Optimal Packet Scheduling Strategy for Roadside Units' Bursty Traffic Based on Relaying Vehicles
-
摘要:
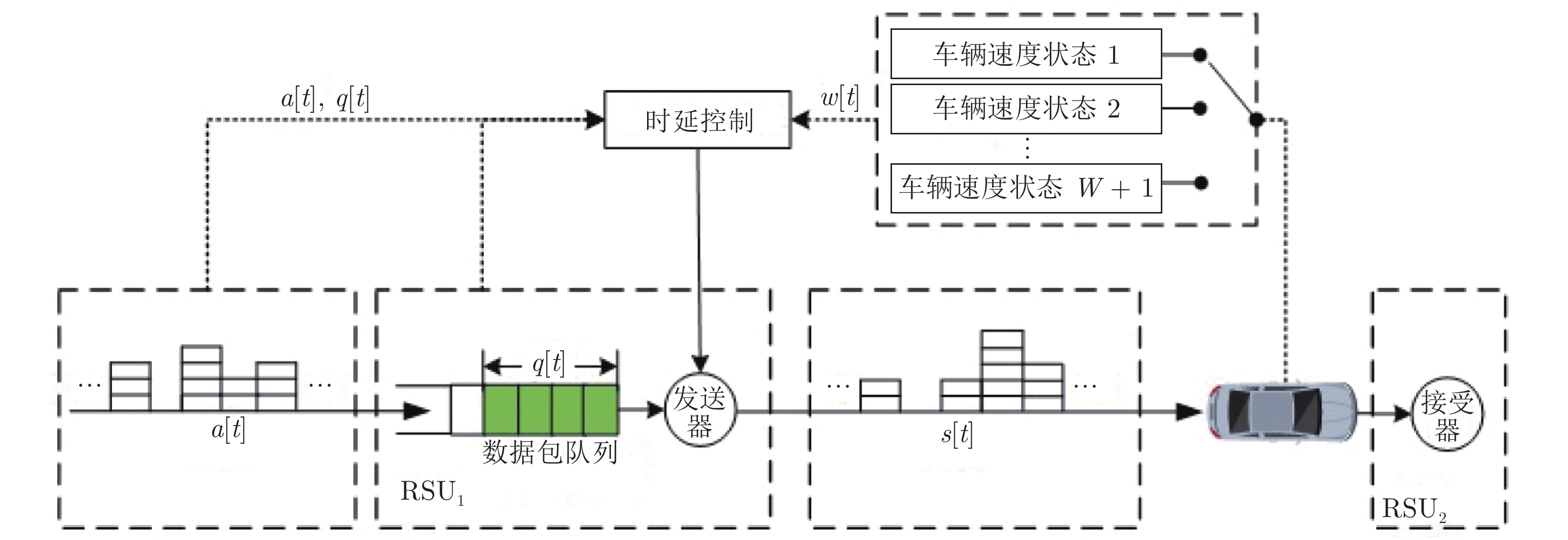
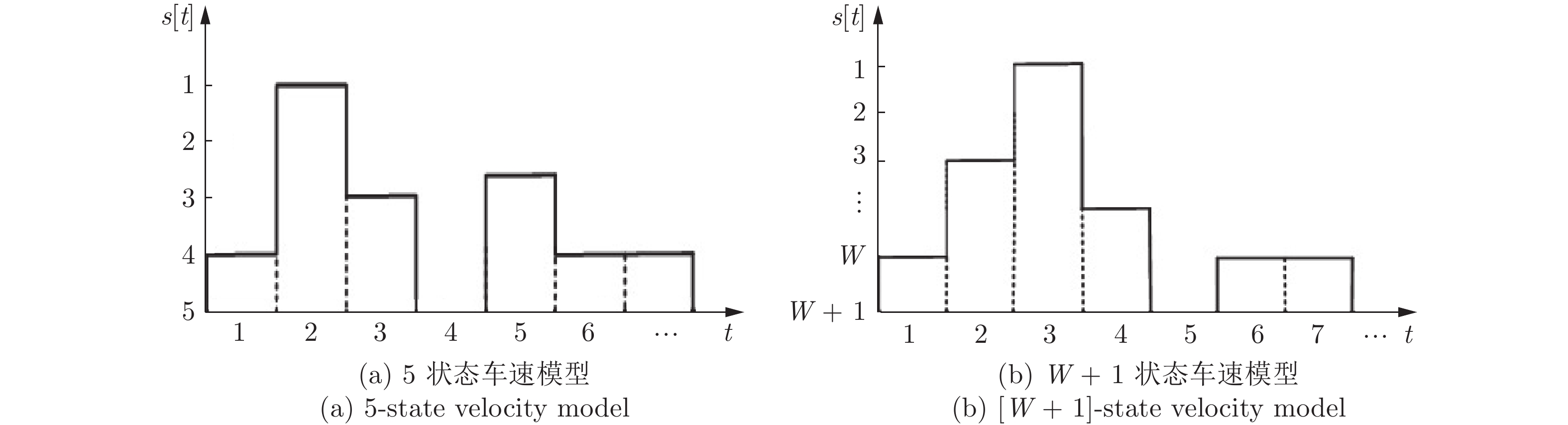
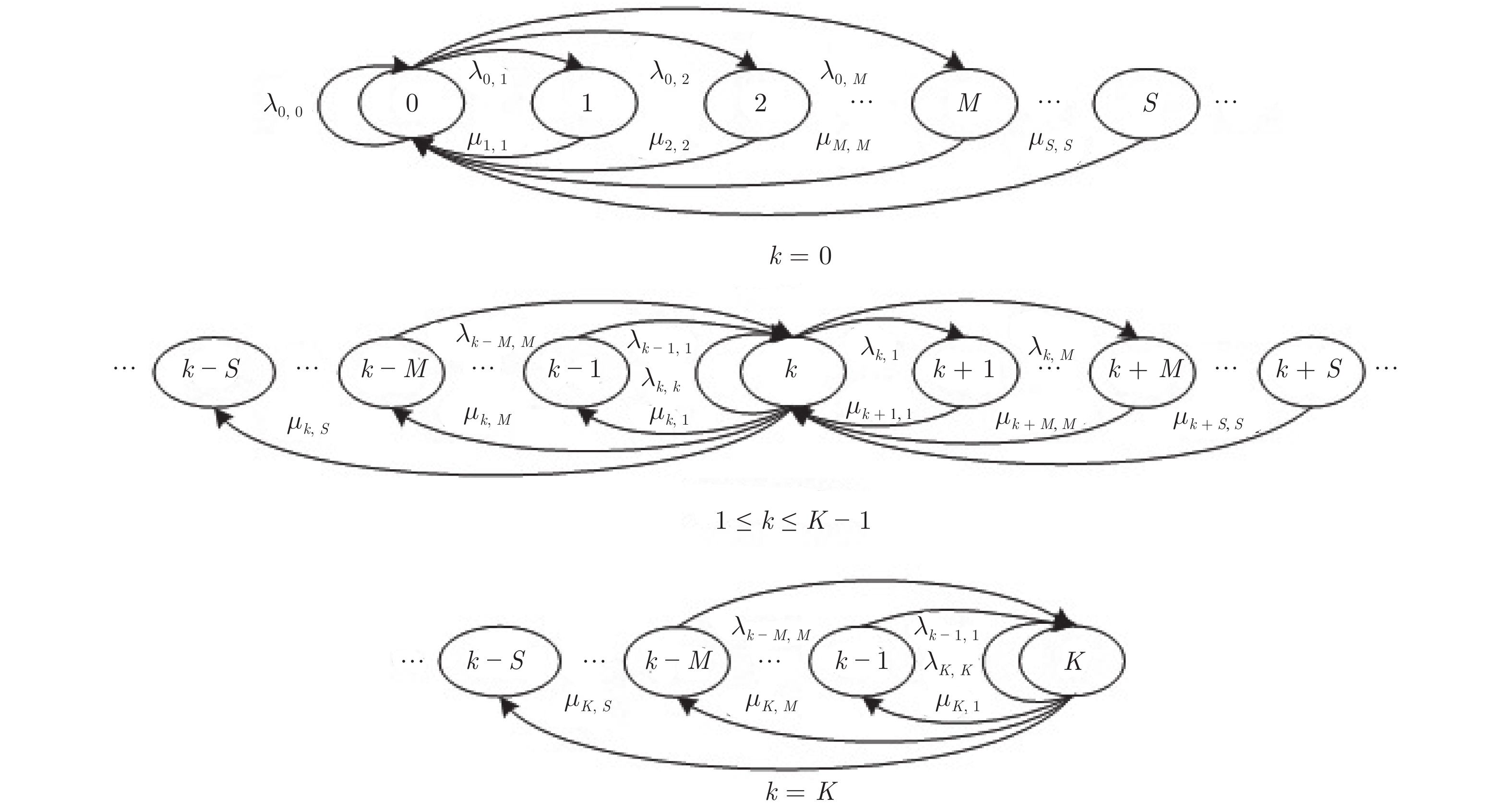
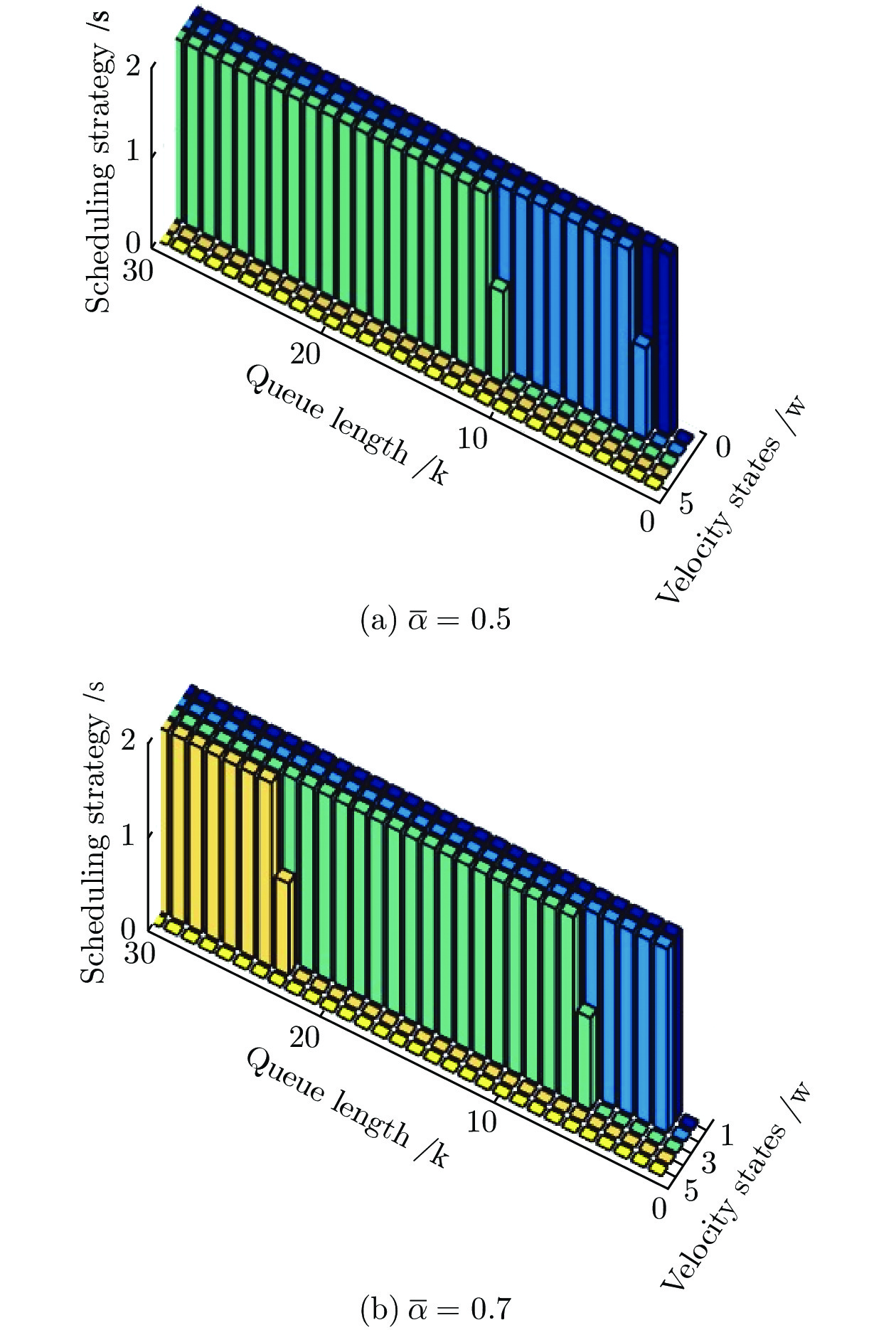
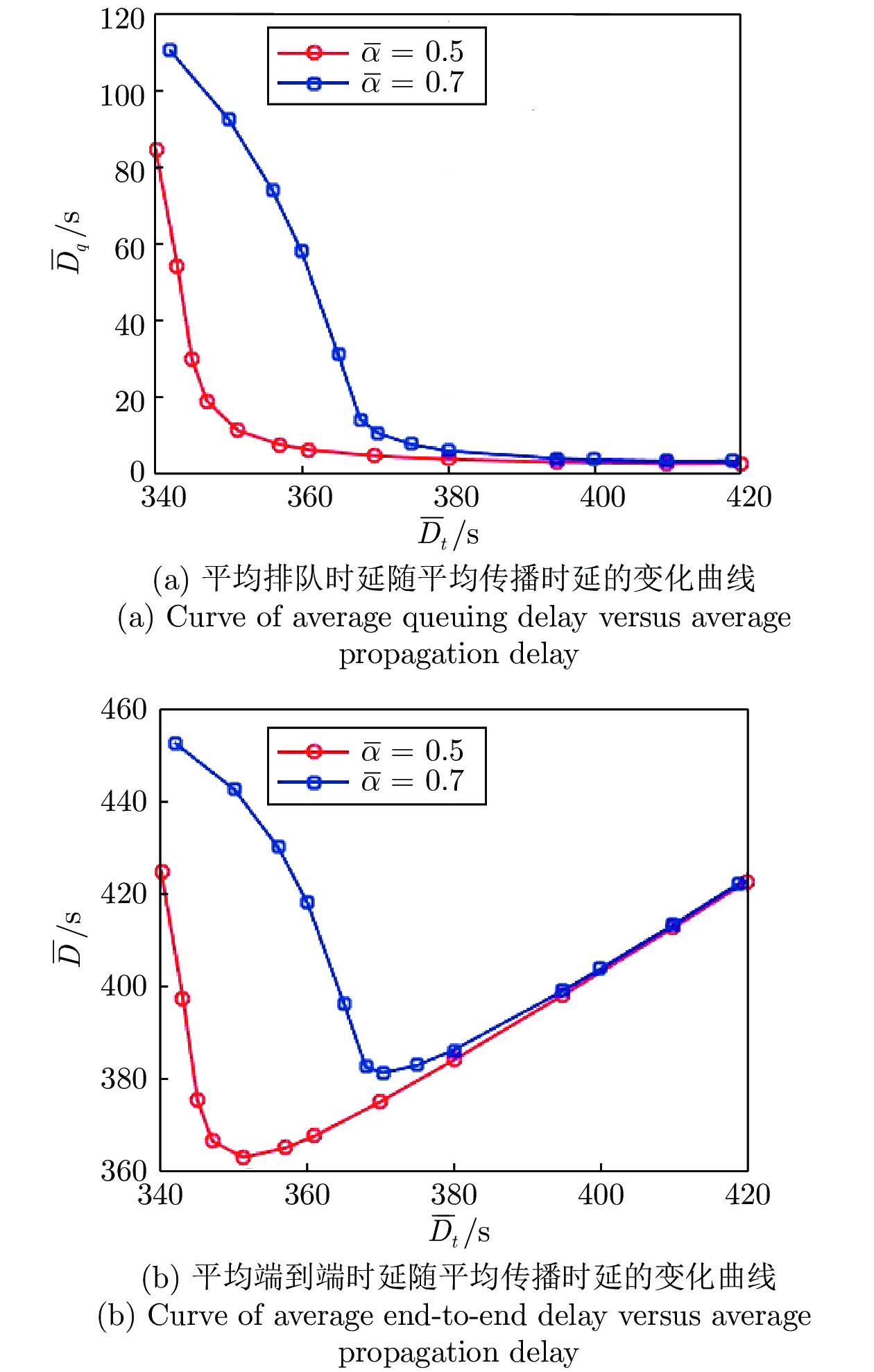
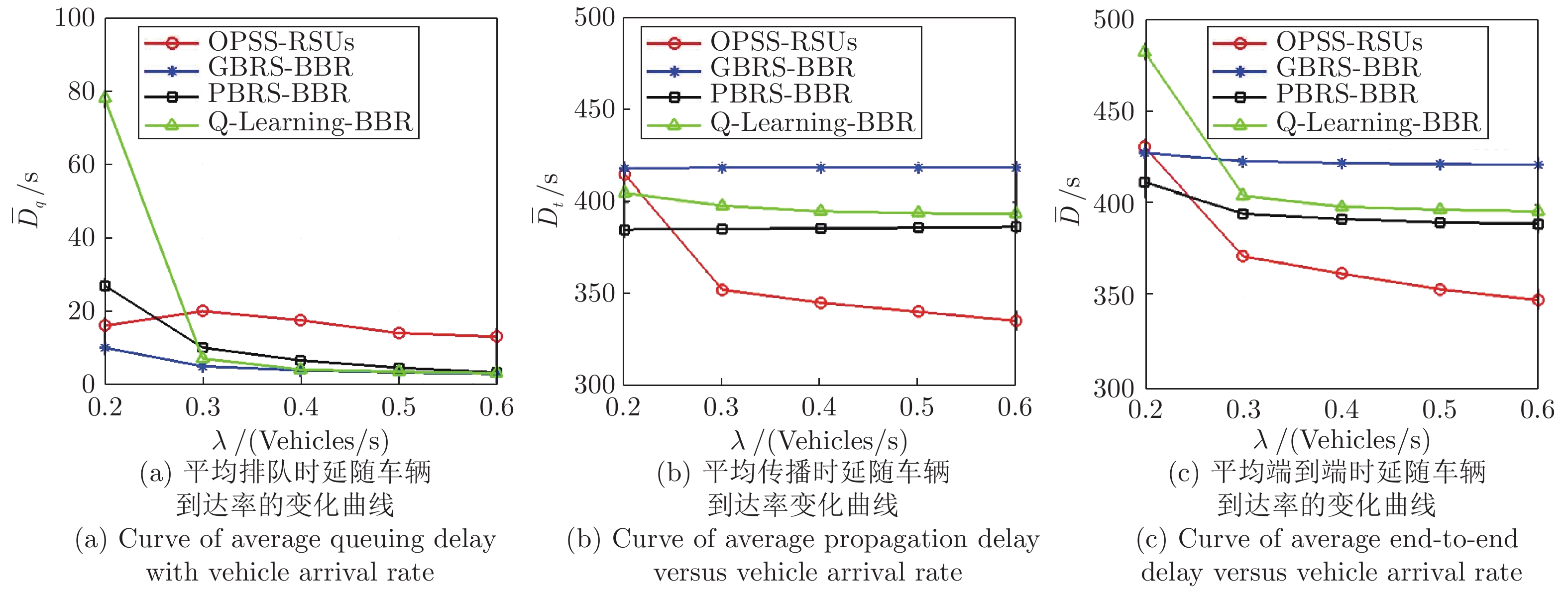
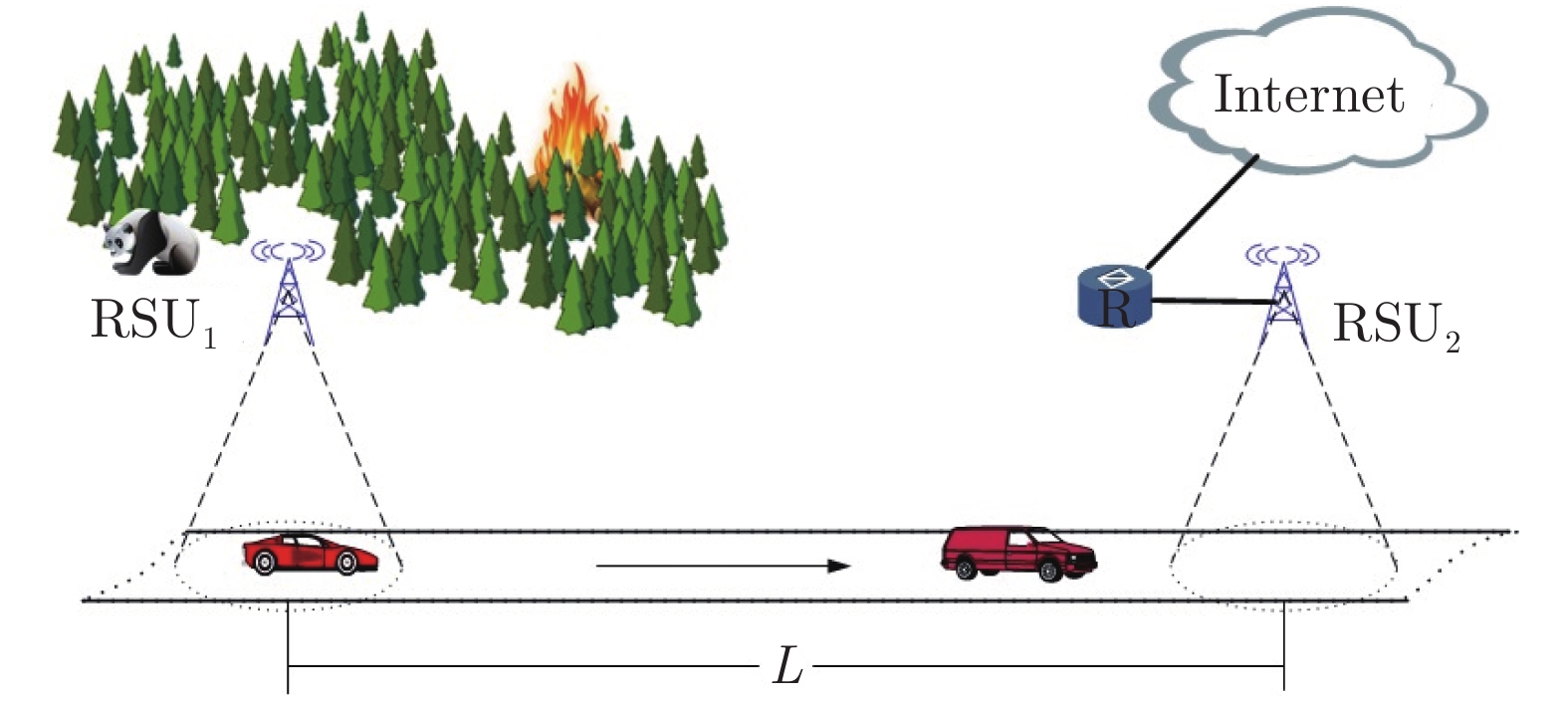
高速公路车联网场景中, 路边单元(Roadside units, RSUs)可作为多种周边监测数据的汇入网关, 其业务具有突发特性, 且可通过移动车辆以“存储−载带−转发”方式传输到与骨干网络互联的RSU. 针对RSU间业务传输问题, 源RSU可根据实时业务到达率按需匹配资源, 以应对业务突发性对分组端到端时延的影响. 本文首先针对RSU突发业务传输过程建立突发业务到达模型、车辆到达模型和离散车速状态模型; 进而利用受限马尔科夫决策过程对系统状态转移过程进行分析, 并建立非线性平均端到端时延最小化问题; 最后通过分析最优解的形式得出最优分组调度策略具有门限结构. 仿真结果验证了RSU间业务传输过程中排队时延和传播时延之间存在折中, 且该分组调度策略能降低业务传输过程的平均端到端时延.
Abstract:In the highway Internet of vehicles scenario, the roadside units (RSUs), whose generated traffic has burst characteristic, served as the gateway of multiple kinds monitored data. Those fused data can be transmitted to the RSU connected with the backbone network through the passing vehicles which serve as opportunistic store-carry-forward devices. For traffic transmission between the RSUs, the source RSU should match resource according to arrival rate of bursty traffic, to control the bursty impact on end-to-end delay. Firstly, the bursty traffic arrival model, the vehicles arrival model, and discrete speed states model were established for bursty traffic transmission between RSUs. Then, the state transition processes were analyzed by constrained Markov decision process, and a non-linear average end-to-end delay minimization problem is established. Finally, it is concluded that the optimal packet scheduling strategy has a threshold structure by analyzing the structure of the optimal solution. The simulation results show that the packet scheduling strategy can reduce the average end-to-end delay of bursty traffic transmission between the RSUs, and verify the tradeoff between average queuing delay and the propagation delay.
-
Key words:
- Internet of vehicles /
- roadside unit /
- busty traffic /
- packet scheduling /
- store-carry-forward
-
表 1 仿真参数表
Table 1 Simulation parameters
参数名称 符号/单位 参数值 RSU缓存容量 $K$/个 100 RSU间隔距离 $L$/m 10 000 速度区间 $[{V_{\min }},{V_{\max }}]$/(m/s) [16.67, 33.33] 速度期望 $\overline V $/(m/s) 25 速度标准差 $\sigma $ 10 车辆到达率 $\lambda $/(辆/s) 0.55 时隙长度 $\Delta t$/s 1 车速状态数量 $W$ 4 发送分组数量上限 $S$ 2 表 2 分组到达参数表
Table 2 Packets arrival parameters
分组到达概率${\theta _i}$ ${\theta _0}$ ${\theta _1}$ ${\theta _2}$ 平均到达率$\bar \alpha $ 方案 1 0.7 0.1 0.2 0.5 方案 2 0.6 0.1 0.3 0.7 -
[1] 王晓, 要婷婷, 韩双双, 曹东璞, 王飞跃. 平行车联网基于ACP的智能车辆网联管理与控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(8): 1391−1404Wang Xiao, Yao Ting-Ting, Han Shuang-Shuang, Cao Dong-Pu, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel internet of vehicles: The ACP-based networked management and control for intelligent vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(8): 1391−1404 [2] 冯建周, 宋沙沙, 孔令富. 物联网语义关联和决策方法的研究. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(11): 1691−1701Feng Jian-Zhou, Song Sha-Sha, Kong Ling-Fu. Research on semantic association and decision method of the internet of things. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(11): 1691−1701 [3] Atallah R F, Khabbaz M J, Assi C M. Modeling and performance analysis of medium access control schemes for drive-thru Internet access provisioning systems. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(6): 3238−3248 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2440447 [4] He J P, Cai L, Pan J P, Cheng P. Delay analysis and routing for two-dimensional VANETs using carry-and-forward mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(7): 1830−1841 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2607748 [5] Huang L J, Jiang H, Zhang Z, Yan Z J. Efficient data traffic forwarding for infrastructure-to-infrastructure communications in VANETs. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(3): 839−853 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2705047 [6] Si P B, He Y, Yao H P, Yang R Z, Zhang Y H. DaVe: Offloading delay-tolerant data traffic to connected vehicle networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(6): 3941−3953 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2550105 [7] Oh S, Schenato L, Chen P, Sastry S. Tracking and coordination of multiple agents using sensor networks: System design, algorithms and experiments. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2007, 95(1): 234−254 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2006.887296 [8] Mencagli G, Torquati M, Danelutto M, Matteis T D. Parallel continuous preference queries over out-of-order and bursty data streams. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2017, 28(9): 2608−2624 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2017.2679197 [9] Chen J Q, Mao G Q, Li C L, Liang W F, Zhang D G. Capacity of cooperative vehicular networks with infrastructure support: Multiuser case. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1546−1560 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2753772 [10] Wang Y, Liu Y S, Zhang J Y, Ye H N, Tan Z H. Cooperative store-carry-forward scheme for intermittently connected vehicular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(1): 777−784 [11] Shahidi R, Ahmed M H. Probability distribution of end-to-end delay in a highway VANET. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(3): 443−446 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.011214.132606 [12] Seliem H, Shahidi R, Ahmed M H, Shehata M S. Probability distribution of the re-healing delay in a one-way highway VANET. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(10): 2056−2059 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2859928 [13] Huang J J, Tseng Y T. The steady-state distribution of rehealing delay in an intermittently connected highway VANET. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(10): 10010−10021 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2865500 [14] Ni Y Z, He J P, Cai L, Bo Y M. Data uploading in hybrid V2V/V2I vehicular networks: Modeling and cooperative strategy. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(5): 4602−4614 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2796563 [15] Kuo Y W, Li C L, Jhang J H, Lin S. Design of a wireless sensor network-based IoT platform for wide area and heterogeneous applications. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(12): 5187−5197 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2832664 [16] Abdrabou A, Zhuang W H. Probabilistic delay control and road side unit placement for vehicular ad hoc networks with disrupted connectivity. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(1): 129−139 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2011.110113 [17] Carpenter S E, Sichitiu M L. BUR-GEN: A bursty packet generator for vehicular communication channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(11): 10232−10242 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2866946 [18] Katsaros K. End-to-end delay bound analysis for location-based routing in hybrid vehicular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(9): 7462−7475 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2482362 [19] Hu Y, Li H Y, Chang Z, Han Z. End-to-end backlog and delay bound analysis for multi-hop vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(10): 6808−6821 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2731847 [20] Li Y, Jin D P, Hui P, Chen S. Contact-aware data replication in roadside unit aided vehicular opportunistic networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2016, 15(2): 306−321 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2416185 [21] Zhang S, Zhang N, Fang X J, Yang P, Shen X S. Self-sustaining caching stations: Toward cost-effective 5G-enabled vehicular networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(11): 202−208 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1700129 [22] Zhang N, Zhang S, Yang P, Alhussein O, Zhuang W H, Shen X S. Software defined space-air-ground integrated vehicular networks: Challenges and solutions. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(7): 101−109 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1601156 [23] Khabbaz M J, Fawaz W F, ASSI C M. Probabilistic bundle relaying schemes in two-hop vehicular delay tolerant networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 2011, 15(3): 281−283 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2011.011011.102512 [24] Khabbaz M J, Fawaz W F, Assi C M. Modeling and delay analysis of intermittently connected roadside communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2012, 61(6): 2698−2706 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2012.2200001 [25] Khabbaz M J, Fawaz W F, Assi C M. A probabilistic bundle relay strategy in two-hop vehicular delay tolerant networks. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Communications. Kyoto, Japan, IEEE, 2011. 1−6 [26] Khabbaz M J, Alazemi H M K, Assi C M. Stochastic data delivery delay analysis in intermittently connected vehicular networks. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Global Communications Conference. Anaheim, CA, USA: IEEE, 2012. 183−188 [27] Khabbaz M J, Alazemi H M K, Assi C M. Delay-aware data delivery in vehicular intermittently connected networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(3): 1134−1143 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2012.122712.120222 [28] Khabbaz M J, Alazemi H M K, Assi C M. Modeling and delay analysis of a retransmission-based bundle delivery scheme for intermittent roadside communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2): 700−708 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2228192 [29] Ramaiyan V, Altman E, Kumar A. Delay optimal scheduling in a two-hop vehicular relay network. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2010, 15(1): 97−111 [30] Badia L, Scalabrin M. Stochastic analysis of delay statistics for intermittently connected vehicular networks. In: Proceedings of the 20th European Wireless Conference. Barcelona, Spain: VDE, 2014. 1−6 [31] Khabbaz M J, Fawaz W F, Assi C M. A probabilistic and traffic-aware bundle release scheme for vehicular intermittently connected networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2012, 60(11): 3396−3406 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2012.082712.110473 [32] Khabbaz M J, Fawaz W F, Assi C M. Modeling and analysis of bulk bundle release schemes in two-hop vehicular DTNs. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference. Houston, TX, USA: IEEE, 2011. 1−6 [33] Fawaz W F, Atalla R F, Khabbaz M J. A first step towards the resolution of the starvation problem in multi-point-to-point ICRCNs. IEEE Communications Letters, 2013, 17(11): 2104−2107 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2013.091913.131740 [34] Arafa A, Baknina A, Ulukus S. Online fixed fraction policies in energy harvesting communication systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(5): 2975−2986 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2805336 [35] Wang M, Liu J, Chen W. On delay-power tradeoff of rate adaptive wireless communications with random arrivals. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference. Singapore, Singapore: IEEE, 2017. 1−6 [36] Khabbaz M J, Fawaz W F, Assi C M. A simple free-flow traffic model for vehicular intermittently connected networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(3): 1312−1326 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2188519 [37] 徐昕, 沈栋, 高岩青, 王凯. 基于马氏决策过程模型的动态系统学习控制: 研究前沿与展望. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(5): 673−687Xu Xin, Shen Dong, Gao Yan-Qing, Wang Kai. Learning control of dynamical systems based on Markov decision processes: Research frontiers and outlooks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(5): 673−687 [38] Puterman M L. Markov Decision Processes: Discrete Stochastic Dynamic Programming. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley, 1994. -




 下载:
下载: