A Subspace Clustering Algorithm of Categorical Data Using Multiple Attribute Weights
-
摘要: 采用多属性频率权重以及多目标簇集质量聚类准则,提出一种分类数据子空间聚类算法.该算法利用粗糙集理论中的等价类,定义了一种多属性权重计算方法,有效地提高了属性的聚类区分能力;在多目标簇集质量函数的基础上,采用层次凝聚策略,迭代合并子簇,有效地度量了各类尺度的聚类簇;利用区间离散度,解决了使用阈值删除噪音点所带来的参数问题;利用属性对簇的依附程度,确定了聚类簇的属性相关子空间,提高了聚类簇的可理解性.最后,采用人工合成、UCI和恒星光谱数据集,实验验证了该聚类算法的可行性和有效性.Abstract: In this paper, we propose a subspace clustering algorithm using frequencies of multiple attributes of categorical data. An attribute-value weight is calculated on the basis of equivalence class in rough set theory by using frequencies of multiple attributes. Attribute-value weights offer ample opportunities to improve classiffication ability of clustering. The well-known parameter problem, which is caused by using a threshold to delete noise points, is solved by the virtue of interval dispersion degrees. By adopting the hierarchical clustering method to iteratively merge sub-clusters, we effectively measure various scale clusters on the basis of a multi-objective clusters quality function. An attribute subspace is determined with the relevance degree of dimension to a cluster, so as to improve the cluster's interpretability. Finally, we validate the feasibility and effectiveness of our algorithm through extensive experiments using synthetic data as well as UCI and stellar spectral data sets.1) 本文责任编委 曾志刚
-
表 1 符号表示及含义
Table 1 Symbol and notation
符号表示 符号含义 U 数据集 $x_k$ 第 $k$ 个数据点 $a_j$ 第 $j$ 维属性 $NOS$ 由噪音点组成的集合 $SA_s$ 簇 $C_s$ 的相关属性子空间 A 属性集 $x_{ki}$ 数据 $x_k$ 在第 $i$ 维属性上的属性取值 $C_s$ 第 $s$ 个类簇 $SD_s$ 簇 $C_s$ 的数据集合 $V_{a_i}$ 属性 $a_i$ 的值域 S 一个分类信息系统 ${[x_k]}_{a_i}$ 包含数据点 $x_k$ 的 $a_i$ 等价类 $n$ 数据点的总数 $d$ 属性空间的总维数 SC 子簇集 表 2 数据集
Table 2 Dataset
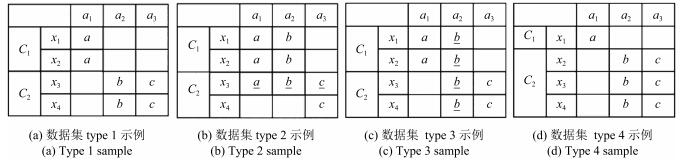
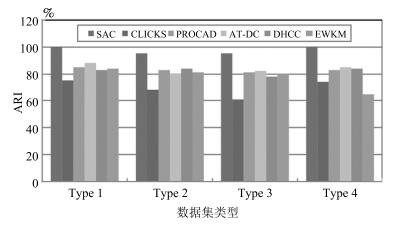
类别 数据集 数据量 维数 簇数 平衡数据 实验目的 合成数据 Type 1 10 000 50 6 是 抗噪性对比实验 Type 2 10 000 200 6 是 维度可扩展性对比实验 Type 3 60 000 50 6 是 数据量可扩展性对比实验 Type 4 10 000 50 6 否 非平衡数据集聚类效果对比实验 UCI Voting 435 16 2 否 属性值域元素少对聚类效果的影响 Splice 3 190 60 3 否 高维UCI数据集的效果对比实验 Mushroom 8 124 22 2 是 大数据量聚类效果对比实验 Zoo 101 17 7 否 多簇数据集性能实验; 属性子空间实验 真实数据 光谱数据 8 315 208 7 否 真实数据聚类效果对比实验 表 3 SAC在光谱数据上性能指标变化
Table 3 Noise immunity on the spectral data for SAC
加入噪音数 去除噪音数 ARI $(\%)$ Purity $(\%)$ Jaccard $(\%)$ RI $(\%)$ 1 000 993 2.56 $\downarrow$ 0.13 $\downarrow$ 2.28 $\downarrow$ 2.08 $\downarrow$ 2 000 1 984 2.94 $\downarrow$ 0.57 $\downarrow$ 2.72 $\downarrow$ 2.21 $\downarrow$ 3 000 2 971 3.25 $\downarrow$ 0.92 $\downarrow$ 3.01 $\downarrow$ 2.52 $\downarrow$ 表 4 UCI数据集上的算法性能
Table 4 Algorithm performance on UCI
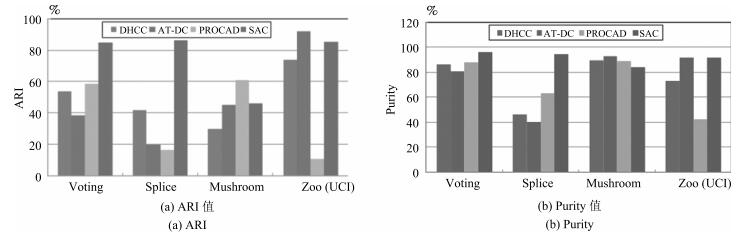
算法 UCI ARI $(\%)$ Purity $(\%)$ Jaccard $(\%)$ RI $(\%)$ DHCC Voting 53.67 86.67 63.17 76.84 Splice 41.75 46.08 38.96 75.11 Mushroom 29.90 89.50 38.22 63.52 Zoo 73.79 73.26 68.05 89.21 AT-DC Voting 38.5 80.92 54.23 69.28 Splice 19.78 40.22 35.31 61.28 Mushroom 45.20 93.21 48.81 72.63 Zoo 92.00 92.08 88.55 97.03 PROCAD Voting 58.49 88.28 66.39 79.11 Splice 16.57 63.29 34.31 59.30 Mushroom 61.10 89.11 68.22 80.56 Zoo 10.91 42.57 23.79 28.81 SAC Voting 84.88 96.09 86.80 92.47 Splice 86.26 94.76 84.23 93.54 Mushroom 46.21 84.25 59.62 73.13 Zoo 85.37 92.08 79.53 94.95 表 5 Voting集上的实验结果
Table 5 Experimental results on Voting
算法 簇的总数 簇编号 democrat republican DHCC 2 0 49 159 1 218 9 AT-DC 2 0 186 1 1 81 166 PROCAD 2 0 226 10 1 41 158 SAC 2 0 2 153 1 265 15 表 6 Splice集上的实验结果
Table 6 Experimental results on Splice
算法 簇的总数 簇编号 EI IE Neither DHCC 6 0 15 10 419 1 668 19 28 2 40 3 393 3 11 0 369 4 28 728 34 5 5 8 412 AT-DC 3 0 55 78 513 1 151 644 1 058 2 561 46 84 PROCAD 4 0 304 0 0 1 462 747 687 2 1 20 909 3 0 1 59 SAC 7 0 765 82 37 1 2 0 1 2 0 682 45 3 0 1 1 566 4 0 2 0 5 0 1 4 6 0 0 2 表 7 Zoo集上的实验结果
Table 7 Experimental results on Zoo
算法 簇的总数 簇编号 Mammal Bird Reptile Fish Amphibian Insect Invertebrate DHCC 3 0 41 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 5 13 4 0 8 2 0 20 0 0 0 8 2 AT-DC 7 0 41 0 2 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 2 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 8 2 4 0 20 0 0 0 0 0 5 0 0 3 13 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 PROCAD 2 0 41 18 5 12 4 7 10 1 0 2 0 1 0 1 0 SAC 9 0 37 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 4 0 0 13 0 0 0 2 0 20 0 0 3 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 4 0 0 0 0 0 8 1 5 0 0 2 0 3 0 0 6 0 0 3 0 1 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 表 8 Mushroom集上的实验结果
Table 8 Experimental results on Mushroom
算法 簇的总数 簇编号 poisonous edible DHCC 10 0 24 32 1 1 728 0 2 1 296 0 3 0 16 4 736 2 880 5 72 808 6 0 216 7 44 0 8 16 64 9 0 192 AT-DC 8 0 360 3 536 1 0 288 2 1 734 0 3 456 192 4 1 296 0 5 64 0 6 0 129 7 6 0 PROCAD 2 0 3 050 20 1 866 4 188 SAC 3 0 1 258 4 185 1 2 615 23 2 43 0 表 9 Zoo数据集中的相关子空间
Table 9 Relevant subspace on Zoo data set
簇号 簇内数据分布 子空间上的属性及其取值 $C_1$ 100%Mammal hair = 1; eggs = 0; milk = 1; fins = 0; legs = 4 $C_2$ 76.5%Fish; 23.5%Mammal fins = 1; legs = 0; aquatic = 1 $C_3$ 100%Bird feathers = 1; airborne = 1; legs = 2 $C_4$ 100%Invertebrate backbone = 0; legs = 0 $C_5$ 88.8%Insect; 11.2%Invertebrate backbone = 0; legs = 6 $C_6$ 60%Amphibian; 40%Reptile hair = 0; predator = 1; toothed = 1 $C_7$ 75%Reptile; 25%Amphibian breathes = 1; legs = 4; tail = 1 $C_8$ 100%Invertebrate legs = 8 $C_9$ 100%Invertebrate legs = 5 表 10 各种离散化方法下的SAC聚类性能指标对比
Table 10 Clustering performance of different discretization methods
ARI $(\%)$ Purity $(\%)$ Jaccard $(\%)$ RI $(\%)$ 7等距离散 45.18 67.55 36.86 85.20 11等距离散 46.65 84.02 36.12 87.38 15等距离散 41.75 91.34 31.06 87.13 18等距离散 36.68 91.61 26.61 86.46 22等距离散 31.40 92.71 22.22 85.78 表 11 各算法在光谱数据上的对比实验
Table 11 Algorithm performance on spectral data
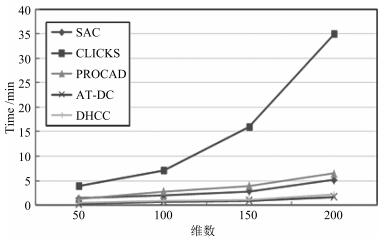
ARI $(\%)$ Purity $(\%)$ Jaccard $(\%)$ RI $(\%)$ SAC 46.65 84.02 36.12 87.38 PROCAD 43.41 80.18 32.41 82.72 DHCC 40.79 78.31 31.23 79.67 AT-DC 41.38 79.84 31.86 80.21 EWKM 33.47 70.08 30.11 71.64 CLICKS 40.65 71.66 30.83 75.79 -
[1] Wu X H, Wu B, Sun J, Qiu S W, Li X. A hybrid fuzzy K-harmonic means clustering algorithm. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39(12):3398-3409 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2014.11.041 [2] 蒋亦樟, 邓赵红, 王骏, 钱鹏江, 王士同.熵加权多视角协同划分模糊聚类算法.软件学报, 2014, 25(10):2293-2311 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004510.htmlJiang Yi-Zhang, Deng Zhao-Hong, Wang Jun, Qian Peng-Jiang, Wang Shi-Tong. Collaborative partition multi-view fuzzy clustering algorithm using entropy weighting. Journal of Software, 2014, 25(10):2293-2311 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004510.html [3] Bai L, Liang J Y. Cluster validity functions for categorical data:a solution-space perspective. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2015, 29(6):1560-1597 doi: 10.1007/s10618-014-0387-5 [4] Bouguettaya A, Yu Q, Liu X, Zhou X, Song A. Efficient agglomerative hierarchical clustering. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(5):2785-2797 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.09.054 [5] 周晨曦, 梁循, 齐金山.基于约束动态更新的半监督层次聚类算法.自动化学报, 2015, 41(7):1253-1263 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18699.shtmlZhou Chen-Xi, Liang Xun, Qi Jin-Shan. A semi-supervised agglomerative hierarchical clustering method based on dynamically updating constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(7):1253-1263 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18699.shtml [6] Jeon Y, Yoon S. Multi-threaded hierarchical clustering by parallel nearest-neighbor chaining. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2015, 26(9):2534-2548 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2014.2355205 [7] Kim Y, Shim K, Kim M S, Sup Lee J. DBCURE-MR:an efficient density-based clustering algorithm for large data using MapReduce. Information Systems, 2014, 42:15-35 doi: 10.1016/j.is.2013.11.002 [8] Mansoori E G. GACH:a grid-based algorithm for hierarchical clustering of high-dimensional data. Soft Computing, 2014, 18(5):905-922 doi: 10.1007/s00500-013-1105-8 [9] Shang R H, Zhang Z, Jiao L C, Wang W B, Yang S Y. Global discriminative-based nonnegative spectral clustering. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 55:172-182 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.01.035 [10] 孙吉贵, 刘杰, 赵连宇.聚类算法研究.软件学报, 2008, 19(1):48-61 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb200801006Sun Ji-Gui, Liu Jie, Zhao Lian-Yu. Clustering algorithms research. Journal of Software, 2008, 19(1):48-61 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb200801006 [11] Park I K, Choi G S. Rough set approach for clustering categorical data using information-theoretic dependency measure. Information Systems, 2015, 48:289-295 doi: 10.1016/j.is.2014.06.008 [12] Chen L F, Wang S R, Wang K J, Zhu J P. Soft subspace clustering of categorical data with probabilistic distance. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 51:322-332 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.09.027 [13] Cao F Y, Liang J Y, Bai L, Zhao X W, Dang C Y. A framework for clustering categorical time-evolving data. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(5):872-882 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2050891 [14] Li M, Deng S B, Wang L, Feng S Z, Fan J P. Hierarchical clustering algorithm for categorical data using a probabilistic rough set model. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2014, 65:60-71 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2014.04.008 [15] He X, Feng J, Konte B, Mai S T, Plant C. Relevant overlapping subspace clusters on categorical data. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York, USA: ACM, 2014. 213-222 [16] Ji J C, Pang W, Zheng Y L, Wang Z, Ma Z Q. A novel artificial bee colony based clustering algorithm for categorical data. PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(5):e0127125 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4439097/ [17] Gan G, Wu J, Yang Z. PARTCAT: a subspace clustering algorithm for high dimensional categorical data. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Network Proceedings. IEEE, 2006: 4406-4412 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1716710 [18] Bouveyron C, Girard S, Schmid C. High-dimensional data clustering. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2007, 52(1):502-519 doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2007.02.009 [19] Guha S, Rastogi R, Shim K. ROCK: a robust clustering algorithm for categorical attributes. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Data Engineering. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 1999. 512-521 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=754967&tag=1 [20] Barbará D, Li Y, Couto J. COOLCAT: an entropy-based algorithm for categorical clustering. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. McLean, VA, USA: ACM, 2002. 582-589 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=584888 [21] Cao L J, Chu K S, Chong W K, Lee H P, Gu Q M. A comparison of PCA, KPCA and ICA for dimensionality reduction in support vector machine. Neurocomputing, 2003, 55(1-2):321-336 doi: 10.1016/S0925-2312(03)00433-8 [22] Hu Q H, Xie Z X, Yu D R. Hybrid attribute reduction based on a novel fuzzy-rough model and information granulation. Pattern Recognition, 2007, 40(12):3509-3521 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.03.017 [23] Shang R H, Zhang Z, Jiao L C, Liu C Y, Li Y Y. Self-representation based dual-graph regularized feature selection clustering. Neurocomputing, 2016, 171:1242-1253 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.07.068 [24] Parsons L, Haque E, Liu H. Subspace clustering for high dimensional data:a review. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2004, 6(1):90-105 doi: 10.1145/1007730 [25] Yip K Y, Cheung D W, Ng M K. HARP:a practical projected clustering algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2004, 16(11):1387-1397 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2004.74 [26] Müller E, Günnemann S, Assent I, Seidl T. Evaluating clustering in subspace projections of high dimensional data. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2009, 2(1):1270-1281 doi: 10.14778/1687627 [27] Bouguessa M, Wang S R. Mining projected clusters in high-dimensional spaces. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2009, 21(4):507-522 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2008.162 [28] Gan G J, Wu J H. Subspace clustering for high dimensional categorical data. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2004, 6(2):87-94 doi: 10.1145/1046456 [29] Zaki M J, Peters M, Assent I, Seidl T. CLICKS:an effective algorithm for mining subspace clusters in categorical datasets. Data and Knowledge Engineering, 2007, 60(1):51-70 doi: 10.1016/j.datak.2006.01.005 [30] Bouguessa M. Clustering categorical data in projected spaces. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2015, 29(1):3-38 doi: 10.1007/s10618-013-0336-8 [31] Cesario E, Manco G, Ortale R. Top-down parameter-free clustering of high-dimensional categorical data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2007, 19(12):1607-1624 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2007.190649 [32] Xiong T K, Wang S R, Mayers A, Monga E. DHCC:divisive hierarchical clustering of categorical data. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2012, 24(1):103-135 doi: 10.1007/s10618-011-0221-2 [33] Bai L, Liang J Y, Dang C Y, Cao F Y. A novel attribute weighting algorithm for clustering high-dimensional categorical data. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(12):2843-2861 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.04.024 [34] Chan E Y, Ching W K, Ng M K, Huang J Z. An optimization algorithm for clustering using weighted dissimilarity measures. Pattern Recognition, 2004, 37(5):943-952 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2003.11.003 [35] Jing L P, Ng M K, Huang J Z. An entropy weighting k-means algorithm for subspace clustering of high-dimensional sparse data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2007, 19(8):1026-1041 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2007.1048 [36] Xiong H, Wu J J, Chen J. K-means clustering versus validation measures:a data-distribution perspective. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B:Cybernetics, 2009, 39(2):318-331 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.2004559 [37] Liang J Y, Bai L, Dang C Y, Cao F Y. The k-means-type algorithms versus imbalanced data distributions. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(4):728-745 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2182354 [38] 曲开社, 翟岩慧, 梁吉业, 李德玉.形式概念分析对粗糙集理论的表示及扩展.软件学报, 2007, 18(9):2174-2182 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rjxb200709012Qu Kai-She, Zhai Yan-Hui, Liang Ji-Ye, Li De-Yu. Representation and extension of rough set theory based on formal concept analysis. Journal of Software, 2007, 18(9):2174-2182 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rjxb200709012 [39] 刘少辉, 盛秋戬, 吴斌, 史忠植, 胡斐. Rough集高效算法的研究.计算机学报, 2003, 26(5):524-529 http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90818X/200305/7812506.htmlLiu Shao-Hui, Sheng Qiu-Jian, Wu Bin, Shi Zhong-Zhi, Hu Fei. Research on efficient algorithms for rough set methods. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2003, 26(5):524-529 http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90818X/200305/7812506.html [40] Kim M, Ramakrishna R S. Projected clustering for categorical datasets. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 27(12):1405-1417 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2006.01.011 [41] 张继福, 蒋义勇, 胡立华, 蔡江辉, 张素兰.基于概念格的天体光谱离群数据识别方法.自动化学报, 2008, 34(9):1060-1066 http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90250X/200809/28192750.htmlZhang Ji-Fu, Jiang Yi-Yong, Hu Li-Hua, Cai Jiang-Hui, Zhang Su-Lan. A concept lattice based recognition method of celestial spectra outliers. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(9):1060-1066 http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90250X/200809/28192750.html [42] Zhang J F, Zhao X J, Zhang S L, Yin S, Qin X. Interrelation analysis of celestial spectra data using constrained frequent pattern trees. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2013, 41:77-88 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2012.12.013 -





 下载:
下载: