Modeling and Solving the Repair Crew Scheduling for the Damaged Road Networks Based on Q-Learning
-
摘要: 受损路网的修复是灾害应急响应中的一个重要环节, 主要研究如何规划道路抢修队的修复活动, 为灾后救援快速打通生命通道.本文首先构建了抢修队修复和路线规划的数学模型, 然后引入马尔科夫决策过程来模拟抢修队的修复活动, 并基于Q学习算法求解抢修队的最优调度策略.对比实验结果表明, 本文方法能够让抢修队从全局和长远角度实施受损路段的修复活动, 在一定程度上提高了运输效率和修复效率, 可以为政府实施应急救援和快速安全疏散灾民提供有益的参考.Abstract: Repairing the damaged road network is an important issue in disaster emergency response, which mainly focuses on how to schedule the repair activities of the repair crew to clear the life path as soon as possible. In this paper, we first present a mathematical model of the repairing and scheduling of the repair crew. Next, we introduce the Markov decision process to simulate the repair activities of the repair crew. Additionally, the Q-learning algorithm is proposed to search for the optimal scheduling strategy of the repair crew for the damaged road network. Finally, the comparative experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach is able to make the repair crew repair the damaged road network from the global and long-term perspective, improves the transport and repair efficiencies to a certain extent, and provides a useful reference for our government to carry out the emergency rescue and evacuate the victims as quickly and safely as possible.
-
Key words:
- Disaster emergency response /
- damaged road network /
- repair crew scheduling /
- Markov decision process /
- Q-learning
1) 本文责任编委 张敏灵 -
表 1 受损路网和Q-learning算法的基本参数设置
Table 1 Basic parameter settings of the damaged road network and the Q-learning algorithm
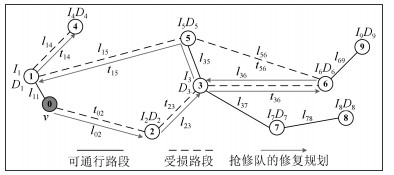
$|V|$ $\frac{|E_r|}{|E|}$ $\frac{D_i}{\mathcal{D}_{i0}}$ $I_i$ $l_{ij}$ $t_{ij}$ $v$ $\lambda$ 训练周期数 $\varepsilon$ $\alpha$ $\gamma$ $\{26, 31, 36, 41\}$ $\{0.1, 0.25, 0.5\}$ $\{1.05, 1.25, 1.5\}$ [1,10] [1,10] [1,10] 1 0.9 $[100, 10\, 000]$ 0.1 0.4 0.2 表 2 36个不同测试实例的参数设置
Table 2 Parameter settings of the 36 different test instances
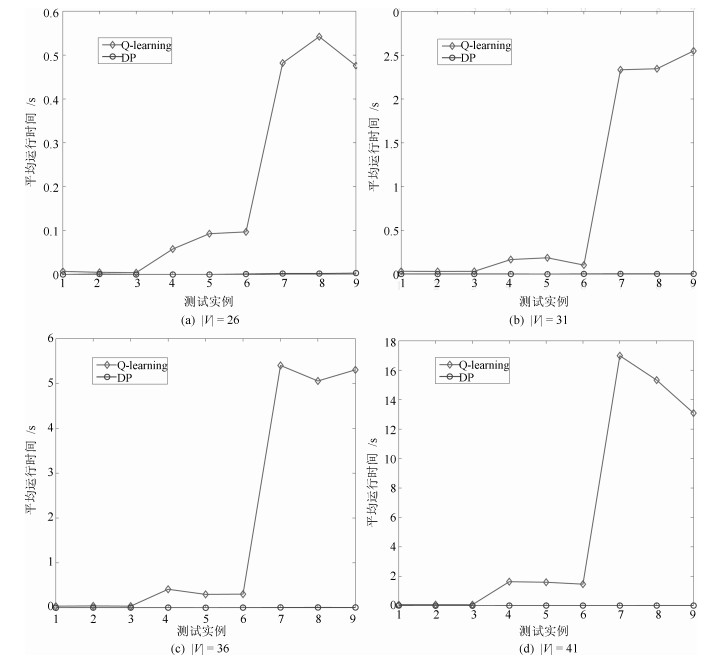
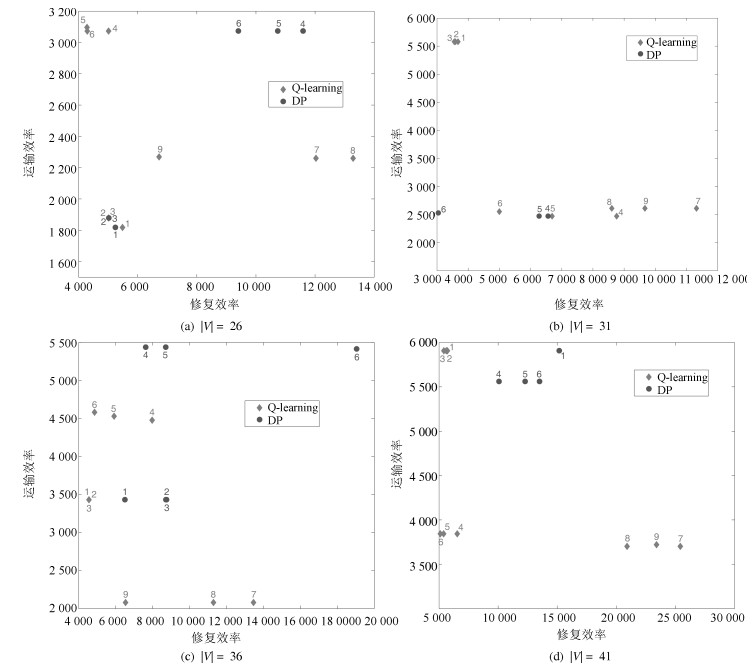
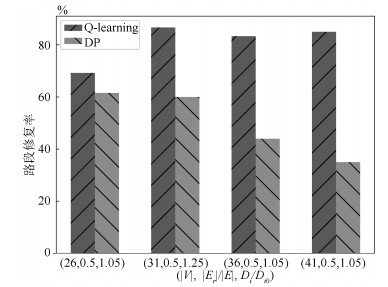
测试实例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 $|V| = 26$ $\frac{|E_r|}{|E|}$ 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.5 0.5 0.5 $\frac{D_i}{\mathcal{D}_{i0}}$ 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 训练周期数 100 100 100 500 500 500 1 000 1 000 1 000 $|V| = 31$ $\frac{|E_r|}{|E|}$ 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.5 0.5 0.5 $\frac{D_i}{\mathcal{D}_{i0}}$ 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 训练周期数 500 500 500 1 000 1 000 1 000 3 000 3 000 3 000 $|V| = 36$ $\frac{|E_r|}{|E|}$ 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.5 0.5 0.5 $\frac{D_i}{\mathcal{D}_{i0}}$ 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 训练周期数 300 300 300 900 900 900 5 000 5 000 5 000 $|V| = 41$ $\frac{|E_r|}{|E|}$ 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.5 0.5 0.5 $\frac{D_i}{\mathcal{D}_{i0}}$ 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 1.05 1.25 1.5 训练周期数 300 300 300 3 000 3 000 3 000 10 000 10 000 10 000 表 3 36个不同测试实例的加权目标函数值(均值$\pm$标准差)
Table 3 Weighted objective function values (mean and standard deviation) of the 36 different test instances
测试实例 $|V| = 26$ $|V| = 31$ $|V| = 36$ $|V| = 41$ Q-learning DP Q-learning DP Q-learning DP Q-learning DP 1 2 176.40 ± 4.21 2 160.05 5 388.19 ± 0.91 - 3 655.55 ± 34.83 3 739.2 6 096.11 ± 63.38 6 832.49 2 2 201.18 ± 1.7 2 192.71 5 438.54 ± 53.68 - 3 540.41 ± 0.76 3 964.6 6 005.27 ± 56.46 - 3 2 201.18 ± 1.7 2 192.71 5 427.4 ± 41.31 - 3 625.27 ± 36.28 3 960.7 6 276.5 ± 126.58 - 4 3 265.48 ± 4.71 3 924.92 2 800.84 ± 63.33 2 880.5 4 919.75 ± 33.79 5 657.62 4 844.56 ± 288.19 6 011.95 5 3 318.17 ± 43.28 3 839.56 2 697.35 ± 43.7 2 851.61 4 756.02 ± 94.22 5 765.13 4 586.82 ± 238.45 6 233.67 6 3 367.82 ± 75.62 3 705.91 2 784.31 ± 82.92 2 578.67 4 663.86 ± 71.74 6 777.95 4 309.49 ± 129.79 6 355.16 7 3 222.2 ± 179.3 - 4 405.91 ± 39.26 - 3 566.12 ± 62.31 - 6 189.04 ± 125.91 - 8 2 813.94 ± 15.41 - 3 824.53 ± 145 - 3 350.95 ± 76.4 - 5 891.23 ± 184.08 - 9 2 930.07 ± 69.46 - 3 919.55 ± 201.8 - 3 004.85 ± 135.9 - 5 356.4 ± 177.42 - -
[1] 苏兆品, 张婷, 张国富, 等.基于云模型和模糊聚合的应急方案评估.模式识别与人工智能, 2014, 27(11): 1047-1055 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2014.11.012Su Zhao-Pin, Zhang Ting, Zhang Guo-Fu, et al. Evaluation of emergency disposal schemes based on cloud model and fuzzy aggregation. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2014, 27(11): 1047-1055 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2014.11.012 [2] 张国富, 王永奇, 苏兆品, 等.应急救援物资多目标分配与调度问题建模与求解.控制与决策, 2017, 32(1): 86-92 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201701012Zhang Guo-Fu, Wang Yong-Qi, Su Zhao-Pin, et al. Modeling and solving multi-objective allocation-scheduling of emergency relief supplies. Control and Decision, 2017, 32(1): 86-92 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201701012 [3] Su Z, Zhang G, Liu Y, et al. Multiple emergency resource allocation for concurrent incidents in natural disasters. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2016, 17: 199-212 doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2016.05.003 [4] 苏兆品, 张国富, 蒋建国, 等.基于非支配排序差异演化的应急资源多目标分配算法.自动化学报, 2017, 43(2): 188-207 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160076Su Zhao-Pin, Zhang Guo-Fu, Jiang Jian-Guo, et al. Multi-objective approach to emergency resource allocation using none-dominated sorting Based differential evolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(2): 188-207 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160076 [5] Averbakh I. Emergency path restoration problems. Discrete Optimization, 2012, 9(1): 58-64 doi: 10.1016/j.disopt.2012.01.001 [6] Çelik M. Network restoration and recovery in humanitarian operations: Framework, literature review, and research directions. Surveys in Operations Research and Management Science, 2016, 21(2): 47-61 [7] Chen S Y. Optimal scheduling of logistical support for an emergency roadway repair work schedule. Engineering Optimization, 2012, 44(9): 1035-1055 doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2011.628389 [8] 霍建顺.震后应急期道路抢修优化排程研究[硕士学位论文].西南交通大学, 2007Huo Jian-Shun. A Study on Optimal Scheduling of Emergency Roadway Repair after Earchquake[Master dissertation]. Southwest Jiaotong University, 2007 [9] Nurre S G, Cavdaroglu B, Mitchell J E, et al. Restoring infrastructure systems: an integrated network design and scheduling (INDS) problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 2012, 223(3): 794-806 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0227984818/ [10] Yan S, Shih Y L. Optimal scheduling of emergency roadway repair and subsequent relief distribution. Computers & Operations Research, 2009, 36(6): 2049-2065 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b27299f7cd4edd8e32a76db1061f104f [11] Yan S, Shih Y L. An ant colony system-based hybrid algorithm for an emergency roadway repair time-space network flow problem. Transportmetrica, 2012, 8(5): 361-386 doi: 10.1080/18128602.2010.515550 [12] 花丙威, 魏琳, 王芳, 等.基于脆弱性的灾后路网修复优化.公路工程, 2013, 38(3): 18-21 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znglgc201303005Hua Bing-Wei, Wei Lin, Wang Fang, et al. Based on vulnerability to optimization the post-disaster road network restores. Highway Engineering, 2013, 38(3): 18-21 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znglgc201303005 [13] 邱慧.灾后公路网修复序列研究[硕士学位论文].长安大学, 2016Qiu Hui. Study on the Restoration Sequence of Highway Network after Disaster[Master dissertation]. Chang$'$an University, 2016 [14] Aksu D T, Özdamar L. A mathematical model for post-disaster road restoration: enabling accessibility and evacuation. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2014, 61(1): 56-67 [15] Özdamar L, Aksu D T, Ergüneş B. Coordinating debris cleanup operations in post disaster road networks. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 2014, 48(4): 249-262 doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2014.08.001 [16] Kasaei M, Salman F S. Arc routing problems to restore connectivity of a road network. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2016, 95: 177-206 doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2016.09.012 [17] Akbari V, Salman F S. Multi-vehicle synchronized arc routing problem to restore post-disaster network connectivity. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 257(2): 625-640 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=de62558a942c10f1dbae9194f6a97c59 [18] 李爱庆.震后紧急道路抢修与救灾物资配送调度研究[硕士学位论文].西南交通大学, 2007Li Ai-Qing. Scheduling Research of Emergency Roadway Repair and Relief Material Distribution after An Earchquake[Master dissertation]. Southwest Jiaotong University, 2007 [19] Duque P A M, Dolinskaya I S, Sörensen K. Network repair crew scheduling and routing for emergency relief distribution problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 248(1): 272-285 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2c5b24d4c6cf2944220767bf780796eb [20] Kim S, Park Y, Lee K, et al. Repair crew scheduling considering variable disaster aspects. In: Proceedings of IFIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems. Hamburg, Germany: Springer, 2017. 57-63 [21] Delgado K V, Barros L N D, Dias D B, et al. Real-time dynamic programming for Markov decision processes with imprecise probabilities. Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 230: 192-223 doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2015.09.005 [22] Su Z, Jiang J, Liang C, et al. Path selection in disaster response management based on Q-learning. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 2011, 8(1): 100-106 doi: 10.1007/s11633-010-0560-2 [23] Dijkstra E W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numerische Mathematik, 1959, 1(1): 269-271 doi: 10.1007/BF01386390 [24] 杨超林, 沈厚才, 高春燕.按单装配系统中组件生产和库存分配控制策略研究.自动化学报, 2011, 37(2): 234-240 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.00234Yang Chao-Lin, Shen Hou-Cai, Gao Chun-Yan. Joint control of component production and inventory allocation in an assemble-to-order system with lost sales. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(2): 234-240 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.00234 [25] 李稚, 谭德庆.基于马尔科夫决策过程的ATO系统独立组件与产品双需求最优决策研究.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 782-791 doi: 10.16383/j.ass.2016.c150488Li Zhi, Tan De-Qing. Optimal control of ATO system with individual components and product demands based on Markov decision process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 782-791 doi: 10.16383/j.ass.2016.c150488 [26] 莫立坡, 于永光.多智能体系统的有限时间旋转环绕控制.自动化学报, 2017, 43(9): 1665-1672 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.e160260Mo Li-Po, Yu Yong-Guang. Finite-time rotating encirclement control of multi-agent systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(9): 1665-1672 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.e160260 [27] 唐昊, 裴荣, 周雷, 谭琦.基于状态聚类的多站点CSPS系统的协同控制方法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(5): 901-908 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00901Tang Hao, Pei Rong, Zhou Lei, Tan Qi. Coordinate control of multiple CSPS system based on state aggregation method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(5): 901-908 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00901 [28] 徐茂鑫, 张孝顺, 余涛.基迁移蜂群优化算法及其在无功优化中的应用.自动化学报, 2017, 43(1): 83-93 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150791Xu Mao-Xin, Zhang Xiao-Shun, Yu Tao. Transfer bees optimizer and its application on reactive power optimization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1): 83-93 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150791 [29] Gomes E R, Kowalczyk R. Dynamic analysis of multiagent Q-learning with $\varepsilon$-greedy exploration. In: Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Machine Learning. Montreal, Canada: Omnipress, 2009. 369-376 [30] Panait L, Luke S. Cooperative multi-agent learning: the state of the art. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2005, 11(3): 387-434 doi: 10.1007/s10458-005-2631-2 [31] Gu S, Lillicrap T, Sutskever I, et al. Continuous deep Q-learning with model-based acceleration. In: Proceedings of 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, NY, USA: ACM Press, 2016. 2829-2838 -




 下载:
下载: