Structure Design for Recurrent Fuzzy Neural Network Based on Wavelet Transform Fuzzy Markov Chain
-
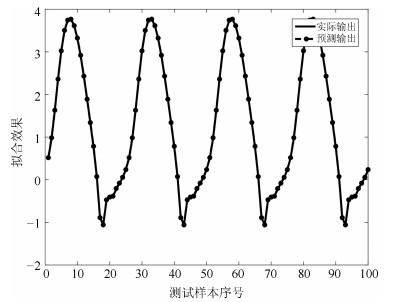
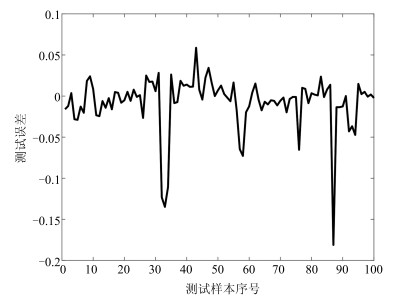
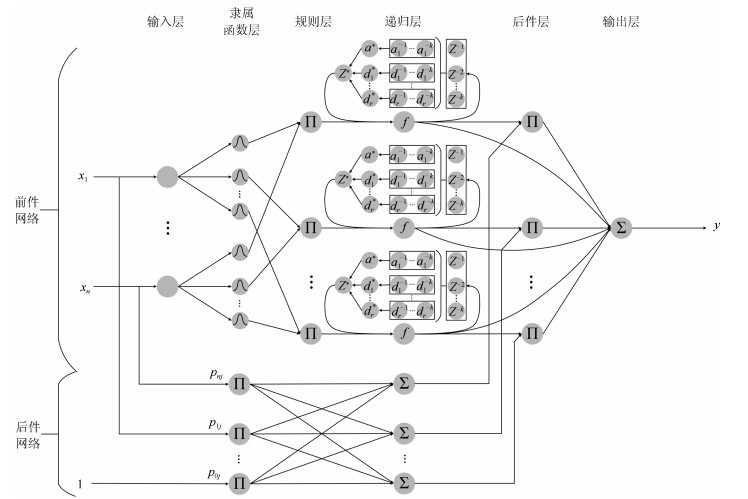
摘要: 针对递归模糊神经网络(Recurrent fuzzy neural network, RFNN)的递归量难以自适应的问题, 提出一种基于小波变换–模糊马尔科夫链(Wavelet transform fuzzy Markov chain, WTFMC)算法的RFNN模型.首先, 在时间维度上记录隐含层神经元的模糊隶属度, 并采用小波变换将该时间序列进行分解, 通过模糊马尔科夫链对子序列的未来时段进行预测, 之后将各预测量合并后代入递归函数中得到具有自适应性的递归量.其次, 利用梯度下降算法更新RFNN的参数来保证神经网络的精度.最后, 通过非线性系统建模中几个基准问题和实际污水处理中关键水质参数的预测实验, 证明了该神经网络模型的可行性和有效性.Abstract: Aiming to solve the problem that the recursive variable in the recurrent fuzzy neural network (RFNN) is difficult to be self-adaptive, this paper proposes an RFNN structure model based on wavelet transform fuzzy Markov chain (WTFMC). Firstly, it records the fuzzy membership degree of hidden layer neurons in time dimension, and decomposes the time series by wavelet transform. The future period of the subsequence is predicted by fuzzy Markov chain, and the adaptive recursive variables are obtained by combining the predictors into the recursive function. Secondly, the gradient descent algorithm is utilized to update the parameters of RFNN in order to ensure the accuracy of neural network. Finally, the feasibility and validity of the neural network model are demonstrated by several benchmark problems in nonlinear system modeling and the prediction of key water quality parameters in the practical wastewater treatment.
-
Key words:
- Recurrent fuzzy neural network /
- wavelet transform /
- fuzzy Markov chain /
- dynamic modeling /
- wastewater treatment
1) 本文责任编委 刘艳军 -
表 1 不同网络对Henon混沌时间序列的预测结果
Table 1 Prediction results of Henon chaotic time series with different networks
表 2 不同网络对动态系统的预测结果
Table 2 Prediction results of dynamic network with different networks
表 3 不同网络对Mackey-Glass时间序列的预测结果
Table 3 Prediction results of Mackey-Glass time series with different networks
表 4 不同网络对非线性系统的预测结果
Table 4 Prediction results of nonlinear system identification with different networks
表 5 不同网络对出水氨氮的预测结果
Table 5 Prediction results of effluent NH$_4$-N with different networks with different networks
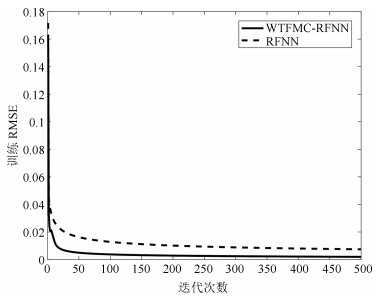
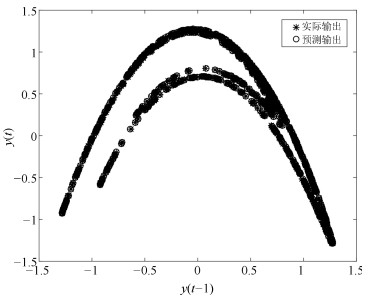
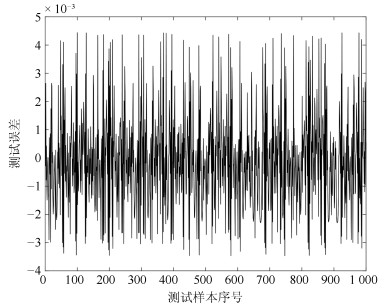
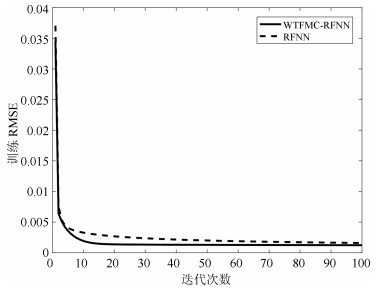
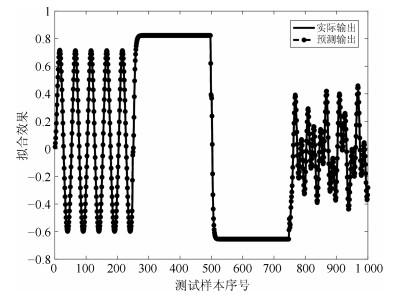
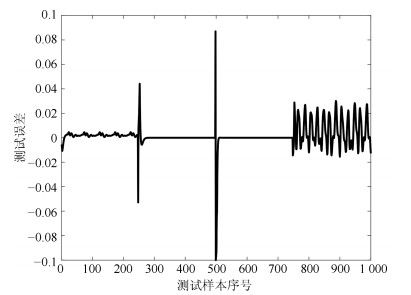
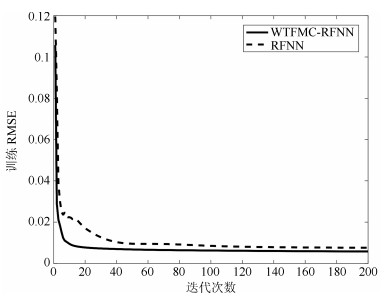
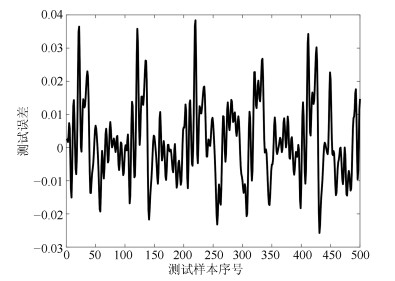
网络 规则数 训练RMSE 测试RMSE WTFMC-RFNN 12 0.0041 0.0351 IRSFNN (TSK) 16 0.0052 0.0468 RSEFNN-LF 12 0.0048 0.0404 TRFN-S 14 0.0045 0.0394 WRFNN 15 0.0053 0.0529 HO-RNFS 15 0.0047 0.0458 RFNN 12 0.0041 0.0437 -
[1] Shihabudheen K V, Pillai G N. Recent advances in neuro-fuzzy system:a survey. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 152: 136-162 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.04.014 [2] Wang J J. A new type of fuzzy membership function designed for interval type-2 fuzzy neural network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1425-1433 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zdhxb201708014 [3] Ebadzadeh M M, Salimibadr A. IC-FNN: A novel fuzzy neural network with interpretable intuitive and correlated-contours fuzzy rules for function approximation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(3): 1288-1302 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2718497 [4] Tang J J, Liu F, Zhang W H, Ke R M, Zou Y J. Lane-changes prediction based on adaptive fuzzy neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 91: 452-463 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.09.025 [5] Qiao J F, Cai J, Han H G, Cai J X. Predicting PM2.5 concentrations at a regional background station using second order self-organizing fuzzy neural network. Atmosphere, 2017, 8(12): 10-26 doi: 10.3390/atmos8010010 [6] Premkumar K, Manikandan B V, Kumar C A. Antlion algorithm optimized fuzzy PID supervised on-line recurrent fuzzy neural network based controller for brushless DC motor. Electric Power Components and Systems, 2017, 45(20): 2304-2317 doi: 10.1080/15325008.2017.1402395 [7] Zhu Q D, Yu H, Cai C T, Xiao Y. Robust optimal navigation using nonlinear model predictive control method combined with recurrent fuzzy neural network. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018, 2018: 1-19 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fbcd788ee3726c5ee9168a9b36271452 [8] El-sousy F F M. Adaptive hybrid control system using a recurrent RBFN-based self-evolving fuzzy-neural-network for PMSM servo drives. Applied Soft Computing, 2014, 21(8): 509-532 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0d4fc69ba07453caac6b4cc5ad1850b0 [9] Xue A, Peng D, Guo Y. Modeling of pH neutralization process using fuzzy recurrent neural network and DNA based NSGA-Ⅱ. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2014, 351(7): 3847-3864 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2013.03.014 [10] Pratama M, Lu J, Lughofer E. An incremental learning of concept drifts using evolving type-2 recurrent fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(5): 1175-1192 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2599855 [11] Han S I, Lee J M. Recurrent fuzzy neural network backstepping control for the prescribed output tracking performance of nonlinear dynamic systems. ISA Transactions, 2014, 53(1): 33-43 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9e529f262e1341efe49530c467cd74c7 [12] Juang C F, Hsieh C D. A Locally Recurrent fuzzy neural network with support vector regression for dynamic-system modeling. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(2): 261-273 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=90839892df2adf02ac77881e12a73ba6 [13] Wai R J, Lin Y W. Adaptive moving-target tracking xontrol of a vision-based mobile robot via a dynamic petri recurrent fuzzy neural network. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2013, 21(4): 688-701 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2012.2227974 [14] Lin F J, Shyu K K, Wai R J. Recurrent-fuzzy-neural-network sliding-mode controlled motor-toggle servome-chanism. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2010, 6(4): 453-466 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/974859 [15] Wu G D, Zhu Z W. An enhanced discriminability recurrent fuzzy neural network for temporal classification problems. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2014, 237(2): 47-62 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a602f825b73d4d2f559367279b270377 [16] Qiao J F, Han G T, Han H G. Wastewater treatment control method based on a rule adaptive recurrent fuzzy neural network. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics, 2017, 10(2): 94-110. doi: 10.1108/IJICC-12-2016-0069 [17] Jang J S R. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1993, 23(3): 665-685 http://psycnet.apa.org/psycinfo/1994-15814-001 [18] Zhang Y, Xiong R, He H, Pecht M G. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(7): 5695-5705 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2805189 [19] Kam H J, Jin O S, Park R W. Prediction of daily patient numbers for a regional emergency medical center using time series analysis. Healthcare Informatics Research, 2010, 16(3): 158-165 doi: 10.4258/hir.2010.16.3.158 [20] Joo T W, Kim S B. Time series forecasting based on wavelet filtering. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(8): 3868-3874 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.01.026 [21] Sun W, Xu Y. Research on China's energy supply and demand using an improved Grey-Markov chain model based on wavelet transform. Energy, 2017, 118: 969-984 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.10.120 [22] 薛婷, 钟麦英.基于SWT与等价空间的LDTV系统故障检测.自动化学报, 2017, 43(11): 1920-1930 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160479Xue Ting, Zhong Mai-Ying. SWT and parity space based fault detection for linear discrete time-varying systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(11): 1920-1930 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160479 [23] Bardenet R, Doucet A, Holmes C. On Markov chain Monte Carlo methods for tall data. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(1): 1515-1557 http://www.oalib.com/paper/4116218 [24] 张熙来, 赵俭辉, 蔡波.针对PM2.5单时间序列数据的动态调整预测模型.自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1790-1798 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170026Zhang Xi-Lai, Zhao Jian-Hui, Cai Bo. Prediction model with dynamic adjustment for single time series of PM2.5. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1790-1798 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170026 [25] 周杉杉, 李文静, 乔俊飞.基于自组织递归模糊神经网络的PM2.5浓度预测.智能系统学报, 2018, 13(4): 509-516 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xdkjyc201804003Zhou Shan-Shan, Li Wen-Jing, Qiao Jun-Fei. Prediction of PM2.5 concentration based on self-organizing recurrent fuzzy neural network. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2018, 13(4): 509-516 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xdkjyc201804003 [26] Lin Y Y, Chang J Y, Lin C T. Identification and prediction of dynamic systems using an interactively recurrent self-evolving fuzzy neural network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2013, 24(2): 310-321 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2231436 [27] Juang C F, Lin Y Y, Tu C C. A recurrent self-evolving fuzzy neural network with local feedbacks and its application to dynamic system processing. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2010, 161(19): 2552-2568 doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2010.04.006 [28] Juang C F. A TSK-type recurrent fuzzy network for dynamic systems processing by neural network and genetic algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2002, 10(2): 155-170 doi: 10.1109/91.995118 [29] Lin C J, Chin C C. Prediction and identification using wavelet-based recurrent fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2004, 34(5): 2144-2154 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2004.833330 [30] Juang C F, Lin C T. A recurrent self-organizing neural fuzzy inference network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1999, 10(4): 828-845 doi: 10.1109/72.774232 [31] Theocharis J B. A high-order recurrent neuro-fuzzy system with internal dynamics:application to the adaptive noise cancellation. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2006, 157(4): 471-500 doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2005.07.008 [32] Mastorocostas P A, Theocharis J B. A recurrent fuzzy-neural model for dynamic system identification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2002, 32(2): 176-190 doi: 10.1109/3477.990874 [33] Lin C J, Chen C H, Lin C T. A hybrid of cooperative particle swarm optimization and cultural algorithm for neural fuzzy networks and its prediction applications. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2009, 39(1): 55-68 doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2008.2002333 [34] Wang N, Er M J, Meng X. A fast and accurate online self-organizing scheme for parsimonious fuzzy neural networks. Neurocomputing, 2009, 72(16-18): 3818-3829 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2009.05.006 [35] Wu S, Er M J. Dynamic fuzzy neural networks-a novel approach to function approximation. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2000, 30(2): 358-364 doi: 10.1109/3477.836384 [36] Wu S, Er M J, Gao Y. A fast approach for automatic generation of fuzzy rules by generalized dynamic fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2001, 9(4): 578-594 doi: 10.1109/91.940970 -




 下载:
下载: