Pan-sharpening Model on Account of Edge Enhancement and Spectral Signature Preservation
-
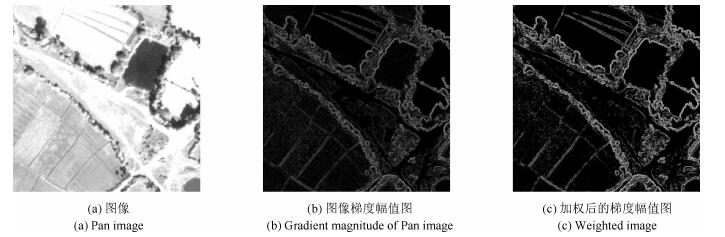
摘要: 为生成兼具高光谱质量与高空间质量的融合图像,本文提出了一种新的Pan-sharpening变分融合模型.通过拟合退化后的全色(Panchromatic,Pan)波段图像与低分辨率多光谱(Multispectral,MS)波段图像间的线性关系得到各波段MS图像的权重系数,计算从Pan图像抽取的空间细节;基于全色波段图像的梯度定义加权函数,增强了图像的强梯度边缘并对因噪声而引入的虚假边缘进行了抑制,有效地保持了全色波段图像中目标的几何结构;基于MS波段传感器的调制传输函数定义低通滤波器,自适应地限制注入空间细节的数量,显著降低了融合MS图像的光谱失真;针对Pan-sharpening模型的不适定性问题,引入L1正则化能量项,保证了数值解的稳定性.采用Split Bregman数值方法求解能量泛函的最优解,提高了算法的计算效率.QuickBird、IKONOS和GeoEye-1数据集上的实验结果表明,模型的综合融合性能优于MTF-CON、AWLP、SparseFI、TVR和MTF-Variational等算法.
-
关键词:
- 全色与多光谱图像融合 /
- 变分方法 /
- 调制传输函数 /
- 边缘增强
Abstract: In order to provide a multispectral (MS) image with both high spectral and spatial qualities, a novel pan-sharpening model is proposed based on the variational method. The weight coefficients of MS bands are obtained by linear regression of the degraded panchromatic (Pan) and the original MS images. After that the spatial details are extracted from the Pan image and are injected into the MS image. The weight function is defined to enhance the strong edges with the gradient of the Pan image and suppress the false edges caused by image noise, so as to reserve the geometrics structure of the Pan image effectively. A low-pass filter is developed with the modulation transfer function (MTF) of the multispectral band sensors, which restrains the number of spatial details merged into MS images adaptively and reduces the spectral distortion of fused MS images. To deal with the ill-posed problem formulated by fusion operation, the L1 regularization term is introduced into the variational framework to ensure the stability of the numerical solution. The split Bregman method, which can improve computational efficiency, is used to acquire the optimization solution of the energy functional. The experimental results on QuickBird/IKONOS/GeoEye-1 datasets demonstrate that the proposed model can achieve competitive fusion performances in comparison with MTF-CON, AWLP, SparseFI, TVR and MTF-Variational methods.1) 本文责任编委 贾云得 -
表 1 IKONOS、QuickBird和GeoEye-1中的权重系数
Table 1 The Weight coefficient of IKONOS, QuickBird, and GeoEye-1
${\alpha _1}$ ${\alpha _2}$ ${\alpha _3}$ ${\alpha _4}$ IKONOS 0.4099 $-$0.0436 0.1154 0.4832 QUICKBIRD 0.2361 0.1593 $-$0.0143 0.6238 GeoEye-1 0.3787 0.1248 0.2304 0.2886 表 2 IKONOS、QuickBird和GeoEye-1在Nyquist频率处的MTF值
Table 2 MTF gains at Nyquist cutoff frequency
${B}$ ${G}$ ${R}$ NIR PAN IKONOS 0.27 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.17 QUICKBIRD 0.34 0.32 0.30 0.22 0.15 GeoEye-1 0.33 0.36 0.40 0.34 0.16 表 3 QuickBird融合结果定量评价
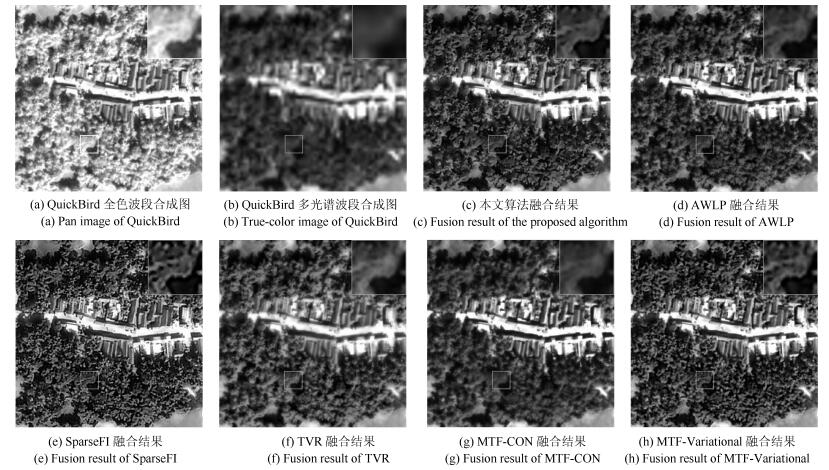
Table 3 Quality assessment of the fused images for QuickBird dataset
${sCC}$ ${ERGAS}$ ${SAM}$ ${QNR}$ ${D_\lambda}$ ${D_s}$ MTF-CON 0.9074 1.1001 1.3404 0.7960 0.1286 0.0865 SparseFI 0.9016 1.2000 1.3428 0.8800 0.0692 0.0545 AWLP 0.9364 1.1306 1.3596 0.8002 0.1248 0.0857 TVR 0.9360 1.4574 1.5448 0.8712 0.0538 0.0793 MTF-Variational 0.9701 0.9920 1.1124 0.8428 0.0925 0.0713 本文方法 0.9564 0.9695 1.0853 0.8816 0.0696 0.0525 表 4 IKONOS融合结果定量评价
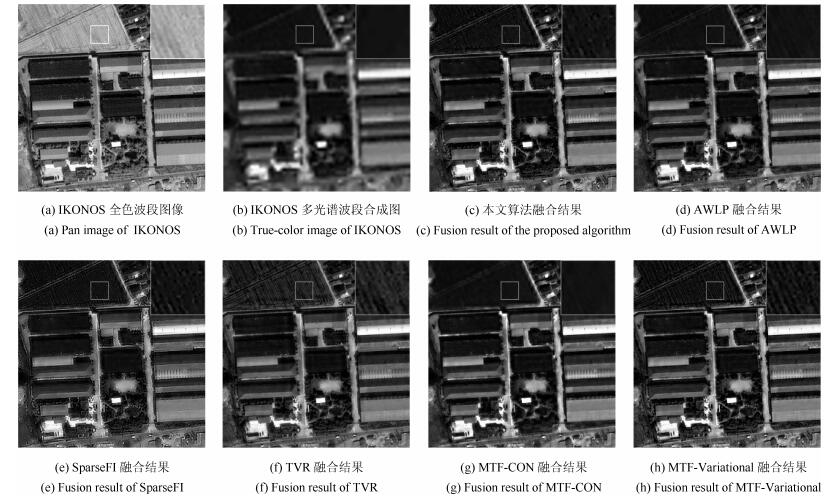
Table 4 Quality assessment of the fused images for IKONOS dataset
${sCC}$ ${ERGAS}$ ${SAM}$ ${QNR}$ ${D_\lambda}$ ${D_s}$ MTF-CON 0.9196 3.4550 4.4411 0.7970 0.0998 0.1146 SparseFI 0.9465 4.0197 4.3311 0.8274 0.0747 0.1058 AWLP 0.9461 3.5247 4.3598 0.8125 0.0838 0.1131 TVR 0.9886 4.3916 4.9391 0.7775 0.0819 0.1531 MTF-Variational 0.9843 3.3412 3.8671 0.7994 0.0880 0.1234 本文方法 0.9613 3.2632 3.6353 0.8432 0.0619 0.1012 表 5 GeoEye-1融合结果定量评价
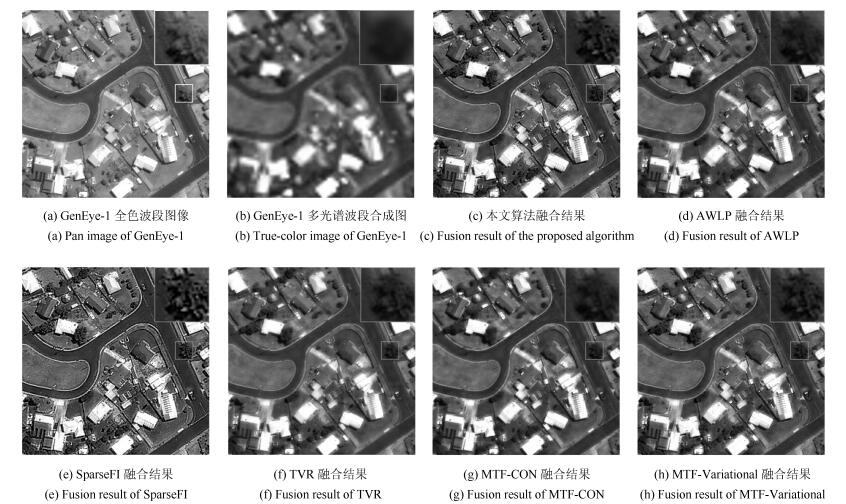
Table 5 Quality assessment of the fused images for GeoEye-1 dataset
${sCC}$ ${ERGAS}$ ${SAM}$ ${QNR}$ ${D_\lambda}$ ${D_s}$ MTF-CON 0.9282 2.0588 2.3398 0.8009 0.1162 0.0938 SparseFI 0.9185 2.4023 2.6090 0.8932 0.0572 0.0526 AWLP 0.9465 1.9823 2.3003 0.8233 0.0986 0.0866 TVR 0.9854 2.4718 2.5682 0.8546 0.0685 0.0826 MTF-Variational 0.0.9827 1.8705 1.8881 0.8520 0.0788 0.0751 本文方法 0.9515 1.8289 1.7632 0.9100 0.0406 0.0515 表 6 不同植被区域融合结果定量分析
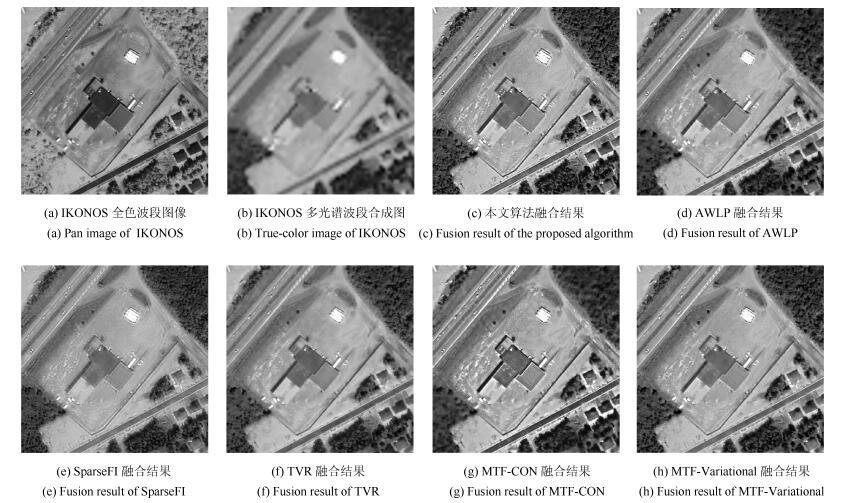
Table 6 Quality assessment of different areas of the fused images
$sCC$ ERGAS $SAM$ $QNR$ ${D_\lambda}$ ${D_s}$ 稀疏植被区域 MTF-CON 0.9147 2.5807 2.1891 0.6347 0.1598 0.2446 AWLP 0.9381 2.5409 2.1481 0.6914 0.1304 0.2049 SparseFI 0.8889 2.3891 1.8947 0.6945 0.1206 0.2103 TVR 0.9458 3.0313 2.5235 0.6096 0.2109 0.2275 MTF-Variational 0.9777 2.3864 1.9506 0.6842 0.1458 0.1990 本文方法 0.9725 2.3521 1.8318 0.7002 0.1122 0.2112 中等植被区域 MTF-CON 0.9008 2.6798 2.5738 0.7178 0.1187 0.1855 AWLP 0.9167 2.5791 2.5158 0.6894 0.1627 0.1767 SparseFI 0.9135 2.4626 2.2991 0.6942 0.1520 0.1814 TVR 0.9611 3.0606 2.8873 0.7503 0.1018 0.1647 MTF-Variational 0.9687 2.4408 2.2390 0.7424 0.1183 0.1580 本文方法 0.9755 2.4400 2.1686 0.7614 0.0883 0.1648 多植被区域 MTF-CON 0.8900 4.1248 4.6158 0.5766 0.2528 0.2283 AWLP 0.9602 4.0810 4.5489 0.5890 0.2396 0.2254 SparseFI 0.9575 4.0404 4.5037 0.7407 0.1304 0.1483 TVR 0.9857 4.7771 5.0041 0.6618 0.1589 0.2132 MTF-Variational 0.9664 4.1813 4.6367 0.7865 0.1043 0.1219 本文方法 0.9751 3.9230 3.7936 0.7879 0.1141 0.1106 -
[1] Vivone G, Alparone L, Chanussot J, Dalla Mura M, Garzelli A, Licciardi G A, Restaino R, Wald L. A critical comparison among pansharpening algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(5):2565-2586 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2361734 [2] Ghassemian H. A review of remote sensing image fusion methods. Information Fusion, 2016, 32:75-89 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.03.003 [3] Carper W J, Lillesand T M, Kiefer R W. The use of intensity-hue-saturation transformations for merging SPOT panchromatic and multispectral image data. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1990, 56(4):459-467 [4] Dehnavi S, Mohammadzadeh A. New edge adaptive GIHS-BT-SFIM fusion method and class-based approach investigation. International Journal of Image and Data Fusion, 2015, 6(1):65-78 doi: 10.1080/19479832.2014.959566 [5] Chavez Jr P S, Kwarteng A Y. Extracting spectral contrast in Landsat Thematic Mapper image data using selective principal component analysis. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1989, 55(3):339-348 [6] Li L J, Liu S G, Peng Y L, Sun Z G. Overview of principal component analysis algorithm. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016, 127(9):3935-3944 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.01.033 [7] Leung Y, Liu J M, Zhang J S. An improved adaptive intensity-hue-saturation method for the fusion of remote sensing images. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(5):985-989 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2284282 [8] Shah V P, Younan N H, King R L. An efficient pan-sharpening method via a combined adaptive PCA approach and contourlets. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(5):1323-1335 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.916211 [9] Vivone G, Restaino R, Dalla Mura M, Licciardi G, Chanussot J. Contrast and error-based fusion schemes for multispectral image pansharpening. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(5):930-934 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2281996 [10] Aiazzi B, Alparone L, Baronti S, Garzelli A. Context-driven fusion of high spatial and spectral resolution images based on oversampled multiresolution analysis. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(10):2300-2312 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803623 [11] 贺康建, 金鑫, 聂仁灿, 周冬明, 王佺, 余介夫.基于简化脉冲耦合神经网络与拉普拉斯金字塔分解的彩色图像融合.计算机应用, 2016, 36(S1):133-137 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyy2016z1034He Kang-Jian, Jin Xin, Nie Ren-Can, Zhou Dong-Ming, Wang Quan, Yu Jie-Fu. Color image fusion based on simplified PCNN and Laplace pyramid decomposition. Journal of Computer Applications, 2016, 36(S1):133-137 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyy2016z1034 [12] Aiazzi B, Alparone L, Baronti S, Garzelli A. Context-driven fusion of high spatial and spectral resolution images based on oversampled multiresolution analysis. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(10):2300-2312 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803623 [13] Wang X H, Shen Y T, Zhou Z G, Fang L L. An image fusion algorithm based on lifting wavelet transform. Journal of Optics, 2015, 17(5): Article No.055702 [14] 苗启广, 王宝树.基于改进的拉普拉斯金字塔变换的图像融合方法.光学学报, 2007, 27(9):1605-1610 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2007.09.013Miao Qi-Guang, Wang Bao-Shu. Multi-sensor image fusion based on improved Laplacian pyramid transform. Acta Optica Sinica, 2007, 27(9):1605-1610 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2007.09.013 [15] Otazu X, Gonzalez-Audicana M, Fors O, Nunez J. Introduction of sensor spectral response into image fusion methods. Application to wavelet-based methods. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(10):2376-2385 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.856106 [16] Zhang Q, Liu Y, Blum R S, Han J G, Tao D C. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images:a review. Information Fusion, 2018, 40:57-75 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.05.006 [17] Ghahremani M, Ghassemian H. A compressed-sensing-based pan-sharpening method for spectral distortion reduction. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4):2194-2206 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2497309 [18] 李奕, 吴小俊.香农熵加权稀疏表示图像融合方法研究.自动化学报, 2014, 40(8):1819-1835 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18449.shtmlLi Yi, Wu Xiao-Jun. Image fusion based on sparse representation using Shannon entropy weighting. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(8):1819-1835 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18449.shtml [19] Li S T, Yang B. A new pan-sharpening method using a compressed sensing technique. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2):738-746 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2067219 [20] Jiang C, Zhang H Y, Shen H F, Zhang L P. A practical compressed sensing-based pan-sharpening method. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4):629-633 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2177063 [21] Li S T, Yin H T, Fang L Y. Remote sensing image fusion via sparse representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(9):4779-4789 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2230332 [22] Zhu X X, Bamler R. A sparse image fusion algorithm with application to pan-sharpening. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5):2827-2836 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2213604 [23] Socolinsky D A, Wolff L B. Multispectral image visualization through first-order fusion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2002, 11(8):923-931 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2002.801588 [24] 马宁, 周则明, 张鹏, 罗立民.一种新的全色与多光谱图像融合变分模型.自动化学报, 2013, 39(2):179-187 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17866.shtmlMa Ning, Zhou Ze-Ming, Zhang Peng, Luo Li-Min. A new variational model for panchromatic and multispectral image fusion. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(2):179-187 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17866.shtml [25] 周雨薇, 杨平吕, 陈强, 孙权森.基于MTF和变分的全色与多光谱图像融合模型.自动化学报, 2015, 41 (2):342-352 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18613.shtmlZhou Yu-Wei, Yang Ping-Lv, Chen Qiang, Sun Quan-Sen. Pan-sharpening model based on MTF and variational method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(2):342-352 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18613.shtml [26] Palsson F, Sveinsson J R, Ulfarsson M O. A new pansharpening algorithm based on total variation. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1):318-322 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2257669 [27] Zhou Z M, Chen C Q, Meng Y, Hu B. Model-based variational fusion for reducing spectral distortion. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61: Article No.018102 [28] Khan M M, Alparone L, Chanussot J. Pansharpening quality assessment using the modulation transfer functions of instruments. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(11):3880-3891 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2029094 [29] Chu Y J, Mak C M. A new QR decomposition-based RLS algorithm using the split Bregman method for L1-regularized problems. Signal Processing, 2016, 128:303-308 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.04.013 [30] Jagalingam P, Hegde A V. A review of quality metrics for fused image. Aquatic Procedia, 2015, 4:133-142 doi: 10.1016/j.aqpro.2015.02.019 [31] Zhou J, Civco D L, Silander J A. A wavelet transform method to merge Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 19(4):743-757 doi: 10.1080/014311698215973 [32] Wald L. Quality of high resolution synthesised images: is there a simple criterion? In: Proceedings of the 3rd Conference "Fusion of Earth Data: Merging Point Measurements, Raster Maps and Remotely Sensed Images". Nice, France: SEE/URISCA, 2000. 99-103 [33] Choi M, Kim R Y, Nam M R, Kim H O. Fusion of multispectral and panchromatic satellite images using the curvelet transform. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2005, 2(2):136-140 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2005.845313 [34] Alparone L, Aiazzi B, Baronti S, Garzelli A, Nencini F, Selva M. Multispectral and panchromatic data fusion assessment without reference. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2008, 74(2):193-200 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ025012801/ [35] Wang Z, Bovik A C. A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2002, 9(3):81-84 doi: 10.1109/97.995823 -




 下载:
下载: