-
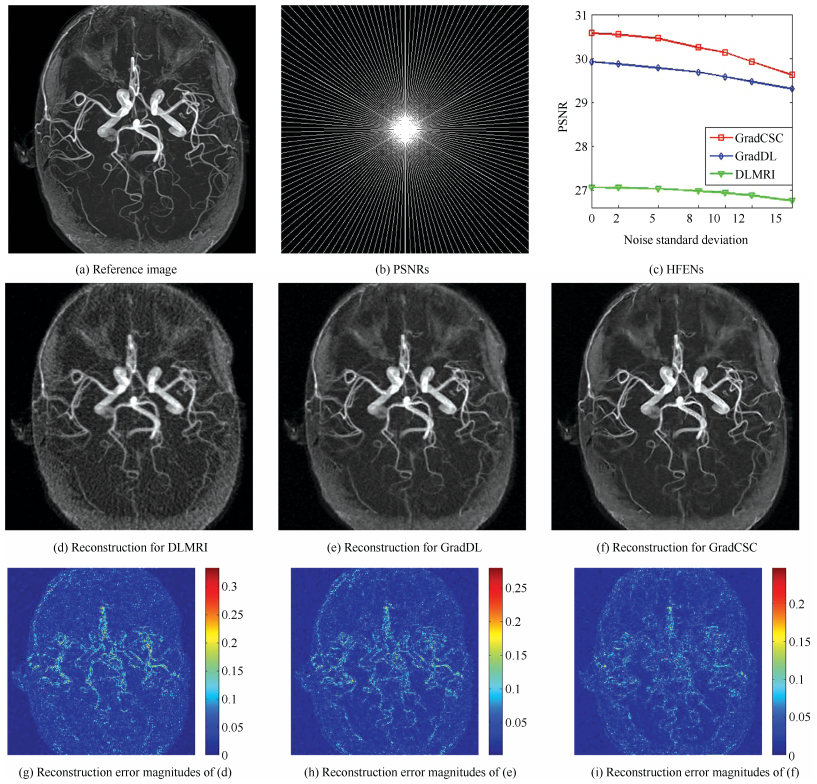
摘要: 从欠采样数据中进行磁共振成像(简称MRI)重建一直是一项具有挑战性和吸引力的任务,因为这是一个病态问题,且伴随着压缩感知理论会具有重要的意义.基于压缩感知的多数先进稀疏表示方法是将图像分割成重叠的图像块,然后每个图像块分开处理.然而,这些方法丢失了信号的重要空间结构,且忽略了对MR图像有强大约束的像素一致性.在文章中我们提出了一种新型的重建方法,这种方法是将最近提出的卷积稀疏编码与梯度域结合起来用于解决上述所提到的问题.不同于基于图像块状的方法,本文提出的算法是直接在整个梯度域图像中获取相邻局部的相关性,利用梯度域图像的全局相关性产生更好的梯度域图像边缘,锐利特征.提出的算法也能够高效的获取暗含在梯度域图像中的局部特征.与对比算法相比,大量的实验结果表明本文算法具有更好的质量重建,且在不同采样方案,不同K-空间加速因子情况下具有更快速的收敛.Abstract: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction from undersampled data has always been a challenging and fascinating task due to its implicit ill-posed nature and its significance accompanied with the emerging compressed sensing (CS) theory. Most state-of-the-art sparse representation based CS approaches partition the image into overlapped patches, and process each patch separately. These methods, however, lose important spatial structures of the signal of interest, and ignore the consistency of pixels, which is a strong constraint for MR image. In this paper, we propose a new reconstruction method, which builds on recently introduced ideas of convolutional sparse coding in gradient domain (GradCSC) to address above mentioned issue. As opposed to patch-based methods, GradCSC directly operates on the whole gradient image to capture the correlation between local neighborhoods and exploits the gradient image global correlation to produce better edges and sharp features of gradient image. It enables local features implicitly existed in the gradient images to be captured effectively. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves higher quality reconstructions than alternative methods and converges quickly at various sampling schemes and k-space acceleration factors.
-
Key words:
- Alternating direction method of multipliers /
- convolutional sparse coding(CSC) /
- filter learning /
- gradient image /
- magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)reconstruction
-
Algorithm 1. The GradCSC algorithm 1: Initialization: ${{z}_{k}}^{0}=0$, ${{d}_{k}}^{0}=0$, ${{({{b}^{(i)}})}^{0}}=0$, $i=1, 2$; ${{u}^{0}}=F_{p}^{T}f$
2: For $j=1, 2, \ldots $ repeat until a stop-criterion is satisfied
3: ${{({{w}^{(i)}})}^{j+1}}=\ \frac{{{\nu }_{2}}[{{({{b}^{(i)}})}^{j}}+{{({{\nabla }^{(i)}}u)}^{j}}]+\sum\limits_{k=1}^{K}{d_{_{k}}^{j}*z_{_{k}}^{j}}}{2{{\nu }_{2}}+1}, \ \ i=1, 2$
4: Updating $\{{{d}_{k}}^{j+1}, {{z}_{k}}^{j+1}\}$ from difference images ${{({{w}^{(i)}})}^{j+1}}$ by (13), $i=1, 2$
5: Updating $\{ r_{1}^{^{\ell +1}}, r_{2}^{^{\ell +1}}, r_{3}^{^{\ell +1}} \}$ from the coefficients, and the filters by (14)
6: ${{u}^{j+1}}={{F}^{\rm{-}1}}( \frac{F[{{\nu }_{1}}F_{p}^{T}f+{{\nu }_{2}}{{\nabla }^{T}}({{({{w}^{(i)}})}^{j}}^{+1}-{{({{b}^{(i)}})}^{j}})]}{{{\nu }_{1}}FF_{p}^{T}{{F}_{p}}{{F}^{T}}+{{\nu }_{2}}F{{\nabla }^{T}}{{F}^{T}}F\nabla {{F}^{T}}} )$
7: ${{({{b}^{(i)}})}^{j+1}}={{({{b}^{(i)}})}^{j}}+{{({{\nabla }^{(i)}}u)}^{j+1}}-{{({{w}^{(i)}})}^{j+1}}$, $i=1, 2$
8: End
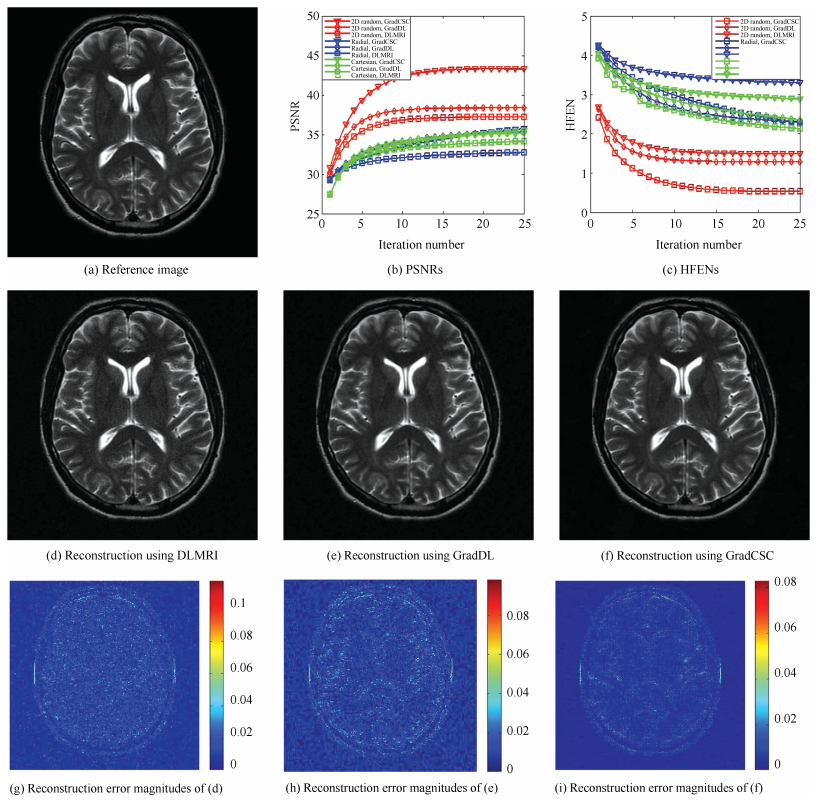
9: Output ${{u}^{j+1}}$Table Ⅰ Reconstruction PSNR Values at Different Undersampling Factors With the Same 2D Random Sampling Trajectories
Undersampling factors 2.5-fold 4-fold 6-fold 8-fold 10-fold 20-fold DLMRI 35.92 35.19 31.26 30.76 30.13 26.39 GradDL 38.26 38.20 34.35 32.89 31.81 27.90 GradCSC 37.39 37.53 35.23 35.45 34.62 30.54 -
[1] M. Lustig, D. Donoho, and J. M. Pauly, "Sparse MRI:The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging, " Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 1182-1195, Dec. 2007. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1522-2594 [2] D. L. Donoho, "Compressed sensing, " IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 1289-1306, Apr. 2006. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [3] D. Liang, B. Liu, J. Wang, and L. Ying, "Accelerating SENSE using compressed sensing, " Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 62, no. 6, pp. 1574-1584, Dec. 2009. doi: 10.1002/mrm.v62:6 [4] M. Lustig, J. M. Santos, D. L. Donoho, and J. M. Pauly, "k-t SPARSE: high frame rate dynamic MRI exploiting spatiotemporal sparsity, " in Proc. 13th Ann. Meeting of ISMRM, Seattle, USA, 2006. [5] S. Q. Ma, W. T. Yin, Y. Zhang, and A. Chakraborty, "An efficient algorithm for compressed MR imaging using total variation and wavelets, " in Proc. IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 2008, pp. 1-8. [6] J. Trzasko and A. Manduca, "Highly undersampled magnetic resonance image reconstruction via homotopic e0-minimization, " IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 106-121, Jan. 2009. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.927346 [7] S. M. Gho, Y. Nam, S. Y. Zho, E. Y. Kim, and D. H. Kim, "Three dimension double inversion recovery gray matter imaging using compressed sensing, " Magn. Reson. Imaging, vol. 28, no. 10, pp. 1395-1402, Dec. 2010. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2010.06.029 [8] M. Guerquin-Kern, M. Haberlin, K. P. Pruessmann, and M. Unser, "A fast wavelet-based reconstruction method for magnetic resonance imaging, " IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 30, no. 9, pp. 1649-1660, Sep. 2011. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2011.2140121 [9] L. Y. Chen, M. C. Schabel, and E. V. R. DiBella, "Reconstruction of dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the breast with temporal constraints, " Magn. Reson. Imaging, vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 637-645, Jun. 2010. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2010.03.001 [10] Q. G. Liu, S. S. Wang, K. Yang, J. H. Luo, Y. M. Zhu, and D. Liang, "Highly undersampled magnetic resonance image reconstruction using two-level Bregman method with dictionary updating, " IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 32, no. 7, pp. 1290-1301, Jul. 2013. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2256464 [11] X. B. Qu, D. Guo, B. D. Ning, Y. K. Hou, Y. L. Lin, S. H. Cai, and Z. Chen, "Undersampled MRI reconstruction with patch-based directional wavelets, " Magn. Reson. Imaging, vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 964-977, Sep. 2012. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.02.019 [12] S. Ravishankar and Y. Bresler, "MR image reconstruction from highly undersampled k-space data by dictionary learning, " IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 1028-1041, May 2011. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2090538 [13] Q. G. Liu, S. S. Wang, L. Ying, X. Peng, Y. J. Zhu, and D. Liang, "Adaptive dictionary learning in sparse gradient domain for image recovery, " IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 4652-4663, Dec. 2013. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2277798 [14] Z. L. Hu, Q. G. Liu, N. Zhang, Y. W. Zhang, X. Peng, P. Z. Wu, H. R. Zheng, and D. Liang, "Image reconstruction from few-view CT data by gradient-domain dictionary learning, " J. X-Ray Sci. Technol., vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 627-638, Jul. 2016. doi: 10.3233/XST-160579 [15] X. M. Luo, Z. Y. Suo, and Q. G. Liu, "Efficient InSAR phase noise filtering based on adaptive dictionary learning in gradient vector domain, " Chin. J. Eng. Math., vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 801-811, Dec. 2015. doi: 10.1162/neco.1995.7.6.1129 [16] M. D. Zeiler, D. Krishnan, G. W. Taylor, and R. Fergus, "Deconvolutional networks, " in Proc. 2010 IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010, pp. 2528-2535. [17] B. A. Olshausen and D. J. Field, "Sparse coding with an overcomplete basis set:a strategy employed by V1?, " Vision Res., vol. 37, no. 23, pp. 3311-3325, Dec. 1997. doi: 10.1016/S0042-6989(97)00169-7 [18] A. Szlam, K. Kavukcuoglu, and Y. LeCun, "Convolutional matching pursuit and dictionary training, " arXiv: 1010. 0422, Oct. 2010. [19] B. Chen, G. Polatkan, G. Sapiro, D. Blei, D. Dunson, and L. Carin, "Deep learning with hierarchical convolutional factor analysis, " IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 1887-1901, Aug. 2013. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.19 [20] K. Kavukcuoglu, P. Sermanet, Y. L. Boureau, K. Gregor, M. Mathieu, and Y. LeCun, "Learning convolutional feature hierarchies for visual recognition, " in Proc. 23rd Int. Conf. Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 2010, pp. 1090-1098. [21] M. D. Zeiler, G. W. Taylor, and R. Fergus, "Adaptive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level feature learning, " in Proc. 2011 IEEE Int. Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV), Barcelona, USA, 2011, pp. 2018-2025. [22] F. Heide, L. Xiao, A. Kolb, M. B. Hullin, and W. Heidrich, "Imaging in scattering media using correlation image sensors and sparse convolutional coding, " Opt. Express, vol. 22, no. 21, pp. 26338-26350, Oct. 2014. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.026338 [23] X. M. Hu, Y. Deng, X. Lin, J. L. Suo, Q. H. Dai, C. Barsi, and R. Raskar, "Robust and accurate transient light transport decomposition via convolutional sparse coding, " Opt. Lett., vol. 39, no. 11, pp. 3177-3180, Jun. 2014. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.003177 [24] J. Y. Xie, L. L. Xu, and E. H. Chen, "Image denoising and inpainting with deep neural networks, " in Proc. 25th Int. Conf. Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA, 2012, pp. 341-349. [25] S. H. Gu, W. M. Zuo, Q. Xie, D. Y. Meng, X. C. Feng, and L. Zhang, "Convolutional sparse coding for image superresolution, " in Proc. 2015 IEEE Int. Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015, pp. 1823-1831. [26] A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. E. Hinton, "Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks, " in Proc. 25th Int. Conf. Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA, 2012, pp. 1097-1105. [27] Y. Y. Zhu, M. Cox, and S. Lucey, "3D motion reconstruction for real-world camera motion, " in Proc. 2011 IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 2011, pp. 1-8. [28] Y. Y. Zhu and S. Lucey, "Convolutional sparse coding for trajectory reconstruction, " IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 529-540, Mar. 2015. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.2295311 [29] Y. Y. Zhu, D. Huang, F. De La Torre, and S. Lucey, "Complex non-rigid motion 3D reconstruction by union of subspaces, " in Proc. 2014 IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 2014, pp. 1542-1549. [30] A. Serrano, F. Heide, D. Gutierrez, G. Wetzstein, and B. Masia, "Convolutional sparse coding for high dynamic range imaging, " Computer Graphics, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 153-163, May 2016. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3028600 [31] J. F. Yang, Y. Zhang, and W. T. Yin, "A fast alternating direction method for TVL1-L2 signal reconstruction from partial Fourier data, " IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 288-297, Apr. 2010. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2042333 [32] H. Bristow, A. Eriksson, and S. Lucey, "Fast convolutional sparse coding, " in Proc. 2013 IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 2013, pp. 391-398. [33] B. Wohlberg, "Efficient convolutional sparse coding, " in Proc. 2014 IEEE Int. Conf. Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 2014, pp. 7173-7177. -




 下载:
下载: