-
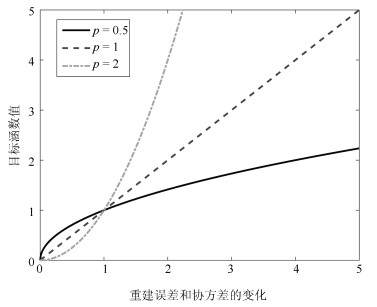
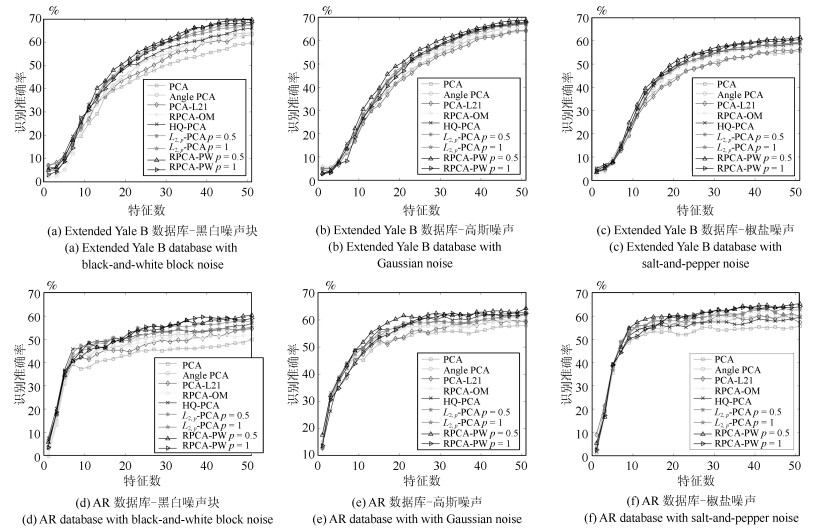
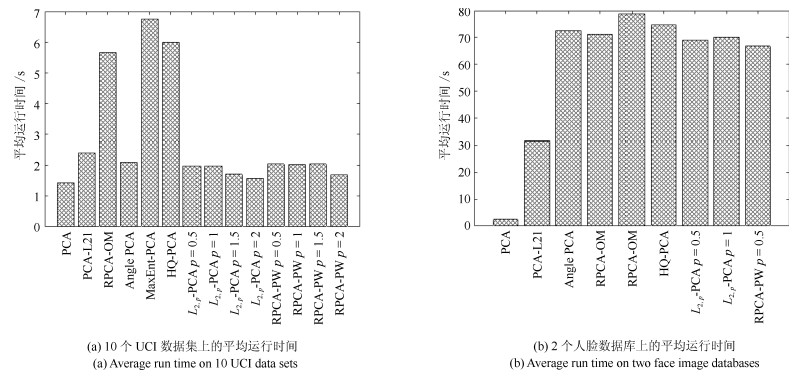
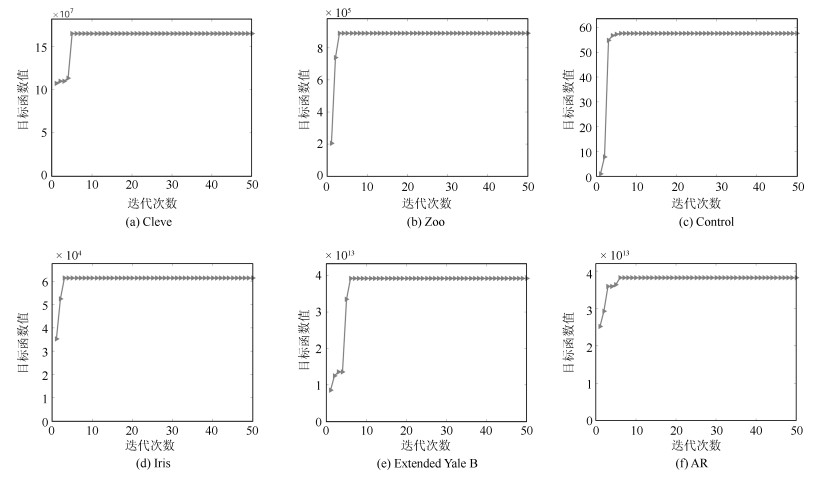
摘要: 主成分分析(Principal component analysis, PCA) 是处理高维数据的重要方法. 近年来, 基于各种范数的PCA模型得到广泛研究, 用以提高PCA对噪声的鲁棒性. 但是这些算法一方面没有考虑重建误差和投影数据描述方差之间的关系; 另一方面也缺少确定样本点可靠性(不确定性)的度量机制. 针对这些问题, 本文提出一种新的鲁棒PCA模型. 首先采用$L_{2, p}$模来度量重建误差和投影数据的描述方差. 基于重建误差和描述方差之间的关系建立自适应概率误差极小化模型, 据此计算主成分对于数据描述的不确定性, 进而提出了鲁棒自适应概率加权PCA模型(RPCA-PW). 此外, 本文还设计了对应的求解优化方案. 对人工数据集、UCI数据集和人脸数据库的实验结果表明, RPCA-PW在整体上优于其他PCA算法.Abstract: Principal component analysis (PCA) is an important method for processing high-dimensional data. In recent years, PCA models based on various norms have been extensively studied to improve the robustness. However, on the one hand, these algorithms do not consider the relationship between reconstruction error and covariance; on the other hand, they lack the uncertainty of considering the principal component to the data description. Aiming at these problems, this paper proposes a new robust PCA algorithm. Firstly, the $L_{2, p}$-norm is used to measure the reconstruction error and the description variance of the projection data. Based on the reconstruction error and the description variance, the adaptive probability error minimization model is established to calculate the uncertainty of the principal component's description of the data. Based on the uncertainty, the adaptive probability weighting PCA is established. The corresponding optimization method is designed. The experimental results of artificial data sets, UCI data sets and face databases show that RPCA-PW is superior than other PCA algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Principle component analysis (PCA) /
- weighted principal component analysis (WPCA) /
- dimensionality reduction /
- robustness
1) 本文责任编委 白翔 -
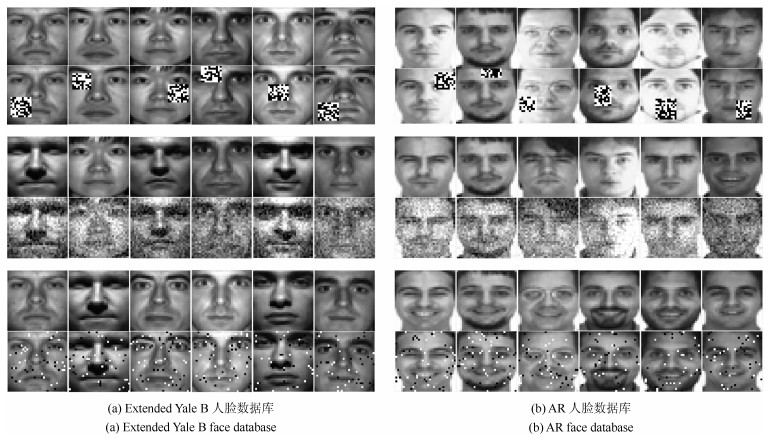
图 6 人脸重构效果图, 每一列从左到右依次是原图、PCA、PCA-L21、RPCA-OM、Angle PCA、HQ-PCA、$L{_{2, p}}$-PCA $p=0.5$、$L_{2, p}$-PCA $p=1$、RPCA-PW $p=0.5$、RPCA-PW $p=1$
Fig. 6 Face reconstruction pictures, each column represents original image, PCA, PCA-L21, RPCA-OM, Angle PCA, HQ-PCA, $L_{2, p}$-PCA $p=0.5$, $L_{2, p}$-PCA $p=1$, RPCA-PW $p=0.5$ and RPCA-PW $p=1$ from left to right
表 1 实验中使用的UCI数据集
Table 1 UCI data sets used in the experiment
数据集 维数 类别数 样本数 Australian 14 2 690 Cars 8 3 392 Cleve 13 8 303 Solar 12 6 323 Zoo 19 7 101 Control 60 6 600 Crx 15 2 690 Glass 9 6 214 Iris 4 3 150 Wine 13 3 178 表 2 UCI数据集上各算法的平均分类正确率(%)
Table 2 Average classification accuracy of each algorithm on UCI data sets (%)
数据集 Australian Cars Cleve Solar Zoo Control Crx Glass Iris Wine PCA 57.32 69.27 52.16 64.11 96.00 91.83 54.93 74.35 96.00 73.04 PCA-$L$21 62.41 69.17 52.74 64.44 95.60 92.50 53.39 75.33 97.33 74.13 RPCA-OM 63.04 69.93 52.16 65.27 95.00 92.83 56.96 74.35 96.00 74.15 Angle PCA 60.39 69.43 52.16 65.60 94.00 84.28 59.59 73.94 95.53 74.15 MaxEnt-PCA 60.14 69.17 52.45 64.76 95.10 92.15 59.32 74.42 95.33 73.59 HQ-PCA 60.77 69.27 52.46 65.46 95.80 91.50 60.87 76.16 92.00 75.55 $L{_{2, p}}$-PCA $p=0.5$ 60.68 69.60 52.84 65.42 93.40 92.10 60.29 73.56 96.47 73.59 $p=1$ 62.39 69.58 52.16 64.51 94.90 92.50 59.43 73.73 96.67 73.59 $p=1.5$ 62.81 69.43 52.16 65.28 95.00 92.50 58.20 75.57 96.33 73.04 $p=2$ 62.32 69.43 52.16 64.11 96.00 91.83 54.93 75.82 96.00 73.59 RPCA-PW $p=0.5 $ 63.77 71.21 53.76 66.85 95.00 92.50 58.84 74.35 95.33 74.15 $p=1 $ 63.04 69.43 52.49 65.94 95.00 91.67 60.14 73.94 96.00 74.15 $p=1.5$ 62.17 69.43 52.16 64.72 95.00 97.83 61.16 76.28 96.67 74.15 $p=2$ 62.32 69.43 52.16 64.11 96.00 92.33 54.93 75.82 96.00 73.59 表 3 UCI数据集上各算法的重建误差
Table 3 Reconstruction error of each algorithm on UCI data sets
数据集 Australian Cars Cleve Solar Zoo Control Crx Glass Iris Wine PCA 197.53 1 979.82 5.47 2.97 1.43 115.06 6 265.42 37.91 0.67 24.49 PCA-$L$21 197.21 1 979.16 6.90 2.90 1.56 132.84 6 545.72 38.59 1.56 34.44 RPCA-OM 193.23 1 977.98 5.61 2.65 1.51 108.13 5 684.38 38.64 0.64 24.85 Angle PCA 197.96 1 981.34 13.27 2.95 2.04 123.62 6 583.82 38.42 0.59 25.85 MaxEnt-PCA 203.82 1 976.70 6.24 2.61 1.44 113.01 6 805.98 38.12 0.58 25.01 HQ-PCA 195.79 1 929.26 5.92 2.37 1.39 131.35 6 987.68 36.38 4.31 25.85 $L_{2, p}$-PCA $p=0.5$ 193.29 1 978.76 9.22 2.93 2.05 106.69 6 601.74 38.33 1.04 26.14 $p=1$ 193.71 1 978.33 5.60 2.75 1.72 108.06 6 588.17 38.37 0.84 25.44 $p=1.5 $ 193.50 1 977.93 5.50 2.69 1.44 109.69 6 807.38 37.82 0.72 25.05 $ p=2$ 193.53 1 977.82 5.47 2.97 1.43 115.06 5 865.42 37.91 0.67 24.49 RPCA-PW $p=0.5$ 192.93 1 976.94 5.75 2.95 1.57 106.11 6 467.83 38.43 0.52 24.12 $p=1$ 193.27 1 979.96 6.84 2.84 1.83 110.46 6491.19 38.17 0.70 24.36 $p=1.5$ 193.36 1 977.82 5.06 2.83 1.46 110.45 6 073.11 37.91 0.71 25.26 $p=2$ 193.53 1 977.82 5.47 2.97 1.43 115.06 5 865.42 37.91 0.67 24.49 -
[1] Jolliffe I. Principal Component Analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1986. 115-128 [2] 高全学, 潘泉, 梁彦, 张洪才, 程咏梅. 基于描述特征的人脸识别研究. 自动化学报, 2006, 32(3): 386-392 http://www.aas.net.cn/article/id/15824Gao Quan-Xue, Pan Quan, Liang Yan, Zhang Hong-Cai, Cheng Yong-Mei. Face recognition based on expressive features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 32(3): 386-392 http://www.aas.net.cn/article/id/15824 [3] 张先鹏, 陈帆, 红杰. 结合多种特征的高分辨率遥感影像阴影检测. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(2): 290-298 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150196Zhang Xian-Peng, Chen Fan, He Hong-Jie. Shadow detection in high resolution remote sensing images using multiple features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(2): 290-298 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150196 [4] Gao Q X, Ma L, Liu Y, Gao X B, Nie F P. Angle 2DPCA: A new formulation for 2DPCA. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(5): 1672-1678 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2712740 [5] Koren Y, Carmel L. Robust linear dimensionality reduction. IEEE Transactions on Visualization & Computer Graphics, 2004, 10(4): 459-470 doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2004.17 [6] Schölkopf B, Smola A, Müller K R. Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem. MIT Press, 1998, 10(5): 1299-1319 http://icesjms.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.1162/089976698300017467&link_type=DOI [7] 李春娜, 陈伟杰, 邵元海. 鲁棒的稀疏$L_{p}$模主成分分析. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(1): 142-151 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201306024.htmLi Chun-Na, Chen Wei-Jie, Shao Yuan-Hai. Robust sparse $L_{p}$-norm principal component analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1): 142-151 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201306024.htm [8] Xu L, Yuille A L. Robust principal component analysis by self-organizing rules based on statistical physics approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1995, 6(1): 131-143 doi: 10.1109/72.363442 [9] Ke Q, Kanade T. Robust ${\rm{L}}_1$-norm factorization in the presence of outliers and missing data by alternative convex Programming. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2005, 1: 739-746 [10] Kwak N. Principal component analysis based on L1-norm maximization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(9): 1672-1680 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.114 [11] Nie F, Huang H, Ding C, Luo D, Wang H. Robust principal component analysis with non-greedy L1-norm maximization. In: Proceedings of IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain: AAAI, 2011, 22(1): 1433 [12] Ng A Y. Feature selection, L1 vs. L2 regularization, and rotational invariance. In: Proceedings of the 21st international conference on Machine learning. Banff, Canada: ACM, 2004, 78 [13] He R, Hu B, et al. Principal component analysis based on non-parametric maximum entropy. Neurocomputing, 2010, 73(10): 1840-1852 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092523121000144X [14] He R, Hu B, et al. Robust principal component analysis based on maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(6): 1485-1494 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2103949 [15] He R, Tan T, Wang L. Robust recovery of corrupted low-rank matrix by implicit regularizers. IEEE Transactions on Patteren Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(4): 770-783 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.188 [16] Ding C, Zhou D, He X F, Zha H Y. R1-PCA: Rotational invariant L1-norm principal component analysis for robust subspace factorization. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning. Pittsburgh, USA: ACM, 2006. 281-288 [17] Nie F, Yuan J, Huang H. Optimal mean robust principal component analysis. In: Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: ACM 2014. 2755-2763 [18] Nie, F, Huang, H. Non-greedy L21-norm maximization for principal component analysis. arXiv 2016, arXiv: 1603.08293 [19] Wang Q, Gao Q, Gao X, Nie F. ${{\rm{L}}_{2, p}}$-norm based PCA for image recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(3): 1336-1346 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2777184 [20] Wang Q, Gao Q, Gao X, Nie F. Angle principal component analysis. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Melbourne, Australia: AAAI, 2017. 2936-2942 [21] Liu Y, Gao Q, Miao S, et al. A non-greedy algorithm for L1-norm LDA. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 1-1 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7707468 [22] Guo Y F, Li S J, Yang J Y, Shu T T, Wu L D. A generalized Foley--Sammon transform based on generalized fisher discriminant criterion and its application to face recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2003, 24(1-3): 147-158 doi: 10.1016/S0167-8655(02)00207-6 [23] Cover T, Hart P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1967, 13(1): 21-27 doi: 10.1109/TIT.1967.1053964 -





 下载:
下载: