-
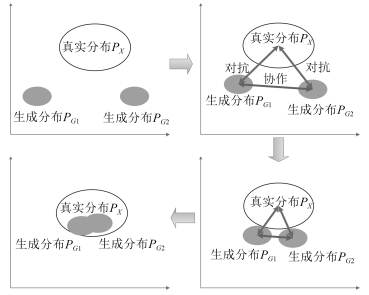
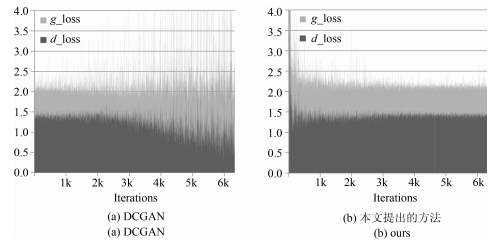
摘要: 生成对抗网络(Generative adversarial nets,GANs)将生成模型与判别模型进行了巧妙结合,采用无监督的训练方式,通过相互对抗共同提高,其在学术界掀起了一股新的机器学习热潮.GANs的学习目标是可以完整拟合任意真实样本的数据分布,然而在实际当中,真实样本分布的复杂程度难以预计,容易发生模式坍塌(Mode collapse)等问题,从而导致结果冗余,模型不收敛等.为提高无监督条件下的GANs生成能力,减少或消除模式坍塌,本文提出一种全新的协作式生成网络结构,通过构建多个生成模型,引入协作机制,使得生成模型在训练过程中能够相互学习,共同进步,从而提高模型对真实数据的拟合能力,进一步提高生成质量.通过在三组不同类型的数据集上进行实验,分析对比结果后发现新模型在二维图像生成方面,特别是人脸图片,有着显著的效果,协作机制不仅可以加快模型收敛速度,提高训练效率,还能消除损失函数噪声,在三维模型生成方面也产生了一定的影响.通过调整模型参数,模式坍塌问题也得到了遏制.本文还设计了一种动态学习方法,动态调节模型的学习速率,有效减少了过大或过小的梯度惩罚.Abstract: Generative adversarial nets (GANs) combine the generative model with the discriminative model. With unsupervised training methods, the two types of models mutually improve through the adversarial process. It sets off a new machine learning boom in academia. The final goal of GANs learning is to fit any real-world data distribution. In practice, however, the real-world data distribution is difficult to estimate. The major problem is mode collapse, which may lead to redundancy and non-convergence. To improve the unsupervised generator and eliminate the risk of mode collapse, this paper proposes a novel co-operative network structure for GANs. Multiple generative models are constructed with a co-operative mechanism. It can help generative models to work together and learn from each other during training. In this way, the fitting ability of generators is largely enhanced, furthermore, the quality of generated data is eventually upgraded. Experiments are conducted on three different types of benchmark datasets. Results show that the new model significantly improves image generation, especially for human face pictures. Additionally, the co-operative mechanism can speed up the convergence, improve network's learning efficiency and deduct loss function noise. It also plays a certain role in 3D model generation and suppress the problem of mode collapse. In order to solve the inconsistency between generation model and discriminative model, a dynamic learning method is developed which can dynamically adjust learning frequency. It ultimately reduces unnecessary gradient penalties.1) 本文责任编委 李力
-
图 5 CelebA人脸数据集训练结果(左侧为深度卷积生成对抗网络, 右侧为协作式生成对抗网络, (a)迭代500次; (b)迭代1 000次; (c) $\sim$ (h)迭代1 $\sim$ 6回合)
Fig. 5 Training results on CelebA human faces dataset (left side is trained by DCGAN, right side is trained by ours after, (a) 500 iterations; (b) 1 000 iterations; (c) $\sim$ (h) 1 $\sim$ 6 epochs)
-
[1] Hinton G E. To recognize shapes, first learn to generate images. Progress in Brain Research, 2007, 165:535-547 doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)65034-6 [2] Taylor G W, Hinton G E, Roweis S. Modeling human motion using binary latent variables. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Canada: MIT Press, 2006. 1345-1352 [3] Taylor G W, Hinton G E. Factored conditional restricted Boltzmann machines for modeling motion style. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. Montreal, Quebec, Canada: ACM, 2009. 1025-1032 [4] Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786):504-507 doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [5] Mohamed A, Dahl G E, Hinton G. Acoustic modeling using deep belief networks. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2012, 20(1):14-22 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2109382 [6] Hinton G, Deng L, Yu D, Dahl G E, Mohamed A R, Jaitly N, et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition:the shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6):82-97 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597 [7] Liu Y, Zhou S S, Chen Q C. Discriminative deep belief networks for visual data classification. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(10-11):2287-2296 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2010.12.012 [8] Le Cun Y, Boser B, Denker J S, Howard R E, Habbard W, Jackel L D, et al. Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1990. 396-404 [9] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2014. 2672-2680 [10] Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. Caribe Hilton, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016. 97-108 [11] Xue T F, Wu J J, Bouman K L, Freeman W T. Visual dynamics: probabilistic future frame synthesis via cross convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 91-99 [12] Denton E L, Chintala S, Szlam A, Fergus R. Deep generative image models using a Laplacian pyramid of adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 1486-1494 [13] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA: Curran Associates, Inc., 2012. 1097-1105 [14] Liu M Y, Tuzel O. Coupled generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 469-477 [15] Mirza M, Osindero S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv: 1411. 1784, 2014 [16] van den Oord A, Kalchbrenner N, Espeholt L, Kavukcuoglu K, Vinyals O, Graves A. Conditional image generation with PixelCNN decoders. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 4790-4798 [17] Reed S, Akata Z, Mohan S, Tenka S, Schiele B, Lee H. Learning what and where to draw. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 217-225 [18] Salimans T, Goodfellow I, Zaremba W, Cheung V, Radford A, Chen X, et al. Improved techniques for training GANs. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 2226-2234 [19] Chen X, Chen X, Duan Y, Houthooft R, Schulman J, Sutskever I, et al. InfoGAN: interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 2172-2180 [20] Odena A, Olah C, Shlens J. Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier GANs. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia, 2017. 2642-2651 [21] Ghosh A, Kulharia V, Namboodiri V, Torr P H S, Dokania P K. Multi-agent diverse generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1704. 02906, 2017 [22] Arjovsky M, Bottou L. Towards principled methods for training generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1701. 04862, 2017 [23] LeCun Y, Cortes C, Burges C J C. The MNIST database of handwritten digits[Online], available: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist, June 3, 2017. [24] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11):2278-2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [25] Liu Z W, Luo P, Wang X G, Tang X O. Large-scale CelebFaces Attributes (CelebA) Dataset[Online], available: http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/CelebA.html, July 20, 2017. [26] Liu Z W, Luo P, Wang X G, Tang X O. Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 3730-3738 [27] Princeton ModelNet[Online], available: http://modelnet.cs.princeton.edu, August 13, 2017. [28] Wu Z R, Song S R, Khosla A, Yu F, Zhang L G, Tang X O, et al. 3D ShapeNets: a deep representation for volumetric shapes. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1912-1920 [29] Wu J J, Zhang C K, Xue T F, Freeman B, Tenenbaum J. Learning a probabilistic latent space of object shapes via 3D generative-adversarial modeling. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 82-90 -





 下载:
下载: