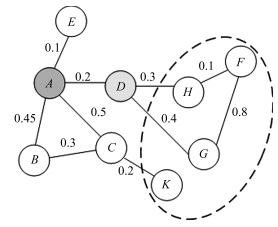
-
摘要: 精确注释蛋白质功能是从分子水平理解生物体的关键.由于内在的困难和昂贵的开销,实验方法注释蛋白质功能已经很难满足日益增长的序列数据.为此,提出了许多基于蛋白质相互作用(Protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络的计算方法预测蛋白质功能.当今蛋白质功能预测的趋势是融合蛋白质相互作用网络和异构生物数据.本文提出一种基于多关系网络中关键功能模块挖掘的蛋白质功能预测算法.关键功能模块由一组紧密联系且共享生物功能的蛋白质组成,它们能与网络中的剩余部分较好地区分开来.算法通过从多关系网络的每一个简单网络中挖掘高内聚、低耦合的子图形成关键功能模块.关键功能模块中邻居蛋白质的功能用于注释待预测功能的蛋白质.每一个简单网络在蛋白质功能预测中的重要性各不相同.实验结果表明,提出的方法性能优于现有的蛋白质功能预测方法.Abstract: The accurate annotation of protein functions is a key to understanding living organisms at the molecular level. With its inherent difficulty and expense, experimental characterization of protein functions cannot scale up to accommodate the vast amount of sequence data. As a result, many computational methods based on protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks have been proposed to predict the functions of proteins. Nowadays, the trend in protein functions prediction is to integrate PPI networks and heterogeneous biological data. A novel protein functions prediction algorithm was proposed based on mining essential functional modules from a multi-relational network. An essential functional module is a group of densely connected proteins with shared biological function and can be well-separated from the rest of the network. The proposed algorithm identified subgraph with high cohesion and low coupling on each single network derived from the multi-relational network to form essential functional modules. Functions of neighbor proteins within essential functional modules were used to annotate the testing protein. Each single network has different importance on the prediction of protein functions. Experiment results show that our method outperforms other protein functions prediction methods.1) 本文责任编委 张学工
-
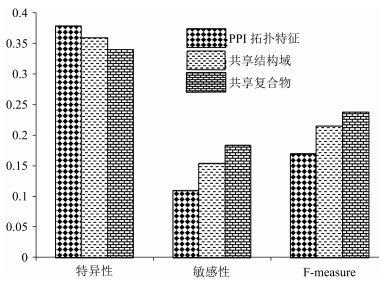
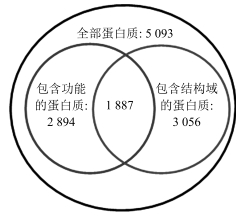
表 1 蛋白质功能数量统计
功能数量 蛋白质数量 共享结构域的蛋白质数量 所占比例(%) 1 1 512 523 34.59 2 703 318 45.23 3 317 166 52.37 4 140 77 55.00 5 106 54 50.94 > 5 116 77 66.38 表 2 Krogan, Gavin和BioGrid运行结果
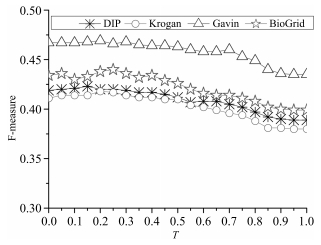
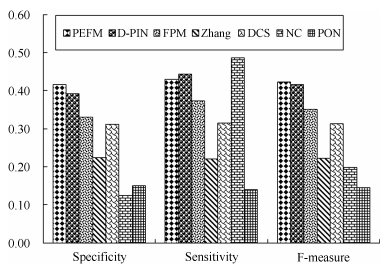
Table 2 Results of methods on Krogan, Gavin and BioGrid
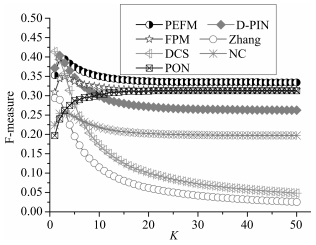
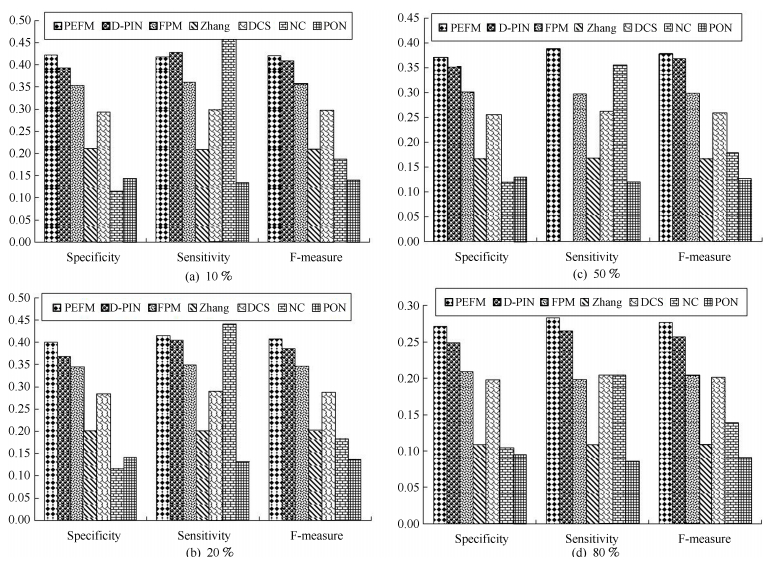
Dataset Method Specificity Sensitivity F-Measure Krogan PEFM 0.412 0.423 0.418 Krogan D-PIN 0.367 0.405 0.385 Krogan FPM 0.317 0.342 0.329 Krogan Zhang 0.231 0.221 0.226 Krogan DCS 0.316 0.321 0.318 Krogan NC 0.076 0.583 0.135 Krogan PON 0.170 0.161 0.165 Gavin PEFM 0.466 0.472 0.469 Gavin D-PIN 0.443 0.486 0.463 Gavin FPM 0.401 0.404 0.403 Gavin Zhang 0.197 0.190 0.194 Gavin DCS 0.381 0.393 0.387 Gavin NC 0.210 0.603 0.311 Gavin PON 0.155 0.145 0.150 BioGrid PEFM 0.433 0.447 0.440 BioGrid D-PIN 0.392 0.445 0.417 BioGrid FPM 0.393 0.415 0.403 BioGrid Zhang 0.236 0.233 0.235 BioGrid DCS 0.370 0.375 0.372 BioGrid NC 0.076 0.583 0.135 BioGrid PON 0.170 0.161 0.165 -
[1] Zhao B H, Wang J X, Li M, Li X Y, Li Y H, Wu F X, Pan Y. A new method for predicting protein functions from dynamic weighted interactome networks. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 2016, 15(2):131-139 doi: 10.1109/TNB.2016.2536161 [2] Schwikowski B, Uetz P, Fields S. A network of protein-protein interactions in yeast. Nature Biotechnology, 2000, 18(12):1257-1261 doi: 10.1038/82360 [3] Dutkowski J, Ideker T. Protein networks as logic functions in development and cancer. PLoS Computational Biology, 2011, 7(9):e1002180 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002180 [4] 胡赛, 熊慧军, 赵碧海, 李学勇, 王晶.动态加权蛋白质相互作用网络构建及其应用研究.自动化学报, 2015, 41(11):1893-1900 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18764.shtmlHu Sai, Xiong Hui-Jun, Zhao Bi-Hai, Li Xue-Yong, Wang Jing. Construction of dynamic-weighted protein interactome network and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(11):1893-1900 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18764.shtml [5] Zhao B H, Wang J X, Li X Y, Wu F X. Essential protein discovery based on a combination of modularity and conservatism. Methods, 2016, 110:54-63 doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.07.005 [6] Li X Y, Wang J X, Zhao B H, Wu F X, Pan Y. Identification of protein complexes from multi-relationship protein interaction networks. Human Genomics, 2016, 10(S2):17 doi: 10.1186/s40246-016-0069-z [7] 胡赛, 熊慧军, 李学勇, 赵碧海, 倪问尹, 杨品红, 刘臻.多关系蛋白质网络构建及其应用研究.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12):2155-2163 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18788.shtmlHu Sai, Xiong Hui-Jun, Li Xue-Yong, Zhao Bi-Hai, Ni Wen-Yin, Yang Pin-Hong, Liu Zhen. Construction of multi-relation protein networks and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12):2155-2163 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18788.shtml [8] Peng W, Wang J X, Cai J, Chen L, Li M, Wu F X. Improving protein function prediction using domain and protein complexes in PPI networks. BMC Systems Biology, 2014, 8(1):35 doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-35 [9] Zotenko E, Mestre J, O'Leary D P, Przytycka T M. Why do hubs in the yeast protein interaction network tend to be essential:reexamining the connection between the network topology and essentiality. PLoS Computational Biology, 2008, 4(8):e1000140 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000140 [10] Nepusz T, Yu H Y, Paccanaro A. Detecting overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction networks. Nature Methods, 2012, 9(5):471-472 doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1938 [11] Xenarios I, Rice D W, Salwinski L, Baron M K, Marcotte E M, Eisenberg D. DIP:the database of interacting proteins. Nucleic Acids Research, 2000, 28(1):289-291 doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.289 [12] Stark C, Breitkreutz B J, Chatr-Aryamontri A, Boucher L, Oughtred R, Livstone M S, Nixon J, Van Auken K, Wang X D, Shi X Q, Reguly T, Rust J M, Winter A, Dolinski K, Tyers M. The BioGRID interaction database:2011 update. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(S1):D698-D704 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5846950_The_BioGRID_interaction_database_2008_update [13] Gavin A C, Aloy P, Grandi P, Krause R, Boesche M, Marzioch M, Rau C, Jensen L J, Bastuck S, Dümpelfeld B, Edelmann A, Heurtier M A, Hoffman V, Hoefert C, Klein K, Hudak M, Michon A M, Schelder M, Schirle M, Remor M, Rudi T, Hooper S, Bauer A, Bouwmeester T, Casari G, Drewes G, Neubauer G, Rick J M, Kuster B, Bork P, Russell R B, Superti-Furga G. Proteome survey reveals modularity of the yeast cell machinery. Nature, 2006, 440(7084):631-636 doi: 10.1038/nature04532 [14] Krogan N J, Cagney G, Yu H Y, Zhong G Q, Guo X H, Ignatchenko A, Li J, Pu S Y, Datta N, Tikuisis A P, Punna T, Peregrín-Alvarez J M, Shales M, Zhang X, Davey M, Robinson M D, Paccanaro A, Bray J E, Sheung A, Beattie B, Richards D P, Canadien V, Lalev A, Mena F, Wong P, Starostine A, Canete M M, Vlasblom J, Wu S, Orsi C, Collins S R, Chandran S, Haw R, Rilstone J J, Gandi K, Thompson N J, Musso G, Onge P S, Ghanny S, Lam M H Y, Butland G, Altaf-Ul A M, Kanaya S, Shilatifard A, O'Shea E, Weissman J S, Ingles C J, Hughes T R, Parkinson J, Gerstein M, Wodak S J, Emili A, Greenblatt J F. Global landscape of protein complexes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature, 2006, 440(7084):637-643 doi: 10.1038/nature04670 [15] Martin D M A, Berriman M, Barton G J. GOtcha:a new method for prediction of protein function assessed by the annotation of seven genomes. BMC Bioinformatics, 2004, 5(1):178 doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-178 [16] Lima T, Auchincloss A H, Coudert E, Keller G, Michoud K, Rivoire C, Bulliard V, de Castro E, Lachaize C, Baratin D, Phan I, Bougueleret L, Bairoch A. HAMAP:a database of completely sequenced microbial proteome sets and manually curated microbial protein families in UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(S1):D471-D478 http://www.citeulike.org/user/neils/article/3398716 [17] Hawkins T, Chitale M, Luban S, Kihara D. PFP:automated prediction of gene ontology functional annotations with confidence scores using protein sequence data. Proteins:Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 2009, 74(3):566-582 doi: 10.1002/prot.v74:3 [18] Pu S Y, Wong J, Turner B, Cho E, Wodak S J. Up-to-date catalogues of yeast protein complexes. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(3):D825-D831 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1005 [19] Zhang S, Chen H, Liu K, Sun Z R. Inferring protein function by domain context similarities in protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 2009, 10(1):395 doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-395 [20] Liang S D, Zheng D D, Standley D M, Guo H R, Zhang C. A novel function prediction approach using protein overlap networks. BMC Systems Biology, 2013, 7(1):61 doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-61 -




 下载:
下载: