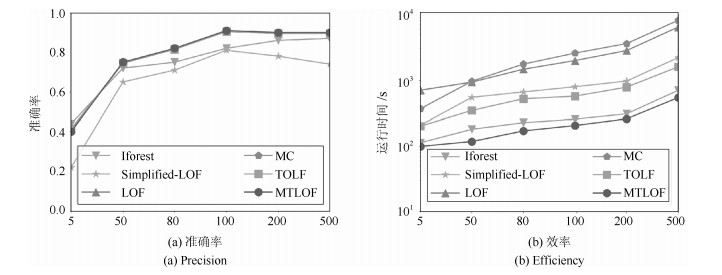
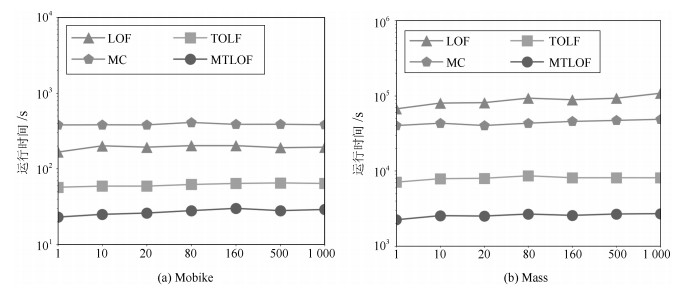
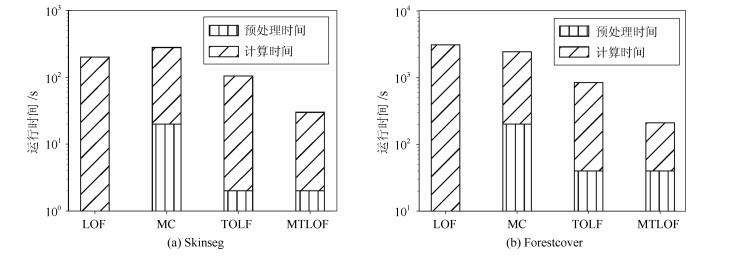
-
摘要: 局部异常检测(Local outlier factor,LOF)能够有效解决数据倾斜分布下的异常检测问题,在很多应用领域具有较好的异常检测效果.本文面向大数据异常检测,提出了一种快速的Top-n局部异常点检测算法MTLOF(Multi-granularity upper bound pruning based top-n LOF detection),融合索引结构和多层LOF上界设计了多粒度的剪枝策略,以快速发现Top-n局部异常点.首先,提出了四个更接近真实LOF值的上界,以避免直接计算LOF值,并对它们的计算复杂度进行了理论分析;其次,结合索引结构和UB1、UB2上界,提出了两层的Cell剪枝策略,不仅采用全局Cell剪枝策略,还引入了基于Cell内部数据对象分布的局部剪枝策略,有效解决了高密度区域的剪枝问题;再次,利用所提的UB3和UB4上界,提出了两个更加合理有效的数据对象剪枝策略,UB3和UB4上界更加接近于真实LOF值,有利于剪枝更多数据对象,而基于计算复用的上界计算方法,大大降低了计算成本;最后,优化了初始Top-n局部异常点的选择方法,利用区域划分和建立的索引结构,在数据稀疏区域选择初始局部异常点,有利于将LOF值较大的数据对象选为初始局部异常点,有效提升初始剪枝临界值,使得初始阶段剪枝掉更多的数据对象,进一步提高检测效率.在六个真实数据集上的综合实验评估验证MTLOF算法的高效性和可扩展性,相比最新的TOLF(Top-n LOF)算法,时间效率提升可高达3.5倍.Abstract: Local outlier factor (LOF) effectively addresses the problem of outlier detection in skewed datasets, which has been shown remarkable detection performance in variety of applications. In this paper, we propose an efficient Top-n local outlier detection algorithm, called MTLOF (Multi-granularity upper bound pruning based top-n LOF detection), for fast detecting top-n local outliers in large-scale datasets. First, we propose four LOF upper bounds that are closer to the real LOF value to avoid the computations of LOF values, and analyze their computational complexity theoretically. Second, by combining with index structure and the upper bounds UB1 and UB2, we propose a two-layer Cell pruning strategy, not only adopting the global Cell pruning strategy, but also introducing a local pruning strategy based on the internal data objects of Cells, which effectively prunes the high-density regions. Third, we propose two more reasonable and effective data object pruning strategies using the proposed upper bounds UB3 and UB4. UB3 and UB4 are closer to the real LOF value, which benefits to pruning more data objects. On the other hand, the upper bound calculation method based on computation reuse greatly reduces the computational cost. Finally, we optimize the selecting method of initial Top-n local outliers leveraging the established index structure. Specifically, we select the initial Top-n local outliers in sparse regions, which is conducive to selecting the data objects with a larger LOF value as the initial local outliers. Experimental study on six real-world datasets demonstrates the efficiency and scalability of our proposed MTLOF-up to 3.5 times faster than the state-of-the-art TOLF (Top-n LOF) method.
-
Key words:
- Outlier detection /
- local outlier detection /
- Top-n /
- pruning strategy
1) 本文责任编委 黎铭 -
算法1. MTLOF算法 输入. Dataset $ D $, the number of nearest neighbors $ k $, top outliers $ n $, parameters $ diff $ and $ t $. 输出. Top-$ n $ LOF outliers. 1) $ Set_{\rm area} \leftarrow GenerateArea(D, diff) $. 2) for $ A_i \in Set_{\rm area} $ do 3) if $ |A_i| \geq t\cdot k $ 4) $ rtree \leftarrow Rtree(A_i, k) $; then 5) $ Set_{\rm Rtree} \leftarrow Set_{\rm Rtree} \cup \{rtree\} $; 6) else if $ cp_{\rm min}^{A_i} \geq \max\nolimits_{A_j \in Set_{\rm area}\setminus Set_{\rm ini}}\{cp_{\rm min}^{A_j}\} $ 7) $ Set_{\rm ini} \leftarrow Set_{\rm ini} \cup A_i $ 8) if $ |Set_{\rm ini}|\geq n $ then 9): $ Top_{n}, ct \leftarrow Random (Set_{\rm ini}, n) $; 10) else 11) $ Set_{\rm ini} \leftarrow Set_{\rm ini} \cup MaxLeaf(Set_{\rm Rtree}) $ 12) $ Top_{n}, ct \leftarrow Random(Set_{\rm ini}, n) $; 13) for $ p \in Set_{\rm ini}-Top_{n} $ do 14) if $ {UB}_3(p) \leq ct $ or $ {UB}_4(p) \leq ct $ then 15) $ p.st \leftarrow prune $; 16) else if $ LOF(p) \leq ct $ then 17) $ p.st \leftarrow prune $; 18) else 19) $ Top_{n}.replace(p) $; update $ ct $; 20) for $ rtree \in Set_{\rm Rtree} $ do 21) for $ node \in rtree $ from top to bottom 22) if $ node.st = = prune $ 23) continue; 24) else if $ |node| > k \land node.len_{\rm side} \leq {ct\cdot cp_{\rm min}}/{(2\sqrt{d}}) $ then 25) $ node.st \leftarrow prune $; 26) $ node.allchilden \leftarrow prune $; 27) else if $ node.len_{\rm side} \leq {ct\cdot \overline{kd}_{\rm min}}/{(2\sqrt{d})} $ 28) $ node.st \leftarrow prune $; 29) $ node.allchilden \leftarrow prune $; 30) else 31) for $ p \in node $ 32) if $ {UB}_3(p) \leq ct $ or $ {UB}_4(p) \leq ct $ 33: $ p.st \leftarrow prune $; 34) else if $ {LOF(p)} \leq ct $ then 35) $ p.st \leftarrow prune $; 36) else 37) $ Top_{n}.replace(p) $; update $ ct $; 38) return $ Top_{n} $. 表 1 实验数据集统计信息
Table 1 The statistical information of experimental data sets
数据集 数据对象数量 数据维度 数据大小($\times10^{6}$) Mobike 1 082 732 2 43.1 Gowalla 5 127 211 2 376 Geolife 11 065 399 2 851 Massachusetts 31 136 410 2 1 228 Skinseg 245 057 3 12 Forestcover 581 012 10 71.6 Subforestcover 283 402 10 28.3 表 2 MTLOF剪枝数量(%)
Table 2 The pruning number of MTLOF (%)
Mobike Gowalla Geolife Mass Cell剪枝 26.9 20.9 42.1 30.2 数据对象剪枝 71.5 40.9 43.8 68.7 总剪枝数量 98.4 61.8 85.9 98.9 表 3 TOLF剪枝数量(%)
Table 3 The pruning number of TOLF (%)
Mobike Gowalla Geolife Mass Cell剪枝 0 0 9.2 5.9 数据对象剪枝 62.3 19.5 52.4 80.1 总剪枝数量 62.3 19.5 61.6 86 表 4 MTLOF每个上界剪枝数量(%)
Table 4 The pruning number of each upper bound in MTLOF (%)
Mobike Gowalla Geolife Mass $UB_1$ 6.1 9.4 25.3 16.8 $UB_1+UB_2$ 26.9 20.2 42.1 30.2 $UB_1+UB_2+UB_3$ 88.4 50.2 70.5 74.7 总剪枝数量 98.4 61.8 85.9 98.9 -
[1] Du B W, Liu C R, Zhou W J, Hou Z S, Xiong H. Catch me if you can: detecting pickpocket suspects from large-scale transit records. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco, California: ACM, 2016. 87-96 [2] Chandola V, Banerjee A, Kumar V. Anomaly detection: a survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2009, 41(3): Article No. 15 [3] Gupta M, Gao J, Aggarwal C C, Han J W. Outlier detection for temporal data:a survey. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering, 2014, 26(9):2250-2267 [4] Aggarwal C C. Outlier analysis. Data Mining. Switzerland: Springer, 2015. 237-263 [5] Knorr E M, Ng R T. Algorithms for mining distance-based outliers in large datasets. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases. San Francisco, CA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1998. 392-403 [6] Knorr E M, Ng R T, Tucakov V. Distance-based outliers:algorithms and applications. The VLDB Journal, 2000, 8(3-4):237-253 doi: 10.1007/s007780050006 [7] 王习特, 申德荣, 白梅, 聂铁铮, 寇月, 于戈. BOD:一种高效的分布式离群点检测算法.计算机学报, 2016, 39(1):36-51 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb200102003Wang Xi-Te, Shen De-Rong, Bai Mei, Nie Tie-Zheng, Kou Yue, Yu Ge. BOD:an efficient algorithm for distributed outlier detection. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2016, 39(1):36-51 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb200102003 [8] Bay S D, Schwabacher M. Mining distance-based outliers in near linear time with randomization and a simple pruning rule. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Washington, D.C.: ACM, 2003. 29-38 [9] Ramaswamy S, Rastogi R, Shim K. Efficient algorithms for mining outliers from large data sets. In: Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. Dallas, Texas, USA: ACM, 2000. 427-438 [10] Angiulli F, Pizzuti C. Fast outlier detection in high dimensional spaces. In: European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2002. 15-27 [11] Solberg H E, Lahti A. Detection of outliers in reference distributions:performance of Horn's algorithm. Clinical Chemistry, 2005, 51(12):2326-2332 doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.058339 [12] Aggarwal C C, Yu P S. Outlier detection for high dimensional data. In: Proceedings of the 2001 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ACM, 2001. 37-46 [13] Aggarwal C C, Yu P S. Outlier detection with uncertain data. In: Proceedings of the 2008 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining. Atlanta, Georgia, USA: SIAM, 2008. 483-493 [14] Yu D T, Sheikholeslami G, Zhang A D. FindOut:finding outliers in very large datasets. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2002, 4(4):387-412 doi: 10.1007/s101150200013 [15] He Z Y, Xu X F, Deng S C. Discovering cluster-based local outliers. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2003, 24(9-10):1641-1650 doi: 10.1016/S0167-8655(03)00003-5 [16] Breunig M M, Kriegel H P, Ng R T, Sander J. LOF: identifying densitybased local outliers. In: Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. Dallas, Texas, USA: ACM, 2000. 93-104 [17] Lazarevic A, Ertoz L, Kumar V, Ozgur A, Srivastava J. A comparative study of anomaly detection schemes in network intrusion detection. In: Proceedings of the 2003 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining. San Francisco, CA, USA: SIAM, 2003. 25-36 [18] Campos G O, Zimek A, Sander J, Campello R J G B, Micenková B, Schubert E, et al. On the evaluation of unsupervised outlier detection:measures, datasets, and an empirical study. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2016, 30(4):891-927 doi: 10.1007/s10618-015-0444-8 [19] Yan Y Z, Cao L, Rundensteiner E A. Scalable top-n local outlier detection. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Halifax, NS, Canada: ACM, 2017. 1235-1244 [20] Jin W, Tung A K H, Han J W. Mining top-n local outliers in large databases. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco, California: ACM, 2001. 293-298 [21] Zhang T, Ramakrishnan R, Livny M. BIRCH: an efficient data clustering method for very large databases. In: Proceedings of the 1996 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. Montreal, Quebec, Canada: ACM, 1996. 103-114 [22] Tang J, Chen Z X, Fu A W C, Cheung D W. Enhancing effectiveness of outlier detections for low density patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2002 Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2002. 535-548 [23] 朱利, 邱媛媛, 于帅, 原盛.一种基于快速k-!近邻的最小生成树离群检测方法.计算机学报, 2017, 40(12):2856-2870 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.02856Zhu Li, Qiu Yuan-Yuan, Yu Shuai, Yuan Sheng. A fast kNN-based MST outlier detection method. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(12):2856-2870 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.02856 [24] Papadimitriou S, Kitagawa H, Gibbons P B, Faloutsos C. Loci: fast outlier detection using the local correlation integral. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Data Engineering. Bangalore, India: IEEE, 2003. 315-326 [25] 杨宜东, 孙志挥, 朱玉全, 杨明, 张柏礼.基于动态网格的数据流离群点快速检测算法.软件学报, 2006, 17(8):1796-1803 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb200608014Yang Yi-Dong, Sun Zhi-Hui, Zhu Yu-Quan, Yang Ming, Zhang Bo-Li. A fast outlier detection algorithm for data streams based on dynamic grids. Journal of Software, 2006, 17(8):1796-1803 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb200608014 [26] Zhang K, Hutter M, Jin H D. A new local distance-based outlier detection approach for scattered real-world data. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2009. 813-822 [27] Kriegel H P, Kröger P, Schubert E, Zimek A. LoOP: local outlier probabilities. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Hong Kong, China: ACM, 2009. 1649-1652 [28] Schubert E, Zimek A, Kriegel H P. Local outlier detection reconsidered:a generalized view on locality with applications to spatial, video, and network outlier detection. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2014, 28(1):190-237 doi: 10.1007/s10618-012-0300-z [29] Schubert E, Zimek A, Kriegel H P. Generalized outlier detection with flexible kernel density estimates. In: Proceedings of the 2014 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA: SIAM, 2014. 542-550 [30] Liu J, Deng H F. Outlier detection on uncertain data based on local information. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2013, 51:60-71 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2013.07.005 [31] Cao K Y, Shi L X, Wang G R, Han D H, Bai M. Density-based local outlier detection on uncertain data. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Web-Age Information Management. Macau, China: Springer, 2014. 67-71 [32] 曹科研, 栾方军, 孙焕良, 丁国辉.不确定数据基于密度的局部异常点检测.计算机学报, 2017, 40(10):2231-2244 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.02231Cao Ke-Yan, Luan Fang-Jun, Sun Huan-Liang, Ding Guo-Hui. Density-based local outlier detection on uncertain data. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(10):2231-2244 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.02231 [33] Liu F T, Ting K M, Zhou Z H. Isolation forest. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Pisa, Italy: IEEE, 2008. 413-422 [34] Liu F T, Ting K M, Zhou Z H. Isolation-based anomaly detection. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data (TKDD), 2012, 6(1): Article No. 3 [35] Cho E, Myers S A, Leskovec J. Friendship and mobility: user movement in location-based social networks. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Diego, California, USA: ACM, 2011. 1082-1090 [36] Zheng Y, Xie X, Ma W Y. GeoLife:a collaborative social networking service among user, location and trajectory. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, 2010, 33(2):32-40 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0234713955/ [37] Haklay M, Weber P. OpenStreetMap:user-generated street maps. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 2008, 7(4):12-18 doi: 10.1109/MPRV.2008.80 [38] Bhatt R B, Sharma G, Dhall A, Chaudhury S. Efficient skin region segmentation using low complexity fuzzy decision tree model. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Annual IEEE India Conference. Gujarat, India: IEEE, 2009. 1-4 [39] Blackard J A, Dean D J. Comparative accuracies of artificial neural networks and discriminant analysis in predicting forest cover types from cartographic variables. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 1999, 24(3):131-151 doi: 10.1016/S0168-1699(99)00046-0 -




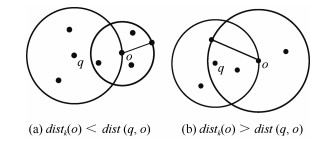
 下载:
下载: