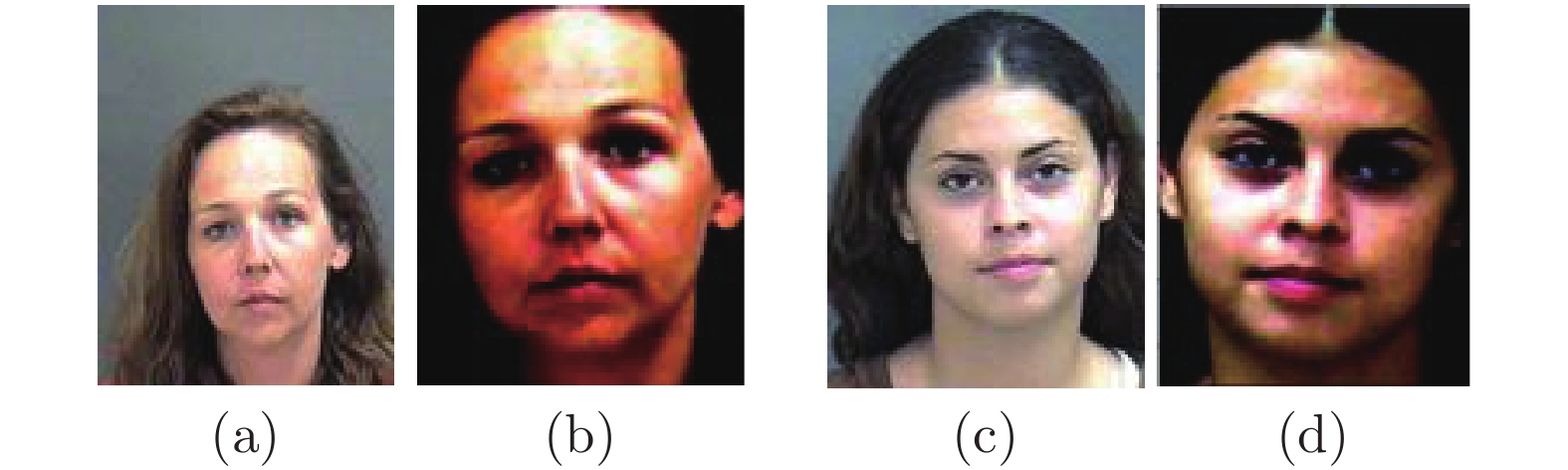
-
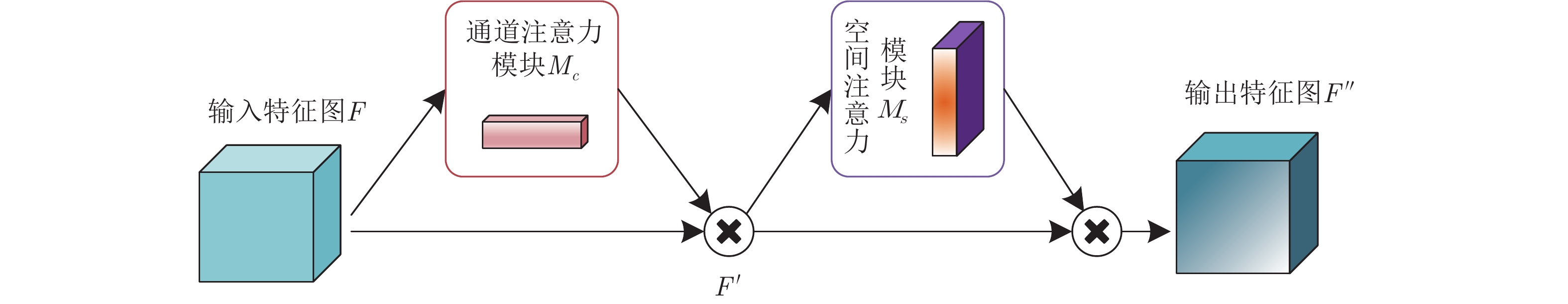
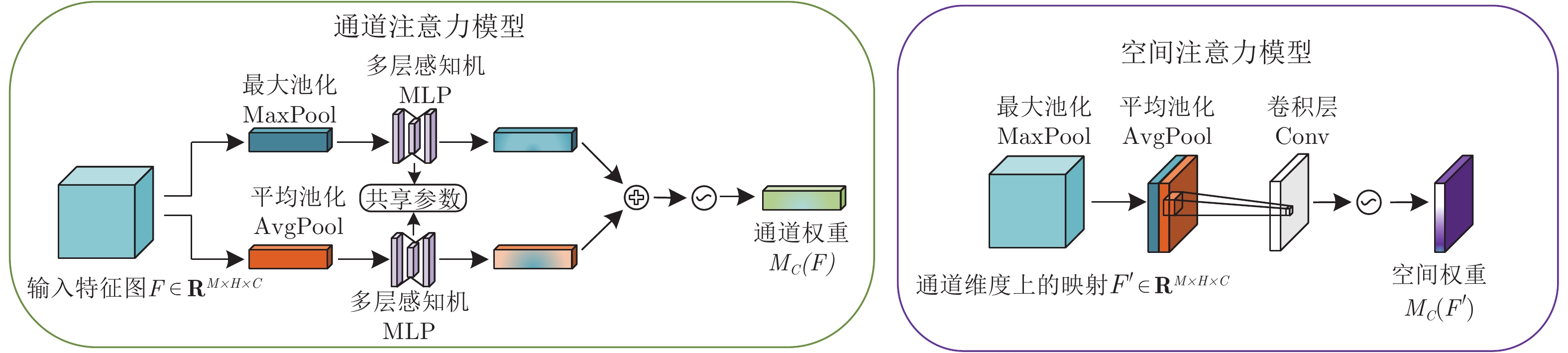
摘要: 随着年龄的增长, 人脸的形状、纹理等特征会随之发生较明显的改变从而造成显著的类内干扰, 这使得人脸识别的性能大大降低. 为了解决上述问题, 本文基于深度卷积神经网络将年龄估计任务和人脸识别任务相结合, 提出了一种抗年龄干扰的人脸识别新方法AD-CNN (Age decomposition convolution neural network), 首先将卷积块注意力模型(Convolutional block attention module, CBAM)嵌入到残差网络中以学习更具有代表性的面部特征, 随后利用线性回归指导年龄估计任务, 提取出年龄干扰因子, 通过多层感知机将整个面部特征与年龄干扰特征投影到同一线性可分空间, 最后从面部稳定的特征中将年龄干扰分离, 得到与年龄无关的面部特征, 并采用改进后的角度损失函数基于年龄无关的身份特征进行人脸识别任务, 从而达到抑制年龄干扰的目的. 本文在MORPH和FGNET数据集上的识别正确率分别达到了98.93%, 和90.0%, 充分证实了本文所提方法的先进性和有效性.
-
关键词:
- 人脸识别 /
- 年龄干扰 /
- 深度学习 /
- 年龄估计 /
- 卷积神经网络注意力模型
Abstract: Facial appearances such as shape and texture are subject to significant intra-class variations caused by the aging process over time, resulting in the performance reduction of face recognition. To overcome this problem, this paper proposes a novel method (age decomposition convolution neural network, AD-CNN) based on deep convolution neural network to learn age-invariant face features. Firstly, the AD-CNN utilizes convolutional block attention module (CBAM) to extract facial features and estimates age factors by linear regression. Then, the facial features and age factors are projected into the same linear separable space by multi-layer perceptron. Finally, the age-invariant face features can be obtained by separating age factors from the whole facial features. Here, the improved angle loss function is considered to guide the training process. The proposed AD-CNN achieves 98.93%, and 90.0% recognition accuracy on MORPH and FGNET datasets, respectively, which demonstrates the AD-CNN with a great potential for age-invariant face recognition. -
表 1 不同方法在FGNET数据库上的识别率
Table 1 Recognition rate of different method on FGNET
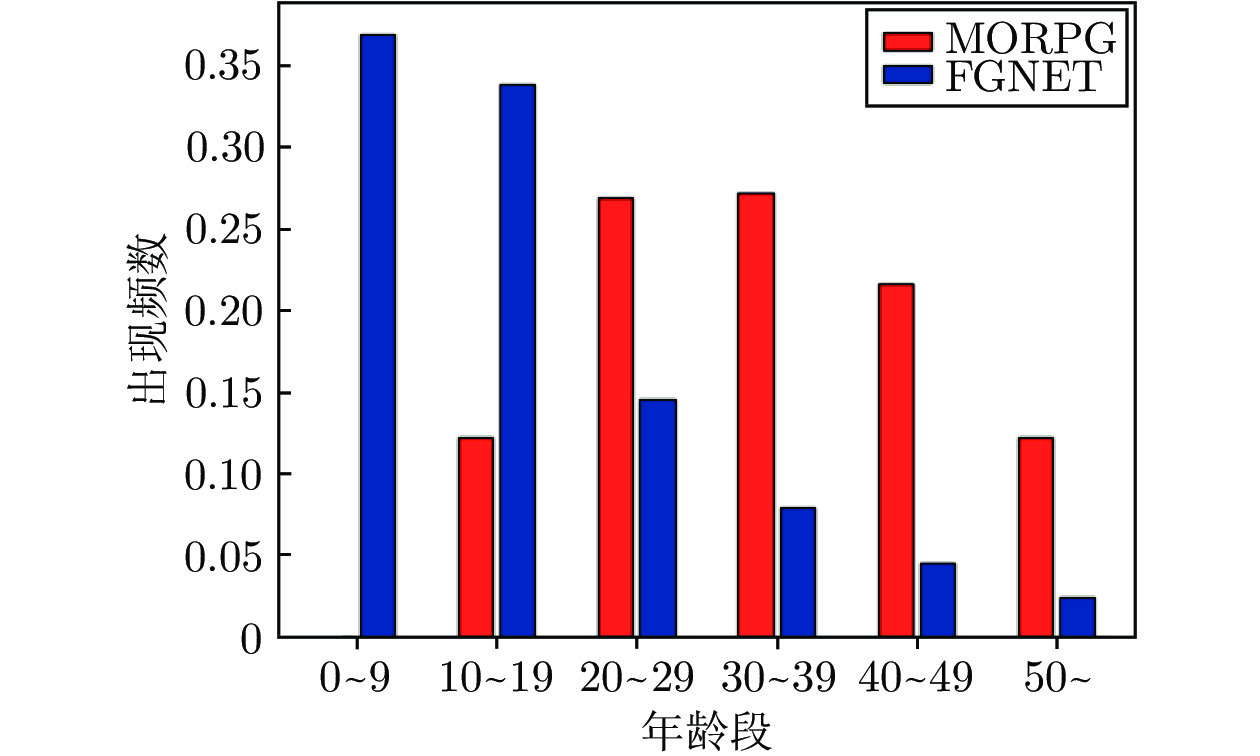
表 2 本文方法在FGNET数据库上各个年龄段的识别正确率
Table 2 Performance of our method on different age groups on FGNET
年龄组 数量 原始特征提取网络 (%) 本文方法 (%) 0 ~ 4 193 60.40 67.30 5 ~ 10 218 86.86 89.12 11 ~ 16 201 92.43 95.81 17 ~ 24 182 94.63 98.01 25 ~ 69 208 99.09 99.54 0 ~ 16 612 80.30 84.43 17 ~ 69 390 97.01 98.87 表 3 不同方法在MORPH数据库上的识别率
Table 3 Recognition rate of different method on MORPH
-
[1] Schroff F, Kalenichenko D, Philbin J. FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 815−823 [2] Wang H, Wang Y T, Zhou Z, Ji X, Gong D H, Zhou J C, et al. CosFace: Large margin cosine loss for deep face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 5265−5274 [3] Zhao J, Xiong L, Cheng Y, Cheng Y, Li J S, Zhou L, et al. 3D-aided deep pose-invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm, Sweden: AAAI Press, 2018. 1184−1190 [4] 胡扬, 张东波, 段琪. 目标鲁棒识别的抗旋转HDO局部特征描述. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(4): 665−673Hu Yang, Zhang Dong-Bo, Duan Qi. An improved rotation-invariant HDO local description for object recognition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(4): 665−673 [5] 王存睿, 张庆灵, 段晓东, 王元刚, 李泽东. 基于流形结构的人脸民族特征研究. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(1): 140−159Wang Cun-Rui, Zhang Qing-Ling, Duan Xiao-Dong, Wang Yuan-Gang, Li Ze-Dong. Research of face ethnic features from manifold structure. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(1): 140−159 [6] 王玉, 申铉京, 陈海鹏. 基于改进的Fisher准则的多示例学习视频人脸识别算法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2179−2187Wang Yu, Shen Xuan-Jing, Chen Hai-Peng. Video face recognition based on modified Fisher criteria and multi-instance learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2179−2187 [7] Chen B C, Chen C S, Hsu W H. Face recognition and retrieval using cross-age reference coding with cross-age celebrity dataset. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(6): 804−815 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2015.2420374 [8] Geng X, Zhou Z H, Smith-Miles K. Automatic age estimation based on facial aging patterns. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(12): 2234−2240 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70733 [9] Lanitis A, Taylor C J, Cootes T F. Toward automatic simulation of aging effects on face images. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(4): 442−455 doi: 10.1109/34.993553 [10] Park U, Tong Y Y, Jain A K. Age-invariant face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(5): 947−954 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.14 [11] Zhang Z F, Song Y, Qi H R. Age progression/regression by conditional adversarial autoencoder. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4352−4360 [12] Antipov G, Baccouche M, Dugelay J L. Face aging with conditional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2017. 2089−2093 [13] Duong C N, Quach K G, Luu K, Le T H N, Savvides M. Temporal non-volume preserving approach to facial age-progression and age-invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 3755−3763 [14] Ling H B, Soatto S, Ramanathan N, Jacobs D W. Face verification across age progression using discriminative methods. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2010, 5(1): 82−91 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2009.2038751 [15] Gong D H, Li Z F, Lin D H, Liu J Z, Tang X O. Hidden factor analysis for age invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 2872−2879 [16] Gong D H, Li Z F, Tao D C, Liu J Z, Li X L. A maximum entropy feature descriptor for age invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 5289−5297 [17] Li Z F, Gong D H, Li X L, Tao D C. Aging face recognition: A hierarchical learning model based on local patterns selection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(5): 2146−2154 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2535284 [18] Li Z F, Park U, Jain A K. A discriminative model for age invariant face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2011, 6(3): 1028−1037 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2011.2156787 [19] Lin L, Wang G R, Zuo W M, Feng X C, Zhang L. Cross-domain visual matching via generalized similarity measure and feature learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1089−1102 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2567386 [20] Wang Y T, Gong D H, Zhou Z, Ji X, Wang H, Li Z F, et al. Orthogonal deep features decomposition for age-invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 764−779 [21] Wen Y D, Li Z F, Qiao Y. Latent factor guided convolutional neural networks for age-invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 4893−4901 [22] Xu C F, Liu Q H, Ye M. Age invariant face recognition and retrieval by coupled auto-encoder networks. Neurocomputing, 2017, 222: 62−71 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.10.010 [23] Yi D, Lei Z, Liao S C, Li S Z. Learning face representation from scratch [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.7923, November 28, 2014 [24] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [25] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: JMLR.org, 2015. 448−456 [26] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, Kweon I S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 3−19 [27] Liu W Y, Wen Y D, Yu Z D, Li M, Raj B, Song L. SphereFace: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6738−6746 [28] Ricanek K, Tesafaye T. MORPH: A longitudinal image database of normal adult age-progression. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FGR06). Southampton, UK: IEEE, 2006. 341−345 [29] Liang Y X, Liu L B, Xu Y, Xiang Y, Zou B J. Multi-task GLOH feature selection for human age estimation. In: Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Brussels, Belgium: IEEE, 2011. 565−568 [30] Zhang K P, Zhang Z P, Li Z F, Qiao Y. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(10): 1499−1503 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2603342 [31] Wang F, Xiang X, Cheng J, Yuille A L. NormFace: L2 Hypersphere embedding for face verification. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Multimedia Conference. Mountain View, USA: ACM, 2017. 1041−1049 -




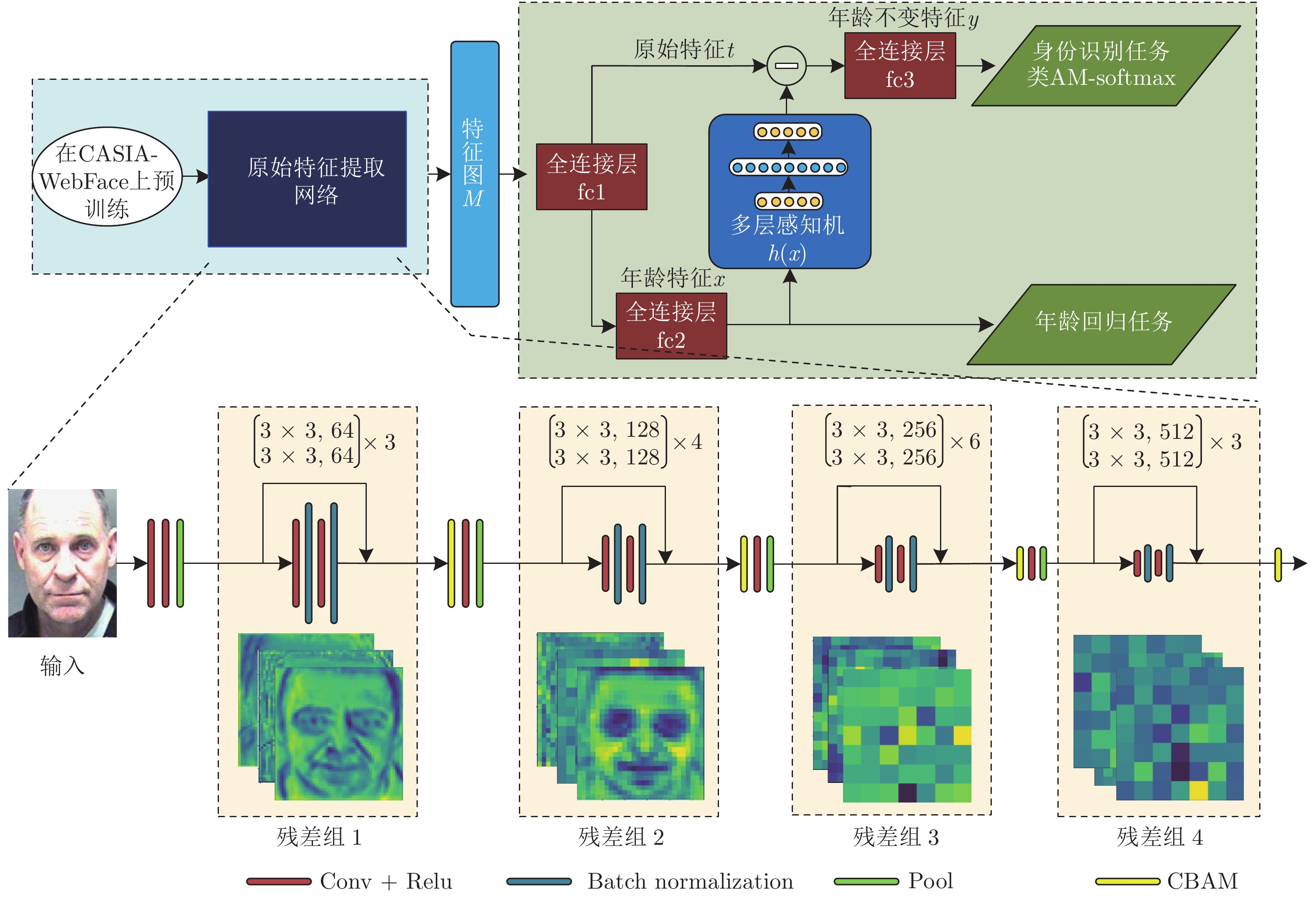
 下载:
下载: