-
摘要: 高斯过程回归(Gaussian process regression,GPR)是一种广泛应用的回归方法,可以用于解决输入输出均为多元变量的人体姿态估计问题.计算复杂度是高斯过程回归的一个重要考虑因素,而常用的降低计算复杂度的方法为稀疏表示算法.在稀疏算法中,完全独立训练条件(Fully independent training conditional,FITC)法是一种较为先进的算法,多用于解决输入变量彼此之间完全独立的回归问题.另外,输入变量的噪声问题是高斯过程回归的另一个需要考虑的重要因素.对于测试的输入变量噪声,可以通过矩匹配的方法进行解决,而训练输入样本的噪声则可通过将其转换为输出噪声的方法进行解决,从而得到更高的计算精度.本文基于以上算法,提出一种基于噪声输入的稀疏高斯算法,同时将其应用于解决人体姿态估计问题.本文实验中的数据集来源于之前的众多研究人员,其输入为从视频序列中截取的图像或通过特征提取得到的图像信息,输出为三维的人体姿态.与其他算法相比,本文的算法在准确性,运行时间与算法稳定性方面均达到了令人满意的效果.Abstract: Gaussian process regression (GPR) is a common method for structured prediction and human pose estimation, in which input and output are both multivariate. Computational complexity is a significant consideration of GP regression and it can be reduced by sparse Gaussian algorithm. The fully independent training conditional (FITC) algorithm is a good method for sparse Gaussian process, and it can be applied to fully-independent input problems. Input noise is another significant consideration of GP regression. Moment matching can be used to solve trial input noise while training input noise can be modeled as output noise to achieve higher accuracy. On the basis of above algorithms, this study proposes a sparse Gaussian process with input noise for human pose estimation. A dataset from multiple people is used for experiments, in which the input is the image from video processing or image descriptor obtained by feature extraction, and the output is a three-dimensional human pose. The accuracy, runtime and stability of the algorithm are all satisfactory compared with other methods for human pose estimation.1) 本文责任编委 黄庆明
-
表 1 GP, FITC, NIGP和SGPIN算法比较
Table 1 Comparison of GP, FITC, NIGP and SGPIN
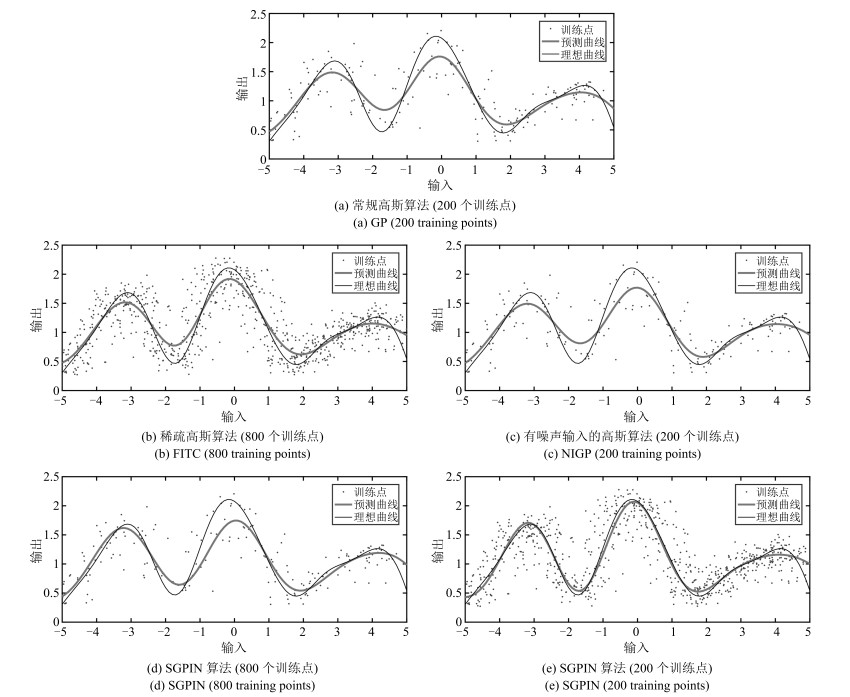
算法 训练点个数 MSE ($10^{-3}$) 运行时间(s) GP 200 31.1326 1.876034 FITC 800 18.6279 0.062001 NIGP 200 18.6279 13.630882 SGPIN 800 8.6265 0.003087 200 18.4946 0.002612 表 2 实验数据集
Table 2 Experimental set
特征 动作 个体1 个体2 个体3 总数 HoG Walking 1 176 876 895 2 947 Jogging 439 795 831 2 065 Throw/Catch 217 806 0 1 023 Gestures 801 681 214 1 696 Box 502 464 933 1 889 Total 3 135 3 622 2 873 9 630 表 3 基于HumanEva-I数据集HoG特征的不同算法的平均误差
Table 3 Evaluation of average error of difierent algorithms based on HoG feature of HumanEva-I
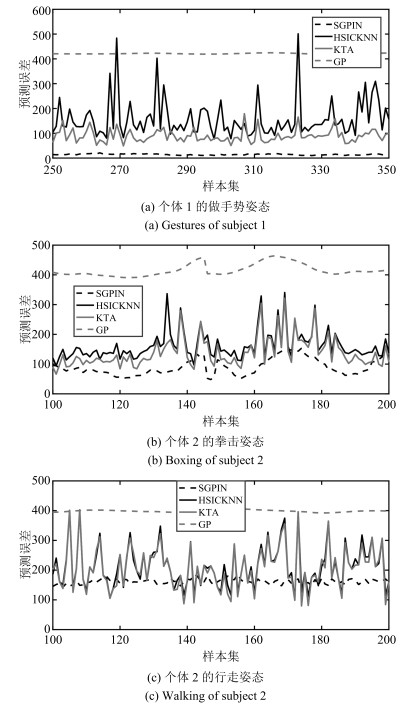
研究个体 动作 样本数 GP TGP TGPKNN KTA HSICKNN SGPIN S1 Walking 1 176 398.5823 197.1179 193.9949 213.5265 218.6241 161.2112 Jogging 439 383.7747 212.3234 212.2018 188.6683 196.0839 154.5919 Throw/Catch 217 414.5873 174.2834 / / / 100.7592 Gestures 801 415.3106 98.6237 102.5520 92.1541 156.6464 20.1770 Box 502 426.6358 162.6801 163.3203 118.0500 149.5003 82.3949 S2 Walking 876 398.5817 197.1496 195.5694 206.7040 211.9735 160.4342 Jogging 795 405.1201 213.0572 207.2430 227.3562 231.1777 176.1768 Throw/Catch 806 421.5898 210.1543 199.3265 173.2717 189.7417 92.6742 Gestures 681 410.0671 201.1053 201.7576 153.9103 173.0548 63.2473 Box 464 421.3947 171.6007 109.1912 137.1031 159.5833 98.3920 S3 Walking 895 412.0019 219.2579 214.8589 236.1566 239.6487 177.3461 Jogging 831 441.7053 211.1343 206.1400 233.5746 236.5287 184.2251 Throw/Catch 0 / / / / / / Gestures 214 473.7616 159.7482 / / / 40.3100 Box 933 483.6534 214.1621 207.7578 186.5170 195.9815 120.6541 总数 9 630 284.0985 160.1196 162.0768 / / 155.3066 表 4 基于HumanEva-I数据集HoG特征的不同算法的运行时间
Table 4 Evaluation of runtime of difierent algorithms based on HoG feature of HumanEva-I
研究个体 动作 样本数 GP TGP TGPKNN KTA HSICKNN SGPIN S1 Walking 1 176 0.11 26.77 24.67 28.16 27.87 18.02 Jogging 439 0.03 8.47 10.43 10.18 10.26 21.65 Throw/Catch 217 0.01 3.77 / / / 22.44 Gestures 801 0.07 27.15 27.31 18.64 19.42 19.78 Box 502 0.03 10.11 11.19 11.75 11.84 21.90 S2 Walking 876 0.08 20.86 25.83 20.03 20.26 22.04 Jogging 795 0.07 18.06 17.86 17.64 17.74 23.32 Throw/Catch 806 0.02 18.56 26.59 20.13 20.02 21.69 Gestures 681 0.04 14.32 15.52 15.91 16.64 18.38 Box 464 0.03 9.02 10.35 10.71 11.43 23.69 S3 Walking 895 0.09 22.78 22.63 20.75 20.95 21.13 Jogging 831 0.08 21.83 20.13 18.51 19.01 20.36 Throw/Catch 0 / / / / / / Gestures 214 0.04 6.13 / / / 22.62 Box 933 0.10 23.70 23.67 22.68 23.57 21.69 总数 9 630 11 1928 442 491 495 41 表 5 个体3行走姿态的预测误差
Table 5 Predicting errors of subject 3 walking
GP TGP TGPKNN HSICKNN KTA SGPIN 1 412.0 219.1 214.8 236.3 239.6 177.6 2 412.0 218.0 214.9 232.5 235.7 176.9 3 412.0 220.2 214.6 237.1 240.9 177.7 4 412.0 220.4 215.6 241.6 244.8 177.5 5 412.0 218.7 214.5 233.4 237.3 177.0 方差 0.00 1.04 0.18 12.89 12.38 0.14 -
[1] 沈建冬, 陈恒.融合HOG和颜色特征的人体姿态估计新算法.计算机工程与应用, 2017, 53(21):190-194 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1606-0319Shen Jian-Dong, Chen Heng. New human pose estimation algorithm based on HOG and color features. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2017, 53(21):190-194 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1606-0319 [2] Wang J M, Fleet D J, Hertzmann A. Gaussian process dynamical models for human motion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(2):283-298 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1167 [3] 袁紫华, 李峰, 周书仁.基于Haar型LBP纹理特征的人体姿态估计.计算机工程, 2015, 41(4):199-204 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2015.04.038Yuan Zi-Hua, Li Feng, Zhou Shu-Ren. Human pose estimation based on Haar characteristics LBP texture feature. Computer Engineering, 2015, 41(4):199-204 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2015.04.038 [4] Zhao X, Ning H Z, Liu Y C, Huang T. Discriminative estimation of 3D human pose using Gaussian processes. In:Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Tampa, FL, USA:IEEE, 2008. 1-4 [5] Bratieres S, Quadrianto N, Ghahramani Z. GPstruct:Bayesian structured prediction using gaussian processes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(7):1514-1520 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2366151 [6] Ding M, Fan G L. Articulated Gaussian kernel correlation for human pose estimation. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Boston, MA, USA:IEEE, 2015. 57-64 [7] Rasmussen C E, Ghahramani Z. Infinite mixtures of Gaussian process experts. In:Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems:Natural and Synthetic. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada:MIT Press, 2002. 881-888 [8] 俞斌峰, 季海波.稀疏贝叶斯混合专家模型及其在光谱数据标定中的应用.自动化学报, 2016, 42(4):566-579 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18844.shtmlYu Bin-Feng, Ji Hai-Bo. Sparse Bayesian mixture of experts and its application to spectral multivariate calibration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):566-579 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18844.shtml [9] 刘长红, 杨扬, 陈勇.增量式人体姿态映射模型的学习方法.计算机科学, 2010, 37(3):268-270 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2010.03.067Liu Chang-Hong, Yang Yang, Chen Yong. Incrementally learning human pose mapping model. Computer Science, 2010, 37(3):268-270 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2010.03.067 [10] 闫小喜, 韩崇昭.基于增量式有限混合模型的多目标状态极大似然估计.自动化学报, 2011, 37(5):577-584 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17393.shtmlYan Xiao-Xi, Han Chong-Zhao. Maximum likelihood estimation of multiple target states based on incremental finite mixture model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(5):577-584 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17393.shtml [11] Csató L, Opper M. Sparse on-line Gaussian processes. Neural Computation, 2002, 14(3):641-668 doi: 10.1162/089976602317250933 [12] Bijl H, van Wingerden J W, Schön T B, Verhaegen M. Online sparse Gaussian process regression using FITC and PITC approximations. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(28):703-708 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.12.212 [13] Snelson E, Ghahramani Z. Sparse Gaussian processes using pseudo-inputs. In:Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada:MIT Press, 2006. 1257-1264 [14] McHutchon A, Rasmussen C E. Gaussian process training with input noise. In:Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Granada, Spain:ACM, 2011. 1341-1349 [15] HumanEva Dataset[Online], available:http://humaneva.is.tue.mpg.de/, November 3, 2017 [16] Sigal L, Balan A O, Black M J. HumanEva:synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2006, 87(1-2):Article No. 4 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0224696659/ [17] Poppe R. Evaluating example-based pose estimation:experiments on the HumanEva sets. In:Proceedings of the 2007 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop on Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion and Pose Estimation (EHuM2). Minneapolis, USA:IEEE, 2007. [18] 苏本跃, 蒋京, 汤庆丰, 盛敏.基于函数型数据分析方法的人体动态行为识别.自动化学报, 2017, 43(5):866-876 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19064.shtmlSu Ben-Yue, Jiang Jing, Tang Qing-Feng, Sheng Min. Human dynamic action recognition based on functional data analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5):866-876 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19064.shtml [19] Shakhnarovich G, Viola P, Darrell T. Fast pose estimation with parameter-sensitive hashing. In:Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Nice, France:IEEE, 2003. 750-757 [20] 韩贵金, 朱虹.一种基于图结构模型的人体姿态估计算法.计算机工程与应用, 2013, 49(14):30-33 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1302-0153Han Gui-Jin, Zhu Hong. Human pose estimation algorithm based on pictorial structure model. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2013, 49(14):30-33 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1302-0153 [21] Jiang H. Human pose estimation using consistent max covering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(9):1911-1918 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.92 [22] Yang W L, Wang Y, Mori G. Recognizing human actions from still images with latent poses. In:Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, USA:IEEE, 2010. 2030-2037 [23] 徐峰, 张军平.人脸微表情识别综述.自动化学报, 2017, 43(3):333-348 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19013.shtmlXu Feng, Zhang Jun-Ping. Facial microexpression recognition:a survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3):333-348 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19013.shtml [24] 徐渊, 许晓亮, 李才年, 姜梅, 张建国.结合SVM分类器与HOG特征提取的行人检测.计算机工程, 2016, 42(1):56-60, 65 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2016.01.011Xu Yuan, Xu Xiao-Liang, Li Cai-Nian, Jiang Mei, Zhang Jian-Guo. Pedestrian detection combining with SVM classifier and HOG feature extraction. Computer Engineering, 2016, 42(1):56-60, 65 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2016.01.011 [25] Bo L F, Sminchisescu C. Twin gaussian processes for structured prediction. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 87(1-2):28-52 doi: 10.1007/s11263-008-0204-y [26] Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J, Elisseeff A, Kandola J. On kernel-target alignment. In:Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems:Natural and Synthetic. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada:MIT Press, 2001. 367-373 [27] Gretton A, Bousquet O, Smola A J, Schölkopf B. Measuring statistical dependence with Hilbert-Schmidt norms. Algorithmic Learning Theory. Berlin Heidelberg, Germany:Springer-Verlag, 2005. -




 下载:
下载: