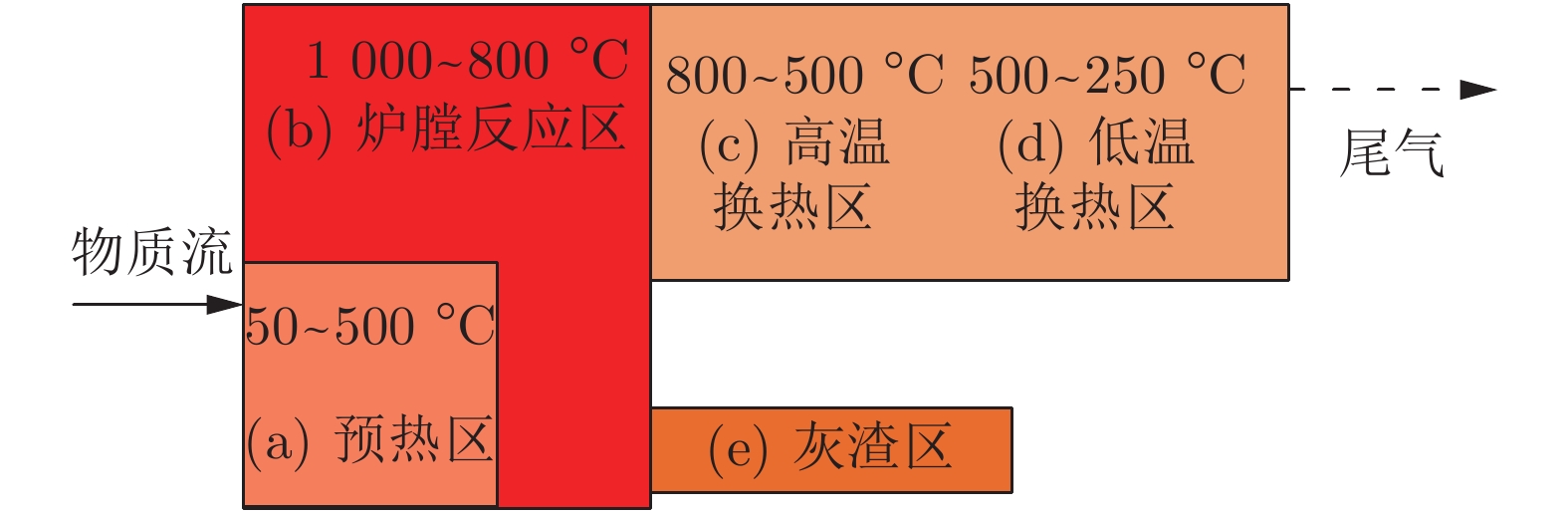
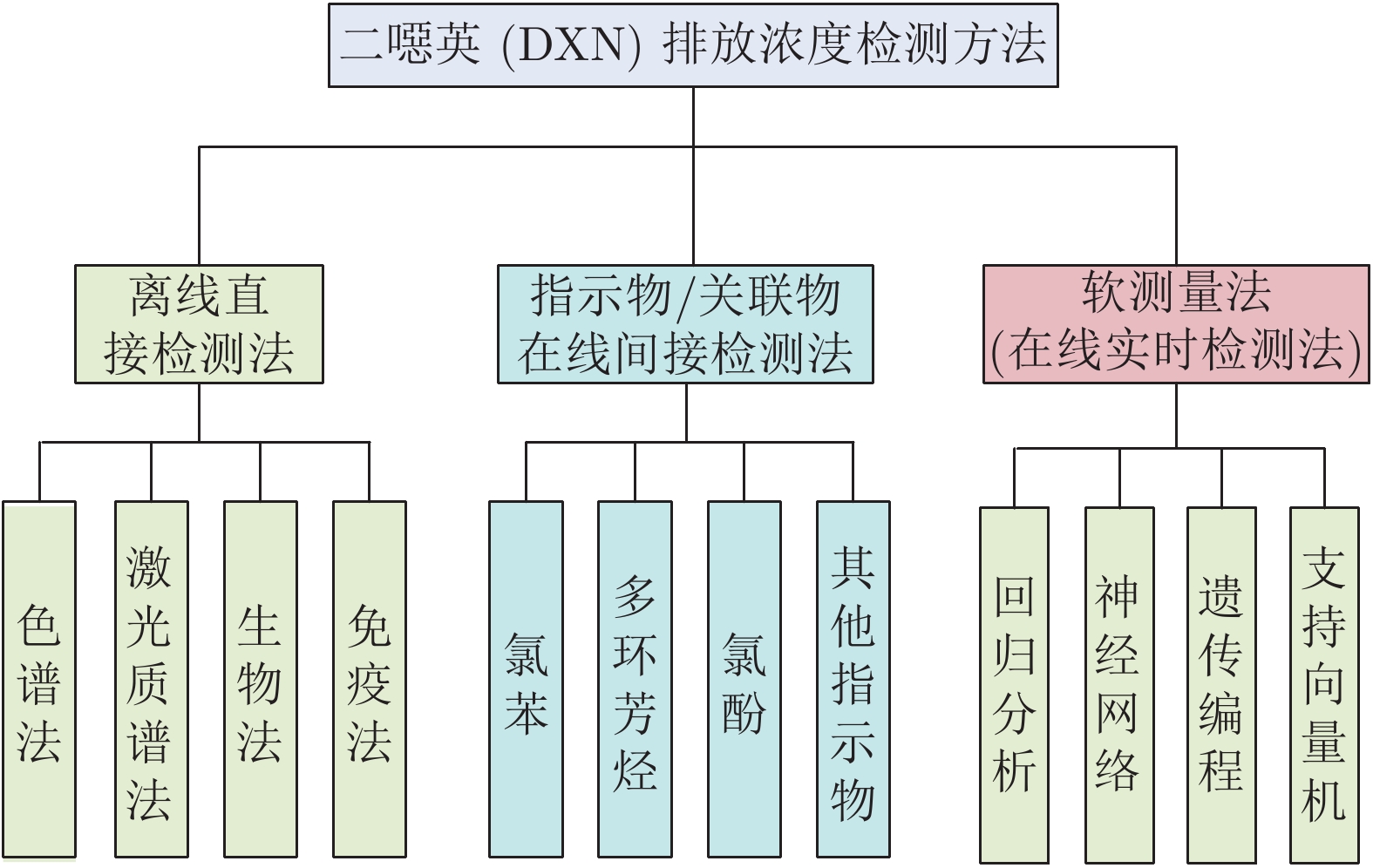
Dioxin Emission Concentration Measurement Approaches for Municipal Solid Wastes Incineration Process: A Survey
-
摘要: 焚烧在城市固体废物(Municipal solid wastes, MSW)的无害化、减量化和资源化处理方面优势显著. MSW焚烧(MSW incineration, MSWI)过程副产品之一的剧毒持久性污染物二噁英(Dioxins, DXN)是造成焚烧建厂“邻避效应”的主要原因. DXN排放浓度难以在线实时检测的工业现状已成为制约MSWI过程运行优化与城市环境污染控制的瓶颈. 首先, 结合典型MSWI过程分析DXN的生成特性与排放控制策略; 接着, 将DXN排放浓度检测方法从测量原理、复杂度和时间尺度等视角分为离线直接检测法、指示物/关联物在线间接检测法和软测量法并进行综述; 然后, 对不同方法的发展阶段和关联性进行分析, 指出各自的优劣性和相互间的互补性, 结合MSWI过程特点归纳基于过程数据进行DXN排放浓度软测量的难点, 并将其提炼为一类面向小样本高维稀疏标记数据的智能建模问题; 最后, 指出进行DXN排放浓度智能软测量的未来研究方向和发展前景.Abstract: Incineration has significant advantages in the harmless, reduction and recycling treatment of municipal solid waste (MSW). Dioxins (DXN), a highly toxic and persistent pollutant that is a by-product of the MSW incineration (MSWI) process, is the main cause of the “not in my back yard” effect of incineration plant construction. The industrial status of DXN emission concentration that is difficult to detect real time online has become a bottleneck restricting the optimization of MSWI process operation and municipal environmental pollution control. First, the generation characteristics and emission control strategies of DXN based on a typical MSWI processes are analyzed. Then, the DXN emission concentration detection methods are divided into offline direct detection method, indicator/association online indirect detection method, and soft measurement method in terms of measurement principle, complexity, and time scale. Further, these methods are reviewed in detail. Thirdly, the development stage and correlation of these different methods are addressed, and their respective advantages and disadvantages and complementarity with each other are indicated. Based on the characteristics of MSWI process, the difficulties of DXN emission concentration soft measurement based on process data are summarized. Moreover, it is refined as a class intelligent modeling problem based on small sample high dimensional sparse labeled data. Finally, the future research direction and development prospects of DXN emission concentration intelligent soft measurement are suggested.
-
表 1 DXN生物检测法优缺点的对比[87]
Table 1 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of DXN bioassay detection method[87]
方法 预处理 检测周期 (天) 检测成本 (美元) 灵敏度 (pg/g) 实验室投入 (美元) 酶活力诱导生物法 简便 3 1 000~1 200 1.000 200 000 酶免疫法 简便 2 200~900 0.500 200 000 荧光素酶法 简便 1 200~900 0.025 200 000 表 2 DXN检测标准的发展历程
Table 2 Development of DXN detection standards
序号 标准号 描述 年份 国家 文献 1 EPA 1613 (美) 同位素稀释法测定八氯二噁英及其呋喃 1994年10月 美国 [100] 2 EPA 23 (美) MSWI过程中多氯化二苯并二噁英的测定 1995年12月 美国 [101] 3 EPA 8280 (美) 多氯化二苯并二噁英和呋喃的分析测定, 高分辨气相低分辨质谱法 1996年12月 美国 [102] 4 EPA 1668A (美) 高分辨气质联用测定水、土壤、沉积物、生物体和组织中的多氯联苯 1999年12月 美国 [103] 5 JIS K0311 (日) 排入空气中的PCDDs、PCDFs以及Co-PCBs的气相色谱–质谱联用检测 方法 1999年9月 日本 [104] 6 EN1948-1 (欧盟) DXN排放统一检测标准 2006年 欧盟 [105] 7 HJ/T77-2001 (中) 多氯代二苯并二噁英和多氯代二苯并呋喃的测定, 同位素稀释高分辨毛 细管气相色谱–高分辨质谱法 2001年 中国 [106] 8 HJ 77.3-2008 (中) 固体废物二噁英类的测定, 同位素稀释, 高分辨气相色谱–高分辨质谱法 2008年 中国 [107] 9 HJ/T 365-2007 (中) 规定危险废物焚烧处置设施二噁英排放监测技术要求 2007年 中国 [108] 10 GB 18485-2001 (中) 生活垃圾焚烧污染控制标准 2001年 中国 [109] 11 GB 18485-2014 (中) 生活垃圾焚烧污染控制标准 2014年 中国 [110] 注: 中国的HJ/T 77-2001标准改进于美国的EPA 1613, HJ 77.3-2008改进于美国的EPA 8280. 表 3 DXN检测方法统计
Table 3 DXN detection method statistics
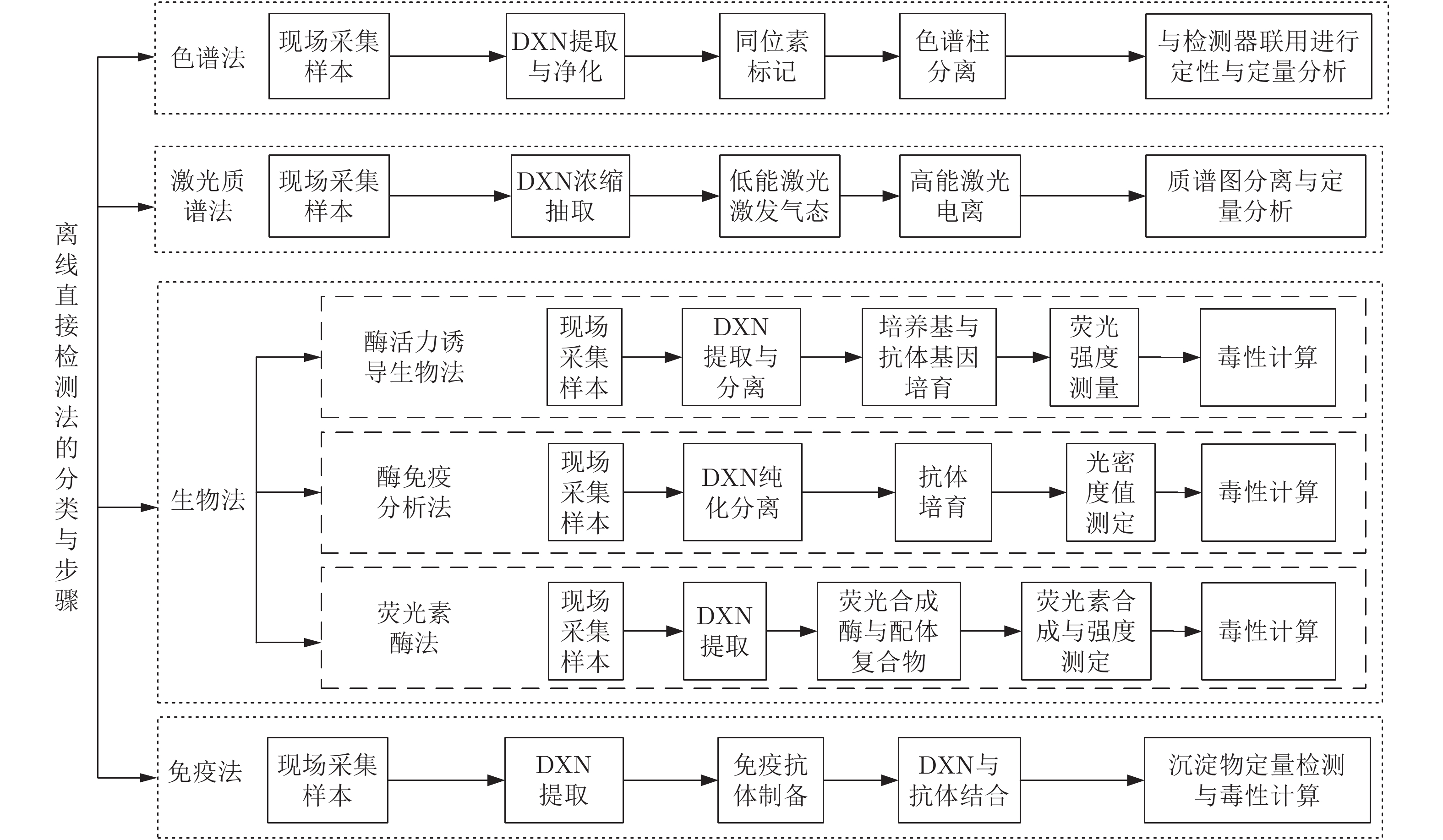
类别 名称 方法简述 优点和缺点 侧重点 年份与文献 离线直接检测法 色谱法 首先对样本进行采集、提取与净化、同位素标记、色谱柱分离, 然后与检测器联用进行定性与定量分析 优点: 可分离DXN类物质组分
和准确度量
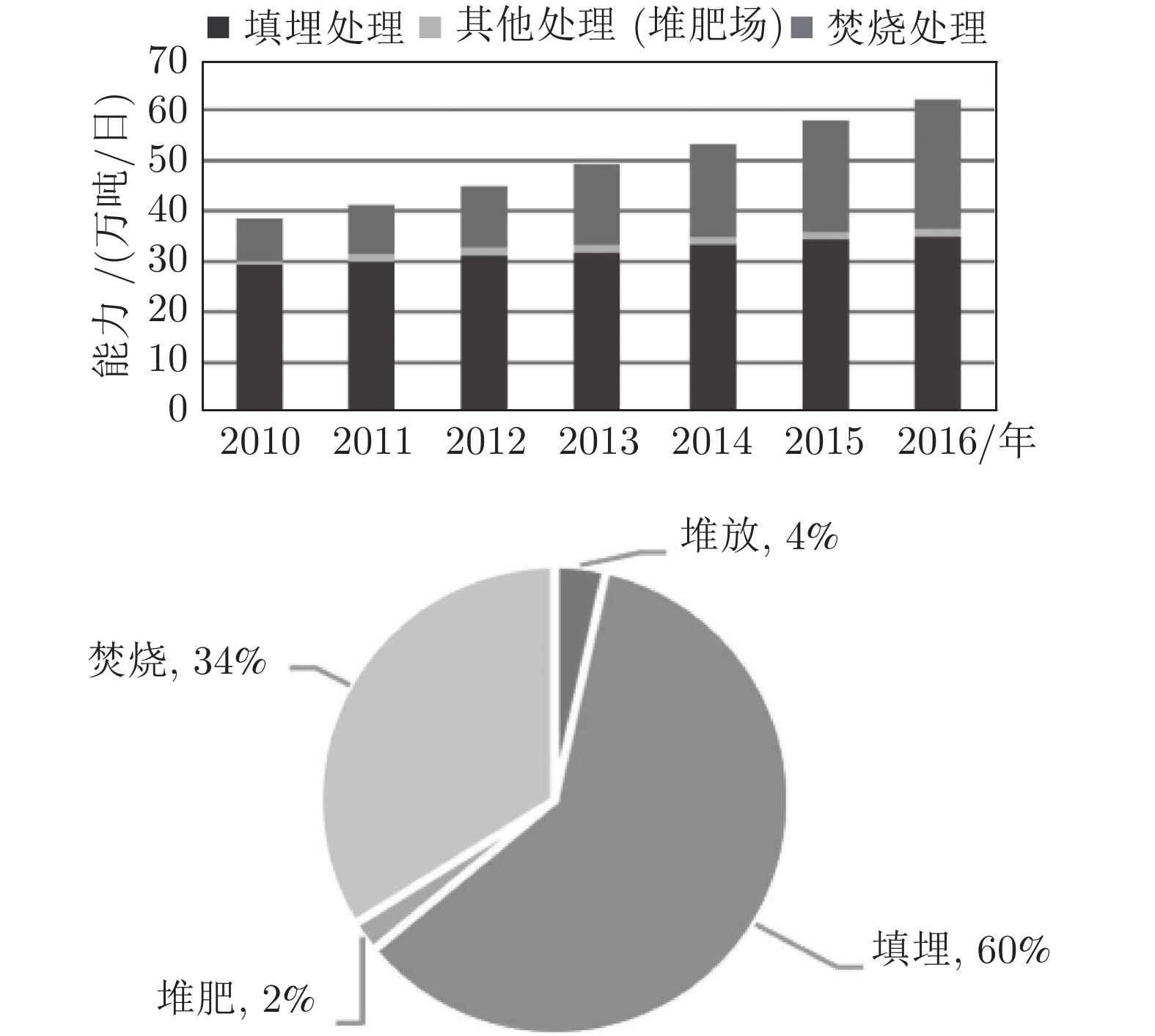
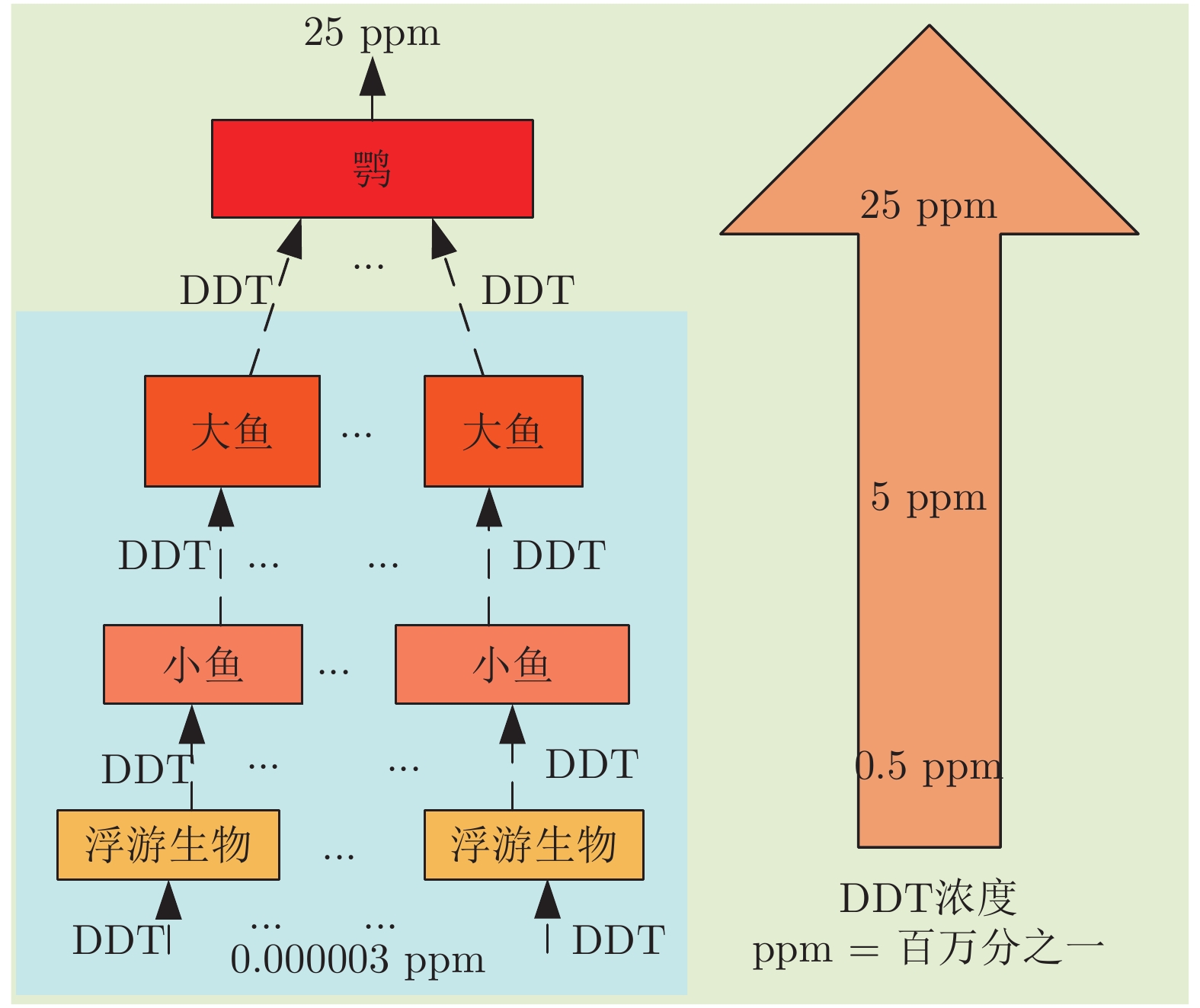
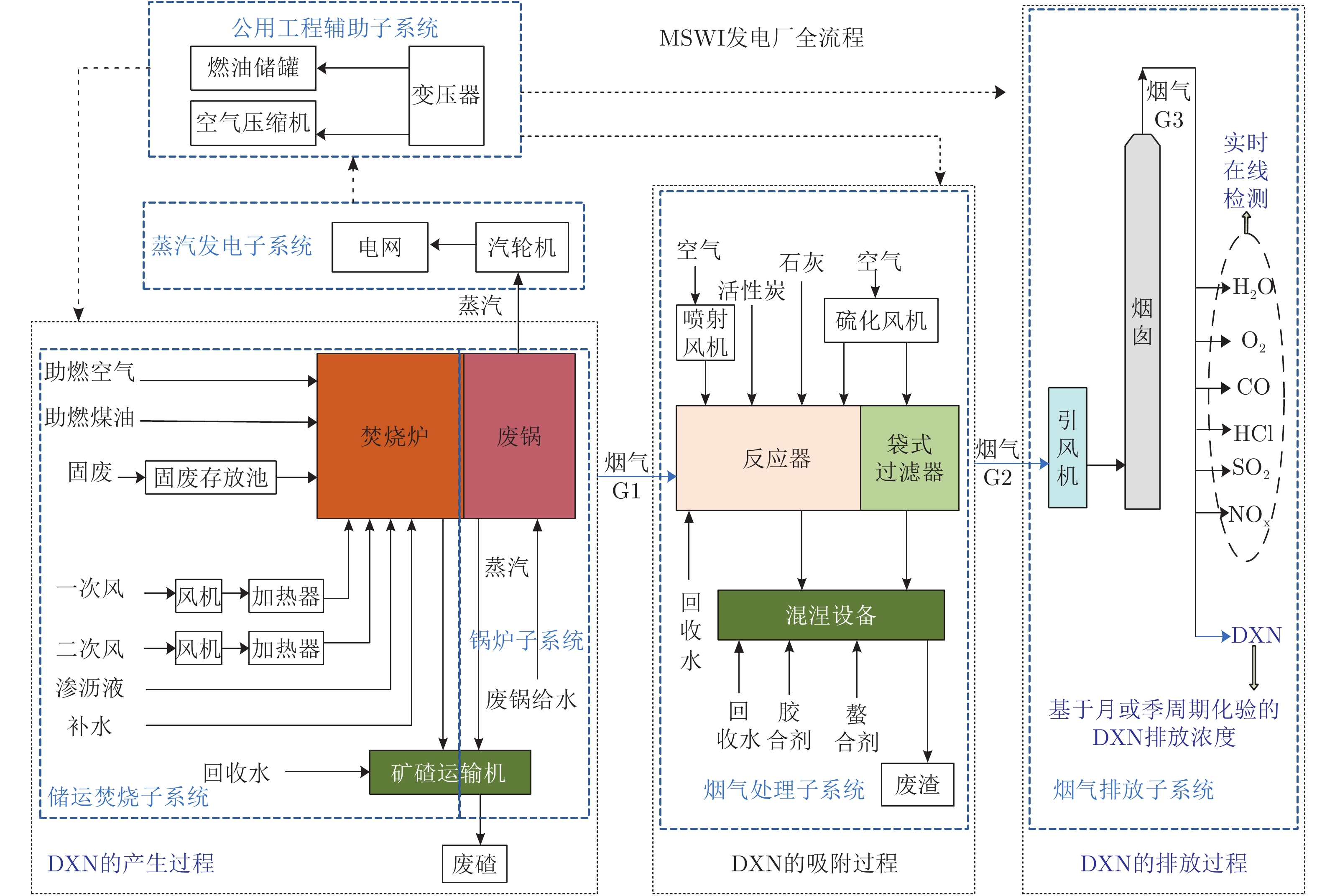
缺点: 周期长、费用高、对操
作人员与设备要求高DXN类物质的超痕量分析 1993[146] DXN类物质萃取方法 1994[147] MSWI过程DXN排放浓度检测 1992[148] 空气中DXN浓度的检测 1989[149], 1996[150] 论述DXN的提取方法 1995[151], 1996[152] 检测土壤中的DXN 1994[153] 激光质谱法 基于激光波长选择性电离, 再采用飞行时间质谱仪进行质量选择 优点: 快速、高灵敏度
缺点: 前期准备过程复杂指出DXN同类物具有独特光谱结构和较窄带宽 2010[88] 简述激光质谱法原理 1998[89] 激光质谱法在环境监测中的应用 2001[90] 可移动式激光质谱仪对MSWI过程中产生的DXN排放浓度进行检测 1996[154] 生物法 酶活力诱导生物法: 通过特殊受体芳香烃测量DXN毒性 优点: 周期短、成本低、大量样品可同时测定
缺点: 仅能测总体的毒性当量简述酶活力诱导生物法 1985[155], 1989[156] 简述酶活力诱导生物法在国内DXN检测中的应用 1996[91] 酶免疫分析法: 单克隆或复合克隆抗体与DXN同类物高度结合的特性, 建立竞争抑制酶免疫方法 优点: 分析简便、易操作、测定周期较短
缺点: 不能测出DXN同类物的具体量值、需测定标准曲线、样品量大时误差较大简述酶免疫分析法 1987[157], 1997[92], 1999[93] 简述酶免疫法在国内DXN检测方面的应用 1997[158] 提出酶免疫法与光谱法联合使用 2006[94] 与酶活力免疫法进行比较, 其准确性较高 2001[95] 荧光素酶法: 利用基因工程, 重组染色体配体复合物, 进一步合成荧光素 优点: 灵敏度高、检测时间短
缺点: 无法测出DXN同类物的具体量值简述荧光素酶法 1984[96] 荧光素酶法与其他生物法的比较 2001[97], 2001[98] 对MSWI过程DXN的排放进行检测, 并与色谱法比较 2011[99] 免疫法 基于DXN类抗体获得样本毒性当量, 计算出DXN含量 优点: 操作简便, 检测仪器要求低
缺点: 抗体制作复杂, DXN同类物检测种类有限采用单克隆抗体对DXN进行检测 1980[159] 采用单克隆与血清蛋白结合, 缩短检测时间 1986[160] 指示物/
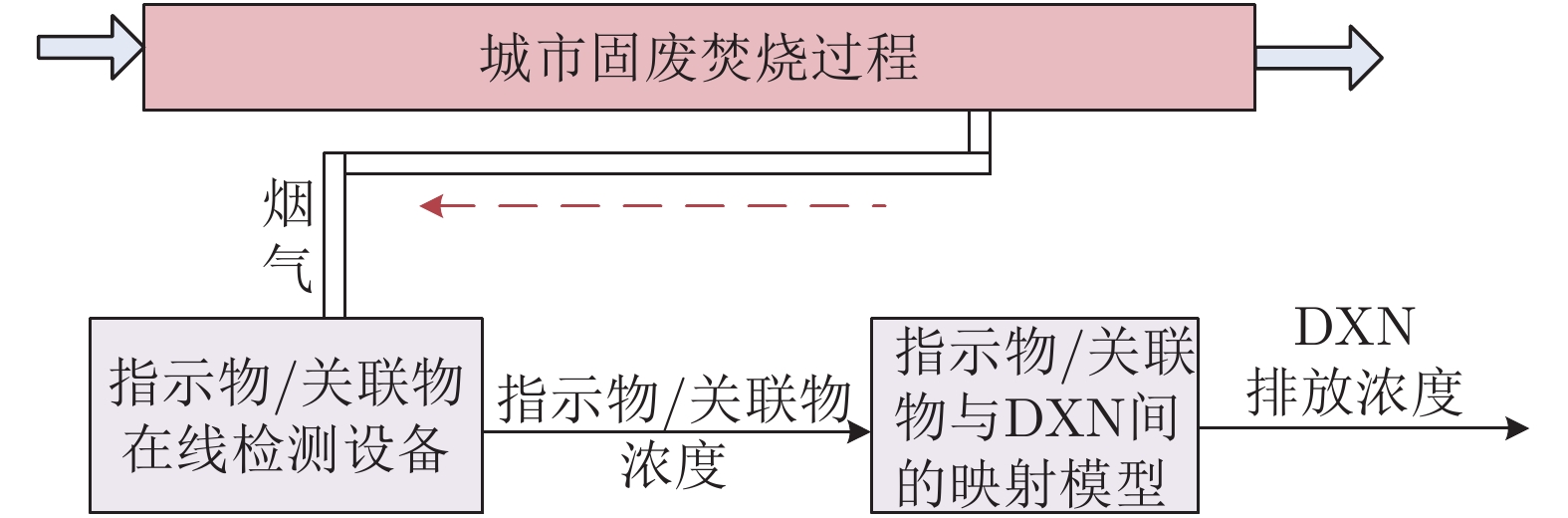
关联物在
线间接检
测法基于氯苯与DXN映射关系进行检测 研究多种氯苯与DXN之间的映射关系 优点: 检测周期短
缺点: 不够稳定, 映射模型本身存在误差, 存在时间滞后性六氯苯与DXN映射关系 1985[114] 五氯苯与DXN映射关系 2006[115] 多氯联苯与DXN映射关系 1994[116] 其他氯苯与DXN映射关系 1996[118], 1999[121], 2001[122], 2002[117], 2005[48], 2005[119], 2010[123], 2012[51], 2016[124], 2017[120], 2018[39] 基于多环芳烃与DXN映射关系进行检测 研究多环芳烃与DXN映射关系 同上 多环芳烃与DXN映射关系 2003[125], 2006[126], 2009[127] 实时在线跟踪多环芳烃的质谱仪 1999[128] 基于氯酚与DXN映射关系进行检测 研究氯酚与DXN映射关系 同上 氯酚与DXN之间的映射关系 2002[117], 1999[129] 氯苯和氯酚与DXN映射关系 2000[131], 2001[130], 2016[133] 氯苯与氯酚与DXN之间的映射关系的精度对比 1987[132], 2005[48] 其他指示物与DXN映射关系进行检测 研究其他指示物与DXN映射关系 同上 有机卤素化合物与DXN之间的映射关系 2010[134] 松针表面DXN浓度检测 2018[135] 低挥发性有机氯与DXN之间的映射关系 2010[136] 软测量法 回归分析法 构建线性映射关系模型 优点: 周期短, 成本低;
缺点: 无法描述非线性映射关系温度与DXN之间的回归模型 1989[137] 焚烧尾气CO含量与DXN之间的回归模型 2002[138], 2002[117] 过量空气与DXN之间的回归模型 1989[139] 烟气处理设备前的烟气与DXN之间的回归模型 2013[140] 神经网络 构建非线性单模型 优点: 周期短, 成本低;
缺点: 基于小样本的神经网络模型稳定性差, 泛化能力差欧美研究结构收集的焚烧炉数据, 单神经网络模型 1995[59], 2018[141] 中国实验规模的焚烧炉, 单神经网络与集成神经网络模型 2008[62], 2012[63] 中国台湾地区焚烧炉, 单神经网络模型 2003[142] 遗传编程 构建非线性模型 优点: 周期短, 检测成本低;
缺点: 泛化能力差, 计算复杂度高欧美研究结构收集的3种类型焚烧炉数据, 基于遗传编程构建非线性模型 2000[60] 支持向量机 构建非线性模型 优点: 周期短, 成本低;
缺点: 泛化能力差, 样本有限
未进行特征选择中国华南地区某焚烧炉, 单模型 2017[143] 欧美研究结构收集的焚烧炉数据, 选择性集成模型 2019[144] -
[1] Korai M S, Mahar R B, Uqaili M A. The feasibility of municipal solid waste for energy generation and its existing management practices in Pakistan. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 72: 338−353 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.051 [2] Kolekar K A, Hazra T, Chakrabarty S N. A review on prediction of municipal solid waste generation models. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2016, 35: 238−244 doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.087 [3] Arafat H A, Jijakli K, Ahsan A, 2015. Environmental performance and energy recovery potential of five processes for municipal solid waste treatment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 105: 233−240 [4] Lu J W, Zhang S K, Hai J, Lei M. Status and perspectives of municipal solid waste incineration in China: A comparison with developed regions. Waste Management, 2017, 69: 170−186 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.04.014 [5] Database of Waste Management Technologies [Online], available: http://www.epem.gr/waste-c-control/database/html/WtE-01.htm [6] Bajić B Ž, Dodić S N, Vučurović D G, Dodić J M, Grahovac J A. Waste-to-energy status in Serbia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 50: 1437−1444 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.05.079 [7] Kalyani K A, Pandey K K. Waste to energy status in India: A short review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 31: 113−120 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.11.020 [8] Kumar A, Samadder S R. A review on technological options of waste to energy for effective management of municipal solid waste. Waste Management, 2017, 69: 407−422 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.046 [9] Liu Y L, Sun W X, Liu J G. Greenhouse gas emissions from different municipal solid waste management scenarios in China: Based on carbon and energy flow analysis. Waste Management, 2017, 68: 653−661 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.06.020 [10] Pan S Y, Du M A, Huang I T, Liu I H, Chang E E, Chiang P C. Strategies on implementation of waste-to-energy (WTE) supply chain for circular economy system: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 2015: 409−421 [11] Liu Y L, Xing P X, Liu J G. Environmental performance evaluation of different municipal solid waste management scenarios in China. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2017, 125: 98−106 doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.06.005 [12] 徐海云. 城市生活垃圾处理行业2017年发展综述. 中国环保产业, 2017, (4): 9−15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5377.2017.04.002Xu Hai-Yun. Development report on treatment industry of urban domestic refuse in 2017. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2017, (4): 9−15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5377.2017.04.002 [13] Khandelwal H, Dhar H, Thalla A K, Kumar S. Application of life cycle assessment in municipal solid waste management: A worldwide critical review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 209: 630−654 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.233 [14] Lombardi L, Carnevale E A. Evaluation of the environmental sustainability of different waste-to-energy plant configurations. Waste Management, 2018, 73: 232−246 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.07.006 [15] Mavrotas G, Gakis N, Skoulaxinou S, Katsouros V, Georgopoulou E. Municipal solid waste management and energy production: Consideration of external cost through multi-objective optimization and its effect on waste-to-energy solutions. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 51: 1205−1222 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.029 [16] Zhang D Q, Tan S K, Gersberg R M. Municipal solid waste management in China: Status, problems and challenges. Journal of Environmental Management, 2010, 91(8): 1623−1633 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.03.012 [17] Hu Y A, Cheng H F, Tao S. The growing importance of waste-to-energy (WTE) incineration in China's anthropogenic mercury emissions: Emission inventories and reduction strategies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 97: 119−137 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.08.026 [18] Huang T, Zhou L L, Liu L F, Xia M. Ultrasound-enhanced electrokinetic remediation for removal of Zn, Pb, Cu and Cd in municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes. Waste Management, 2018, 75: 226−235 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.029 [19] Dong J, Tang Y J, Nzihou A, Chi Y, Weiss-Hortala E, Ni M J, Zhou Z Z. Comparison of waste-to-energy technologies of gasification and incineration using life cycle assessment: Case studies in Finland, France and China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 203: 287−300 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.139 [20] Zheng L J, Song J C, Li C Y, Gao Y G, Geng P L, Qu B N, Lin L Y. Preferential policies promote municipal solid waste (MSW) to energy in China: Current status and prospects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 36: 135−148 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.04.049 [21] 柴天佑. 自动化科学与技术发展方向. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 1923−1930Chai Tian-You. Development directions of automation science and technology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 1923−1930 [22] 柴天佑. 复杂工业过程运行优化与反馈控制. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1744−1757 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01744Chai Tian-You. Operational optimization and feedback control for complex industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1744−1757 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01744 [23] Hoyos A, Cobo M, Aristizábal B, Córdoba F, de Correa C M. Total suspended particulate (TSP), polychlorinated dibenzodioxin (PCDD) and polychlorinated dibenzofuran (PCDF) emissions from medical waste incinerators in Antioquia, Colombia. Chemosphere, 2008, 73(1): S137−S142 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.079 [24] 罗建松. 二噁英指示物的反应特性及其在线检测研究[硕士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2007.Luo Jian-Song. Study on the Reaction Performances and On-line Detecting of Dioxin Indicator [Master thesis], Zhejiang University, China, 2007. [25] 解艳, 薛科社. 二噁英分析检测方法研究进展及展望. 环境科学与管理, 2011, 36(3): 84−86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2011.03.021Xie Yan, Xue Ke-She. The research progress and outlook in analytical and test method of dioxin. Environmental Science and Management, 2011, 36(3): 84−86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2011.03.021 [26] Bai J, Sun X M, Zhang C X, Gong C, Hu J T, Zhang J H. Mechanism and kinetics study on the ozonolysis reaction of 2,3,7,8-TCDD in the atmosphere. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(1): 181−188 doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60396-4 [27] 罗阿群, 刘少光, 林文松, 谷东亮, 陈成武. 二噁英生成机理及减排方法研究进展. 化工进展, 2016, 35(3): 910−916Luo A-Qun, Liu Shao-Guang, Lin Wen-Song, Gu Dong-Liang, Chen Cheng-Wu. Progress of formation mechanisms and emission reduction methods of PCDD/Fs. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(3): 910−916 [28] Kanan S, Samara F. Dioxins and furans: A review from chemical and environmental perspectives. Trends in Environmental analytical Chemistry, 2018, 17: 1−13 doi: 10.1016/j.teac.2017.12.001 [29] Li X M, Zhang C M, Li Y Z, Zhi Q. The status of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) in China and its clean development. Energy Procedia, 2016, 104: 498−503 doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2016.12.084 [30] Phillips K J O, Longhurst P J, Wagland S T. Assessing the perception and reality of arguments against thermal waste treatment plants in terms of property prices. Waste Management, 2014, 34(1): 219−225 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.08.018 [31] McKay G. Dioxin characterisation, formation and minimisation during municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration: Review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2002, 86(3): 343−368 doi: 10.1016/S1385-8947(01)00228-5 [32] Ni Y W, Zhang H J, Fan S, Zhang X P, Zhang Q, Chen J P. Emissions of PCDD/Fs from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere, 2009, 75(9): 1153−1158 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.02.051 [33] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 生活垃圾焚烧污染控制标准[Online], available: http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/gthw/gtfwwrkzbz/200201/t20020101_63051.shtmlMinistry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Standard for pollution control on the municipal solid waste incineration. [Online], available: http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/gthw/gtfwwrkzbz/200201/t20020101_63051.shtml [34] 唐娜, 李馥琪, 罗伟铿, 石运刚, 王美欢, 郑佳, 任明忠. 废物焚烧及工业金属冶炼烟气中二噁英的排放水平及同系物分布. 安全与环境学报, 2018, 18(4): 1496−1502Tang Na, Li Fu-Qi, Luo Wei-Keng, Shi Yun-Gang, Wang Mei-Huan, Zheng Jia, Ren Ming-Zhong. Concentrations and congener distributions of PCDD/Fs in the flue gas from combustion and metallurgical processing. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2018, 18(4): 1496−1502 [35] 俞明锋, 付建英, 詹明秀, 林晓青, 陈彤. 生活废弃物焚烧处置烟气中二噁英排放特性研究. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(5): 1983−1988Yu Ming-Feng, Fu Jian-Ying, Zhan Ming-Xiu, Lin Xiao-Qing, Chen Tong. The research of PCDD/Fs emission characteristics in flue gas from municipal solid waste incinerations. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(5): 1983−1988 [36] 严建华, 陈彤, 谷月玲, 李晓东, 陆胜勇, 章骥, 岑可法. 垃圾焚烧炉飞灰中二噁英的低温热处理试验研究. 中国电机工程学报, 2005, 25(23): 95−99 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2005.23.017Yan Jian-Hua, Chen Tong, Gu Yue-Ling, Li Xiao-Dong, Lu Sheng-Yong, Zhang Ji, Cen Ke-Fa. Experimental study on low temperature thermal treatment of PCDD/Fs in fly ASH. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2005, 25(23): 95−99 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2005.23.017 [37] 赵英孜, 蒋友胜, 张建清, 刘德全, 周志华, 周健, 等. 深圳市废弃物焚烧炉飞灰中二噁英含量水平和特征分析. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(9): 2739−2744Zhao Ying-Zi, Jiang You-Sheng, Zhang Jian-Qing, Liu De-Quan, Zhou Zhi-Hua, Zhou Jian, et al. Levels and characteristic analysis of dioxins in fly ash from waste incinerators of Shenzhen. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(9): 2739−2744 [38] 钱莲英, 潘淑萍, 徐哲明, 徐茵茵. 生活垃圾焚烧炉烟气中二噁英排放水平及控制措施. 环境监测管理与技术, 2017, 29(3): 57−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2017.03.014Qian Lian-Ying, Pan Shu-Ping, Xu Zhe-Ming, Xu Yin-Yin. Concentration of dioxins in flue gas of waste incinerator and control measures. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2017, 29(3): 57−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2017.03.014 [39] 林斌斌, 李晓东, 王天娇, 陈彤, 林晓青, 陆胜勇. 生活垃圾焚烧炉中二噁英、氯苯排放特性及关联. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 428−436 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017080102Lin Bin-Bin, Li Xiao-Dong, Wang Tian-Jiao, Chen Tong, Lin Xiao-Qing, Lu Sheng-Yong. Emission characteristics and correlation between PCDD/Fs and chlorobenzens in the municipal solid waste incierators. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 428−436 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017080102 [40] 张益. 我国生活垃圾焚烧处理技术回顾与展望. 环境保护, 2016, 44(13): 20−26Zhang Yi. Review and prospect of living garbage incineration technologies in China. Environmental Protection, 2016, 44(13): 20−26 [41] 李大中, 唐影. 垃圾焚烧发电污染物排放过程建模与优化. 可再生能源, 2015, 33(1): 118−123Li Da-Zhong, Tang Ying. Modeling and optimization of pollutants emission of waste incineration. Renewable Energy Resources, 2015, 33(1): 118−123 [42] 林海鹏, 于云江, 李琴, 王丽丽, 王先良, 车飞. 二噁英的毒性及其对人体健康影响的研究进展. 环境科学与技术, 2009, 32(9): 93−97 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2009.09.022Lin Hai-Peng, Yu Yun-Jiang, Li Qin, Wang Li-Li, Wang Xian-Liang, Che Fei. Research progress on the Dioxin’s toxicity and its effect on human health. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 32(9): 93−97 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2009.09.022 [43] 李海英, 张书廷, 赵新华. 城市生活垃圾焚烧产物中二噁英检测方法. 燃料化学学报, 2005, 33(3): 379−384 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2005.03.025Li Hai-Ying, Zhang Shu-Ting, Zhao Xin-Hua. Detection methods of dioxins emitted from municipal solid waste incinerator. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2005, 33(3): 379−384 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2005.03.025 [44] 张诺, 孙韶华, 王明泉, 肖芙蓉, 许燕, 贾瑞宝. 荧光素酶表达基因法(CALUX)用于二噁英检测的研究进展. 生态毒理学报, 2014, 9(3): 391−397Zhang Nuo, Sun Shao-Hua, Wang Ming-Quan, Xiao Fu-Rong, Xu Yan, Jia Rui-Bao. Research progress of dioxins’ detection using chemical-luciferase gene expression (CALUX). Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2014, 9(3): 391−397 [45] Bunsan S, Chen W Y, Chen H W, Chuang Y H, Grisdanurak N. Modeling the dioxin emission of a municipal solid waste incinerator using neural networks. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(3): 258−264 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.083 [46] Urano K, Kato M, Nagayanagi Y, Saito Y, Aono A, Nagata J, Syudo H. Convenient dioxin measuring method using an efficient sampling train, an efficient HPLC system and a highly sensitive HRGC/LRMS with a PTV injector. Chemosphere, 2001, 43(4–7): 425−431 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00390-8 [47] Hung P C, Chang S H, Buekens A, Chang M B. Continuous sampling of MSWI dioxins. Chemosphere, 2016, 145: 119−124 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.111 [48] Lavric E D, Konnov A A, de Ruyck J. Surrogate compounds for dioxins in incineration: A review. Waste Management, 2005, 25(7): 755−765 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2004.12.026 [49] Lavric E D, Konnov A A, Ruyck J D. Implementation of a detailed reaction mechanism for the modeling of dioxins precursors formation. Organohalogen Compounds, 2002, 56: 201−204 [50] 尹雪峰, 李晓东, 陆胜勇, 罗建松, 谷月玲, 严建华, 等. 模拟烟气中痕量有机污染物生成的在线实时监测. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(17): 29−33 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2007.17.006Yin Xue-Feng, Li Xiao-Dong, Lu Sheng-Yong, Luo Jian-Song, Gu Yue-Ling, Yan Jian-Hua, et al. On-line real-time monitoring of trace organic pollutant formation in the simulated flue gas. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2007, 27(17): 29−33 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2007.17.006 [51] Gullett B K, Oudejans L, Tabor D, Touati A, Ryan S. Near-real-time combustion monitoring for PCDD/PCDF indicators by GC-REMPI-TOFMS. Environmental Science and Technology, 2012, 46(2): 923−928 [52] 郭颖, 陈彤, 杨杰, 曹轩, 陆胜勇, 李晓东. 基于关联模型的二噁英在线检测研究. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(8): 3524−3529Guo Ying, Chen Tong, Yang Jie, Cao Xuan, Lu Sheng-Yong, Li Xiao-Dong. Study on on-line detection of dioxins based on correlation model. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2014, 8(8): 3524−3529 [53] 李阿丹, 洪伟, 王晶. 激光解吸/激光电离–质谱法二噁英及其关联物的在线检测. 燕山大学学报, 2015, 39(6): 511−515 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2015.06.007Li A-Dan, Hong Wei, Wang Jing. Online detection of dioxin and dioxin-related substances using laser desoption/laser ionization-mass spectrometry. Journal of Yanshan University, 2015, 39(6): 511−515 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2015.06.007 [54] 曹轩, 尚凡杰, 潘登皋. 用于二恶英在线检测的气相色谱–质谱间传输线系统, 中国 CN206378474U, 2017-08-04Cao Xuan, Shang Fan-Jie, Pan Deng-Gao. Gas chromatography who is used for dioxin on-line measuring transmission line system between mass spectrum, China CN206378474U, August 4, 2017 [55] Yan M, Li X D, Chen T, Lu S Y, Yan J H, Cen K F. Effect of temperature and oxygen on the formation of chlorobenzene as the indicator of PCDD/Fs. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 22(10): 1637−1642 doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60300-4 [56] Everaert K, Baeyens J. The formation and emission of dioxins in large scale thermal processes. Chemosphere, 2002, 46(3): 439−448 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00143-6 [57] Nakui H, Koyama H, Takakura A, Watanabe N. Online measurements of low-volatile organic chlorine for dioxin monitoring at municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere, 2011, 85(2): 151−155 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.042 [58] 汤健, 田福庆, 贾美英, 李东. 基于频谱数据驱动的旋转机械设备负荷软测量. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2015.Tang Jian, Tian Fu-Qing, Jia Mei-Ying, Li Dong. Soft Measurement of Rotating Machinery Equipment Load Based on Spectrum Data Drive. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2015. [59] Chang N B, Huang S H. Statistical modelling for the prediction and control of PCDDs and PCDFs emissions from municipal solid waste incinerators. Waste Management and Research, 1995, 13(4): 379−400 [60] Chang N B, Chen W C. Prediction of PCDDs/PCDFs emissions from municipal incinerators by genetic programming and neural network modeling. Waste Management and Research, 2000, 18(4): 341−351 doi: 10.1177/0734242X0001800406 [61] 胡文金. 面向无害化垃圾焚烧发电的二噁英软测量精简化建模研究. 国家自然科学基金资助项目结题报告, 批准号: 61174015, 2016Hu Wen-Jin. Modeling of dioxin soft sensor for harmless waste incineration power generation. Final Report on the Subsidized Projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, China, 61174015, 2016 [62] 王海瑞, 张勇, 王华. 基于GA和BP神经网络的二噁英软测量模型研究. 微计算机信息, 2008, 24(21): 222−224, 233 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0570.2008.21.091Wang Hai-Rui, Zhang Yong, Wang Hua. A study of GA-BP based prediction model of dioxin emission from MSW incinerator. Control and Automation, 2008, 24(21): 222−224, 233 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0570.2008.21.091 [63] 胡文金, 苏盈盈, 汤毅, 易军. 基于小样本数据的垃圾焚烧二噁英软测量建模. 第 32 届中国控制会议论文集. 西安, 中国: 中国自动化学会控制理论专业委员会, 中国系统工程学会, 2012.Hu Wen-Jin, Su Ying-Ying, Tang Yi, Yi Jun. Soft sensing modeling of dioxins for waste incineration based on small data sets. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Process Control Conference. Xi'an, China: Control Theory Committee of China Automation Society, China Society of Systems Engineering, 2012. [64] Olie K, Vermeulen P L, Hutzinger O. Chlorodibenzo-p-dioxins and chlorodibenzofurans are trace components of fly ash and flue gas of some municipal incinerators in the Netherlands. Chemosphere, 1977, 6(8): 455−459 doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(77)90035-2 [65] Palmer D, Pou J O, Gonzalez-Sabaté L, Díaz-Ferrero J. Multiple linear regression based congener profile correlation to estimate the toxicity (TEQ) and dioxin concentration in atmospheric emissions. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622–623: 510−516 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.344 [66] Gouin T, Harner T, Daly G L, Wania F, Mackay D, Jones K C. Variability of concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in air: Implications for monitoring, modeling and control. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(1): 151−166 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.09.022 [67] 郑明辉, 余立风, 丁琼, 田亚静. 二噁英类生物检测技术. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2013.Zheng Ming-Hui, Yu Li-Feng, Ding Qiong, Tian Ya-Jing. Biodetection Technologies for Dioxins. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2013. [68] 金艳勤. 二噁英类化合物快速检测系统的初步构建[硕士学位论文], 天津大学, 中国, 2010.Jin Yan-Qin. The Initial Construction of Rapid Detection System for Dioxins [Master thesis], Tianjin University, China, 2010. [69] Shaub W M, Tsang W. Dioxin formation in incinerators. Environmental Science and Technology, 1983, 17(12): 721−730 [70] Huang H, Buskens A. Comparison of dioxin formation levels in laboratory gas-phase flow reactors with those calculated using the Shaub-Tsang mechanism. Chemosphere, 1999, 38(7): 1595−1602 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00386-5 [71] Zhou H, Meng A H, Long Y Q, Li Q H, Zhang Y G. A review of dioxin-related substances during municipal solid waste incineration. Waste Management, 2015, 36: 106−118 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.11.011 [72] 姜欣. 日本对二噁英的研究现状. 皮革化工, 2006, 23(4): 39−42Jiang Xin. Present research status of dioxin in Japan. Leather Chemicals, 2006, 23(4): 39−42 [73] 钱原吉, 吴占松. 生活垃圾焚烧炉中二恶英的生成和计算方法. 动力工程, 2007, 27(4): 616−619Qian Yuan-Ji, Wu Zhan-Song. Genesis of dioxin in garbage incinerators and a way of calculating its formation. Journal of Power Engineering, 2007, 27(4): 616−619 [74] Zhang H J, Ni Y W, Chen J P, Zhang Q. Influence of variation in the operating conditions on PCDD/F distribution in a full-scale MSW incinerator. Chemosphere, 2008, 70(4): 721−730 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.054 [75] Mukherjee A, Debnath B, Ghosh S K. A review on technologies of removal of dioxins and furans from incinerator flue gas. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2016, 35: 528−540 doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.037 [76] Lin X Q, Yan M, Dai A H, Zhan M X, Fu J Y, Li X D, Chen T, Lu S Y, Buekens A, Yan J H. Simultaneous suppression of PCDD/F and NOx during municipal solid waste incineration. Chemosphere, 2015, 126: 60−66 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.005 [77] Gerasimov G. Modeling study of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans behavior in flue gases under electron beam irradiation. Chemosphere, 2016, 158: 100−106 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.064 [78] Havukainen J, Zhan M X, Dong J, Liikanen M, Deviatkin L, Li X D, Horttanainen M. Environmental impact assessment of municipal solid waste management incorporating mechanical treatment of waste and incineration in Hangzhou, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 141: 453−461 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.146 [79] Zhang R Z, Luo Y H, Yin R H. Experimental study on dioxin formation in an MSW gasification-combustion process: An attempt for the simultaneous control of dioxins and nitrogen oxides. Waste Management, 2018, 82: 292−301 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.10.042 [80] Chen Z L, Lin X Q, Lu S Y, Li X D, Yan J H. Suppressing formation pathway of PCDD/Fs by S-N-containing compound in full-scale municipal solid waste incinerators. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359: 1391−1399 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.039 [81] Wen Z G, Di J H, Liu S T, Han J, Lee J C K. Evaluation of flue-gas treatment technologies for municipal waste incineration: A case study in Changzhou, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 18: 912−920 [82] Watanabe N, Kawamoto K, Asada S, Fujiyoshi H, Miyata H, Watanabe G, Suzuk S. Surrogate study for dioxins from municipal waste incinerator in startup condition: Applicability as a dioxin control indicator and an organohalogen emission warning. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2010, 12(3): 254−263 doi: 10.1007/s10163-010-0295-8 [83] Donghoon S, Won Y, Jinwhan C, Sangmin C, Yoon-Seok J. The effect of operating conditions on PCDD/F emission in MSWIs: Stack gas measurement and evaluation of operating conditions. Organohalogen Compounds, 1998, 36: 143−146 [84] Gulyurtlu I, Crujeira A T, Abelha P, Cabrita I. Measurements of dioxin emissions during co-firing in a fluidised bed. Fuel, 2007, 86(14): 2090−2100 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2007.01.037 [85] Yan J H, Chen T, Li X D, Zhang J, Lu S Y, Ni M J, Cen K F. Evaluation of PCDD/Fs emission from fluidized bed incinerators co-firing MSW with coal in China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 135(1–3): 47−51 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.007 [86] 张晓翔. 飞行时间质谱仪在线检测二噁英指示物的试验研究[硕士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2010.Zhang Xiao-Xiang. Experimental Study on On-line Monitoring of PCDD/Fs Indicator Using TOF-MS [Master thesis], Zhejiang University, China, 2010. [87] 赵毅, 张秉建, 贺鹏. 二噁英类化合物检测方法的研究现状及展望. 电力环境保护, 2008, 24(6): 44−47Zhao Yi, Zhang Bing-Jian, He Peng. Research status and prospect for detection methods of dioxins-like chemicals. Electric Power Environmental Protection, 2008, 24(6): 44−47 [88] Weickhardt C, Zimmermann R, Boesl U, Schlag E W. Laser mass spectrometry of dibenzodioxin, dibenzofuran and two isomers of dichlorodibenzodioxins: Selective ionization. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2010, 7(3): 183−185 doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290070303 [89] Allen M G. Diode laser absorption sensors for gas-dynamic and combustion flows. Measurement Science and Technology, 1998, 9(4): 545−562 doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/9/4/001 [90] 李子尧, 魏杰, 张冰. 激光质谱法: 原理及其在环境监测中的应用. 量子电子学报, 2001, 18(1): 1−8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2001.01.001Li Zi-Yao, Wei Jie, Zhang Bing. Laser mass spectrometry: Principles and applications in environmental monitoring. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2001, 18(1): 1−8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2001.01.001 [91] Wu W Z, Schwirzer S M G, Schramm K W, Wiebel F J, Xu Y, Zhang Y Y, et al. Rapid bioassay as indicator of potentially harmful effects for dioxin-like compounds in sample of Ya-Er Lake, China: Requirements for clean-up and comparison to chemical analysis. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 1996, 5(7–8): 374−379 [92] Harrison R O, Carlson R E. An immunoassay for TEQ screening of dioxin/furan samples: Current status of assay and applications development. Chemosphere, 1997, 34(5–7): 915−928 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00395-0 [93] Harrison R O, Eduljee G H. Immunochemical analysis for dioxins-progress and prospects. Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 239(1–3): 1−18 doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00306-X [94] 王承智, 胡筱敏, 石荣, 祁国恕, 李锐. 二噁英类物质的生物检测方法. 中国安全科学学报, 2006, 16(5): 135−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.05.027Wang Cheng-Zhi, Hu Xiao-Min, Shi Rong, Qi Guo-Shu, Li Rui. Bioassay of dioxin-like chemicals. China Safety Science Journal, 2006, 16(5): 135−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.05.027 [95] 黎雯, 徐盈, 吴文忠, Schramm K W, Kettrup A. 利用离体大白鼠肝癌细胞的EROD诱导指示二恶英的复合毒性效应. 动物学报, 2001, 47(1): 64−70 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5507.2001.01.011Li Wen, Xu Ying, Wu Wen-Zhong, Schramm K W, Kettrup A. Combined toxicities of dioxins indicated by erod in rat hepatoma cells in vitro. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 2001, 47(1): 64−70 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5507.2001.01.011 [96] Rappe C, Bergqvist P A, Buser H R, Garå A, Marklund S, Nygren M. Analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environmental Specimen Banking and Monitoring as Related to Banking. Dordrecht: Springer, 1984. 323–330 [97] 张志仁, 徐顺清, 周宜开, 任恕, 刘志伟. 虫荧光素酶报告基因用于二噁英类化学物质的检测. 分析化学, 2001, 29(7): 825−827 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2001.07.023Zhang Zhi-Ren, Xu Shun-Qing, Zhou Yi-Kai, Ren Shu, Liu Zhi-Wei. Detection of dioxin-type chemicals by luciferase reporter gene. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 29(7): 825−827 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2001.07.023 [98] van Overmeire I, Clark G C, Brown D J, Chu M D, Cooke W M, Denison M S, et al. Trace contamination with dioxin-like chemicals: Evaluation of bioassay-based TEQ determination for hazard assessment and regulatory responses. Environmental Science and Policy, 2001, 4(6): 345−357 [99] 周志广, 任玥, 许鹏军, 李楠, 张烃, 刘爱民, 黄业茹. 荧光素酶报告基因法测定废气中二噁英类物质. 环境科学研究, 2011, 24(12): 1416−1421Zhou Zhi-Guang, Ren Yue, Xu Peng-Jun, Li Nan, Zhang Ting, Liu Ai-Min, Huang Ye-Ru. Determination of dioxins in flue gas by chemical-activated luciferase gene expression. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 24(12): 1416−1421 [100] EPA. Tetra-Through Octa-Chlorinated Dioxins and Furans by Isotope Dilution HRGC/HRMS, EPA Method 1613, 1994. [101] EPA. Determination of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-P-Dioxins and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans from Municipal Waste Combustors, EPA Method 23, 1995. [102] EPA. The Analysis of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-P-Dioxins and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans by High Resolution Gas Chromatography/Low Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRGC/LRMS), EPA 8280, 1996. [103] EPA. Method 1668, revision A: Chlorinated biphenyl congeners in water, soil, sediment, and tissue by HRGC/HRMS, EPA Method 1668A, 1999. [104] Method for Determination of Tetra-Through Octachlorodibenzo-P-Dioxins, Tetra-Through Octachlorodibenzofurans and Dioxin-Like Polychlorinatedbiphenyls in Stationary Source Emissions, Standard JIS K0311: 2005, Japan, 2005. [105] DIN. Stationary Source Emissions - Determination of the Mass Concentration of PCDDs/PCDFs and Dioxin-Like PCBs—Part 1: Sampling of PCDDs/PCDFs English Version of DIN EN, DIN EN 1948-1-2006, 2006. [106] 多氯代二苯并二噁英和多氯代二苯并呋喃的测定同位素稀释高分辨毛细管气相色谱/高分辨质谱法, HJ/T 77-2001, 2001.Determination of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins and Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Furans by Isotope Dilution HRGC/HRMS, HJ/T 77-2001, 2001. [107] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 固体废物二噁英类的测定同位素稀释高分辨气相色谱–高分辨质谱法, HJ 77.3-2008, 2009.Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. Solid Waste Determination of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins (PCDDs) and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans (PCDFs) ISOTOPE Dilution HRGC-HRMS, HJ 77.3-2008, 2009. [108] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 危险废物(含医疗废物)焚烧处置设施二噁英排放监测技术规范, HJ/T 365-2007, 2008.Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. Technical Guideline of Monitoring on Dioxins Emission from Hazardous Waste (Including Medical Waste) Incinerators, HJ/T 365-2007, 2008. [109] 国家环境保护总局, 国家质量监督验检疫总局. 生活垃圾焚烧污染控制标准, GB 18485-2001, 2002.State Environmental Protection Administration, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Standard for Pollution Control on the Municipal Solid Waste Incineration, GB 18485-2001, 2002. [110] 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 生活垃圾焚烧污染控制标准, GB 18485-2014, 2014.Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Standard for Pollution Control on the Municipal Solid Waste Incineration, GB 18485-2014, 2014. [111] 蒋蕾. 二噁英前生体在线检测飞行时间质谱仪的研究与应用.吉林大学, 2014.Jiang Lei. Development and Application of TOFMS for Online Monitoring of Dioxin Precursors [Master thesis], Jilin University, China, 2014. [112] Organtini K L, Myers A L, Jobst K J, Reiner E J, Ross B, Ladak A, Mullin L, Stevens D, Dorman F L. Quantitative analysis of mixed halogen dioxins and furans in fire debris utilizing atmospheric pressure ionization gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(20): 151001152931009 [113] 尚凡杰. 二噁英关联模型及其在线监测初步研究[硕士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2015.Shang Fan-Jie. Study on Dioxin Correlation Model and On-Line Monitoring [Master thesis], Zhejiang University, China, 2015. [114] Öberg T, Bergström J G T. Hexachlorobenzene as an indicator of dioxin production from combustion. Chemosphere, 1985, 14(8): 1081−1086 doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(85)90028-1 [115] Pandelova M, Lenoir D, Schramm K W. Correlation between PCDD/F, PCB and PCBz in coal/waste combustion. Influence of various inhibitors. Chemosphere, 2006, 62(7): 1196−1205 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.07.068 [116] Kaune A, Lenoir D, Nikolai U, Kettrup A. Estimating concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the stack gas of a hazardous waste incinerator from concentrations of chlorinated benzenes and biphenyls. Chemosphere, 1994, 29(9–11): 2083−2096 doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(94)90376-X [117] Yoneda K, Ikeguchi T, Yagi Y, Tamade Y, Omori K. A research on dioxin generation from the industrial waste incineration. Chemosphere, 2002, 46(9–10): 1309−1319 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00246-6 [118] Manninen H, Perkiö A, Vartiainen T, Ruuskanen J. Formation of PCDD/PCDF: Effect of fuel and fly ash composition on the formation of PCDD/PCDF in the co-combustion of refuse-derived and packaging-derived fuels Multivariate analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1996, 3(3): 129−134 doi: 10.1007/BF02985518 [119] Kuzuhara S, Sato H, Tsubouchi N, Ohtsuka Y, Kasai E. Effect of nitrogen-containing compounds on polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin/dibenzofuran formation through de novo synthesis. Environmental Science and Technology, 2005, 39(3): 795−799 [120] Yang F, Jiang L, Wang S M, Cao Z T, Liu L, Wang M M, Lu Y F. Emission enhancement of femtosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by combining nanoparticle and dual-pulse on crystal SiO2. Optics and Laser Technology, 2017, 931: 194−200 doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(96)80126-3 [121] Zimmermann R, Heger H J, Blumenstock M, Dorfner R, Schramm K W, Boesl U, Kettrup A. On-line measurement of chlorobenzene in waste incineration flue gas as a surrogate for the emission of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans (I-TEQ) using mobile resonance laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 1999, 13(5): 307−314 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0231(19990315)13:5<307::AID-RCM482>3.0.CO;2-A [122] Blumenstock M, Zimmermann R, Schramm K W, Kettrup A. Identification of surrogate compounds for the emission of PCDD/F (I-TEQ value) and evaluation of their on-line real-time detectability in flue gases of waste incineration plants by REMPI-TOFMS mass spectrometry. Chemosphere, 2001, 42(5–7): 507−518 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00223-X [123] 严密, 李晓东, 陈彤, 陆胜勇, 严建华. 垃圾焚烧炉烟气中二噁英指示物研究. 燃烧科学与技术, 2010, 16(3): 257−261Yan Mi, Li Xiao-Dong, Chen Tong, Lu Sheng-Yong, Yan Jian-Hua. Investigation of PCDD/Fs indicators in flue gas from waste incinerators. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2010, 16(3): 257−261 [124] Liu W, Jiang J C, Hou K Y, Wang W G, Qi Y C, Wang Y, Xie Y Y, Hua L, Li H Y. Online monitoring of trace chlorinated benzenes in flue gas of municipal solid waste incinerator by windowless VUV lamp single photon ionization TOFMS coupled with automatic enrichment system. Talanta, 2016, 161: 693−699 doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.09.026 [125] Dyke P H, Foan C, Fiedler H. PCB and PAH releases from power stations and waste incineration processes in the UK. Chemosphere, 2003, 50(4): 469−480 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00627-6 [126] 李晓东, 尹雪峰, 陆胜勇, 谷月玲, 严建华, 倪明江, 岑可法. 原生垃圾和煤混烧时多环芳烃和二噁英的生成关联. 工程热物理学报, 2006, 27(4): 691−694 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2006.04.049Li Xiao-Dong, Yin Xue-Feng, Lu Sheng-Yong, Gu Yue-Ling, Yan Jian-Hua, Ni Ming-Jiang, Cen Ke-Fa. The correlation between PAHs and dioxins formation during coal and municipal solid waste co-incineration process. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2006, 27(4): 691−694 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2006.04.049 [127] 田福林. 受体模型应用于典型环境介质中多环芳烃、二噁英和多氯联苯的来源解析研究[博士学位论文], 大连理工大学, 中国, 2009.Tian Fu-Lin. Source Apportionment of Persistent Toxic Substances in Typical Environmental Media by Receptor Modeling: Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Dioxins and Polychlorinated Biphenyls [Ph.D. dissertation], Dalian University of Technology, China, 2009. [128] Heger H J, Zimmermann R, Dorfner R, Beckmann M, Griebel H, Kettrup A, Boesl O. On-line emission analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons down to pptv concentration levels in the flue gas of an incineration pilot plant with a mobile resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Analytical Chemistry, 1999, 71(1): 46−57 doi: 10.1021/ac980611y [129] Tuppurainen K, Aatamila M, Ruokojärvi P, Halonen I, Ruuskanen J. Effect of liquid inhibitors on PCDD/F formation. Prediction of particle-phase PCDD/F concentrations using PLS modelling with gas-phase chlorophenol concentrations as independent variables. Chemosphere, 1999, 38(10): 2205−2217 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00439-1 [130] Yamada M, Hashimoto Y, Suga M, Waki I, Sakairi M, Hori Y, Sakamoto M. Real-time monitoring of chlorobenzenes in flue gas. Organohalogen Compd, 2001, 54: 380−383 [131] Yamada M, Hashimoto Y, Suga M, Takada Y, Hirabayashi A, Sakairi M, et al. An online system for monitoring dioxin precursor in flue gas. Organohalogen Compounds, 2000, 45: 149−152 [132] Öberg T, Bergström J G T. Emission and chlorination pattern of PCDD/PCDF predicted from indicator parameters. Chemosphere, 1987, 16(6): 1221−1230 doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(87)90059-2 [133] Peng Y Q, Chen J H, Lu S Y, Huang J X, Zhang M M, Buekens A, et al. Chlorophenols in municipal solid waste incineration: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 292: 398−414 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.01.102 [134] Watanabe N, Kawamoto K, Asada S, Fujiyoshi H, Miyata H, Watanabe G, Suzuki S. Surrogate study for dioxins from municipal waste incinerator in startup condition: Applicability as a dioxin control indicator and an organohalogen emission warning. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2010, 12(3): 254−263 [135] Haddad A, Moqbel S. Modeling of dioxin levels in pine needles exposed to solid waste open combustion emissions. Waste Management, 2018, 79: 510−515 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.08.020 [136] Watanabe N, Kawamoto K, Asada S, Fujiyoshi H, Miyata H, Watanabe G, Suzuki S. Surrogate study for dioxins from municipal waste incinerator in startup condition: Applicability as a dioxin control indicator and an organohalogen emission warning. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2010, 12(2): 254−263 [137] Hasberg W, May H, Dorn I. Description of the residence-time behaviour and burnout of PCDD, PCDF and other higher chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons in industrial waste incineration plants. Chemosphere, 1989, 19(1–6): 565−571 doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(89)90372-X [138] Weber R, Sakurai T, Ueno S, Nishino J. Correlation of PCDD/PCDF and CO values in a MSW incinerator — indication of memory effects in the high temperature/cooling section. Chemosphere, 2002, 49(2): 127−134 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00187-X [139] Tillman D A, Rossi A J, Vick K M. Incineration of Municipal and Hazardous Solid Wastes. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1989. [140] Chen Q X, Wang S J. Variable selection for multiply-imputed data with application to dioxin exposure study. Statistics in Medicine, 2013, 32(21): 3646−3659 [141] Tang J, Qiao J F, Li W T. Simplified stochastic configuration network-based optimised soft measuring model by using evolutionary computing framework with its application to dioxin emission concentration estimation. International Journal of System Control and Information Processing, 2018, 2(4): 332−365 doi: 10.1504/IJSCIP.2018.097202 [142] Götz R, Lauer R. Analysis of sources of dioxin contamination in sediments and soils using multivariate statistical methods and neural networks. Environmental Science and Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5559−5565 [143] 肖晓东, 卢加伟, 海景, 廖利. 垃圾焚烧烟气中二噁英类浓度的支持向量回归预测. 可再生能源, 2017, 35(8): 1107−1114Xiao Xiao-Dong, Lu Jia-Wei, Hai Jing, Liao Li. Prediction of dioxin emissions in flue gas from waste incineration based on support vector regression. Renewable Energy Resources, 2017, 35(8): 1107−1114 [144] 汤健, 乔俊飞. 基于选择性集成核学习算法的固废焚烧过程二噁英排放浓度软测量. 化工学报, 2019, 70(2): 696−706Tang Jian, Qiao Jun-Fei. Dioxin emission concentration soft measuring approach of municipal solid waste incineration based on selective ensemble kernel learning algorithm. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2019, 70(2): 696−706 [145] Stanmore B R. Modeling the formation of PCDD/F in solid waste incinerators. Chemosphere, 2002, 47(6): 565−573 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00005-X [146] de Jong A P J M, Liem A K D. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in ultra trace analysis of polychlorinated dioxins and related compounds. TrAc Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 1993, 12(3): 115−124 doi: 10.1016/0165-9936(93)88011-S [147] Barnabas I J, Dean J R, Owen S P. Supercritical fluid extraction of analytes from environmental samples. A review. Analyst, 1994, 119(11): 2381−2394 doi: 10.1039/an9941902381 [148] Piispanen W H, Czuczwa J M, Sobeih I M. Work area air monitoring for chlorinated dioxins and furans at a municipal waste power boiler facility. Environmental Science and Technology, 1992, 26(9): 1841−1843 [149] Edgerton S A, Czuczwa J M, Rench J D, Hodanbosi R F, Koval R J. Ambient air concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in Ohio: Sources and health risk assessment. Chemosphere, 1989, 18(9–10): 1713−1730 doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(89)90455-4 [150] Kjeller L O, Jones K C, Johnston A E, Rappe C. Evidence for a decline in atmospheric emissions of PCDD/Fs in the U.K. Environmental Science and Technology, 1996, 30(4): 1398−1403 [151] Feltz K P, Tillitt D E, Gale R W, Peterman P H. Automated HPLC fractionation of PCDDs and PCDFs and planar and nonplanar PCBs on C18-dispersed PX-21 carbon. Environmental Science and Technology, 1995, 29(3): 709−718 [152] Brzuzy L P, Hites R A. Global mass balance for polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environmental Science and Technology, 1996, 30(6): 1797−1804 [153] Hilarides R J, Gray K A, Guzzetta J, Cortellucci N, Sommer C. Radiolytic degradation of 2,3,7,8-TCDD in artificially contaminated soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 1994, 28(13): 2249−2258 [154] Ralf Z, Dieter L, Antonius K, Holger N, Ulrich B. On-line emission control of combustion processes by laser-induced resonance-enhanced multi-photon ionization/mass spectrometry. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1996, 26(2): 2859−2868 [155] Smith P K, Krohn R I, Hermanson G T, Mallia A K, Gartner F H, Provenzano M D, et al. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Analytical Biochemistry, 1985, 150(1): 76−85 doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7 [156] Deml E, Wiebel F J, Oesterle D. Biological activity of 2, 4, 8-trichlorodibenzofuran: Promotion of rat liver foci and induction of cytochrome P-450-dependent monooxygenases. Toxicology, 1989, 59(3): 229−238 doi: 10.1016/0300-483X(89)90194-7 [157] Stanker L H, Watkins B, Rogers N, Vanderlaan M. Monoclonal antibodies for dioxin: Antibody characterization and assay development. Toxicology, 1987, 45(3): 229−243 doi: 10.1016/0300-483X(87)90015-1 [158] Wu W Z, Schramm K W, Henkelmann B, Xu Y, Yediler A, Kettrup A. PCDD/F_s, PCB_s, HCH_s, and HCB in sediments and soils of Ya-Er Lake area in China: Results on residual levels and correlation to the organic carbon and the particle size. Chemosphere, 1997, 34(1): 191−202 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(96)00351-7 [159] Rennard S I, Berg R, Martin G R, Foidart J M, Robey P G. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) for connective tissue components. Analytical Biochemistry, 1980, 104(1): 205−214 doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90300-0 [160] Manning A R, Robert F S. [1,4] Benzodioxin and [1,4] Benzoxazine Derivatives, EP EP0204148, April 1986. [161] Tan P F, Hurtado I, Neuschütz D, Eriksson, G. Thermodynamic modeling of PCDD/Fs formation in thermal processes. Environmental Science and Technology, 2001, 35(9): 1867−1874 [162] Soria J, Gauthier D, Flamant G, Rodriguez R, Mazza G. Coupling scales for modelling heavy metal vaporization from municipal solid waste incineration in a fluid bed by CFD. Waste Management, 2015, 43: 176−187 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.05.021 [163] Wang J F, Xue Y Q, Zhang X X, Shu X R. Numerical study of radiation effect on the municipal solid waste combustion characteristics inside an incinerator. Waste Management, 2015, 44: 116−124 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.07.025 [164] Wissing F, Wirtz S, Scherer V. Simulating municipal solid waste incineration with a DEM/CFD method—influences of waste properties, grate and furnace design. Fuel, 2017, 206: 638−656 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.06.037 [165] Alobaid F, Al-Maliki W A K, Lanz T, Haaf M, Brachthäuser A, Epple B, Zorbach I. Dynamic simulation of a municipal solid waste incinerator. Energy, 2018, 149: 230−249 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.170 [166] Costa M, Curcio C, Piazzullo D, Rocco V, Tuccillo R. RDF incineration modelling trough thermo-chemical conversion and gaseous combustion coupling. Energy, 2018, 161: 974−987 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.07.142 [167] Ding G C, He B S, Cao Y, Wang C J, Su L B, Duan Z P, et al. Process simulation and optimization of municipal solid waste fired power plant with oxygen/carbon dioxide combustion for near zero carbon dioxide emission. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 157: 157−168 doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.11.087 [168] Bensch M, Schröder M, Bogdan M, Rosenstiel W. Feature selection for high-dimensional industrial data. In: Proceedings of the 2005 European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks. Bruges, Belgium: D-Side Published, 2005. 375−380 [169] 谢翀. 基于数据驱动的锅炉燃烧系统动态建模与优化控制方法研究[硕士学位论文], 东南大学, 中国, 2015.Xie Chong. Data-Driven Based Research on Dynamic Modeling and Optimal Control of Boiler Combustion System [Master thesis], Southeast University, China, 2015. [170] Lieber D, Stolpe M, Konrad B, Deuse J, Morik K. Quality prediction in interlinked manufacturing processes based on supervised and unsupervised machine learning. Procedia CIRP, 2013, 7: 193−198 doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2013.05.033 [171] You W J, Yang Z J, Ji G L. PLS-based recursive feature elimination for high-dimensional small sample. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2014, 55: 15−28 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2013.10.004 [172] Zhang M J, Zhang S Z, Iqbal J B. Key wavelengths selection from near infrared spectra using Monte Carlo sampling-recursive partial least squares. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2013, 128: 17−24 doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2013.07.009 [173] 汤健, 柴天佑, 赵立杰, 岳恒, 郑秀萍. 基于振动频谱的磨矿过程球磨机负荷参数集成建模方法. 控制理论与应用, 2012, 29(2): 183−191Tang Jian, Chai Tian-You, Zhao Li-Jie, Yue Heng, Zheng Xiu-Ping. Ensemble modeling for parameters of ball-mill load in grinding process based on frequency spectrum of shell vibration. Control Theory and Applications, 2012, 29(2): 183−191 [174] Yue H H, Qin S J, Markle R J, Nauert C, Gatto M. Fault detection of plasma etchers using optical emission spectra. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 2000, 13(3): 374−385 doi: 10.1109/66.857948 [175] Tang J, Zhao L J, Li Y M, Chai T Y, Qin S J. Feature selection of frequency spectrum for modeling difficulty to measure process parameters. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Neural Networks. Shenyang, China: Springer, 2012. 82–91 [176] Tang J, Qiao J F, Liu Z, Zhou X J, Yu G, Zhao J J. Optimized ensemble modeling based on feature selection using simple sphere criterion for multi-scale mechanical frequency spectrum. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(16): 7263−7278 doi: 10.1007/s00500-018-3373-9 [177] Poggio T, Vetter T. Recognition and Structure from One 2D Model View: Observations on Prototypes, Object Classes and Symmetries. Technical Report, A. I. Memo No. 1347, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [178] Li L J, Peng Y L, Qiu G Y, Sun Z G, Liu S G. A survey of virtual sample generation technology for face recognition. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2018, 50(1): 1−20 doi: 10.1007/s10462-016-9537-z [179] Du Y, Wang Y. Generating virtual training samples for sparse representation of face images and face recognition. Journal of Modern Optics, 2016, 63(6): 536−544 doi: 10.1080/09500340.2015.1083131 [180] Wang F-Y. A big-data perspective on AI: Newton, Merton, and analytics intelligence. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2012, 27(5): 2−4 doi: 10.1109/MIS.2012.91 [181] Li D C, Lin Y S. Using virtual sample generation to build up management knowledge in the early manufacturing stages. European Journal of Operational Research, 2006, 175(1): 413−434 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2005.05.005 [182] Chang C J, Li D C, Chen C C, Chen C S. A forecasting model for small non-equigap data sets considering data weights and occurrence possibilities. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2014, 67: 139−145 [183] Li D C, Wen I H. A genetic algorithm-based virtual sample generation technique to improve small data set learning. Neurocomputing, 2014, 143: 222−230 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.06.004 [184] Chen Z S, Zhu B, He Y L, Yu L A. A PSO based virtual sample generation method for small sample sets: Applications to regression datasets. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2017, 59: 236−243 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2016.12.024 [185] Gong H F, Chen Z S, Zhu Q X, He Y L. A Monte Carlo and PSO based virtual sample generation method for enhancing the energy prediction and energy optimization on small data problem: An empirical study of petrochemical industries. Applied Energy, 2017, 197: 405−415 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.04.007 [186] Coqueret G. Approximate NORTA simulations for virtual sample generation. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 73: 69−81 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.12.027 [187] 朱宝. 虚拟样本生成技术及建模应用研究[博士学位论文], 北京化工大学, 中国, 2017.Zhu Bao. Research on Virtual Sample Generation Technologies and Their Modeling Application [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China, 2017. [188] Tang J, Jia M Y, Liu Z, Chai T Y, Yu W. Modeling high dimensional frequency spectral data based on virtual sample generation technique. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation. Lijiang, China: IEEE, 2015. 1090−1095 [189] 汤健, 乔俊飞, 柴天佑, 刘卓, 吴志伟. 基于虚拟样本生成技术的多组分机械信号建模. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1569−1589Tang Jian, Qiao Jun-Fei, Chai Tian-You, Liu Zhuo, Wu Zhi-Wei. Modeling multiple components mechanical signals by means of virtual sample generation technique. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1569−1589 [190] Guo Z H, Tang J, Qiao J F. Mathematic simulation model of dioxin emission concentration of municipal solid waste incineration based on aspen-plus software. In: Proceedings of the 37th Chinese Control Conference. USA: IEEE, 2018. 25−27 [191] Tang J, Qiao J F, Gu K, Yan A J. Dioxin soft measuring method in municipal solid waste incineration based on virtual sample generation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress. Jinan, China: IEEE, 2017. [192] LeCun Y, Boser B, Denker J S, Henderson D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(4): 541−551 doi: 10.1162/neco.1989.1.4.541 [193] Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527−1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [194] 尹宝才, 王文通, 王立春. 深度学习研究综述. 北京工业大学学报, 2015, 41(1): 48−59Yin Bao-Cai, Wang Wen-Tong, Wang Li-Chun. Review of deep learning. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2015, 41(1): 48−59 [195] Yao L, Ge Z Q. Deep learning of semisupervised process data with hierarchical extreme learning machine and soft sensor application. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(2): 1490−1498 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2733448 [196] 段艳杰, 吕宜生, 张杰, 赵学亮, 王飞跃. 深度学习在控制领域的研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 643−654Duan Yan-Jie, Lv Yi-Sheng, Zhang Jie, Zhao Xue-Liang, Wang Fei-Yue. Deep learning for control: The state of the art and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 643−654 [197] Lei Y G, Jia F, Lin J, Xing S B, Ding S X. An intelligent fault diagnosis method using unsupervised feature learning towards mechanical big data. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(5): 3137−3147 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2519325 [198] Ge Z Q, Song Z H. Multimode process monitoring based on Bayesian method. Journal of Chemometrics, 2009, 23(12): 636−650 [199] Tsang C H, Kwong S. Multi-agent intrusion detection system in industrial network using ant colony clustering approach and unsupervised feature extraction. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2005. 51−56 [200] Susto G A, Schirru A, Pampuri S, McLoone S. Supervised aggregative feature extraction for big data time series regression. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(3): 1243−1252 doi: 10.1109/TII.2015.2496231 [201] Shang C, Yang F, Huang D X, Lyu W X. Data-driven soft sensor development based on deep learning technique. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24(3): 223−233 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.01.012 [202] 王宇红, 狄克松, 张姗, 尚超, 黄德先. 基于DBN-ELM的聚丙烯熔融指数的软测量. 化工学报, 2016, 67(12): 5163−5168Wang Yu-Hong, Di Ke-Song, Zhang Shan, Shang Chao, Huang De-Xian. Melt index prediction of polypropylene based on DBN-ELM. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2016, 67(12): 5163−5168 [203] 任荣荣, 周明全, 耿国华, 刘晓宁, 王恒. 基于深度神经网络的多尺度特征提取方法. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(2): 215−221Ren Rong-Rong, Zhou Ming-Quan, Geng Guo-Hua, Liu Xiao-Ning, Wang Heng. The multi-scale features extraction method based on deep neural network. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 47(2): 215−221 [204] Chen C L P, Zhang C Y, Chen L, Gan M. Fuzzy restricted Boltzmann machine for the enhancement of deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(6): 2163−2173 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2015.2406889 [205] 张婷, 李玉鑑, 胡海鹤, 张亚红. 基于跨连卷积神经网络的性别分类模型. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 858−865Zhang Ting, Li Yu-Jian, Hu Hai-He, Zhang Ya-Hong. A gender classification model based on cross-connected convolutional neural networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 858−865 [206] Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2261−2269 [207] 耿志强, 张怡康. 一种基于胶质细胞链的改进深度信念网络模型. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 943−952Geng Zhi-Qiang, Zhang Yi-Kang. An improved deep belief network inspired by glia chains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 943−952 [208] Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing System. Canada, 2006: 153−160 [209] Yang Y, Sun J, Li H B, Xu Z B. ADMM-CSNet: A deep learning approach for image compressive sensing. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(3): 521−538 [210] Bai Y, Chen Z Q, Xie J J, Li C. Daily reservoir inflow forecasting using multiscale deep feature learning with hybrid models. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 532: 193−206 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.11.011 [211] Zhang C, Lim P, Qin A K, Tan K C. Multiobjective deep belief networks ensemble for remaining useful life estimation in prognostics. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(10): 2306−2318 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2582798 [212] 汤健, 乔俊飞, 韩红桂, 李晓理. 一种自适应选择深度特征的随机权神经网络集成建模方法, 中国, CN108445752A, 2018-08-24Tang Jian, Qiao Jun-Fei, Han Hong-Gui, Li Xiao-Li. An adaptive modeling method for adaptive selection of depth features based on random weight neural network. China, CN108445752A, August 24, 2018 [213] Setyan A, Patrick M, Wang J. Very low emissions of airborne particulate pollutants measured from two municipal solid waste incineration plants in Switzerland. Atmospheric Environment, 2017, 166: 99−109 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.07.018 [214] Asefi H, Lim S. A novel multi-dimensional modeling approach to integrated municipal solid waste management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 166: 1131−1143 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.061 -




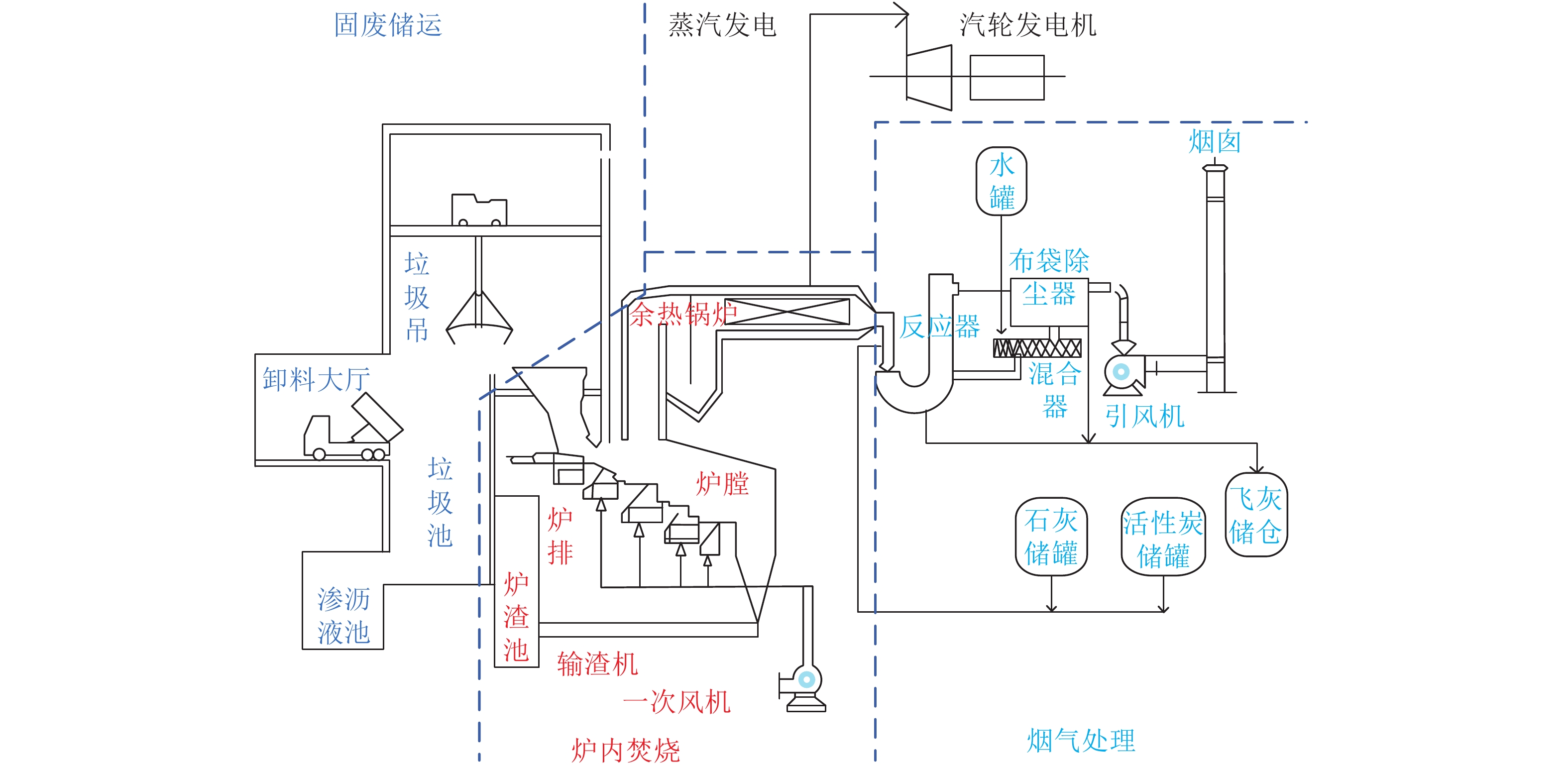
 下载:
下载: