-
摘要: 湿法冶金过程具有反应机理复杂、工艺流程长、工序众多等特点,由于模型误差等因素,基于模型得到的生产过程最优工作点不是实际生产过程的最优工作点.如何保持湿法冶金生产流程运行在经济效益最优的状态成为生产优化控制的难点.本文提出了一种基于数据的湿法冶金过程操作量优化设定补偿方法.该方法在基于模型得到的最优工作点基础上,采用即时学习(Just-in-time learning,JITL)的思想,在当前工作点附近利用历史数据建立操作量补偿值和经济效益增量的相关模型,优化求解在当前工作点下,使经济效益增量最大化的操作量补偿值,施加到生产流程,并在新工作点进行迭代补偿.将所提出的方法仿真应用于某精炼厂的湿法冶金生产流程,仿真结果验证了所提出方法的有效性.Abstract: Hydrometallurgical process has the characteristics of complicated reaction mechanism, long process flow and many sub-processes. The optimal setpoint of a model-based process based on the model is not the optimal working point of the actual process due to model error and so on. How to keep the hydrometallurgical process running in the state with optimal economic efficiency has become the difficulty of production optimization control. In this paper, a method based on data is proposed to optimize the operation of hydrometallurgical process. Based on the optimal setpoint of the model, the just-in-time learning (JITL) idea is used to establish a relevant model of the manipulative compensation value and the economic benefit increment in the vicinity of the current working point. At the work point, the amount of compensation that maximizes the economic gain is applied to the production process and iterated at the new work point. Simulation is carried out to verify the proposed method with the hydrometallurgical production process of a refinery, and the results show its effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Hydrometallurgy /
- data-based /
- optimized compensating /
- JITL (Just-in-time learning)
1) 本文责任编委 苏宏业 -
表 1 模型参数拟合结果
Table 1 Model parameters fltting results
组别 kAu kCN 参数组1 4.86 2.94 参数组2 4.95 2.91 表 2 模型参数取值
Table 2 Model parameter values
参数 取值 Qs 10 160 ds 80 Cw 0.30 D0, r 35 D0, Au 0 C0, CN 0 表 3 优化结果
Table 3 Optimization results
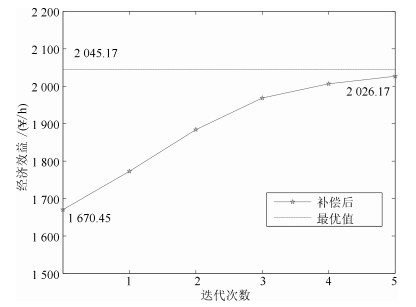
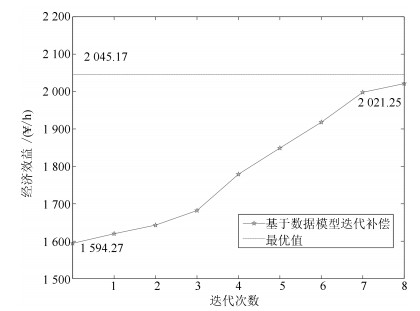
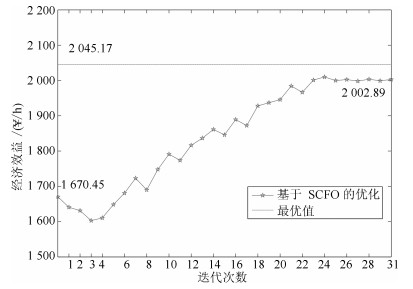
变量名称 机理模型最优值 实际过程最优值 J(¥/h) 1670.45 2045.17 q1, CN(kg/h) 65.49 76.92 q2, CN(kg/h) 67.15 76.11 q3, CN(kg/h) 57.34 64.25 q4, CN(kg/h) 52.61 52.98 q5, CN(kg/h) 32.85 21.13 q6, CN(kg/h) 30.11 15.62 qZn(kg/h) 2.43 2.43 表 4 参数取值
Table 4 Parameter values
参数名称 数值 Const 19.47 σ 0.05 δ 0.01 表 5 迭代补偿结果
Table 5 Iterative compensation results
迭代次数 △q1, CN △q2, CN △q3, CN △q4, CN △q5, CN △q6, CN △qZn △yp 1 3.47 3.52 2.41 1.02 -3.58 -5.75 0 102.4 2 2.42 2.23 2.12 0.34 -2.94 -3.53 0 111.21 3 2.31 1.95 1.24 -0.21 -3.05 -2.58 0 84.57 4 2.12 0.25 0.78 0.17 -1.24 -1.93 0 37.92 5 0.24 0.11 0.28 -0.52 -0.21 -0.19 0 20.17 表 6 补偿后操作量和最优值比较
Table 6 Comparison of the operation and the optimal values after compensation
最优值 补偿后 q1, CN(kg/h) 76.92 76.05 q2, CN(kg/h) 76.11 75.21 q3, CN(kg/h) 64.25 64.17 q4, CN(kg/h) 52.98 53.41 q5, CN(kg/h) 21.13 21.83 q6, CN(kg/h) 15.62 16.13 qZn(kg/h) 2.43 2.43 表 7 数据模型优化结果
Table 7 Data model optimization results
变量名称 机理模型最优值 实际过程最优值 J(¥,/h) 1594.27 2045.17 q1,CN(kg/h) 66.38 76.92 q2,CN(kg/h) 69.12 76.11 q3,CN(kg/h) 60.69 64.25 q4,CN(kg/h) 53.42 52.98 q5,CN(kg/h) 31.78 21.13 q6,CN(kg/h) 30.26 15.62 qZn(kg/h) 2.43 2.43 -
[1] de Andrade Lima L R P, Hodouin D. A lumped kinetic model for gold ore cyanidation. Hydrometallurgy, 2005, 79(3-4): 121-137 doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2005.06.001 [2] de Andrade Lima L R P, Hodouin D. Optimization of reactor volumes for gold cyanidation. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(7): 671-679 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2004.12.007 [3] de Andrade Lima L R P. Some remarks on the reactor network synthesis for gold cyanidation. Minerals Engineering, 2006, 19(2): 154-161 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2005.08.004 [4] Dagadu C P K, Akaho E H K, Danso K A, Stegowski Z, Furman L. Radiotracer investigation in gold leaching tanks. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2012, 70(1): 156-161 doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.09.003 [5] Yuan Q Y, Wang F L, He D K, Jia R D, Wang C. Study on the plant-wide modeling of gold hydrometallurgical process. In: Proceedings of the 26th Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Changsha, China: IEEE, 2014. 4013-4018 [6] Zhang J, Mao Z Z, Jia R D. Real-time optimization based on SCFO for gold cyanidation leaching process. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 134: 467-476 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2015.05.020 [7] Liu Y, Chang Y Q, Wang F L. Online process operating performance assessment and nonoptimal cause identification for industrial processes. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24(10): 1548-1555 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.08.001 [8] 李海波, 郑秀萍, 柴天佑.浮选过程混合智能优化设定控制方法.东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(1): 1-5 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB200812004.htmLi Hai-Bo, Zheng Xiu-Ping, Chai Tian-You. Hybrid intelligent optimal control in flotation processes. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2012, 33(1): 1-5 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB200812004.htm [9] 彭晓波, 桂卫华, 胡志坤, 李勇刚, 王凌云.基于混沌遗传算法的铜闪速熔炼过程操作模式智能优化系统.信息与控制, 2008, 37(1): 87-92 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYK200801013.htmPeng Xiao-Bo, Gui Wei-Hua, Hu Zhi-Kun, Li Yong-Gang, Wang Ling-Yun. Intelligent operation pattern optimization system in copper flash smelting process based on chaotic genetic algorithm. Information and Control, 2008, 37(1): 87-92 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYK200801013.htm [10] MacGregor J F, Yu H L, Muñoz S G, Flores-Cerrillo J. Data-based latent variable methods for process analysis, monitoring and control. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2005, 29(6): 1217-1223 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098135405000128 [11] MacGregor J F, Bruwer M J, Miletic I, Cardin M, Liu Z. Latent variable models and big data in the process industries. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(8): 520-524 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.09.020 [12] Yacoub F, MacGregor J F. Product optimization and control in the latent variable space of nonlinear PLS models. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2004, 70(1): 63-74 doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2003.10.004 [13] Kadlec P, Gabrys B, Strandt S. Data-driven soft sensors in the process industry. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2009, 33(4): 795-814 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098135409000076 [14] 贾润达, 毛志忠, 常玉清.基于非线性偏鲁棒M-回归的萃余液pH值软测量.自动化学报, 2009, 35(5): 583-587 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract15762.shtmlJia Run-Da, Mao Zhi-Zhong, Chang Yu-Qing. Soft sensing for pH value of raffinate solution based on nonlinear partial robust M-regression. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(5): 583-587 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract15762.shtml [15] 高莹莹, 朱维彬.深层神经网络中间层可见化建模.自动化学报, 2015, 41(9): 1627-1637 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18736.shtmlGao Ying-Ying, Zhu Wei-Bin. Deep neural networks with visible intermediate layers. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(9): 1627-1637 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18736.shtml [16] 王琴, 沈远彤.基于压缩感知的多尺度最小二乘支持向量机.自动化学报, 2016, 42(4): 631-640 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18849.shtmlWang Qin, Shen Yuan-Tong. Multi-scale least squares support vector machine using compressive sensing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4): 631-640 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18849.shtml [17] Yuan Q Y, Wang F L, He D K, Wang H, Liu T. A new plant-wide optimization method and its application to hydrometallurgy process. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 94(2): 273-280 doi: 10.1002/cjce.v94.2 [18] He D K, Yuan Q Y, Wang F L, Zhao L P, Liu T, Jia R D. Plant-wide hierarchical optimization based on a minimum consumption model. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 94(6): 1158-1166 doi: 10.1002/cjce.v94.6 [19] Zhang J, Mao Z Z, Jia R D, He D K. Real time optimization based on a serial hybrid model for gold cyanidation leaching process. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 70: 250-263 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2014.09.021 [20] Serralunga F J, Mussati M C, Aguirre P A. Model adaptation for real-time optimization in energy systems. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(47): 16795-16810 doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b01946 [21] Kaneko H, Funatsu K. Classification of the degradation of soft sensor models and discussion on adaptive models. AIChEJournal, 2013, 59(7): 2339-2347 doi: 10.1002/aic.v59.7 [22] Cheng C, Chiu M S. A new data-based methodology for nonlinear process modeling. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 59(13): 2801-2810 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009250904002453 [23] Saptoro A. State of the art in the development of adaptive soft sensors based on just-in-time models. Procedia Chemistry, 2014, 9: 226-234 doi: 10.1016/j.proche.2014.05.027 [24] Nomikos P, MacGregor J F. Multi-way partial least squares in monitoring batch processes. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 1995, 30(1): 97-108 doi: 10.1016/0169-7439(95)00043-7 -





 下载:
下载: