Multivariable Inverted Decoupling Active Disturbance Rejection Control and Its Application to a Distillation Column Process
-
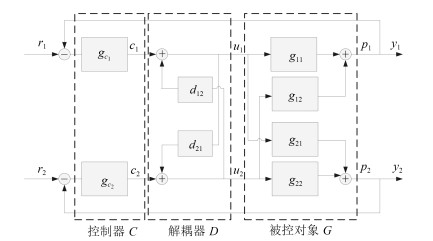
摘要: 化工生产是一类典型的多变量过程对象,该类对象具有时变性、耦合性、时滞性等特点,传统的单变量控制方法很难在此类系统中取得良好的控制效果.针对时变性,本文在假设对象模型未知的前提下,利用阶跃响应数据,研究了基于最小二乘的一阶、二阶时滞系统辨识方法.针对多变量系统存在耦合性的特点,采用逆解耦方法实现对象的解耦.再对解耦后的时滞子系统设计了自抗扰控制器.仿真实验中,以精馏塔的Wood-Berry模型和Ogunnaike-Ray模型为例,验证了算法的有效性.Abstract: Chemical industry is a class of typical multivariable process plants, and has the characteristics of time-varying, coupling, and time delay. It is difficult to achieve good control effect in such systems by using traditional single variable control methods. In this paper, aiming at time-varying behavior, it is assumed that the model of the plant is unknown. By using step response data, an identification method for first-order and second-order delay systems is studied based on least squares method. For the coupling of multivariable systems, the inverted decoupling method is used to decouple the plant. And then an active disturbance rejection controller is designed for the decoupled delay subsystem. In the simulation experiment, the effectiveness of the algorithm is verified by the Wood-Berry model and the Ogunnaike-Ray model of the distillation column.1) 本文责任编委 王伟
-
表 1 Wood-Berry模型辨识结果的均方误差
Table 1 Mean square error of the Wood-Berry model
G11 G12 G21 G22 NSR=1% 1.93×10-4 6.37×10-5 2.98×10-5 4.69×10-5 NSR=10% 4.88×10-5 6.32×10-4 6.62×10-4 2.10×10-3 表 2 三种算法IAE指标对比
Table 2 Comparison of IAE for three methods
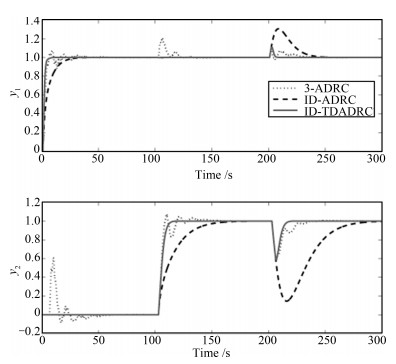
IAE1 IAE2 Sum 3-ADRC 6.01 15.15 21.16 ID-ADRC 5.25 21.09 26.34 ID-TDADRC 2.59 8.77 11.36 表 3 采用辨识数据控制下的IAE指标
Table 3 IAE by using identiflcation data
IAE1 IAE2 Sum NSR=1% 2.62 8.78 11.40 NSR=10% 2.73 8.77 11.50 表 4 三种算法IAE指标对比
Table 4 Comparison of IAE for three methods
G11 G12 G13 G21 G22 G23 G31 G32 G33 NSR=1% 1.62×10-7 5.19×10-7 7.08×10-12 3.63×10-6 1.94×10-6 1.07×10-10 5.60×10-4 4.69×10-5 1.38×10-6 NSR=10% 2.36×10-8 1.35×10-6 1.95×10-10 1.61×10-6 3.45×10-6 3.12×10-10 2.70×10-3 2.00×10-3 2.38×10-4 表 5 三种算法IAE指标对比
Table 5 Comparison of IAE for three methods
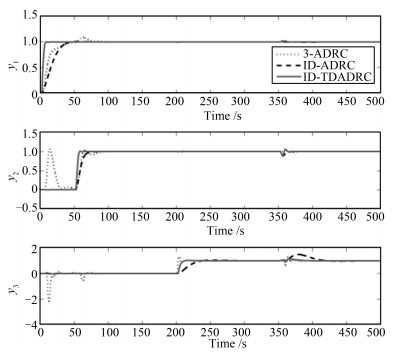
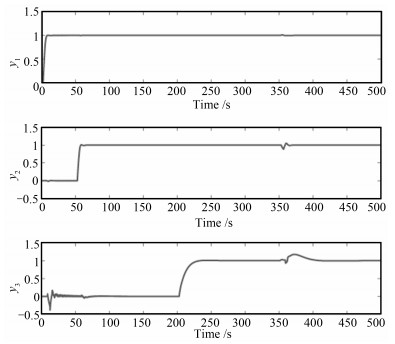
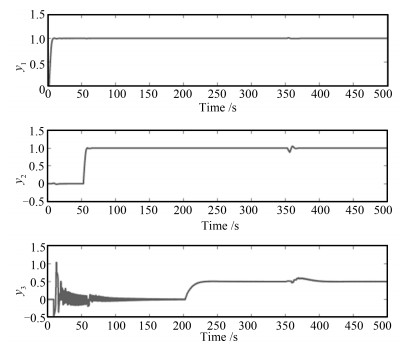
IAE1 IAE2 IAE3 Sum 3-ADRC 15.22 23.41 19.23 57.86 ID-ADRC 17.75 10.65 35.16 63.56 ID-TDADRC 4.59 5.41 8.86 18.86 表 6 采用辨识数据控制下的IAE指标
Table 6 IAE by using identiflcation data
IAE1 IAE2 IAE3 Sum NSR=1% 4.61 5.50 17.85 27.96 NSR=10% 4.63 5.55 38.15 48.33 -
[1] Wood R K, Berry M W. Terminal composition control of a binary distillation column. Chemical Engineering Science, 1973, 28(9): 1707-1717 doi: 10.1016/0009-2509(73)80025-9 [2] Rake H. Step response and frequency response methods. Automatica, 1980, 16(5): 519-526 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(80)90075-8 [3] Unbehauen H, Rao G P. Identification of Continuous Systems. Amsterdam, Netherlands: North-Holland, 1987. [4] Gustavsson I. Survey of applications of identification in chemical and physical processes. Automatica, 1975, 11(1): 3-24 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(75)90005-9 [5] Wang Y G, Cai W J, Ge M. Decentralized relay-based multivariable process identification in the frequency domain. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(5): 873-878 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2003.811271 [6] Bi Q, Cai W J, Lee E L, Wang Q G, Hang C C, Zhang Y. Robust identification of first-order plus dead-time model from step response. Control Engineering Practice, 1999, 7(1): 71-77 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(98)00166-X [7] Wang Q G, Zhang Y. Robust identification of continuous systems with dead-time from step responses. Automatica, 2001, 37(3): 377-390 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(00)00177-1 [8] Wang Q G, Guo X, Zhang Y. Direct identification of continuous time delay systems from step responses. Journal of Process Control, 2001, 11(5): 531-542 doi: 10.1016/S0959-1524(00)00031-7 [9] Ahmed S, Huang B, Shah S L. Identification from step responses with transient initial conditions. Journal of Process Control, 2008, 18(2): 121-130 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2007.07.009 [10] Zhu Y C, Patwardhan R, Wagner S, Zhao J. Toward a low cost and high performance MPC: the role of system identification. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2013, 51(14): 124-135 [11] Van Overschee P, De Moor B L. Subspace identification for linear systems: theory-implementation-applications. US: Springer, 1996. [12] Lee J H. Model predictive control: review of the three decades of development. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2011, 9(3): 415-424 doi: 10.1007/s12555-011-0300-6 [13] 席裕庚, 李德伟, 林姝.模型预测控制—现状与挑战.自动化学报, 2013, 39(3): 222-236 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17874.shtmlXi Yu-Geng, Li De-Wei, Lin Shu. Model predictive control: status and challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(3): 222-236 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17874.shtml [14] 杨剑锋, 赵均, 钱积新, 牛健.一类化工过程多变量系统的自适应非线性预测控制.化工学报, 2008, 59(4): 934-940 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ200804023.htmYang Jian-Feng, Zhao Jun, Qian Ji-Xin, Niu Jian. Adaptive nonlinear model predictive control for a class of multivariable chemical processes. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2008, 59(4): 934-940 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ200804023.htm [15] Wade H L. Inverted decoupling: a neglected technique. ISA Transactions, 1997, 36(1): 3-10 doi: 10.1016/S0019-0578(97)00008-6 [16] Luan X L, Chen Q, Albertos P, Liu F. Compensator design based on inverted decoupling for non-square processes. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 11(7): 996-1005 [17] Garrido J, Vázquez F, Morilla F. An extended approach of inverted decoupling. Journal of Process Control, 2011, 21(1): 55-68 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2010.10.004 [18] Garrido J, Vázquez F, Morilla F, Hägglund T. Practical advantages of inverted decoupling. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part Ⅰ: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2011, 225(7): 977-992 https://lup.lub.lu.se/search/publication/2223536 [19] Garrido J, Vázquez F, Morilla F. Inverted decoupling internal model control for square stable multivariable time delay systems. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24(11): 1710-1719 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.09.003 [20] Sun L, Dong J Y, Li D H, Lee K Y. A practical multivariable control approach based on inverted decoupling and decentralized active disturbance rejection control. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(7): 2008-2019 doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03738 [21] 韩京清.自抗扰控制器及其应用.控制与决策, 1998, 13(1): 19-23 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10532-2009164398.htmHan Jing-Qing. Auto-disturbance-rejection controller and its applications. Control and Decision, 1998, 13(1): 19-23 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10532-2009164398.htm [22] Zheng Q, Gao Z Q. Active disturbance rejection control: between the formulation in time and the understanding in frequency. Control Theory and Technology, 2016, 14(3): 250-259 doi: 10.1007/s11768-016-6059-9 [23] Zheng Q, Chen Z Z, Gao Z Q. A dynamic decoupling control approach and its applications to chemical processes. In: Proceedings of the 2007 American Control Conference (ACC'07). New York, USA: IEEE, 2007. 5176-5181 [24] 张园, 孙明玮, 陈增强.强制循环蒸发系统线性自抗扰解耦控制的鲁棒设计.化工学报, 2015, 66(S2): 263-270 doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20141914Zhang Yuan, Sun Ming-Wei, Chen Zeng-Qiang. Robust design of linear active disturbance rejection decoupling control for forced-circulation evaporation system. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(S2): 263-270 doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20141914 [25] Tian L L, Li D H, Huang C E. Decentralized controller design based on 3-order active-disturbance-rejection-control. In: Proceedings of the 10th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2012. 2746-2751 [26] 王丽君, 李擎, 童朝南, 尹怡欣.时滞系统的自抗扰控制综述.控制理论与应用, 2013, 30(12): 1521-1533 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201312008.htmWang Li-Jun, Li Qing, Tong Chao-Nan, Yin Yi-Xin. Overview of active disturbance rejection control for systems with time-delay. Control Theory & Applications, 2013, 30(12): 1521-1533 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201312008.htm [27] Zhao S, Gao Z Q. Modified active disturbance rejection control for time-delay systems. ISA transactions, 2014, 53(4): 882-888 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2013.09.013 [28] Zheng Q L, Gao Z Q. On active disturbance rejection for systems with input time-delays and unknown dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2016. 95-100 [29] 唐德翠, 高志强, 张绪红.浊度大时滞过程的预测自抗扰控制器设计.控制理论与应用, 2017, 34(1): 101-108 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201701013.htmTang De-Cui, Gao Zhi-Qiang, Zhang Xu-Hong. Design of predictive active disturbance rejection controller for turbidity. Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 34(1): 101-108 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201701013.htm [30] Gao Z Q. Scaling and bandwidth-parameterization based controller tuning. In: Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference. Denver, USA: IEEE, 2003. 4989-4996 [31] Zheng Q, Gao L Q, Gao Z Q. On stability analysis of active disturbance rejection control for nonlinear time-varying plants with unknown dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2007. 3501-3506 [32] 陈增强, 孙明玮, 杨瑞光.线性自抗扰控制器的稳定性研究.自动化学报, 2013, 39(5): 574-580 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17868.shtmlChen Zeng-Qiang, Sun Ming-Wei, Yang Rui-Guang. On the stability of linear active disturbance rejection control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(5): 574-580 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17868.shtml -




 下载:
下载: