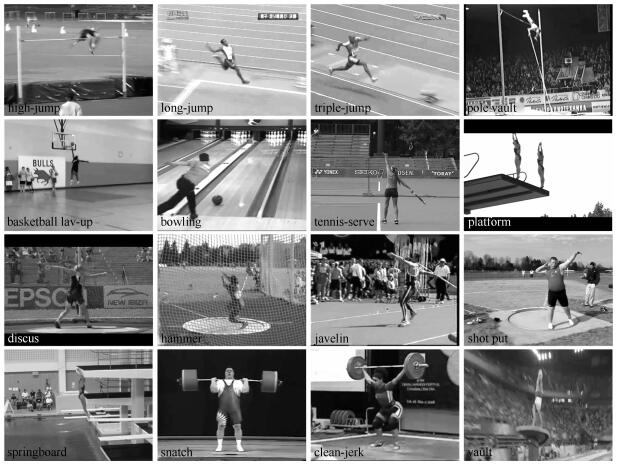
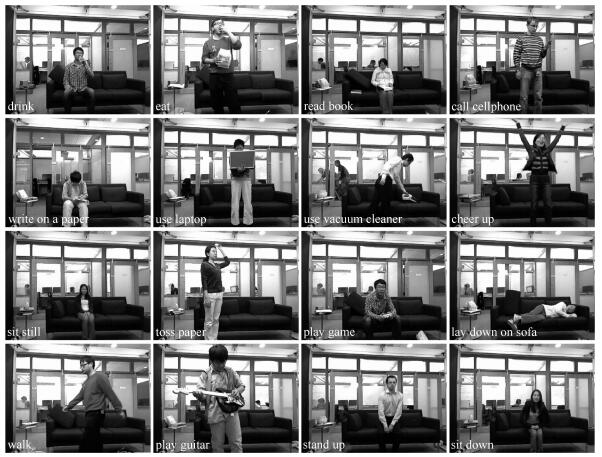
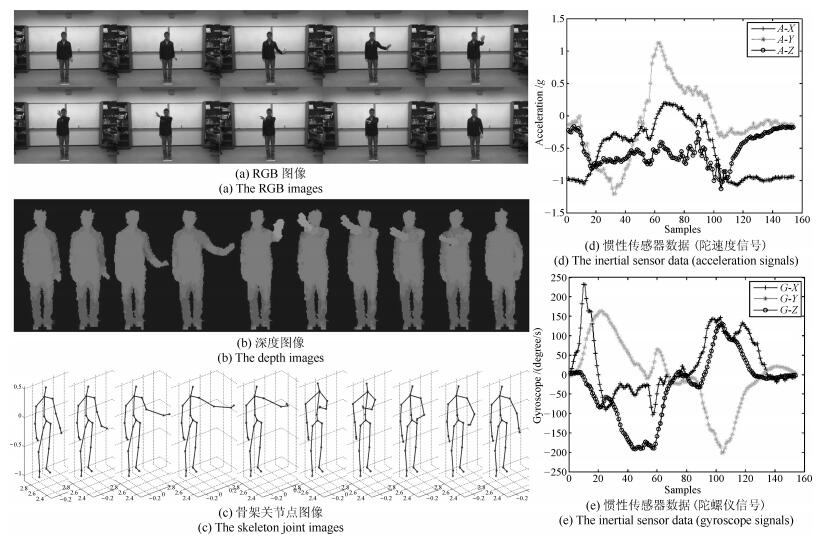
-
摘要: 人体行为识别是计算机视觉领域的一个研究热点,具有重要理论价值和现实意义.近年来,为了评价人体行为识别方法的性能,大量的公开数据集被创建.本文系统综述了人体行为识别公开数据集的发展与前瞻:首先,对公开数据集的层次与内容进行归纳.根据数据集的数据特点和获取方式的不同,将人体行为识别的公开数据集分成4类.其次,对4类数据集分别描述,并对相应数据集的最新识别率及其研究方法进行对比与分析.然后,通过比较各数据集的信息和特征,引导研究者选取合适的基准数据集来验证其算法的性能,促进人体行为识别技术的发展.最后,给出公开数据集未来发展的趋势与人体行为识别技术的展望.Abstract: Human activity recognition is an important research field of computer vision with important theoretical value and practical significance. In recent years, a large number of public datasets have been created for evaluation of human activity recognition methodologies. This paper reviews the progress and forecast the future of public datasets for human activity recognition. First, the hierarchy and contents of the public datasets are summarized, and the public datasets are divided into four categories according to the characteristics and acquiring methods. Then, the four categories are described and analyzed separately. Meantime, the state-of-the-art research results and corresponding methods of the public datasets are introduced to researchers. By comparing the information and characteristics of each dataset, researchers can be guided in the selection of the most suitable dataset for benchmarking their algorithms, so as to promote the technology progress of human activity recognition. Finally, the future trends of the public datasets and the prospects of human activity recognition are discussed.
-
Key words:
- Computer vision /
- activity recognition /
- real scenes /
- multi-view /
- multimodality
1) 本文责任编委 桑农 -
表 1 通用数据集的最新研究成果概览表
Table 1 Summary of state-of-the-art research results on general datasets
数据集名称 最新识别率 年份 研究方法 评价方案 98.83 %[23] 2016 MLDF CS: Tr: 16; Te: 9 KTH 98.67 %[22] 2016 Semantic context feature-tree (MKL) CS: Tr: 16; Te: 9 98.5 %[43] 2015 Local region tracking (HBRT/VOC) CS: Tr: 16; Te: 9 100 %[44] 2017 3D-TCCHOGAC+3D-HOOFGAC LOOCV 100 %[45] 2016 $\Re$ transform + LLE (SVM) LOOCV Weizmann 100 %[46] 2016 SDEG + $\Re$ transform LOOCV 100 %[47] 2014 3D cuboids + mid-level feature (RF) LOSOCV 100 %[25] 2008 Metric learning LOSOCV 100 %[26] 2008 Mid-level motion features LOOCV *Tr: training set; Te: test set; CS: cross-subject; LOOCV: leave-one-out cross validation; LOSOCV: leave-one-subject-out cross validation 表 2 真实场景数据集的最新研究成果概览表
Table 2 Summary of state-of-the-art research results on real scene datasets
数据集名称 最新识别率 年份 研究方法 评价方案 62 %[37] 2012 Asymmetric motions (BoW) Tr: 219 vedios; Te: 211vedios Hollywood 59.9 %[36] 2015 DFW (BoW) Tr: 219 vedios; Te: 211vedios 56.51 %[76] 2016 STG-MIL Tr: 219 vedios; Te: 211vedios 78.6 %[41] 2017 EPT + DT + VideoDarwin (TCNN) Tr: 823 videos; Te: 884 videos Hollywood 2 78.5 %[40] 2017 HC-MTL + L/S Reg Tr: 823 videos; Te: 884 videos 76.7 %[38] 2016 HRP + iDT (VGG-16) Tr: 823 videos; Te: 884 videos 96.2 %[43] 2015 Local region tracking (HBRT/VOC) all classes UCF Sports 96 %[44] 2017 3D-TCCHOGAC + 3D-HOOFGAC LOOCV 95.50 %[47] 2014 3D cuboids + mid-level feature (RF) LOOCV 94.50 %[53] 2016 HboW LOOCV UCF YouTube 94.4 %[52] 2016 CNRF (CNN) LOVOCV 93.77 %[51] 2014 FV + SFV LOGOCV 96.60 %[55] 2016 VLAD$^3$ + iDT (CNN) each class video: Tr: 40; Te: 10 Olympic Sports 96.5 %[54] 2015 iDT + HD (multi-layer FV) not mentioned 93.6 %[77] 2017 Bag-of-Sequencelets Tr: 649 videos; Te: 134 videos 73.6 %[58] 2016 scene + motion (DCNN) three train/test splits HMDB51 69.40 %[57] 2016 TSN (TCNN) three train/test splits 69.2 %[56] 2016 spatiotemporal fusion (TCNN) three train/test splits 99.98 %[61] 2016 GA (CNN) 5-fold cross-validatin UCF50 94.4 %[60] 2015 MIFS LOGOCV 94.1 %[78] 2013 weighted SVM 5-fold LOGOCV 94.20 %[57] 2016 TSN (TCNN) three train/test splits UCF101 94.08 %[62] 2016 RNN-FV (C3D + VGG-CCA) + iDT three train/test splits 93.5 %[56] 2016 spatiotemporal fusion (TCNN) three train/test splits 80.8 %[55] 2016 VLAD$^3$ + iDT (CNN) 5-fold cross-validation 76.8 %[55] 2016 VLAD$^3$ (CNN) 5-fold cross-validation THUMOS'15 74.6 %[66] 2015 VLAD + LCD (VGG-16) 5-fold cross-validation 70.0 %[79] 2015 Stream Fusion + Linear SVM (VGG-19) Tr: UCF101 dataset; Te: val15 65.5 %[80] 2015 iDT + LCD + VLAD (VGG-16) Tr: UCF101 dataset; Vs: val15
Te: UCF101 dataset + val1575.9 %[67] 2016 RLSTM-g3 (GoogLeNet) not mentioned Sports-1M 73.4 %[67] 2016 RLSTM-g1 (GoogLeNet) not mentioned (Hit$@$1) 73.10 %[81] 2015 LSTM on Raw Frames LSTM on Optical Flow
(GoogLeNet)1.1 million videos *LOVOCV: leave-one-video-out cross validation; LOGOCV: leave-one-group-out cross validation; Vs: validation set 表 3 多视角数据集的最新研究成果概览表
Table 3 Summary of state-of-the-art research results on multi-view datasets
数据集名称 最新识别率 年份 研究方法 评价方案 备注 IXMAS 91.6 %[72] 2015 epipolar geometry not mentioned 5种行为 (单视角) 92.7 %[73] 2016 multi-view transition HMM LOSOCV 11种行为 IXMAS 95.54 %[75] 2014 MMM-SVM Tr: one camera's data 11种行为; 5个视角 (多视角) 95.3 %[74] 2016 Cuboid + supervised dictionary learning LOAOCV; CV 11种行为; 5个视角 95.1 %[74] 2016 STIP + supervised dictionary learning LOAOCV; CV 11种行为; 5个视角 95.54 %[75] 2014 MMM-SVM Tr: one camera's data 11种行为; 4个视角 Ts: LOSOCV 94.7 %[40] 2017 HC-MTL + L/S Reg LOSOCV 11种行为; 4个视角 93.7 %[92] 2017 eLR ConvNet(TCNN) LOSOCV 12种行为; 5个视角 85.8 %[46] 2016 SDEG + $\Re$ transform LOOCV 13种行为; 5个视角 MuHAVi 97.48 %[83] 2012 Visual + Correlation (LKSSVM) LOOCV 4个视角 92.1 %[82] 2014 sectorial extreme points (HMM) LOSOCV 4个视角 91.6 %[84] 2016 CMS + multilayer descriptor (Multiclass K-NN) LOOCV 8个视角 MuHAVi-14 98.53 %[86] 2014 Pose dictionary learning + maxpooling LOOCV 98.5 %[85] 2013 radial summary feature + Feature Subset leave-one-sequence-out Selection 95.6 %[84] 2016 CMS + multilayer descriptor(Multiclass K-NN) LOOCV 94.12 %[88] 2014 CMS (K-NN) multi-training MuHAVi-8 100 %[84] 2016 CMS + multilayer descriptor (Multiclass K-NN) LOOCV 100 %[88] 2014 CMS (K-NN) multi-training 100 %[87] 2014 radial silhouette-based feature (multiview learing) leave-one-sequence-out 100 %[85] 2013 radial summary feature + Feature Subset leave-one-sequence-out Selection LOSOCV *CV: cross-view 表 4 MSR Action 3D数据集的子集
Table 4 The subsets of MSR Action 3D dataset
数据子集 包含行为类别 AS$_{1}$ a02、a03、a05、a06、a10、a13、a18、a20 AS$_{2}$ a01、a04、a07、a08、a09、a11、a14、a12 AS$_{3}$ a06、a14、a15、a16、a17、a18、a19、a20 表 5 特殊数据集的最新研究成果概览表
Table 5 Summary of state-of-the-art research results on special datasets
数据集名称 最新识别率 年份 研究方法 评价方案 备注 WARD 99.02 %[100] 2015 PCA+RLDA (SVM) CS: Tr: 15; Te: 5 98.78 %[99] 2012 GDA+RVM+WLOGP 3-fold cross-validation 97.5 %[122] 2017 FDA (SVM) 20-fold cross-validation 10种行为 近100 %[101] 2016 SCN (1-NN) CS 5种行为 200个样本 CMU Mocap 98.27 %[123] 2010 HGPLVM 3-fold cross-validation 5种行为 98.13 %[124] 2014 3D joint position features+Actionlet not mentioned 5种行为 Ensemble 98.6 %[102] 2015 DisCoSet (SVM) All 12种行为 164个样本 99.6 %[103] 2014 TSVQ (Pose-Histogram SVM) 5-fold cross-validation 30种行为 278个样本 MSR Action 3D 100 %[108] 2015 DMM-LBP-FF/DMM-LBP-DF Tr: 2/3; Te: 1/3 (AS$_1$、AS$_2$和AS$_3$) 98.9 %[107] 2013 DL-GSGC Tr: 2/3; Te: 1/3 98.9 %[107] 2013 DL-GSGC Tr: 1/3; Te: 2/3 98.7 %[108] 2015 DMM-LBP-FF Tr: 1/3; Te: 2/3 96.7 %[107] 2013 DL-GSGC CS 96.1 %[125] 2016 3D skeleton+two-level hierarchical CS framework 96.0 %[111] 2017 Coarse DS+Sparse coding (RDF) CS MSR Action 3D 100 %[110] 2015 HDMM+3ConvNets Tr:奇数; Te:偶数 (cross-subject) 98.2 %[109] 2015 TriViews+ PFA Tr:奇数; Te:偶数 98.2 %[126] 2015 Decision-Level Fusion (SUM Rule) Tr: 2/3/5/7/9; Te: 1/4/6/8/10 96.7 %[107] 2013 DL-GSGC+TPM Tr:奇数; Te:偶数 MSR Daily Activity 3D 97.5 %[111] 2017 Coarse DS+Sparse coding (RDF) not mentioned 97.5 %[112] 2016 DSSCA+SSLM CS 95.0 %[107] 2013 DL-GSGC+TPM CS UCF Kinect 98.9 %[114] 2014 MvMF-HMM+$L_2$-normalization 4-fold cross-validation 98.8 %[113] 2017 SGS(p$_{\rm mean}$/p$_{\max}$, skeleton-view-dep.) 4-fold cross-validation 98.7 %[127] 2013 motion-based grouping+adaptive 2-fold cross-validation N-UCLA 92.61 %[115] 2017 Synthesized+Pre-trained (CNN) CV Multiview Action 3D 90.8 %[113] 2017 SGS(p$_{\max}$, skel.-view-inv.+keypoint) CV 89.57 %[115] 2017 Synthesized Samples (CNN) CV 81.6 %[104] 2014 MST-AOG CS; LOOCV 79.3 %[104] 2014 MST-AOG cross-environment UTD-MHAD 88.4 %[117] 2015 DMMs+CT-HOG+LBP+EOH CS 88.1 %[116] 2017 JDM+MSF (CNN) CS 87.9 %[118] 2016 JTM+MSF (CNN) CS NTU RGB+D 76.32 %[118] 2016 JTM+MSF (CNN) CS 76.2 %[116] 2017 JDM+MSF (CNN) CS 62.93 %[106] 2016 2layer P-LSTM CS 82.3 %[116] 2017 JDM+MSF (CNN) CV 81.08 %[118] 2016 JTM+MSF (CNN) CV 70.27 %[106] 2016 2 layer P-LSTM CV 表 6 通用、真实场景及多视角数据集信息表
Table 6 The information of general datasets, real scene datasets and multi-view datasets
类型 数据集名称 年份 行为类别 行为人数 视频数/类 视频总数/样本数 场景 视角 分辨率(最高) fps 通用 KTH[19] 2004 6 25 99 $\sim$ 100 599/2 391 4 1 160$\times$120 25 Weizmann[2] 2005 10 9 9 $\sim$ 10 93 1 1 180$\times$144 25 真实场景 Hollywood[27] 2008 8 N/A 30 $\sim$ 129 475 N/A N/A 544$\times$240 25 UCF Sports[28] 2008 10 N/A 6 $\sim$ 22 150 N/A N/A 720$\times$480 9 UT-Tower[128] 2009 9 6 12 108 2 1 360$\times$240 10 Hollywood 2[29] (Actions) 2009 12 N/A 61 $\sim$ 278 2 517 N/A N/A 720$\times$528 25 ADL[129] 2009 10 5 15 150 1 1 1 280$\times$720 30 UCF YouTube[30] 2009 11 N/A 116 $\sim$ 198 1 600 N/A N/A 320$\times$240 30 Olympic Sports[31] 2010 16 N/A 21 $\sim$ 67 783 N/A N/A - - UT-Interaction[130] 2010 6 N/A 20 120 2 1 720$\times$480 30 HMDB51[32] 2011 51 N/A 102 $\sim$ 548 6 766 N/A N/A 424$\times$240 30 CCV[131] 2011 20 N/A 224 $\sim$ 806 9 317 N/A N/A - - UCF50[33] 2012 50 N/A 100 $\sim$ 197 6 681 N/A N/A 320$\times$240 25 UCF101[34] 2012 101 N/A 100 $\sim$ 167 13 320 N/A N/A 320$\times$240 25 MPII Cooking[132] 2012 65 12 - 44/5 609 1 1 1 624$\times$1 224 29.4 MPII Composites[133] 2012 60 22 - 212 1 1 1 624$\times$1 224 29.4 Sports-1M[35] 2014 487 N/A 1 000 $\sim$ 3 000 1 133 158 N/A N/A 1 280$\times$720 30 Hollywood Extended[134] 2014 16 N/A 2 $\sim$ 11 937 N/A N/A 720$\times$528 25 MPII Cooking 2[135] 2015 67 30 - 273/14 105 1 1 1 624$\times$1 224 29.4 ActivityNet[136] 2015 203 N/A 137(a) 27 801 N/A N/A 1 280$\times$720 30 多视角 IXMAS[68] 2006 13 12 180 180/2 340 1 5 390$\times$291 23 i3DPost[137] 2009 12 8 64 768 1 8 1 920$\times$1 080 25 MuHAVi[69] 2010 17 7 56 952 1 8 720$\times$576 25 MuHAVi-MAS[69] 2010 14 2 4 $\sim$ 16 136 1 2 720$\times$576 25 *a: average; N/A: not applicable 表 7 特殊数据集信息表
Table 7 The information of special human activity recognition datasets
数据集名称 年份 行为类别 行为人数 视频数/类 视频总数/样本数 场景 视角 分辨率 fps 数据格式 骨架关节点 CMU Mocap[94] 2007 23个亚类 N/A 1 $\sim$ 96 2 605 N/A N/A 320 $\times$ 240 30 MS 41 WARD[93] 2009 13 20 64 $\sim$ 66 1 298 1 1 - - M N/A CMU-MMAC[138] 2009 5大类 45 234 $\sim$ 252 1 218 1 6 1 024$\times$768 30 RDMA N/A 640$\times$480 60 MSR Action 3D[95] 2010 20 10 20 $\sim$ 30 567 1 1 640$\times$480 (R)
320$\times$240 (D)15 DS 20 RGBD-HuDaAct[139] 2011 12 30 - 1 189 1 1 640$\times$480 (RD) 30 RD N/A UT Kinect[140] 2012 10 10 - 200 1 1 640$\times$480 (R)
320$\times$240 (D)30 RDS 20 ACT4$^2$[141] 2012 14 24 - 6 844 1 4 640 $\times$ 480 30 RD N/A MSR Daily Activity 3D[96] 2012 16 10 20 320 1 1 640$\times$480 30 RDS 20 UCF Kinect[97] 2013 16 16 80 1 280 1 1 - - S 15 Berkeley MHAD[142] 2013 11 12 54 $\sim$ 55 659 1 4 640$\times$480 30 RDMAIe N/A 3D Action Pairs[143] 2013 12 10 30 360 1 1 640$\times$480 30 RDS 20 Multiview RGB-D event[144] 2013 8 8 477 (a) 3 815 1 3 640$\times$480 30 RDS 20 Online RGBD Action[145] 2014 7 24 48 336 1 1 - - RDS 20 URFD[119] 2014 5 5 6 $\sim$ 60 100 4 2 640$\times$240 30 RD N/A N-UCLA[104] 2014 10 10 140 $\sim$ 173 1 475 1 3 640$\times$480 12 RDS 20 TST Fall detection v1[120] 2014 2 4 10 20 1 1 320$\times$240 (D) 30 D N/A UTD-MHAD[105] 2015 27 8 31 $\sim$ 32 861 1 1 640$\times$480 30 RDSIe 25 TST Fall detection v2[121] 2016 8 11 33 264 1 1 512$\times$424 (D) 25 DSIe 25 NTU RGB+D[106] 2016 60 40 948 56 880 1 80 1 920$\times$720 (R)
512$\times$424 (D)
512$\times$424 (If)30 RDSIf 25 *R: RGB; D: Depht; S: Skeleton; M: Motion; A: Audio; If: Infrared; Ie: Inertrial 表 8 人体行为数据集分类信息表
Table 8 Human activity dataset classification according to different features
分类特征 子类 数据集 场景 室内 ADL、MPII Cooking、MPII Composites、MPII Cooking 2、IXMAS、i3DPost、MuHAVi、MuHAVi-MAS、CMU Mocap、WARD、CMU-MMAC、MSR Action 3D、RGBD-HuDaAct、UT Kinect、ACT4$^2$、MSR Daily Activity 3D、UCF Kinect、MHAD、3D Action Pairs、Multiview RGB-D event、Online RGBD Action、URFD、N- UCLA Multiview Action 3D、TST Fall detection dataset v1、UTD-MHAD、TST Fall detection dataset v2、NTU RGB+D 室外 Weizmann、UT-Tower、UT-Interaction、PETS 内容 室内/室外 KTH、Hollywood、UCF Sports、Hollywood 2、UCF YouTube、Olympic Sports、HMDB51、CCV、UCF50、UCF101、Sports-1M、Hollywood Extended、ActivityNet、THUMOS 日常活动 KTH、Weizmann、ADL、HMDB51、CCV、ActivityNet、IXMAS、i3DPost、MuHAVi、MuHAVi-MAS、CMU Mocap、WARD、MSR Action 3D、RGBD-HuDaAct、UT Kinect、ACT4$^2$、MSR Daily Activity 3D、RGBD- HuDaAct、UCF Kinect、MHAD、3D Action Pairs、Multiview RGB-D event、Online RGBD Action、URFD、N-UCLA Multiview Action 3D、TST Fall detection dataset v1、UTD-MHAD、TST Fall detection dataset v2、NTU RGB+D 体育运动 UCF Sports、UCF YouTube、Olympic Sports、UCF50、UCF101、Sports-1M、THUMOS 厨房活动 MPII Cooking、MPII Composites、MPII Cooking 2、CMU-MMAC 电影 Hollywood、Hollywood 2、Hollywood Extended 监控 UT-Tower、UT-Interaction、PETS 视角 单视角 KTH、Weizmann、ADL、MPII Cooking、MPII Composites、MPII Cooking 2、MSR Action 3D、UT Kinect、MSR Daily Activity 3D、RGBD-HuDaAct、UCF Kinect、3D Action Pairs、Online RGBD Action、TST Fall detection dataset v1、UTD-MHAD、TST Fall detection dataset v2 多视角 IXMAS、i3DPost、MuHAVi、MuHAVi-MAS、ACT4$^2$、MHAD、Multiview RGB-D event、URFD、N-UCLA Multiview Action 3D、NTU RGB+D、PETS 俯瞰 UT-Tower、UT-Interaction、PETS 其他 Hollywood、UCF Sports、Hollywood 2、UCF YouTube、Olympic Sports、HMDB51、CCV、UCF50、UCF101、Sports-1M、Hollywood Extended、ActivityNet、CMU Mocap、WARD、CMU-MMAC、THUMOS 相机 静止 KTH、Weizmann、UT-Tower、ADL、UT-Interaction、MPII Cooking、MPII Composites、MPII Cooking 2、IXMAS、i3DPost、MuHAVi、MuHAVi-MAS、CMU-MMAC、MSR Action 3D、RGBD-HuDaAct、UT Kinect、ACT4$^2$、MSR Daily Activity 3D、UCF Kinect、MHAD、3D Action Pairs、Multiview RGB-D event、Online RGBD Action、URFD、N-UCLA Multiview Action 3D、TST Fall detection dataset v1、UTD-MHAD、TST Fall detection dataset v2、NTU RGB+D、PETS 移动 Hollywood、UCF Sports、Hollywood 2、UCF YouTube、Olympic Sports、HMDB51、CCV、UCF50、UCF101、Sports-1M、Hollywood Extended、ActivityNet、CMU Mocap、THUMOS 应用 行为识别 KTH、Weizmann、Hollywood、UCF Sports、UT-Tower、Hollywood 2、ADL、UCF YouTube、Olympic Sports、UT-Interaction、HMDB51、CCV、UCF50、UCF101、MPII Cooking、MPII Composites、Sports-1M、Hollywood Extended、ActivityNet、MPII Cooking 2、IXMAS、i3DPost、MuHAVi、MuHAVi-MAS、CMU Mocap、WARD、CMU-MMAC、MSR Action 3D、RGBD-HuDaAct、UT Kinect、ACT4$^2$、MSR Daily Activity 3D、UCF Kinect、MHAD、3D Action Pairs、Multiview RGB-D event、Online RGBD Action、N-UCLA Multiview Action 3D、UTD-MHAD、TST Fall detection dataset v2、NTU RGB+D、PETS、THUMOS 领域 检测/跟踪 KTH、Weizmann、UCF Sports、Olympic Sports、UT-Interaction、ADL、UCF YouTube、ACT4$^2$、URFD、TST Fall detection dataset v1、TST Fall detection dataset v2、PETS、UCF50、UCF101、MPII Cooking、MPII Composites、MPII Cooking 2 其他 KTH、Weizmann、UCF YouTube、UT-Tower、UCF50、ActivityNet、MPII Cooking、MPII Composites、MPII Cooking 2、Multiview RGB-D event -
[1] Hu W M, Tan T N, Wang L, Maybank S. A survey on visual surveillance of object motion and behaviors. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2004, 34(3):334-352 doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2004.829274 [2] Kim I S, Choi H S, Yi K M, Choi J Y, Kong S G. Intelligent visual surveillance-a survey. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2010, 8(5):926-939 doi: 10.1007/s12555-010-0501-4 [3] 黄凯奇, 陈晓棠, 康运锋, 谭铁牛.智能视频监控技术综述.计算机学报, 2015, 38(6):1093-1118 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01093Huang Kai-Qi, Chen Xiao-Tang, Kang Yun-Feng, Tan Tie-Niu. Intelligent visual surveillance:a review. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(6):1093-1118 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01093 [4] Dix A. Human-Computer Interaction. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2009. 1327-1331 [5] Myers B A. A brief history of human-computer interaction technology. Interactions, 1998, 5(2):44-54 doi: 10.1145/274430.274436 [6] Rautaray S S, Agrawal A. Vision based hand gesture recognition for human computer interaction:a survey. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2015, 43(1):1-54 doi: 10.1007/s10462-012-9356-9 [7] Park S H, Won S H, Lee J B, Kim S W. Smart home-digitally engineered domestic life. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 2003, 7(3-4):189-196 doi: 10.1007/s00779-003-0228-9 [8] Jeong K-A, Salvendy G, Proctor R W. Smart home design and operation preferences of Americans and Koreans. Ergonomics, 2010, 53(5):636-660 doi: 10.1080/00140130903581623 [9] Komninos N, Philippou E, Pitsillides A. Survey in smart grid and smart home security:Issues, challenges and countermeasures. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2014, 16(4):1933-1954 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ba89261b5387cd451572bd2fd6012175&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [10] Suma E A, Krum D M, Lange B, Koenig S, Rizzo A, Bolas M. Adapting user interfaces for gestural interaction with the flexible action and articulated skeleton toolkit. Computers & Graphics, 2013, 37(3):193-201 [11] Zelnik-Manor L, Irani M. Event-based analysis of video. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Kauai, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2001, 2: Ⅱ-123-Ⅱ-130 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2001.990935 [12] Ahad M A R, Tan J, Kim H, Ishikawa S. Action dataset-a survey. In: Proceedings of the 2011 SICE Annual Conference (SICE). Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 2011. 1650-1655 http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/action-dataset-survey/ [13] Chaquet J M, Carmona E J, Fernández-Caballero A. A survey of video datasets for human action and activity recognition. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2013, 117(6):633-659 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2013.01.013 [14] Zhang J, Li W Q, Ogunbona P O, Wang P C, Tang C. RGB-D-based action recognition datasets:a survey. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 60:86-105 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.019 [15] Aggarwal J K, Ryoo M S. Human activity analysis:a review. ACM Computing Surveys, 2011, 43(3):Article No. 16 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a25e9bf81e9f05da7e7a0358aaeb8ae3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [16] Vishwakarma S, Agrawal A. A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. The Visual Computer, 2013, 29(10):983-1009 doi: 10.1007/s00371-012-0752-6 [17] Chen C, Jafari R, Kehtarnavaz N. A survey of depth and inertial sensor fusion for human action recognition. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(3):4405-4425 doi: 10.1007/s11042-015-3177-1 [18] 单言虎, 张彰, 黄凯奇.人的视觉行为识别研究回顾、现状及展望.计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(1):93-112 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20150403Shan Yan-Hu, Zhang Zhang, Huang Kai-Qi. Visual human action recognition:history, status and prospects. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(1):93-112 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20150403 [19] Schuldt C, Laptev I, Caputo B. Recognizing human actions: a local SVM approach. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Cambridge, UK: IEEE, 2004, 3: 32-36 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1334462 [20] Blank M, Gorelick L, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R. Actions as space-time shapes. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV'05). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005, 2: 1395-1402 http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/17934233 [21] Gorelick L, Blank M, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R. Actions as space-time shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(12):2247-2253 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70711 [22] Zhou T C, Li N J, Cheng X, Xu Q J, Zhou L, Wu Z Y. Learning semantic context feature-tree for action recognition via nearest neighbor fusion. Neurocomputing, 2016, 201:1-11 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.04.007 [23] Xu W R, Miao Z J, Tian Y. A novel mid-level distinctive feature learning for action recognition via diffusion map. Neurocomputing, 2016, 218:185-196 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.057 [24] Gorelick L, Blank M, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R. Actions as space-time shapes[Online], available: http://www.wisdom.weizmann.ac.il/~vision/SpaceTime-Actions.html, January 26, 2016. [25] Tran D, Sorokin A. Human activity recognition with metric learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Marseille, France: Springer, 2008. 548-561 http://www.springerlink.com/content/p2183333585g8845 [26] Fathi A, Mori G. Action recognition by learning mid-level motion features. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Anchorage, AK, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=4587735 [27] Laptev I, Marszalek M, Schmid C, Rozenfeld B. Learning realistic human actions from movies. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Anchorage, AK, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4587756 [28] Rodriguez M D, Ahmed J, Shah M. Action MACH a spatio-temporal maximum average correlation height filter for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Anchorage, AK, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4587727 [29] Marszalek M, Laptev I, Schmid C. Actions in context. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Miami, FL, USA: IEEE, 2009. 2929-2936 [30] Liu J G, Luo J B, Shah M. Recognizing realistic actions from videos "in the wild". In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Miami, FL, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1996-2003 doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2009.5206744 [31] Niebles J C, Chen C W, Li F F. Modeling temporal structure of decomposable motion segments for activity classification. In: Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV): Part Ⅱ. Heraklion, Crete, Greece: Springer, 2010. 392-405 [32] Kuehne H, Jhuang H, Garrote E, Poggio T, Serre T. HMDB: a large video database for human motion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 2556-2563 doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126543 [33] Reddy K K, Shah M. Recognizing 50 human action categories of web videos. Machine Vision and Applications, 2013, 24(5):971-981 doi: 10.1007/s00138-012-0450-4 [34] Soomro K, Zamir A R, Shah M. UCF101: a dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv: 1212. 0402, 2012. 1-7 [35] Karpathy A, Toderici G, Shetty S, Leung T, Sukthankar R, Li F F. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1725-1732 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6909619/ [36] Kulkarni K, Evangelidis G, Cech J, Horaud R. Continuous action recognition based on sequence alignment. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 112(1):90-114 doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0758-9 [37] Shabani A H, Clausi D A, Zelek J S. Evaluation of local spatio-temporal salient feature detectors for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Ninth Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV). Toronto, ON, Canada: IEEE, 2012. 468-475 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2354394 [38] Fernando B, Anderson P, Hutter M, Gould S. Discriminative hierarchical rank pooling for activity recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1924-1932 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.212 [39] Wang H, Schmid C. Action recognition with improved trajectories. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 3551-3558 doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.441 [40] Liu A A, Su Y T, Nie W Z, Kankanhalli M. Hierarchical clustering multi-task learning for joint human action grouping and recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(1):102-114 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2537337 [41] Wang Y, Tran V, Hoai M. Evolution-preserving dense trajectory descriptors. arXiv: 1702. 04037, 2017. [42] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. Advance in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2014, 1(4):568-576 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262974436_Two-Stream_Convolutional_Networks_for_Action_Recognition_in_Videos [43] Al Harbi N, Gotoh Y. A unified spatio-temporal human body region tracking approach to action recognition. Neurocomputing, 2015, 161:56-64 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.11.072 [44] Tong M, Wang H Y, Tian W J, Yang S L. Action recognition new framework with robust 3D-TCCHOGAC and 3D-HOOFGAC. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(2):3011-3030 doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-3279-4 [45] Vishwakarma D K, Kapoor R, Dhiman A. Unified framework for human activity recognition:an approach using spatial edge distribution and R-transform. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2016, 70(3):341-353 doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2015.12.016 [46] Vishwakarma D K, Kapoor R, Dhiman A. A proposed unified framework for the recognition of human activity by exploiting the characteristics of action dynamics. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2016, 77:25-38 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2015.11.013 [47] Liu C W, Pei M T, Wu X X, Kong Y, Jia Y D. Learning a discriminative mid-level feature for action recognition. Science China Information Sciences, 2014, 57(5):1-13 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cb77c2bcda90b6c26f8a2e19405b6342&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [48] Laptev I, Marszalek M, Schmid C, Rozenfeld B. Hollywood2: Human actions and scenes dataset[Online], available: http://www.di.ens.fr/~laptev/actions/hollywood2/, March 12, 2016. [49] Wang H, Kläser A, Schmid C, Liu C L. Dense trajectories and motion boundary descriptors for action recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 103(1):60-79 doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0594-8 [50] Soomro K, Zamir A R. Action recognition in realistic sports videos. Computer vision in sports. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 181-208 [51] Peng X J, Zou C Q, Qiao Y, Peng Q. Action recognition with stacked fisher vectors. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 581-595 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_38 [52] Liu C H, Liu J, He Z C, Zhai Y J, Hu Q H, Huang Y L. Convolutional neural random fields for action recognition. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 59:213-224 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.03.019 [53] Sun Q R, Liu H, Ma L Q, Zhang T W. A novel hierarchical bag-of-words model for compact action representation. Neurocomputing, 2016, 174(Part B):722-732 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283989611_A_novel_hierarchical_Bag-of-Words_model_for_compact_action_representation [54] Sekma M, Mejdoub M, Amar C B. Human action recognition based on multi-layer fisher vector encoding method. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2015, 65(C):37-43 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305284646_Structured_Fisher_vector_encoding_method_for_human_action_recognition [55] Li Y W, Li W X, Mahadevan V, Vasconcelos N. VLAD3: encoding dynamics of deep features for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1951-1960 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.215 [56] Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Zisserman A. Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1933-1941 http://arxiv.org/abs/1604.06573 [57] Wang L M, Xiong Y J, Wang Z, Qiao Y, Lin D H, Tang X O, Van Gool L. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 20-36 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2 [58] Wang H S, Wang W, Wang L. How scenes imply actions in realistic videos? In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Phoenix, AZ, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1619-1623 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7532632/ [59] Wang L M, Guo S, Huang W L, Qiao Y. Places205-VGGNet models for scene recognition. arXiv: 1508. 01667, 2015. [60] Lan Z Z, Lin M, Li X C, Hauptmann A G, Raj B. Beyond Gaussian pyramid: multi-skip feature stacking for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015. 204-212 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298616 [61] Ijjina E P, Chalavadi K M. Human action recognition using genetic algorithms and convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 59:199-212 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.01.012 [62] Lev G, Sadeh G, Klein B, Wolf L. RNN Fisher vectors for action recognition and image annotation. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV): Part Ⅷ . Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 833-850 [63] Jiang Y G, Liu J G, Zamir A R, Laptev I, Piccardi M, Shah M, Sukthankar R. THUMOS challenge: Action recognition with a large number of classes[Online], available: http://crcv.ucf.edu/ICCV13-Action-Workshop/index.html, November 20, 2016. [64] Jiang Y G, Liu J G, Zamir A R, Toderici G, Laptev I, Shah M, Sukthankar R. THUMOS challenge: action recognition with a large number of classes[Online], available: http://crcv.ucf.edu/THUMOS14/home.html, November 20, 2016. [65] Gorban A, Idrees H, Jiang Y G, Zamir A R, Laptev I, Shah M, Sukthankar R. THUMOS challenge: action recognition with a large number of classes[Online], available: http://www.thumos.info/home.html, November 20, 2016. [66] Xu Z, Zhu L, Yang Y, Hauptmann A G. UTS-CMU at THUMOS 2015. In: Proceedings of the 2015 THUMOS Challenge. Boston, MA, USA: CVPR, 2015. 1-3 [67] Mahasseni B, Todorovic S. Regularizing long short term memory with 3D human-skeleton sequences for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3054-3062 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.333 [68] Weinland D, Ronfard R, Boyer E. Free viewpoint action recognition using motion history volumes. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2006, 104(2-3):249-257 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2006.07.013 [69] Singh S, Velastin S A, Ragheb H. MuHAVi: a multicamera human action video dataset for the evaluation of action recognition methods. In: Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2010. 48-55 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5597316 [70] Ferryman J, Shahrokni A. PETS2009: dataset and challenge. In: Proceedings of the 22th IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance (PETS-Winter). Snowbird, UT, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1-6 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5399556 [71] Patino L, Ferryman J. PETS 2014: dataset and challenge. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2014. 355-360 doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2014.6918694 [72] Ashraf N, Foroosh H. Motion retrieval using consistency of epipolar geometry. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Quebec City, QC, Canada: IEEE, 2015. 4219-4223 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7351601/ [73] Ji X F, Ju Z J, Wang C, Wang C H. Multi-view transition HMMs based view-invariant human action recognition method. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2016, 75(19):11847-11864 doi: 10.1007/s11042-015-2661-y [74] Gao Z, Nie W Z, Liu A N, Zhang H. Evaluation of local spatial-temporal features for cross-view action recognition. Neurocomputing, 2016, 173(Part 1):110-117 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1da561fc4b0fcb38d7c20fb3f7e53e43&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [75] Wu D, Shao L. Multi-max-margin support vector machine for multi-source human action recognition. Neurocomputing, 2014, 127(3):98-103 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1985a105fc3d9604d66066b167adf376&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [76] Yi Y, Lin M Q. Human action recognition with graph-based multiple-instance learning. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 53(C):148-162 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d6d8420d7e0ac3354d4a04a9cb76c2dd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [77] Jung H J, Hong K S. Modeling temporal structure of complex actions using bag-of-sequencelets. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2017, 85:21-28 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2016.11.012 [78] Ballas N, Yang Y, Lan Z Z, Delezoide B, Preteux F, Hauptmann A. Space-time robust representation for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Sydney, NSW, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 2704-2711 doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.336 [79] Qiu Z F, Li Q, Yao T, Mei T, Rui Y. MSR Asia MSM at THUMOS challenge 2015. In: Proceedings of the 2015 THUMOS Challenge. Boston, MA, USA: CVPR, 2015. 1-3 http://storage.googleapis.com/www.thumos.info/thumos15_notebooks/TH15_MSRAsia.pdf [80] Ning K, Wu F. ZJUDCD submission at THUMOS challenge 2015. In: Proceedings of the 2015 THUMOS Challenge. Boston, MA, USA: CVPR, 2015. 1-2 [81] Ng J Y H, Hausknecht M, Vijayanarasimhan S, Vinyals O, Monga R, Toderici G. Beyond short snippets: deep networks for video classification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015. 4694-4702 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299101 [82] Moghaddam Z, Piccardi M. Training initialization of Hidden Markov Models in human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2014, 11(2):394-408 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2013.2262940 [83] Wu X X, Jia Y D. View-invariant action recognition using latent kernelized structural SVM. In: Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Florence, Italy: Springer, 2012. 411-424 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2403170 [84] Alcantara M F, Moreira T P, Pedrini H. Real-time action recognition using a multilayer descriptor with variable size. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2016, 25(1):Article No., 013020 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Marlon_Alcantara3/publication/293042223_Real-time_action_recognition_using_a_multilayer_descriptor_with_variable_size/links/5760567508ae2b8d20eb5f9e.pdf?origin=publication_list [85] Chaaraoui A A, Flórez-Revuelta F. Human action recognition optimization based on evolutionary feature subset selection. In: Proceedings of the 15th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: ACM, 2013. 1229-1236 Human action recognition optimization based on evolutionary feature subset selection [86] Cai J X, Tang X, Feng G C. Learning pose dictionary for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Stockholm, Sweden: IEEE, 2014. 381-386 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2704008 [87] Chaaraoui A A, Flórez-Revuelta F. A low-dimensional radial silhouette-based feature for fast human action recognition fusing multiple views. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2014, 2014:Article No., 547069 https://www.hindawi.com/journals/isrn/2014/547069/tab1/ [88] Alcantara M F, Moreira T P, Pedrini H. Real-time action recognition based on cumulative motion shapes. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Florence, Italy: IEEE, 2014. 2917-2921 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6854134/ [89] Li L Z, Nawaz T, Ferryman J. PETS 2015: datasets and challenge. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS). Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 2015. 1-6 doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2015.7301741 [90] Patino L, Cane T, Vallee A, Ferryman J. PETS 2016: dataset and challenge. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1240-1247 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7789647/ [91] PETS 2014[Online], available: http://www.cvg.reading.ac.uk/PETS2014/, April 16, 2016 [92] Chen J W, Wu J, Konrad J, Ishwar P. Semi-coupled two-stream fusion ConvNets for action recognition at extremely low resolutions. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Santa Rosa, California, USA: IEEE, 2017. 139-147 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7926606/ [93] Yang A Y, Jafari R, Sastry S S, Bajcsy R. Distributed recognition of human actions using wearable motion sensor networks. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments, 2009, 1(2):103-115 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2350317 [94] CMU graphics lab motion capture database[Online], available: http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu, September 27, 2016. [95] Li W Q, Zhang Z Y, Liu Z C. Action recognition based on a bag of 3D points. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2010. 9-14 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5543273&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fxpls%2Ficp.jsp%3Farnumber%3D5543273 [96] Wang J, Liu Z C, Wu Y, Yuan J S. Mining actionlet ensemble for action recognition with depth cameras. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1290-1297 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2354966 [97] Ellis C, Masood S Z, Tappen M F, LaViola Jr J J, Sukthankar R. Exploring the trade-off between accuracy and observational latency in action recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 101(3):420-436 doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0550-7 [98] Yang A Y, Iyengar S, Kuryloski P, Jafari R. Distributed segmentation and classification of human actions using a wearable motion sensor network. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW'08). Anchorage, AK, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4563176 [99] Guo Y C, He W H, Gao C. Human activity recognition by fusing multiple sensor nodes in the wearable sensor systems. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 2012, 12(5):Article No., 1250084 doi: 10.1142/S0219519412500844 [100] Guo M, Wang Z L. A feature extraction method for human action recognition using body-worn inertial sensors. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD). Calabria, Italy: IEEE, 2015. 576-581 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7231022/ [101] Jia Q, Fan X, Luo Z X, Li H J, Huyan K, Li Z Z. Cross-view action matching using a novel projective invariant on non-coplanar space-time points. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2016, 75(19):11661-11682 doi: 10.1007/s11042-015-2704-4 [102] Al Aghbari Z, Junejo I N. DisCoSet:discovery of contrast sets to reduce dimensionality and improve classification. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 2015, 8(6):1178-1191 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2cd8cc36bb9e5e545b47cfafa4362aa1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [103] Kadu H, Kuo C C J. Automatic human Mocap data classification. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2014, 16(8):2191-2202 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2014.2360793 [104] Wang J, Nie X H, Xia Y, Wu Y, Zhu S C. Cross-view action modeling, learning, and recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE, 2014. 2649-2656 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6909735 [105] Chen C, Jafari R, Kehtarnavaz N. UTD-MHAD: a multimodal dataset for human action recognition utilizing a depth camera and a wearable inertial sensor. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Quebec City, QC, Canada: IEEE, 2015. 168-172 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7350781 [106] Shahroudy A, Liu J, Ng T T, Wang G. NTU RGB+D: a large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1010-1019 http://arxiv.org/abs/1604.02808 [107] Luo J J, Wang W, Qi H R. Group sparsity and geometry constrained dictionary learning for action recognition from depth maps. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Sydney, NSW, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 1809-1816 doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.227 [108] Chen C, Jafari R, Kehtarnavaz N. Action recognition from depth sequences using depth motion maps-based local binary patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1092-1099 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2764065.2764211 [109] Chen W B, Guo G D. Triviews:a general framework to use 3D depth data effectively for action recognition. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 26:182-191 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.11.008 [110] Wang P C, Li W Q, Gao Z M, Zhang J, Tang C, Ogunbona P. Deep convolutional neural networks for action recognition using depth map sequences. arXiv: 1501. 04686, 2015. 1-8 [111] Zhang H L, Zhong P, He J L, Xia C X. Combining depth-skeleton feature with sparse coding for action recognition. Neurocomputing, 2017, 230:417-426 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.041 [112] Shahroudy A, Ng T T, Gong Y H, Wang G. Deep multimodal feature analysis for action recognition in RGB+D videos. arXiv: 160307120, 2016. [113] Kerola T, Inoue N, Shinoda K. Cross-view human action recognition from depth maps using spectral graph sequences. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2017, 154:108-126 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2016.10.004 [114] Beh J, Han D K, Durasiwami R, Ko H. Hidden Markov model on a unit hypersphere space for gesture trajectory recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 36:144-153 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2013.10.007 [115] Liu M Y, Liu H, Chen C. Enhanced skeleton visualization for view invariant human action recognition. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 68:346-362 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.02.030 [116] Li C K, Hou Y H, Wang P C, Li W Q. Joint distance maps based action recognition with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(5):624-628 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2678539 [117] Bulbul M F, Jiang Y S, Ma J W. DMMs-based multiple features fusion for human action recognition. International Journal of Multimedia Data Engineering & Management, 2015, 6(4):23-39 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=fd27f4caf7ad1b2f08f4f1ee6391f01b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [118] Wang P C, Li W Q, Li C K, Hou Y H. Action recognition based on joint trajectory maps with convolutional neural networks. arXiv: 1612. 09401v1, 2016. 1-11 [119] Kwolek B, Kepski M. Human fall detection on embedded platform using depth maps and wireless accelerometer. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2014, 117(3):489-501 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2014.09.005 [120] Gasparrini S, Cippitelli E, Spinsante S, Gambi E. A depth-based fall detection system using a kinect? sensor. Sensors, 2014, 14(2):2756-2775 doi: 10.3390/s140202756 [121] Gasparrini S, Cippitelli E, Gambi E, Spinsante S, Wåhslén J, Orhan I, Lindh T. Proposal and experimental evaluation of fall detection solution based on wearable and depth data fusion. ICT innovations 2015. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. 99-108 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25733-4_11 [122] 苏本跃, 蒋京, 汤庆丰, 盛敏.基于函数型数据分析方法的人体动态行为识别.自动化学报, 2017, 43(5):866-876 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19064.shtmlSu Ben-Yue, Jiang Jing, Tang Qing-Feng, Sheng Min. Human dynamic action recognition based on functional data analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5):866-876 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19064.shtml [123] Han L, Wu X X, Liang W, Hou G M, Jia Y D. Discriminative human action recognition in the learned hierarchical manifold space. Image and Vision Computing, 2010, 28(5):836-849 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2009.08.003 [124] Wang J, Liu Z C, Wu Y, Yuan J S. Learning actionlet ensemble for 3D human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(5):914-927 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.198 [125] Chen H Z, Wang G J, Xue J H, He L. A novel hierarchical framework for human action recognition. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 55:148-159 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.01.020 [126] Zhu Y, Chen W B, Guo G D. Fusing multiple features for depth-based action recognition. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2015, 6(2):Article No. 18 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b8a609270431fed77692706f168340e8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [127] Jiang X B, Zhong F, Peng Q S, Qin X Y. Robust action recognition based on a hierarchical model. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW). Yokohama, Japan: IEEE, 2013. 191-198 [128] Chen C C, Aggarwal J K. Recognizing human action from a far field of view. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Workshop on Motion and Video Computing (WMVC'09). Snowbird, UT, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1-7 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=5399231 [129] Messing R, Pal C, Kautz H. Activity recognition using the velocity histories of tracked keypoints. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2009. 104-111 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5459154 [130] Ryoo M S, Aggarwal J K. UT-interaction dataset, ICPR contest on semantic description of human activities (SDHA)[Online], available: http://cvrc.ece.utexas.edu/SDHA2010/Human_Interaction.html, December 10, 2016. [131] Jiang Y G, Ye G N, Chang S F, Ellis D, Loui A C. Consumer video understanding: a benchmark database and an evaluation of human and machine performance. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval (ICMR'11). Trento, Italy: ACM, 2011. Article No., 29 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1992025 [132] Rohrbach M, Amin S, Andriluka M, Schiele B. A database for fine grained activity detection of cooking activities. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1194-1201 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2354909 [133] Rohrbach M, Regneri M, Andriluka M, Amin S, Pinkal M, Schiele B. Script data for attribute-based recognition of composite activities. In: Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Florence, Italy: Springer, 2012. 144-157 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2402952 [134] Bojanowski P, Lajugie R, Bach F, Laptev I, Ponce J, Schmid C, Sivic J. Weakly supervised action labeling in videos under ordering constraints. Computer Vision——ECCV 2014. Cham, Germany: IEEE, 2014, 8693: 628-643 [135] Rohrbach M, Rohrbach A, Regneri M, Amin S, Andriluka M, Pinkal M, Schiele B. Recognizing fine-grained and composite activities using hand-centric features and script data. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 119(3):346-373 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0851-8 [136] Heilbron F C, Escorcia V, Ghanem B, Niebles J C. Activitynet: a large-scale video benchmark for human activity understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015. 961-970 doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298698 [137] Gkalelis N, Kim H, Hilton A, Nikolaidis N, Pitas I. The i3DPost multi-view and 3D human action/interaction database. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Conference for Visual Media Production (CVMP). London, UK: IEEE, 2009. 159-168 http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/lookup/external-ref?access_num=20674934&link_type=MED&atom=%2Fbrain%2F135%2F3%2F723.atom [138] De la Torre F, Hodgins J K, Montano J, Valcarcel S. Detailed human data acquisition of kitchen activities: the CMU-multimodal activity database (CMU-MMAC). In: Proceedings of the 2009 Workshop on Developing Shared Home Behavior Datasets to Advance HCI and Ubiquitous Computing Research, in Conjuction with CHI. Boston, MA, USA: ACM, 2009. 1-5 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/242754790_Detailed_Human_Data_Acquisition_of_Kitchen_Activities_the_CMU-Multimodal_Activity_Database_CMU-MMAC [139] Ni B B, Wang G, Moulin P. RGBD-HuDaAct: a color-depth video database for human daily activity recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 1147-1153 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6130379 [140] Xia L, Chen C C, Aggarwal J K. View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3D joints. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2012. 20-27 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6239233 [141] Cheng Z W, Qin L, Ye Y T, Huang Q Q, Tian Q. Human daily action analysis with multi-view and color-depth data. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision, ECCV 2012-Workshops and Demonstrations. Florence, Italy: Springer, 2012. 52-61 [142] Ofli F, Chaudhry R, Kurillo G, Vidal R, Bajcsy R. Berkeley MHAD: a comprehensive multimodal human action database. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Tampa, FL, USA: IEEE, 2013. 53-60 doi: 10.1109/WACV.2013.6474999 [143] Oreifej O, Liu Z C. HON4D: histogram of oriented 4D normals for activity recognition from depth sequences. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Portland, OR, USA: IEEE, 2013. 716-723 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2516099 [144] Wei P, Zhao Y B, Zheng N N, Zhu S C. Modeling 4D human-object interactions for joint event segmentation, recognition, and object localization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6):1165-1179 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2574712 [145] Yu G, Liu Z C, Yuan J S. Discriminative orderlet mining for real-time recognition of human-object interaction. In: Proceedings of the 12th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV). Singapore: Springer, 2014. 50-65 [146] Abu-El-Haija S, Kothari N, Lee J, Natsev P, Toderici G, Varadarajan B, Vijayanarasimhan S. YouTube-8M: a large-scale video classification benchmark. arXiv: 1609. 08675, 2016. 1-10 -





 下载:
下载: