Dimensionality Reduction With Extreme Learning Machine Based on Sparsity and Neighborhood Preserving
-
摘要: 近邻与稀疏保持投影已被广泛应用于降维方法,通过优化得到满足近邻结构或稀疏结构的降维投影矩阵,然而这类方法多数只考虑单一结构特征.此外,多数非线性降维方法无法求出显式的映射函数,极大地限制了降维方法的应用.为克服这些问题,本文借鉴极限学习机的思想,提出面向聚类的基于稀疏和近邻保持的极限学习机降维算法(SNP-ELM).SNP-ELM算法是一种非线性无监督降维方法,在降维过程中同时考虑数据的稀疏结构与近邻结构.在人造数据、Wine数据和6个基因表达数据上进行实验,实验结果表明该算法优于其他降维方法.Abstract: Neighborhood and sparsity structure preserving projections have been widely used in dimensionality reduction, but most of them consider single structures. Moreover, existing nonlinear DR methods can not get an accurate projection function, which limits their applications. To overcome these problems, we propose a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method SNP-ELM by extending the extreme learning machine model. SNP-ELM is a nonlinear unsupervised dimensionlity reduction method, which takes both sparsity structure and neighborhood structure into account. The experimental results on toy data, wine data and six gene expression data show that our method significantly outperforms the compared dimensionality reduction methods.1) 本文责任编委 曾志刚
-
表 1 基因表达数据集描述
Table 1 Summary of gene expression data sets
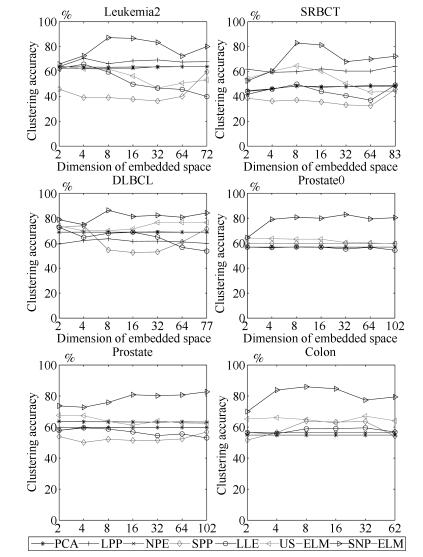
数据集 样本数 基因数(维数) 类别数 SRBCT 83 2 308 4 DLBCL 77 5 469 2 Prostate0 102 6 033 2 Prostate 102 10 509 2 Leukemia2 72 11 225 3 Colon 62 2 000 2 表 2 基因数据集上聚类准确率(%)
Table 2 Clustering accuracy comparison (variance) on gene expression data sets (%)
Data $k$-means PCA LPP NPE SPP LLE US-ELM
$(\lambda)$SNP-ELM
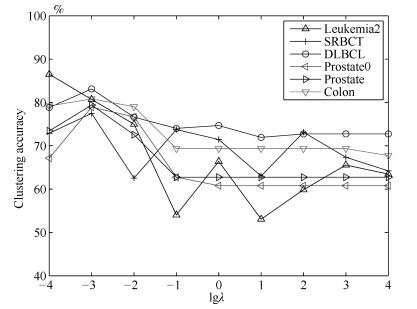
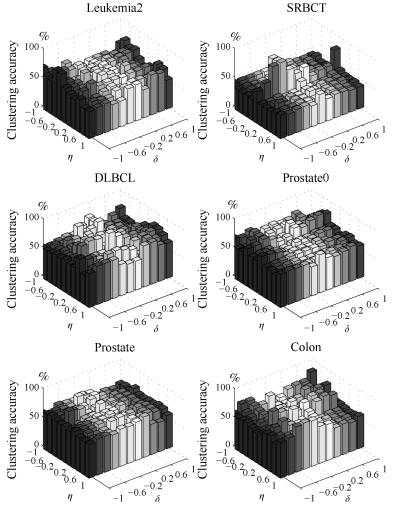
$(\lambda, \eta, \delta)$Leukemia2 63.89 63.89 70.72 63.89 59.72 65.83 64.44 87.17 (0.00) (0.00, 2) (3.20, 4) (0, 32) (0.00, 72) (6.65, 4) (1.34, 2) (3.56, 8) (0.0001) (0.0001, $-$1, $-$1) SRBCT 43.61 48.86 64.19 48.43 38.55 49.76 64.55 82.92 (6.27) (2.09, 83) (2.21, 83) (0.76, 8) (0.00, 2) (4.33, 8) (10.29, 8) (6.03, 8) (0.1) (0.001, $-$0.4, 0) DLBCL 68.83 68.83 63.55 69.09 74.02 72.23 76.62 86.34 (0.00) (0.00, 2) (1.86, 8) (0.82, 32) (0.00, 4) (0.00, 2) (0.00, 32) (1.78, 8) (0.0001) (0.001, 0.2, $-$0.6) Prostate0 56.86 56.83 56.86 56.86 59.80 56.96 64.09 82.92 (0.00) (0.00, 2) (0.00, 2) (0.00, 4) (0.00, 102) (0.93, 4) (5.83, 2) (2.19, 102) (0.01) (0.1, 0.2, 0.8) Prostate 63.33 63.73 59.80 59.80 56.86 59.51 67.57 82.73 (0.83) (0.00, 2) (0.00, 2) (0.00, 4) (0.00, 102) (0.93, 4) (5.83, 2) (2.19, 102) (0.0001) (1, $-$1, 0.6) Colon 54.84 54.84 54.84 56.45 64.19 59.52 67.06 85.95 (0.00) (0.00, 2) (0.00, 2) (0.00, 2) (0.68, 62) (6.99, 32) (4.19, 32) (3.69, 8) (0.0001) (0.001, $-$0.8, 1) -
[1] Jolliffe I T. Principal Component Analysis. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2002. [2] He X F, Niyogi P. Locality preserving projections. In: Proceedings of 2003 Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NIPS, 2004. 153-160 [3] He X F, Cai D, Yan S C, Zhang H J. Neighborhood preserving embedding. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005. 1208-1213 [4] Qiao L S, Chen S C, Tan X Y. Sparsity preserving projections with applications to face recognition. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(1):331-341 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.05.005 [5] Schölkopf B, Smola A J, Müller K R. Kernel principal component analysis. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Switzerland: Springer, 1997. 583-588 [6] Roweis S T, Saul K L. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science, 2010, 290(5500):2323-2326 doi: 10.1126-science.290.5500.2323/ [7] Huang G B, Ding X J, Zhou H M. Optimization method based extreme learning machine for classification. Neurocomputing, 2010, 74(1-3):155-163 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2010.02.019 [8] Peng Y, Wang S H, Long X Z, Lu B L. Discriminative graph regularized extreme learning machine and its application to face recognition. Neurocomputing, 2015, 149:340-353 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.12.065 [9] Peng Y, Lu B L. Discriminative manifold extreme learning machine and applications to image and EEG signal classification. Neurocomputing, 2016, 174:265-277 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.03.118 [10] Zhang K, Luo M X. Outlier-robust extreme learning machine for regression problems. Neurocomputing, 2015, 151:1519-1527 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.09.022 [11] Huang G, Song S J, Gupta J N D, Wu C. Semi-supervised and unsupervised extreme learning machines. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(12):2405-2417 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2307349 [12] 刘展杰, 陈晓云.局部子空间聚类.自动化学报, 2016, 42(8):1238-1247 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18913.shtmlLiu Zhan-Jie, Chen Xiao-Yun. Local subspace clustering. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(8):1238-1247 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18913.shtml [13] 王卫卫, 李小平, 冯象初, 王斯琪.稀疏子空间聚类综述.自动化学报, 2015, 41(8):1373-1384 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18712.shtmlWang Wei-Wei, Li Xiao-Ping, Feng Xiang-Chu, Wang Si-Qi. A survey on sparse subspace clustering. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(8):1373-1384 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18712.shtml [14] Kasun L L C, Yang Y, Huang G B, Zhang Z Y. Dimension reduction with extreme learning machine. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(8):3906-3918 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2570569 [15] Chen S S, Donoho D L, Saunders M A. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Review, 2001, 43(1):129-159 doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X [16] Yu L, Ding C, Loscalzo S. Stable feature selection via dense feature groups. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Las Vegas, USA: ACM, 2008. 803-811 [17] Gene expression model selector[online], available: http://www.gems-system.org, October 9, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: