-
摘要: 排序学习利用机器学习技术去训练排序模型以解决排序问题,是信息检索与机器学习交叉领域的一个新兴研究热点.越来越多的排序学习方法已经应用于实际系统中,如搜索引擎和推荐系统等.本文概括了排序学习的研究进展,并进行展望.首先,阐述了排序学习问题.然后,对排序学习方法进行了分类,并重点分析了依据训练排序模型时所采用的不同机器学习技术的排序学习方法类别.本文还介绍了一些代表性的标准排序学习数据集,对排序学习方法在若干领域的成功应用进行了总结,并归纳了一些排序学习方法软件包.最后,对排序学习的未来发展趋势和挑战进行了展望和探讨.Abstract: Learning to rank utilizes some machine learning techniques to train the ranking models to solve the ranking problems, which is a new research hotspot in the cross field of information retrieval and machine learning. More and more approaches of learning to rank have been applied in practical systems, such as search engines and recommendation systems.This paper summarizes the state of the art of learning to rank and looks into its future. First of all, the problems of learning to rank are described. Then, the approaches of learning to rank are classified, and the categories of the learning to rank approaches according to different machine learning techniques used in the training process of the ranking models are analyzed emphatically. In addition, some representative standard data sets of learning to rank are illustrated, some successful applications in different fields for learning to rank are summarized, and some software packages of the learning to rank approaches are summarized. Finally, some development trends and challenges of learning to rank are prospected and discussed in the future research.1) 本文责任编委 徐昕
-
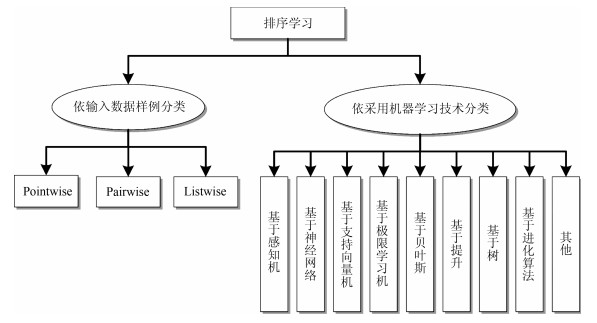
表 1 Pointwise、Pairwise和Listwise排序学习方法对比
Table 1 Comparison of Pointwise, Pairwise and Listwise learning to rank approaches
类别 输入数据 样本复杂度 所转化的主要问题 特点 Pointwise 单个文档 ${\rm O}(n)$ 分类、回归或序数回归问题 考虑单个文档之间的排序特征, 不考虑同一查询下文档间的关系信息, 偏离了排序问题的实质.模型较简单, 训练时间较短. Pairwise 具有偏序关系的文档对 ${\rm O}(n^2)$ 二分类问题 考虑文档对之间的偏序关系, 部分保留了同一查询下文档间的关系信息, 并不考虑文档在文档列表上的位置, 接近排序问题的实质.模型较复杂, 训练时间较长, 需较高效的学习算法. Listwise 所有相关联的整个文档列表 ${\rm O}(n!)$ 最优化问题等 考虑同一查询下不同文档的序列关系, 完全符合排序问题的实质.模型的复杂度以及训练时间的长短很大程度上依赖于文档列表的损失函数或优化目标的定义. 表 2 排序学习方法类别及实例
Table 2 Categories and instances of the learning to rank approaches
类别 Pointwise Pairwise Listwise 感知机 PRank LDM (Percep) PAMM 神经网络 RankNet, LambdaRank, FRank, SortNet ListNet, ListMLE, R-LTR-NTN, PAMM-NTN 支持向量机 Ranking SVM SVM-MAP, SVM-NDCG 极限学习机 Pointwise RankELM Pairwise RankELM, ELMRank 贝叶斯 RankBayes, BLM-Rank Boosting RankBoost AdaRank 树 RF-point LogisticRank LambdaMART, X-DART Oblivious LambdaMART, QuickScorer, RF-list 进化算法 RankGP, RankMGP, MGP-Rank, RankCSA, RankIP, RankGDE, SwarmRank, RankPSO, RankBCA, RankDE, ES-Rank, R$^2$Rank 表 3 排序学习数据集
Table 3 Datasets of learning to rank
数据集 查询个数 文档个数 特征个数 相关性等级标注 来源 HP2003 150 147 606 64 0, 1 LETOR3.0 NP2003 50 148 657 64 0, 1 LETOR3.0 TD2003 50 49 058 64 0, 1 LETOR3.0 HP2004 75 74 409 64 0, 1 LETOR3.0 NP2004 75 73 834 64 0, 1 LETOR3.0 TD2004 75 74 146 64 0, 1 LETOR3.0 OHSUMED 106 16 140 45 0, 1, 2 LETOR3.0 MQ2007 1 692 69 623 46 0, 1, 2 LETOR4.0 MQ2008 784 15 211 46 0, 1, 2 LETOR4.0 MSLR-WEB10K 10 000 1 200 192 136 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Microsoft LTR datasets MSLR-WEB30K 31 531 3 771 125 136 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Microsoft LTR datasets Yahoo! LTR challenge set1 29 921 709 877 519 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 2010 Yahoo! LTR challenge datasets Yahoo! LTR challenge set2 6 330 172 870 596 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 2010 Yahoo! LTR challenge datasets Yandex internet mathematics 2009 9 124 97 290 245 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Yandex internet mathematics 2009 contest WCL2R 79 5 200 29 0, 1, 2, 3 The TodoCL search engine Istella LETOR 33 018 10 454 629 220 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Istella dataset Istella-S LETOR 33 018 3 408 630 220 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Istella dataset 表 4 排序学习方法软件包
Table 4 Software packages of the learning to rank approaches
软件包名 开发语言 特点 来源 RankLib JAVA 支持多种排序学习方法和信息检索的评价指标, 提供多种执行方式评估排序学习方法, 且易于扩展更多的方法和评价指标.包含方法较多、代码开源较早且易于使用, 得到众多研究者的青睐和使用. 美国马萨诸塞大学 QuickRank C++ 支持多种排序学习方法和度量准则, 提供一种柔性、可扩展的和高效率的排序学习框架去开发和实现更多的排序学习方法.适合于从大规模的训练数据集中学习高质量的排序函数, 侧重追求高效率.新近开发的软件包, 代码开源较晚, 有待于研究者的推广和使用. 意大利ISTI-CNR的Istella团队等 Lerot Python 是第一个在线排序学习方法软件包, 可构建原型设计和评估在线排序学习方法的理想环境, 易于使用和扩展, 并易于将已实现的方法与新的在线评估和在线排序学习方法进行比较. 微软剑桥研究院和荷兰阿姆斯特丹大学等 LTR C++ 支持解决分类、回归和排序问题的开源代码, 但目前仅有两种排序学习方法源代码, 不过该软件包易于扩展更多的方法, 也易于使用现有程序.较早开发的排序学习方法的开源库, 但其使用者还有待加强推广. Yandex数据分析学院的学生 L2RLab JAVA 是一个包含设计新排序学习方法各阶段的集成实验环境, 是面向可扩展而设计的一个软件工具包, 有助于实验的展开.但由于该软件包当前仍还未提供访问和开源, 导致融入的排序学习方法较少. 古巴西恩富戈斯大学等 ESRank JAVA 只含有ES-Rank排序学习方法的JAR包.包含方法比较单一且不开源, 该软件包未获得推广. 英国诺丁汉大学和米尼亚大学 MLR-master MATLAB 基于结构化SVM框架, 包含准则排序学习方法和鲁棒的准则排序学习方法, 支持多个核函数评价准则.包含方法比较单一, 该软件包未获得推广. 美国加利福尼亚大学 SVM$^{\rm rank}$ C、C++和Python 使用线性核函数训练排序SVM的一个工具, 拥有多种语言的开源代码.其C语言版的SVM$^{\rm rank}$是一种开源最早的软件包, 后续软件包和数据集的采集大多遵循其思想开发. 美国康乃尔大学 -
[1] Page L, Brin S, Motwani R, Winograd T. The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web, Technical Report SIDL-WP-1999-0120, Stanford InfoLab, Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA, 1999. [2] Kleinberg J M. Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment. Journal of the ACM, 1999, 46(5):604-632 doi: 10.1145/324133.324140 [3] Gyöngyi Z, Garcia-Molina H, Pedersen J. Combating web spam with trustrank. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases. Toronto, Canada: VLDB Endowment, 2004. 576-587 [4] Liu Y T, Gao B, Liu T Y, Zhang Y, Ma Z M, He S Y, et al. BrowseRank: letting web users vote for page importance. In: Proceedings of the 31st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Singapore: ACM, 2008. 451-458 [5] Zhu G Y, Mishne G. Clickrank:learning session-context models to enrich web search ranking. ACM Transactions on the Web, 2012, 6(1):Article No.1 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0226740933/ [6] Wang L D, Bennett P N, Collins-Thompson K. Robust ranking models via risk-sensitive optimization. In: Proceedings of the 35th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Portland, Oregon, USA: ACM, 2012. 761-770 [7] Niu S Z, Guo J F, Lan Y Y, Cheng X Q. Top-k learning to rank: labeling, ranking and evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 35th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Portland, Oregon, USA: ACM, 2012. 751-760 [8] Yin D W, Hu Y N, Tang J L, Daly T, Zhou M W, Ouyang H, et al. Ranking relevance in yahoo search. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco, California, USA: ACM, 2016. 323-332 [9] Wang Y, Yin D W, Luo J, Wang P Y, Yamada M, Chang Y, et al. Beyond ranking: optimizing whole-page presentation. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. San Francisco, California, USA: ACM, 2016. 103-112 [10] Zhao T, King I. Constructing reliable gradient exploration for online learning to rank. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Indianapolis, Indiana, USA: ACM, 2016. 1643-1652 [11] Lucchese C, Nardini F M, Orlando S, Perego R, Tonellotto N, Venturini R. Quickscorer: a fast algorithm to rank documents with additive ensembles of regression trees. In: Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Santiago, Chile: ACM, 2015. 73-82 [12] Liu T Y, Joachims T, Li H, Zhai C X. Introduction to special issue on learning to rank for information retrieval. Information Retrieval, 2010, 13(3):197-200 doi: 10.1007/s10791-009-9120-1 [13] Chapelle O, Chang Y. Yahoo! Learning to rank challenge overview. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Yahoo! Learning to Rank Challenge. Haifa, Israel: JMLR, 2011. 1-24 [14] Liu T Y. Learning to rank for information retrieval. Foundations and Trends in Information Retrieval, 2009, 3(3):225-331 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_1303.2277 [15] Li H. Learning to Rank for Information Retrieval and Natural Language Processing (Second Edition). San Rafael, California:Morgan & Claypool Publishers, 2014. 1-121 [16] Crammer K, Singer Y. Pranking with ranking. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 14(NIPS 2001). La Jolla, Canada: NIPS, 2001. 641-647 [17] Gao J F, Qi H L, Xia X S, Nie J Y. Linear discriminant model for information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Salvador, Brazil: ACM, 2005. 290-297 [18] Xia L, Xu J, Lan Y Y, Guo J F, Cheng X Q. Learning maximal marginal relevance model via directly optimizing diversity evaluation measures. In: Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Santiago, Chile: ACM, 2015. 113-122 [19] Burges C, Shaked T, Renshaw E, Lazier A, Deeds M, Hamilton N, et al. Learning to rank using gradient descent. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Bonn, Germany: ACM, 2005. 89-96 [20] Tsai M F, Liu T Y, Qin T, Chen H H, Ma W Y. FRank: a ranking method with fidelity loss. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ACM, 2007. 383-390 [21] Burges C J, Ragno R, Le Q V. Learning to rank with nonsmooth cost functions. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19(NIPS 2006). Vancouver, B. C., Canada: NIPS, 2007. 193-200 [22] Cao Z, Qin T, Liu T Y, Tsai M F, Li H. Learning to rank: from pairwise approach to listwise approach. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning. Corvalis, Oregon, USA: ACM, 2007. 129-136 [23] Xia F, Liu T Y, Wang J, Zhang W S, Li H. Listwise approach to learning to rank: theory and algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. Helsinki, Finland: ACM, 2008. 1192-1199 [24] Xia L, Xu J, Lan Y Y, Guo J F, Cheng X Q. Modeling document novelty with neural tensor network for search result diversification. In: Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Pisa, Italy: ACM, 2016. 395-404 [25] Rigutini L, Papini T, Maggini M, Scarselli F. SortNet:learning to rank by a neural preference function. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(9):1368-1380 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2160875 [26] Joachims T. Optimizing search engines using clickthrough data. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Edmonton, Alberta, Canada: ACM, 2002. 133-142 [27] Yue Y S, Finley T, Radlinski F, Joachims T. A support vector method for optimizing average precision. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ACM, 2007. 271-278 [28] Chakrabarti S, Khanna R, Sawant U, Bhattacharyya C. Structured learning for non-smooth ranking losses. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: ACM, 2008. 88-96 [29] Zhao X Y, Li X, Zhang Z F. Joint structural learning to rank with deep linear feature learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 27(10):2756-2769 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2015.2426707 [30] Li X, Pi T, Zhang Z F, Zhao X Y, Wang M, Li X L, et al. Learning bregman distance functions for structural learning to rank. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2017, 29(9):1916-1927 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2654250 [31] Zong W W, Huang G B. Learning to rank with extreme learning machine. Neural Processing Letters, 2014, 39(2):155-166 doi: 10.1007/s11063-013-9295-8 [32] Chen H, Peng J T, Zhou Y C, Li L Q, Pan Z B. Extreme learning machine for ranking:generalization analysis and applications. Neural Networks, 2014, 53:119-126 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.01.015 [33] Guo H F, Chu D H, Ye Y M, Li X T, Fan X X. BLM-Rank:a Bayesian linear method for learning to rank and its GPU implementation. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2016, E99.D(4):896-905 doi: 10.1587/transinf.2015DAP0001 [34] Cossock D, Zhang T. Statistical analysis of Bayes optimal subset ranking. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(11):5140-5154 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2008.929939 [35] Wang C, Li S J. CoRankBayes: Bayesian learning to rank under the co-training framework and its application in keyphrase extraction. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Glasgow, Scotland, UK: ACM, 2011. 2241-2244 [36] Freund Y, Iyer R, Schapire R E, Singer Y. An efficient boosting algorithm for combining preferences. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003, 4:933-969 doi: 10.1162-jmlr.2003.4.6.933/ [37] Xu J, Li H. Adarank: a boosting algorithm for information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ACM, 2007. 391-398 [38] Wu Q, Burges C J C, Svore K M, Gao J F. Adapting boosting for information retrieval measures. Information Retrieval, 2010, 13(3):254-270 doi: 10.1007/s10791-009-9112-1 [39] Burges C J C. From RankNet to LambdaRank to LambdaMART: An Overview, Technical Report MSR-TR-2010-82, Microsoft Research, USA, 2010 [40] Capannini G, Lucchese C, Nardini F M, Orlando S, Perego R, Tonellotto N. Quality versus efficiency in document scoring with learning-to-rank models. Information Processing & Management, 2016, 52(6):1161-1177 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/ipm/ipm52.html#CapanniniLNOPT16 [41] Lucchese C, Nardini F M, Orlando S, Perego R, Trani S. X-DART: blending dropout and pruning for efficient learning to rank. In: Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan: ACM, 2017. 1077-1080 [42] Chen K K, Bai J, Zheng Z H. Ranking function adaptation with boosting trees. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2011, 29(4):Article No.18 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=2037661.2037663 [43] Kocsis L, György A, Bán A N. BoostingTree:parallel selection of weak learners in boosting, with application to ranking. Machine Learning, 2013, 93(2-3):293-320 doi: 10.1007/s10994-013-5364-5 [44] Asadi N, Lin J, De Vries A P. Runtime optimizations for tree-based machine learning models. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2014, 26(9):2281-2292 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2013.73 [45] Dato D, Lucchese C, Nardini F M, Orlando S, Perego R, Tonellotto N, et al. Fast ranking with additive ensembles of oblivious and non-oblivious regression trees. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2016, 35(2):Article No.15 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/tois/tois35.html#DatoLNOPTV16 [46] Lucchese C, Nardini F M, Orlando S, Perego R, Silvestri F, Trani S. Post-Learning optimization of tree ensembles for efficient ranking. In: Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Pisa, Italy: ACM, 2016. 949-952 [47] Mohan A, Chen Z, Weinberger K Q. Web-search ranking with initialized gradient boosted regression trees. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Yahoo! Learning to Rank Challenge. Haifa, Israel: JMLR, 2011. 77-89 [48] de Sá C C, Gonçalves M A, Sousa D X, Salles T. Generalized BROOF-L2R: a general framework for learning to rank based on boosting and random forests. In: Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Pisa, Italy: ACM, 2016. 95-104. [49] Ibrahim M, Carman M. Comparing pointwise and listwise objective functions for random-forest-based learning-to-rank. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2016, 34(4):Article No.20 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/tois/tois34.html#IbrahimC16 [50] Yeh J Y, Lin J Y, Ke H R, Yang W P. Learning to rank for information retrieval using genetic programming. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGIR 2007 Workshop on Learning to Rank for Information Retrieval. Amsterdam, Netherlands: ACM, 2007. 41-48 [51] Lin J Y, Yeh J Y, Liu C C. Learning to rank for information retrieval using layered multi-population genetic programming. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Cybernetics. Bali, Indonesia: IEEE, 2012. 45-49 [52] Keyhanipour A H, Moshiri B, Oroumchian F, Rahgozar M, Badie K. Learning to rank:new approach with the layered multi-population genetic programming on click-through features. Genetic Programming and Evolvable Machines, 2016, 17(3):203-230 doi: 10.1007/s10710-016-9263-y [53] Wang S Q, Ma J, Liu J M. Learning to rank using evolutionary computation: immune programming or genetic programming? In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Hong Kong, China: ACM, 2009. 1879-1882 [54] He Q, Ma J, Wang S Q. Directly optimizing evaluation measures in learning to rank based on the clonal selection algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Toronto, ON, Canada: ACM, 2010. 1449-1452 [55] Diaz-Aviles E, Nejdl W, Schmidt-Thieme L. Swarming to rank for information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. Montreal, Québec, Canada: ACM, 2009. 9-16 [56] Alejo Ó, Fernández-Luna J M, Huete J F, Pérez-Vázquez R. Direct optimization of evaluation measures in learning to rank using particle swarm. In: Proceedings of the 2010 Workshops on Database and Expert Systems Applications. Bilbao, Spain: IEEE, 2010. 42-46 [57] Bollegala D, Noman N, Iba H. Rankde: learning a ranking function for information retrieval using differential evolution. In: Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. Dublin, Ireland: ACM, 2011. 1771-1778 [58] Wang S Q, Wu Y, Gao B J, Wang K, Lauw H W, Ma J. A cooperative coevolution framework for parallel learning to rank. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 27(12):3152-3165 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2015.2453952 [59] Ibrahim O A S, Landa-Silva D. ES-Rank: evolution strategy learning to rank approach. In: Proceedings of the 32nd ACM Symposium on Applied Computing. Marrakech, Morocco: ACM, 2017. 944-950 [60] Tian Y L, Zhang H X. Research on B cell algorithm for learning to rank method based on parallel strategy. PLoS One, 2016, 11(8):Article No. e0157994 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157994 [61] Li J Z, Liu G J, Yan C G, Jiang C J. Robust learning to rank based on portfolio theory and AMOSA algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2017, 47(6):1007-1018 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2584786 [62] Moschitti A. Kernel-based learning to rank with syntactic and semantic structures. In: Proceedings of the 36th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Dublin, Ireland: ACM, 2013. 1128-1128. [63] Ailon N, Mohri M. Preference-based learning to rank. Machine Learning, 2010, 80(2-3):189-211 doi: 10.1007/s10994-010-5176-9 [64] Zhou K, Bai J, Zha H Y, Xue G R. Leveraging auxiliary data for learning to rank. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2012, 3(2):Article No.37 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/tist/tist3.html#ZhouBZX12 [65] Macdonald C, Santos R L T, Ounis I. The whens and hows of learning to rank for web search. Information Retrieval, 2013, 16(5):584-628 doi: 10.1007/s10791-012-9209-9 [66] Lai H J, Pan Y, Liu C, Lin L, Wu J. Sparse learning-to-rank via an efficient primal-dual algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2013, 62(6):1221-1233 doi: 10.1109/TC.2012.62 [67] Lai H J, Pan Y, Tang Y, Yu R. FSMRank:feature selection algorithm for learning to rank. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2013, 24(6):940-952 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2247628 [68] Ma Q L, He B, Xu J Q. Direct measurement of training query quality for learning to rank. In: Proceedings of the 31st Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing. Pisa, Italy: ACM, 2016. 1035-1040 [69] Wang X H, Bendersky M, Metzler D, Najork M. Learning to rank with selection bias in personal search. In: Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Pisa, Italy: ACM, 2016. 115-124 [70] Wu O, You Q, Mao X, Xia F, Yuan F, Hu W M. Listwise learning to rank by exploring structure of objects. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2016, 28(7):1934-1939 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2016.2535214 [71] Joachims T, Swaminathan A, Schnabel T. Unbiased learning-to-rank with biased feedback. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. Cambridge, UK: ACM, 2017. 781-789 [72] Calumby R T, Gonçalves M A, da Silva Torres R. On interactive learning-to-rank for IR:overview, recent advances, challenges, and directions. Neurocomputing, 2016, 208:3-24 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.03.084 [73] Qin T, Liu T Y, Xu J, Li H. LETOR:a benchmark collection for research on learning to rank for information retrieval. Information Retrieval, 2010, 13(4):346-374 doi: 10.1007/s10791-009-9123-y [74] Alcântara O D A, Pereira J Á R Jr, de Almeida H M, Gonçalves M A, Middleton C, Baeza-Yates R. WCL2R:a benchmark collection for Learning to rank research with clickthrough data. Journal of Information and Data Management, 2010, 1(3):551-566 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/jidm/jidm1.html#AlcantaraPAGMB10 [75] Zhang M, Kuang D, Hua G C, Liu Y Q, Ma S P. Is learning to rank effective for Web search? In:Proceedings of SIGIR 2008 Workshop:Learning to Rank for Information Retrieval. Boston, US:ACM, 2009. 641-647 [76] Macdonald C, Dinçer B T, Ounis I. Transferring learning to rank models for web search. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on the Theory of Information Retrieval. Northampton, Massachusetts, USA: ACM, 2015. 41-50 [77] Kang C S, Yin D W, Zhang R Q, Torzec N, He J Z, Chang Y. Learning to rank related entities in web search. Neurocomputing, 2015, 166:309-318 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.004 [78] Karatzoglou A, Baltrunas L, Shi Y. Learning to rank for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems. Hong Kong, China: ACM, 2013. 493-494 [79] Sun J K, Wang S Q, Gao B J, Ma J. Learning to rank for hybrid recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Maui, Hawaii, USA: ACM, 2012. 2239-2242 [80] Yao W L, He J, Huang G Y, Zhang Y C. SoRank: incorporating social information into learning to rank models for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web. Seoul, South Korea: ACM, 2014. 409-410 [81] Canuto S D, Belém F M, Almeida J M, Gonçalves M A. A comparative study of learning-to-rank techniques for tag recommendation. Journal of Information and Data Management, 2013, 4(3):453-468 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/jidm/jidm4.html#CanutoBAG13 [82] Ifada N, Nayak R. How relevant is the irrelevant data: leveraging the tagging data for a learning-to-rank model. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. San Francisco, California, USA: ACM, 2016. 23-32. [83] 黄震华, 张佳雯, 田春岐, 孙圣力, 向阳.基于排序学习的推荐算法研究综述.软件学报, 2016, 27(3):691-713 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb201603014Huang Zhen-Hua, Zhang Jia-Wen, Tian Chun-Qi, Sun Sheng-Li, Xiang Yang. Survey on learning-to-rank based recommendation algorithms. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(3):691-713 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb201603014 [84] Berendsen R, Tsagkias M, Weerkamp W, de Rijke M. Pseudo test collections for training and tuning microblog rankers. In: Proceedings of the 36th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Dublin, Ireland: ACM, 2013. 53-62 [85] Dong A L, Zhang R Q, Kolari P, Bai J, Diaz F, Chang Y, et al. Time is of the essence: improving recency ranking using twitter data. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web. Raleigh, North Carolina, USA: ACM, 2010. 331-340 [86] Duan Y J, Jiang L, Qin T, Zhou M, Shum H Y. An empirical study on learning to rank of tweets. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Beijing, China: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2010. 295-303 [87] Chelaru S, Orellana-Rodriguez C, Altingovde I S. How useful is social feedback for learning to rank YouTube videos? World Wide Web, 2014, 17(5):997-1025 doi: 10.1007/s11280-013-0258-9 [88] Yu J, Tao D C, Wang M, Rui Y. Learning to rank using user clicks and visual features for image retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(4):767-779 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2336697 [89] Zhao X Y, Li X, Zhang Z F. Multimedia retrieval via deep learning to rank. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(9):1487-1491 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2410134 [90] Karaoglu S, Liu Y, Gevers T. Detect2rank:combining object detectors using learning to rank. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(1):233-248 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2499702 [91] Wang J, Wang Z, Gao C X, Sang N, Huang R. DeepList:learning deep features with adaptive listwise constraint for person reidentification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(3):513-524 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2586851 [92] Volkovs M N, Larochelle H, Zemel R S. Learning to rank by aggregating expert preferences. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Maui, Hawaii, USA: ACM, 2012. 843-851 [93] Moreira C, Calado P, Martins B. Learning to rank academic experts in the DBLP dataset. Expert Systems, 2015, 32(4):477-493 doi: 10.1111/exsy.v32.4 [94] Zheng H T, Li Q, Jiang Y, Xia S T, Zhang L S. Exploiting multiple features for learning to rank in expert finding. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications. Hangzhou, China: Springer, 2013. 219-230 [95] Chen F Q, Yu Z T, Wu Z J, Mao C L, Zhang Y M. Expert ranking method based on ListNet with multiple features. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2014, 23(2):240-247 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjlgdxxb-e201402016 [96] Delpech E, Daille B, Morin E, Lemaire C. Extraction of domain-specific bilingual lexicon from comparable corpora: compositional translation and ranking. arXiv: 1210. 5751, 2012. [97] Li M X, Jiang A W, Wang M W. Listwise approach to learning to rank for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 14th Machine Translation Summit. Nice, France: The European Association for Machine Translation, 2013. 51-59 [98] Lee J Y, Hong G, Rim H C, Song Y I, Hwang Y. Predicate-argument reordering based on learning to rank for English-Korean machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication. Seoul, South Korea: ACM, 2011. Article No. 2 [99] Farzi S, Faili H. Improving statistical machine translation using syntax-based learning-to-rank system. Digital Scholarship in the Humanities, 2017, 32(1):80-100 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/lalc/lalc32.html#FarziF17 [100] Wu H C, Wu W, Zhou M, Chen E H, Duan L, Shum H Y. Improving search relevance for short queries in community question answering. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York, USA: ACM, 2014. 43-52 [101] Nguyen M T, Phan V A, Nguyen T S, Nguyen M L. Learning to rank questions for community question answering with ranking SVM. arXiv: 1608. 04185, 2016. [102] Verberne S, van Halteren H, Theijssen D L, Raaijmakers S, Boves L. Learning to rank for why-question answering. Information Retrieval, 2011, 14(2):107-132 doi: 10.1007/s10791-010-9136-6 [103] Ciaramita M, Murdock V, Plachouras V. Online learning from click data for sponsored search. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on World Wide Web. Beijing, China: ACM, 2008. 227-236 [104] Tagami Y, Ono S, Yamamoto K, Tsukamoto K, Tajima A. CTR prediction for contextual advertising: Learning-to-rank approach. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Data Mining for Online Advertising. Chicago, Illinois, USA: ACM, 2013. Article No. 4 [105] Karimzadehgan M, Li W, Zhang R F, Mao J C. A stochastic learning-to-rank algorithm and its application to contextual advertising. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web. Hyderabad, India: ACM, 2011. 377-386 [106] Shen C, Li T. Learning to rank for query-focused multi-document summarization. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Data Mining. Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2011. 626-634 [107] Zhu Y D, Lan Y Y, Guo J F, Du P, Cheng X Q. A novel relational learning-to-rank approach for topic-focused multi-document summarization. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Data Mining. Dallas, TX, USA: IEEE, 2013. 927-936 [108] Tran T A, Niederee C, Kanhabua N, Gadiraju U, Anand A. Balancing novelty and salience: adaptive learning to rank entities for timeline summarization of high-impact events. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Melbourne, Australia: ACM, 2015. 1201-1210. [109] Tran G B, Tran T A, Tran N K, Alrifai M, Kanhabua N. Leveraging learning to rank in an optimization framework for timeline summarization. In: Proceedings of SIGIR 2013 Workshop on Time-aware Information Access. Dublin, Ireland: TAIA, 2013. 1-4 [110] Xu B, Lin H F, Lin Y. Assessment of learning to rank methods for query expansion. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 2016, 67(6):1345-1357 doi: 10.1002/asi.23476 [111] Lin Y, Lin H F, Jin S, Ye Z. Social annotation in query expansion: a machine learning approach. In: Proceedings of the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Beijing, China: ACM, 2011. 405-414 [112] Dang V, Bendersky M, Croft W B. Learning to rank query reformulations. In: Proceedings of the 33rd international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Geneva, Switzerland: ACM, 2010. 807-808 [113] Santos R L T, Macdonald C, Ounis I. Learning to rank query suggestions for adhoc and diversity search. Information Retrieval, 2013, 16(4):429-451 doi: 10.1007/s10791-012-9211-2 [114] Liu B, Chen J J, Wang X L. Application of learning to rank to protein remote homology detection. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(21):3492-3498 doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv413 [115] Chen J J, Guo M Y, Li S M, Liu B. ProtDec-LTR2.0:an improved method for protein remote homology detection by combining pseudo protein and supervised Learning to Rank. Bioinformatics, 2017, 33(21):3473-3476 doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx429 [116] Shang Y, Hao H H, Wu J J, Lin H F. Learning to rank-based gene summary extraction. BMC Bioinformatics, 2014, 15(S12):Article No.S10 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/bmcbi/bmcbi15S.html#ShangHWL14 [117] Jing X Y, Dong Q W. MQAPRank:improved global protein model quality assessment by learning-to-rank. BMC Bioinformatics, 2017, 18(1):Article No.275 doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1691-z [118] Saleem M S, Ding C, Liu X M, Chi C H. Personalized decision-strategy based web service selection using a learning-to-rank algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2015, 8(5):727-739 doi: 10.1109/TSC.2014.2377724 [119] Deveaud R, Mothe J, Nia J Y. Learning to rank system configurations. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. Indianapolis, Indiana, USA: ACM, 2016. 2001-2004 [120] Zhou M W, Wang H N, Change K C C. Learning to rank from distant supervision: exploiting noisy redundancy for relational entity search. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Data Engineering. Brisbane, QLD, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 829-840 [121] Chen N, Prasanna V K. Learning to rank complex semantic relationships. International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems, 2012, 8(4):1-19 doi: 10.4018/IJSWIS [122] Kong L L, Lu Z M, Han Z Y, Qi H L. A ranking approach to source retrieval of plagiarism detection. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2017, E100.D(1):203-205 doi: 10.1587/transinf.2016EDL8090 [123] Alejo Ó J, Fernández-Luna J M, Huete J F, Moreno-Cerrud E. L2RLab: integrated experimenter environment for learning to rank. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Flexible Query Answering Systems. Granada, Spain: Springer, 2013. 543-554 [124] Chapelle O, Chang Y, Liu T Y. Future directions in learning to rank. JMLR:Workshop and Conference Proceedings, 2011, 14:91-100 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0224630477 [125] 王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 林懿伦, 郑心湖, 王飞跃.生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望.自动化学报, 2017, 43(3):321-332 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19012.shtmlWang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Duan Yan-Jie, Lin Yi-Lun, Zheng Xin-Hu, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative adversarial networks:the state of the art and beyond. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3):321-332 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19012.shtml [126] Li H, Lu Z D. Deep learning for information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Pisa, Italy: ACM, 2016. 1203-1206 [127] 奚雪峰, 周国栋.面向自然语言处理的深度学习研究.自动化学报, 2016, 42(10):1445-1465 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18934.shtmlXi Xue-Feng, Zhou Guo-Dong. A survey on deep learning for natural language processing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10):1445-1465 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18934.shtml [128] 段艳杰, 吕宜生, 张杰, 赵学亮, 王飞跃.深度学习在控制领域的研究现状与展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):643-654 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18852.shtmlDuan Yan-Jie, Lv Yi-Sheng, Zhang Jie, Zhao Xue-Liang, Wang Fei-Yue. Deep learning for control:the state of the art and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):643-654 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18852.shtml [129] 朱煜, 赵江坤, 王逸宁, 郑兵兵.基于深度学习的人体行为识别算法综述.自动化学报, 2016, 42(6):848-857 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18875.shtmlZhu Yu, Zhao Jiang-Kun, Wang Yi-Ning, Zheng Bing-Bing. A review of human action recognition based on deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6):848-857 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18875.shtml [130] 管皓, 薛向阳, 安志勇.深度学习在视频目标跟踪中的应用进展与展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42(6):834-847 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18874.shtmlGuan Hao, Xue Xiang-Yang, An Zhi-Yong. Advances on application of deep learning for video object tracking. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6):834-847 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18874.shtml [131] Wang B Y, Klabjan D. An attention-based deep net for learning to rank. arXiv: 1702. 06106, 2017. [132] Severyn A, Moschitti A. Learning to rank short text pairs with convolutional deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Santiago, Chile: ACM, 2015. 373-382 [133] 程学旗, 兰艳艳.网络大数据的文本内容分析.大数据, 2015, 1(3):Article No.2015029 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=68837485504849534851484853Cheng Xue-Qi, Lan Yan-Yan. Text content analysis for web big data. Big Data Research, 2015, 1(3):Article No.2015029 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=68837485504849534851484853 [134] 李力, 林懿伦, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃.平行学习——机器学习的一个新型理论框架.自动化学报, 2017, 43(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.01.001Li Li, Lin Yi-Lun, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel learning——a new framework for machine learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.01.001 [135] Dinçer B T, Ounis I, Macdonald C. Tackling biased baselines in the risk-sensitive evaluation of retrieval systems. In: Proceedings of the 36th European Conference on IR. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2014. 26-38 [136] Dinçer B T, Macdonald C, Ounis I. Hypothesis testing for the risk-sensitive evaluation of retrieval systems. In: Proceedings of the 37th international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval. Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia: ACM, 2014. 23-32 [137] Dinçer B T, Macdonald C, Ounis I. Risk-sensitive evaluation and learning to rank using multiple baselines. In: Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Pisa, Italy: ACM, 2016. 483-492. [138] Ding W K, Geng X B, Zhang X D. Learning to rank from noisy data. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2015, 7(1):Article No.1 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_1312.2159 [139] Liang S Q, Ren Z C, de Rijke M. Fusion helps diversification. In: Proceedings of the 37th international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval. Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia: ACM, 2014. 303-312 [140] Liang S S, Cai F, Ren Z C, de Rijke M. Efficient structured learning for personalized diversification. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2016, 28(11):2958-2973 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2016.2594064 [141] Wu S L, Huang C L. Search result diversification via data fusion. In: Proceedings of the 37th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval. Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia: ACM, 2014. 827-830 [142] Deng T, Fan W F. On the complexity of query result diversification. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2013, 6(8):577-588 doi: 10.14778/2536354 [143] Xu J, Xia L, Lan Y Y, Guo J F, Cheng X Q. Directly optimize diversity evaluation measures:a new approach to search result diversification. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2017, 8(3):Article No. 41 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=2983921 [144] Zhu Y D, Lan Y Y, Guo J F, Cheng X Q, Niu S Z. Learning for search result diversification. In: Proceedings of the 37th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval. Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia: ACM, 2014. 293-302 [145] 徐君, 兰艳艳.多样化——排序学习发展的新方向.中国计算机学会通讯, 2016, 12(7):50-52Xu Jun, Lan Yan-Yan. Search result diversification:a new direction of research on learning to rank. Communications of the CCF, 2016, 12(7):50-52 [146] Dai N, Shokouhi M, Davison B D. Multi-objective optimization in learning to rank. In: Proceedings of the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Beijing, China: ACM, 2011. 1241-1242 [147] Svore K M, Volkovs M, Burges C J C. Learning to rank with multiple objective functions. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web. Hyderabad, India: ACM, 2011. 367-376 [148] Kang C S, Wang X H, Chang Y, Tseng B. Learning to rank with multi-aspect relevance for vertical search. In:Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. Seattle, Washington, USA:ACM, 2012. 453-462 [149] Wang L D, Lin J, Metzler D, Han J W. Learning to efficiently rank on big data. In:Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web. Seoul, South Korea:ACM, 2014. 209-210 [150] Cao G Q, Ahmad I, Zhang H L, Xie W Y, Gabbouj M. Balance learning to rank in big data. In:Proceedings of the 22nd European Signal Processing Conference. Lisbon, Portugal:IEEE, 2014. 1422-1426 [151] Sculley D. Large scale learning to rank. In:Proceedings of 2009 NIPS Workshop on Advances in Ranking. La Jolla, CA, USA:NIPS, 2009. 58-63 [152] Shukla S, Lease M, Tewari A. Parallelizing ListNet training using spark. In:Proceedings of the 35th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Portland, Oregon, USA:ACM, 2012. 1127-1128 [153] Grotov A, de Rijke M. Online Learning to rank for information retrieval:SIGIR 2016 tutorial. In:Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Pisa, Italy:ACM, 2016. 1215-1218 [154] Suhara Y, Suzuki J, Kataoka R. Robust online learning to rank via selective pairwise approach based on evaluation measures. Information and Media Technologies Editorial Board, 2013, 8(1):118-129 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/130003366920 [155] Hofmann K, Whiteson S, de Rijke M. Balancing exploration and exploitation in listwise and pairwise online learning to rank for information retrieval. Information Retrieval, 2013, 16(1):63-90 doi: 10.1007/s10791-012-9197-9 [156] Chen Y W, Hofmann K. Online Learning to rank:absolute vs. relative. In:Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web. Florence, Italy:ACM, 2015. 19-20 [157] Schuth A, Oosterhuis H, Whiteson S, de Rijke M. Multileave gradient descent for fast online learning to rank. In:Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. San Francisco, California, USA:ACM, 2016. 457-466 [158] Keyhanipour A H, Moshiri B, Piroozmand M, Oroumchian F, Moeini A. Learning to rank with click-through features in a reinforcement learning framework. International Journal of Web Information Systems, 2016, 12(4):448-476 doi: 10.1108/IJWIS-12-2015-0046 -




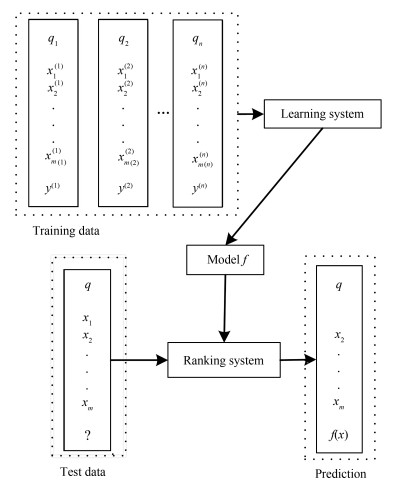
 下载:
下载: