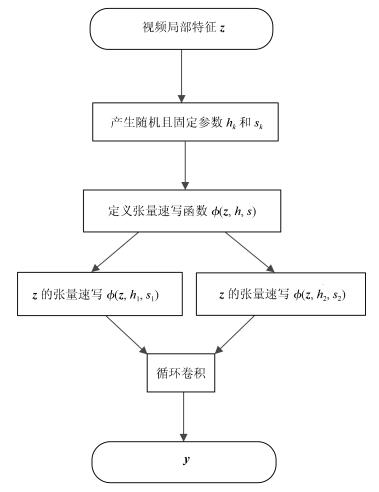
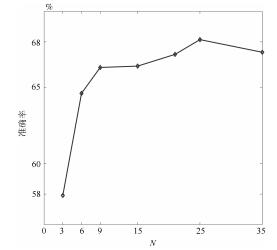
-
摘要: 双流卷积神经网络能够获取视频局部空间和时间特征的一阶统计信息, 测试阶段将多个视频局部特征的分类器分数平均作为最终的预测. 但是, 一阶统计信息不能充分建模空间和时间特征分布, 测试阶段也未考虑使用多个视频局部特征之间的更高阶统计信息. 针对这两个问题, 本文提出一种基于二阶聚合的视频多阶信息融合方法. 首先, 通过建立二阶双流模型得到视频局部特征的二阶统计信息, 与一阶统计信息形成多阶信息. 其次, 将基于多阶信息的视频局部特征分别进行二阶聚合, 形成高阶视频全局表达. 最后, 采用两种策略融合该表达. 实验表明, 本文方法能够有效提高行为识别精度, 在HMDB51和UCF101数据集上的识别准确率比双流卷积神经网络分别提升了8 % 和2.1 %, 融合改进的密集点轨迹(Improved dense trajectory, IDT) 特征之后, 其性能进一步提升.Abstract: The classical two-stream convolutional neural network (CNN) can capture the flrst-order statistics of the local spatial and temporal features from an input video, while making flnal predictions by averaging the softmax scores of the local video features. However, the flrst-order statistics can not fully characterize the distribution of the spatial and temporal features, while higher-order information inherent in local features is discarded at the test stage. To solve the two problems above, this paper proposes a multi-order information fusion method for human action recognition. To this end, we flrst introduce a novel two-stream CNN model for capturing second-order statistics of the local spatial and temporal features, which, together with the original flrst-order statistics, forms the so-called multi-order information. We perform individually second-order aggregation of these extracted local multi-order information to compute global video representations. Finally, two strategies are proposed to fuse video representations for prediction. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method signiflcantly improves recognition accuracy over the original two-stream CNN model, i.e., 8 % and 2.1 % gains on the HMDB51 and UCF101, respectively. The performance of our method is further improved by combining traditional IDT (improved dense trajectory) features.
-
Key words:
- Human action recognition /
- two-stream convolutional neural network /
- multi-order information fusion /
- second-order aggregation
1) 本文责任编委 赖剑煌 -
表 1 一阶、二阶空间和时间流网络在UCF101和HMDB51上准确率的比较
Table 1 Comparisons of first-order spatial and temporal network with second-order spatial and temporal network on UCF101 and HMDB51
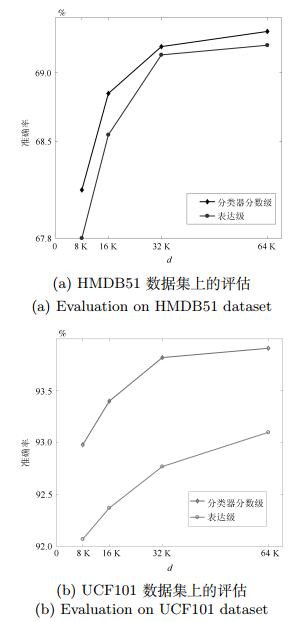
表 2 UCF101和HMDB51上多阶信息融合有效性评估
Table 2 Evaluation of the efiectiveness of multi-order information fusion on UCF101 and HMDB51
一阶空间流 一阶时间流 二阶空间流 二阶时间流 UCF101 (%) HMDB51 (%) √ √ 91.70 61.20 √ √ 92.90 65.17 √ √ 91.34 61.63 √ √ 92.67 63.50 √ √ √ 92.50 65.18 √ √ √ 92.96 66.14 √ √ √ 91.78 60.60 √ √ √ 91.12 58.71 √ √ √ √ 92.75 64.74 表 3 UCF101和HMDB51上基于二阶聚合的视频不同多阶信息融合评估
Table 3 Evaluation of fusing difierent multi-order information of the video based on second-order aggregation on UCF101 and HMDB51
一阶空间信息 一阶时间信息 二阶空间信息 二阶时间信息 UCF101 (%) HMDB51 (%) √ √ 89.28 64.24 √ √ 87.57 59.56 √ √ 92.58 65.93 √ √ 92.07 64.10 √ √ √ 92.68 68.02 √ √ √ 92.60 67.45 √ √ √ 88.64 61.44 √ √ √ 92.55 64.88 √ √ √ √ 92.98 68.15 表 4 不同融合方法测试时间比较
Table 4 Test speed comparison of different fusion methods
方法 测试方式 时间(s/视频) 一阶双流网络融合(基线)[9] 10-crop 9.670 二阶双流网络融合 10-crop 10.459 一阶+二阶双流网络融合 10-crop 20.129 多阶信息二阶聚合 1-crop 6.412 表 5 基于双流卷积神经网络架构的行为识别方法比较
Table 5 Comparison of difierent human action recognition arthogram based on two-stream convolutional network
方法 网络架构 UCF101 (%) HMDB51 (%) Two-stream[6] VGG-M $88.0$ $59.4$ Two-stream 3D卷积+ 3D池化[7] VGG-16 $92.5$ $66.4$ Two-stream[9] ResNet-50 $91.7$ $61.2$ ST-ResNet*[8] ResNet-50 $93.4$ $66.4$ ST-multiplier network[9] ResNet-50 (空间), ResNet-152 (时间) $94.2$ $68.9$ Two-Stream fusion + IDT[7] VGG-16 $93.5$ $69.2$ ST-ResNet + IDT[8] ResNet-50 $94.6$ $70.3$ ST-multiplier + IDT[9] ResNet-50 (空间), ResNet-152 (时间) $94.9$ $72.2$ 本文方法 ResNet-50 93.8 69.2 本文方法+联合训练[8] ResNet-50 94.1 70.7 本文方法+ IDT ResNet-50 94.6 74.4 -
[1] 朱煜, 赵江坤, 王逸宁, 郑兵兵. 基于深度学习的人体行为识别算法综述. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 848-857 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150710Zhu Yu, Zhao Jiang-Kun, Wang Yi-Ning, Zheng Bing-Bing. A review of human action recognition based on deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 848-857 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150710 [2] 苏本跃, 蒋京, 汤庆丰, 盛敏. 基于函数型数据分析方法的人体动态行为识别. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(6): 866-876 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160120Su Ben-Yue, Jiang Jing, Tang Qing-Feng, Sheng Min. Human dynamic action recognition based on functional data analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(6): 866-876 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160120 [3] 周风余, 尹建芹, 杨阳, 张海婷, 袁宪锋. 基于时序深度置信网络的在线人体动作识别. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(7): 1030-1039 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150629Zhou Feng-Yu, Yin Jian-Qin, Yang Yang, Zhang Hai-Ting, Yuan Xian-Feng. Online recognition of human actions based on temporal deep belief neural network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 43(6): 1030-1039 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150629 [4] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA: NIPS Foundation, Inc., 2012. 1097-1105 [5] Wang H, Schmid C. Action recognition with improved trajectories. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 3551-3558 [6] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: NIPS Foundation, Inc., 2014. 568-576 [7] Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Zisserman A. Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1933-1941 [8] Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Wildes R P. Spatiotemporal residual networks for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, ES, Spain: NIPS Foundation, Inc., 2016. 3468-3476 [9] Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Wildes R P. Spatiotemporal multiplier networks for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 7445-7454 [10] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770-778 [11] Wang Y B, Long M S, Wang J M, Yu S P. Spatiotemporal pyramid network for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2097-2106 [12] Wang L M, Xiong Y J, Wang Z, Qiao Y, Lin D H, Tang X D, et al. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 20-36 [13] Hu J, Zheng W, Lai J, Zhang J G. Jointly learning heterogeneous features for RGB-D activity recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2017, 39(11): 2186-2200 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2640292 [14] Shahroudy A, Ng T, Gong Y H, Wang G. Deep multimodal feature analysis for action recognition in RGB+D videos. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2018, 40(5): 1045-1058 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2691321 [15] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 115(3): 211- 252 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [16] Lin T Y, Roychowdhury A, Maji S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1449-1457 [17] Lin T Y, Roychowdhury A, Maji S. Bilinear convolutional neural networks for fine-grained visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1309-1322 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2723400 [18] Li P H, Xie J T, Wang Q L, Zuo W M. Is second-order information helpful for large-scale visual recognition? In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2089-2097 [19] Li P H, Xie J T, Wang Q L, Gao Z L. Towards faster training of global covariance pooling networks by iterative matrix square root normalization. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA, 2018. 947-955 [20] Gao Y, Beijbom O, Zhang N, Darrell T. Compact bilinear pooling. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 317-326 [21] Charikar M, Chen K, Farach-Colton M. Finding frequent items in data streams. In: Proceedings of the 2002 International Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming. Malaga, ES, Spain: Springer, 2002. 693-703 [22] Soomro K, Zamir A R, Shah M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv: 1212. 0402, 2012. 1-7 [23] Kuehne H, Jhuang H, Garrote E, Poggio T, Serre T. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, ES, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 2556- 2563 [24] MatConvNet: CNNs for MATLAB: Source Code [Onlilne], available: http://www.vlfeat.org/matconvnet, November 7, 2018 [25] Peng X J, Wang L M, Wang X X, Qiao Y. Bag of visual words and fusion methods for action recognition: Comprehensive study and good practice. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2016, 150: 109-125 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2016.03.013 -




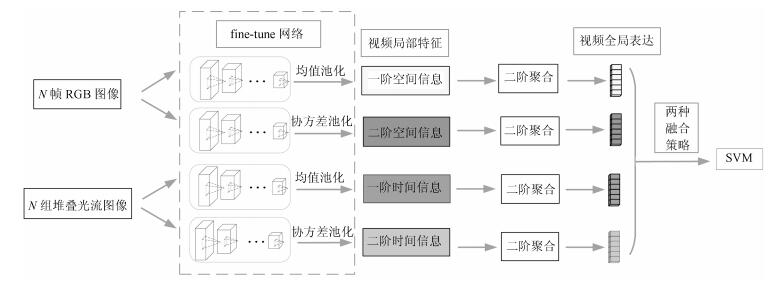
 下载:
下载: