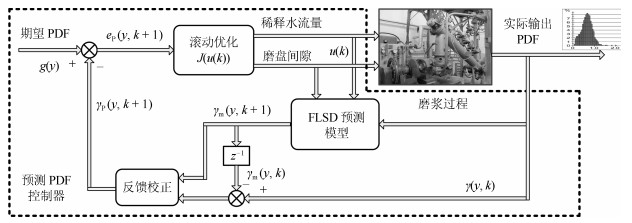
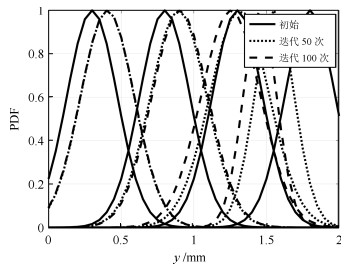
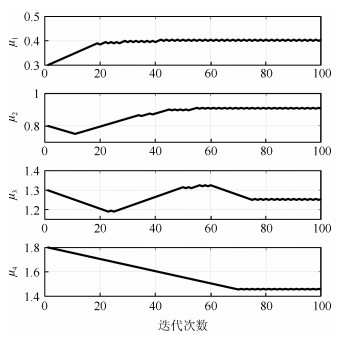
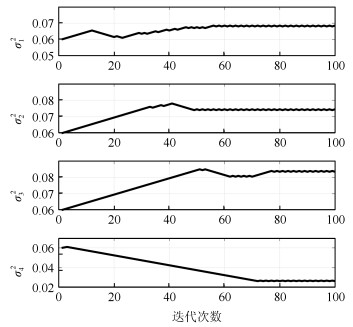
|
[1]
|
Smook G A. Handbook for Pulp and Paper Technologists. Vancouver:Angus Wilde Publications, 1992.
|
|
[2]
|
Sikter D, Karlström A, Sandberg C, Engstrand P. Economic perspectives on quality control in TMP refining processes. Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal, 2008, 23(3):305-314 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=56c4903ed68eeb5396ace5ee2e8162ef&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
|
[3]
|
Lama I, Perrier M, Stuart P. Controllability analysis of a TMP-newsprint refining process. Pulp & Paper Canada, 2006, 107(10):44-48 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4bd9d47cd5d2cadb4d3ae04bfd1de79b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
|
[4]
|
Karlström A, Hill J. Refiner optimization and control Part Ⅰ:fiber residence time and major dynamic fluctuations in TMP refining processes. Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal, 2014, 29(4):635-652
|
|
[5]
|
Harinath E, Biegler L T, Dumont G A. Control and optimization strategies for thermo-mechanical pulping processes:nonlinear model predictive control. Journal of Process Control, 2011, 21(4):519-528 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2011.01.009
|
|
[6]
|
Harinath E, Biegler L T, Dumont G A. Predictive optimal control for thermo-mechanical pulping processes with multi-stage low consistency refining. Journal of Process Control, 2013, 23(7):1001-1011 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2013.05.005
|
|
[7]
|
Gharehkhani S, Sadeghinezhad E, Kazi S N, Yarmanda H, Badarudina A, Safaei M R, Zubira M N M. Basic effects of pulp refining on fiber properties-a review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 115:785-803 doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.047
|
|
[8]
|
Lacerda T M, Zambon M D, Frollini E. Effect of acid concentration and pulp properties on hydrolysis reactions of mercerized sisal. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 93(1):347-356 doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.10.039
|
|
[9]
|
Savastano Jr H, Warden P G, Coutts R S P. Mechanically pulped sisal as reinforcement in cementitious matrices. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2003, 25(3):311-319 doi: 10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00055-0
|
|
[10]
|
Wang H. Bounded Dynamic Stochastic Distributions:Modelling and Control. London:Springer-Verlag, 2000.
|
|
[11]
|
王宏, 岳红.随机系统输出分布的建模、控制与应用.控制工程, 2003, 10(3):193-197 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7848.2003.03.001Wang Hong, Yue Hong. Output PDF control of stochastic distribution systems:modelling, control and applications. Control Engineering of China, 2003, 10(3):193-197 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7848.2003.03.001
|
|
[12]
|
Wang H. Robust control of the output probability density functions for multivariable stochastic systems with guaranteed stability. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1999, 41(11):2103-2107 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=52cd550278df6c8daa22810b321b98de
|
|
[13]
|
Wang H, Zhang J H. Bounded stochastic distributions control for pseudo-ARMAX stochastic systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2001, 46(3):486-490 doi: 10.1109/9.911429
|
|
[14]
|
Wang H. Minimum entropy control of non-Gaussian dynamic stochastic systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(2):398-403 doi: 10.1109/9.983388
|
|
[15]
|
Wang H, Afshar P. ILC-based fixed-structure controller design for output PDF shaping in stochastic systems using LMI techniques. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(4):760-773 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2009.2014934
|
|
[16]
|
Guo L, Wang H. PID controller design for output PDFs of stochastic systems using linear matrix inequalities. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2005, 35(1):65-71 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=388caf48dc43547ca83bb8c05cc5e252
|
|
[17]
|
Yue H, Zhou J L, Wang H. Minimum entropy of B-spline PDF systems with mean constraint. Automatica, 2006, 42(6):989-994 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.02.004
|
|
[18]
|
Zhou J L, Yue H, Zhang J F, Wang H. Iterative learning double closed-loop structure for modeling and controller design of output stochastic distribution control systems. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2014, 22(6):2261-2276 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2014.2306452
|
|
[19]
|
Wang A P, Afshar P, Wang H. Complex stochastic systems modelling and control via iterative machine learning. Neurocomputing, 2008, 71(13-15):2685-2692 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2007.06.018
|
|
[20]
|
Zhang J F, Yue H, Zhou J L. Predictive PDF control in shaping of molecular weight distribution based on a new modeling algorithm. Journal of Process Control, 2015, 30:80-89 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.12.009
|
|
[21]
|
Zhu J Y, Gui W H, Yang C H, Xu H L, Wang X L. Probability density function of bubble size based reagent dosage predictive control for copper roughing flotation. Control Engineering Practice, 2014, 29:1-12 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2014.02.021
|
|
[22]
|
Igelnik B, Pao Y H. Stochastic choice of basis functions in adaptive function approximation and the functional-link net. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1995, 6(6):1320-1329 doi: 10.1109/72.471375
|
|
[23]
|
Stosic D, Stosic D, Zanchettin C, Ludermir T, Stosic B. QRNN:q generalized random neural network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(2):383-390 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2513365
|
|
[24]
|
Zhou P, Lv Y B, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven robust RVFLNs modeling of a blast furnace iron-making process using Cauchy distribution weighted M-estimation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(9):7141-7151 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2686369
|
|
[25]
|
Lu X J, Zou W, Huang M H. A novel spatiotemporal LS-SVM method for complex distributed parameter systems with applications to curing thermal process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(3):1156-1165 doi: 10.1109/TII.2016.2557805
|
|
[26]
|
Zhou P, Chai T Y, Sun J. Intelligence-based supervisory control for optimal operation of a DCS-controlled grinding system. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2013, 21(1):162-175 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2182996
|
|
[27]
|
Zhou P, Lu S W, Chai T Y. Data-driven soft-sensor modeling for product quality estimation using case-based reasoning and fuzzy-similarity rough sets. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2014, 11(4):992-1003 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2013.2288279
|




 下载:
下载: