-
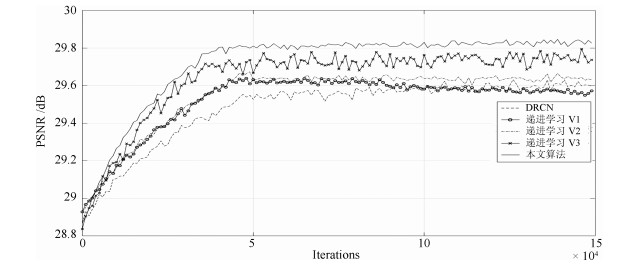
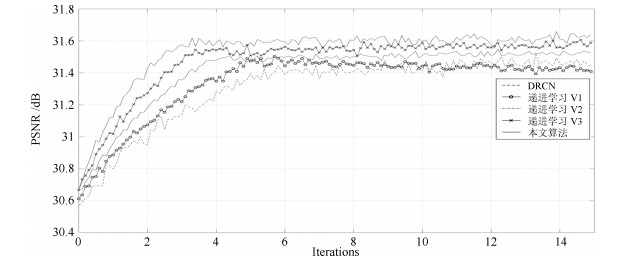
摘要: 本文针对深度学习在单幅图像超分辨率方面难以恢复高频纹理细节的问题, 提出了一种基于递进学习的超分辨率算法.该算法首先采用灰度共生矩阵提取图像纹理特征, 然后利用基于密度峰值的聚类方法实现对整个训练集的分类, 其中每个训练子集具有相似的纹理复杂度.针对传统的递进学习方法会出现对已掌握知识"遗忘"的问题, 本文根据网络模型在各个训练子集上的拟合情况, 实时调整当前训练样本在各个子集上的概率分布, 从而实现快速收敛, 并获得更好的纹理细节复原效果.将本文提出的递进学习用于DRCN、VDSR、SRCNN等超分辨率网络的训练, 实验结果表明超分辨率网络收敛速度得到提升, 同时网络对复杂纹理等细节较多的图像也获得了较好的视觉恢复效果, 峰值信噪比则平均获得0.158 dB、0.18 dB、0.092 dB的提升.Abstract: The main challenge of single image super resolution (SISR) is the recovery of high frequency details such as tiny textures. In order to solve this problem, a curriculum learning-based approach is proposed. In this paper, firstly, gray-level co-occurrence matrix is applied to extract texture features of images. Then, with the clustering algorithm based on density peaks, the training dataset is divided into several subsets on the basis of texture features. As for traditional curriculum learning, the performance is easy to get worse due to the "forgotten" phenomenon of knowledge that has been learned. Different from this, training examples are sampled from all the subsets based on the slope of the learning curve of each subsets. It is helpful for the speed of convergence and the recovery of high frequency details. Experiments show that when SISR networks such as DRCN, VDSR, SRCNN are trained with curriculum learning, training time is shortened and the visual effect is improved. The PSNR (Peak signal to noise ratio) values are increased by 0.158 dB, 0.18 dB and 0.092 dB, respectively.
-
Key words:
- Super resolution /
- curriculum learning /
- co-occurrence matrix /
- density peaks
1) 本文责任编委 王亮 -
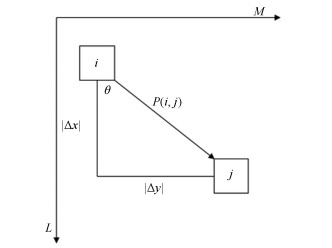
表 1 不同聚类算法在CP、SP、DBI、DVI上的性能指标
Table 1 The performance of different clustering algorithms in CP, SP, DBI and DVI
FCM BIRCH MCLUST STING DP (ours) CP 3.04 2.19 2.86 2.32 1.78 SP 2.67 2.96 3.08 3.12 3.89 DBI 7.23 6.91 8.23 6.58 6.01 DVI 0.52 0.57 0.49 0.55 0.63 表 2 基于不同聚类算法的VDSR在数据集Set5、Set14、BSD 100、Urban100上的性能指标
Table 2 The performance of VDSR based on different clustering algorithms in Set5, Set14, BSD 100, and Urban100
数据集 放大比例 VDSR
(PSNR/SSIM)VDSR + FCM
(PSNR/SSIM)VDSR + BI
(PSNR/SSIM)VDSR + MC
(PSNR/SSIM)VDSR + ST
(PSNR/SSIM)VDSR + DP
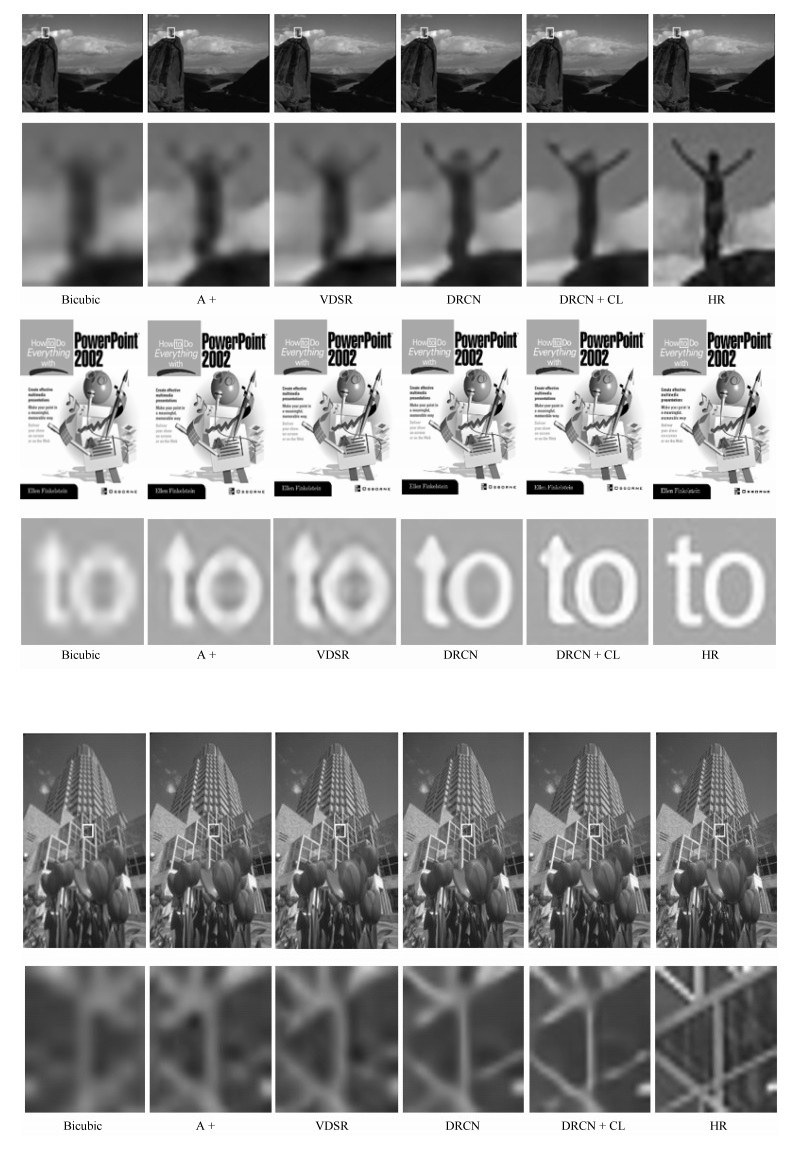
(PSNR/SSIM)Set5 × 2 37.53/0.9587 37.56/0.9462 37.68/0.9538 37.56/0.9589 37.65/0.9581 37.74/0.9592 × 3 33.66/0.9213 33.67/0.9241 33.70/0.9258 33.71/0.9232 33.63/0.9222 33.79/0.9264 × 4 31.35/0.8838 31.38/0.8799 31.53/0.8812 31.41/0.8861 31.47/0.8846 31.49/0.8897 Set14 × 2 33.03/0.9124 33.06/0.9126 33.01/0.9112 33.07/0.9129 33.09/0.9125 33.11/0.9122 × 3 29.77/0.8314 29.80/0.8352 29.86/0.8356 29.79/0.8329 29.81/0.8329 29.91/0.8402 × 4 28.01/0.7674 28.12/0.7650 28.29/0.7710 28.13/0.7703 28.26/0.7717 28.32/0.7738 BSD 100 × 2 31.90/0.8960 31.99/0.8978 31.93/0.9010 32.09/0.8992 32.05/0.8993 32.13/0.9071 × 3 28.82/0.7976 28.84/0.7977 28.92/0.7954 28.89/0.7988 29.04/0.8004 29.11/0.8011 × 4 27.29/0.7251 27.41/0.7196 27.32/0.7260 27.35/0.7273 27.32/0.7278 27.28/0.7310 Urban100 × 2 30.76/0.9140 30.77/0.9139 30.74/0.9123 30.91/0.9169 30.84/0.9156 30.81/0.9193 × 3 27.14/0.8279 27.22/0.8264 27.22/0.8282 27.29/0.8277 27.16/0.8288 27.35/0.8291 × 4 25.18/0.7524 25.33/0.7569 25.21/0.7554 25.29/0.7551 25.32/0.7542 25.41/0.7567 表 3 不同算法在数据集Set5、Set14、BSD 100、Urban100上的性能指标
Table 3 The performance of different algorithms in Set5, Set14, BSD 100, and Urban100
数据集 放大比例 SRCNN
(PSNR/SSIM)SRCNN + CL
(PSNR/SSIM)VDSR
(PSNR/SSIM)VDSR + CL
(PSNR/SSIM)DRCN
(PSNR/SSIM)DRCN + CL
(PSNR/SSIM)Set5 × 2 36.66/0.9542 36.92/0.9623 37.53/0.9587 37.74/0.9592 37.63/0.9588 37.71/0.9591 × 3 32.75/0.9090 32.81/0.9136 33.66/0.9213 33.79/0.9264 33.82/0.9226 33.91/0.9239 × 4 30.48/0.8628 30.56/0.8623 31.35/0.8838 31.49/0.8897 31.53/0.8854 31.61/0.8896 Set14 × 2 32.42/0.9063 32.63/0.9136 33.03/0.9124 33.11/0.9122 33.04/0.9118 33.11/0.9145 × 3 29.28/0.8209 29.41/0.8261 29.77/0.8314 29.91/0.8402 29.76/0.8311 29.81/0.8423 × 4 27.49/0.7503 27.62/0.7501 28.01/0.7674 28.32/0.7738 28.02/0.7670 28.13/0.7722 BSD 100 × 2 31.36/0.8879 31.52/0.8935 31.90/0.8960 32.13/0.9071 31.85/0.8942 31.91/0.9062 × 3 28.41/0.7863 28.63/0.7912 28.82/0.7976 29.11/0.8011 28.80/0.7963 28.92/0.8037 × 4 26.90/0.7101 26.99/0.7234 27.29/0.7251 27.28/0.7310 27.23/0.7233 27.35/0.7274 Urban100 × 2 29.50/0.8946 29.72/0.9064 30.76/0.9140 30.81/0.9193 30.75/0.9133 30.86/0.9201 × 3 26.24/0.7989 26.41/0.8035 27.14/0.8279 27.35/0.8291 27.15/0.8276 27.23/0.8294 × 4 24.52/0.7221 24.69/0.7316 25.18/0.7524 25.41/0.7567 25.14/0.7510 25.21/0.7572 -
[1] Dong C, Chen C L, He K M, Tang X O. Image super-resolution using using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern & Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjfzsjytxxxb201709007 [2] 胡长胜, 詹曙, 吴从中.基于深度特征学习的图像超分辨率重建.自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 814-821 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150634Hu Chang-Sheng, Zhan Shu, Wu Cong-Zhong. Image super-resolution reconstruction based on deep feature learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 814-821 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150634 [3] Sun X, Li X G, Li J F, Zhuo L. Review on deep learning based image super-resolution restoration algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 697-709 [4] 李滔, 何小海, 卿粼波, 滕奇志.基于自适应块组割先验的噪声图像超分辨率重建.自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 765-777 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160268Li Tao, He Xiao-Hai, Qing Lin-Bo, Teng Qi-Zhi. Noisy image super-resolution reconstruction with adaptive patch-group-cuts prior. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 765-777 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160268 [5] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016, 1646-1654 [6] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, Caballero J, Cunn A, Acosta A, et al. Photo-realistic single image superresolution using a generative adversarial network, arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1609.04802, 2016 [7] Lim B, Son S, Kim H, Nah S, MuLee K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, July 2017, 1132-1140 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/318337451_Enhanced_Deep_Residual_Networks_for_Single_Image_Super-Resolution [8] Sajjadi M S, Scholkopf B, Hirsch M. Enhancenet: single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis, arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1612.07919, 2016 [9] Bengio Y, Louradour J, Collobert R, Weston J. Curriculum learning. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. Montreal Quebec, Canada: ACM, 2009 [10] Graves A, Bellemare G, Menick J, Munos R, Kavukcuoglu K. Automated curriculum learning for neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.03003, 2017 [11] Hochreiter, Sepp, Jürgen Schmidhuber. LSTM can solve hard long time lag problems. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 1997 [12] Haralick R M, Shanmugam K. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1973, (6): 610-621 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_16d3aac51c12c1b20a2512bd82d7cd5e [13] Rodriguez A, Laio A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science, 2014, 344(6191): 1492 doi: 10.1126/science.1242072 [14] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016, 1637-1645 [15] Timofte R, Agustsson E, Gool L V, Yang Ming-Hsuan, Zhang L, Lim B, et al. Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017 [16] Bevilacqua M, Roumy A, Guillemot C. Low-complexity singleimage super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding. In: Proceedings of the 2012 British Machine Vision Conference, Surrey, UK: 2012, 135.1-135.10 [17] Zeyde R, Elad M, Protter M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International conference on curves and surfaces. Avignon, France: Springer, 2010, 711-730 http://www.springerlink.com/content/56276x8370377023/ [18] Martin D, Fowlkes C, Tal D. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2001, 2(11): 416-423 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/3906161_A_database_of_human_segmented_natural_images_and_its_application_toevaluating_segmentation_algorithms_and_measuring_ecological_statistics [19] Huang J B, Singh A, Ahuja N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, Massachusetts, USA: 2015, 5197-5206 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/275523282_Single_Image_Super-resolution_from_Transformed_Self-Exemplars [20] Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, Brevdo E, Chen Zhi-Feng, Citro C, et al. Tensorflow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1603.04467, 2016 [21] Bezdek J C, Ehrlich R, Full W. FCM: the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Computers & Geosciences, 1984, 10(2-3): 191-203 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201012036 [22] Zhang T, Raghu R, Miron L. BIRCH: an efficient data clustering method for very large databases. ACM Sigmod Record. 25(2): ACM, 1996 [23] Fraley C, Raftery A E. MCLUST: Software for model-based cluster analysis. Journal of Classification, 1999, 16(2): 297-306 doi: 10.1007/s003579900058 [24] Wang W, Jiong Y, Richard M. STING: A statistical information grid approach to spatial data mining. VLDB. Athens, Greece, Vol. 97, 1997: 186-195 [25] Timofte R, Smet V D, Gool L V. A +: Adjusted anchored neighborhood regression for fast super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV). Singapore: Springer, 2014, 111-126 -




 下载:
下载: