-
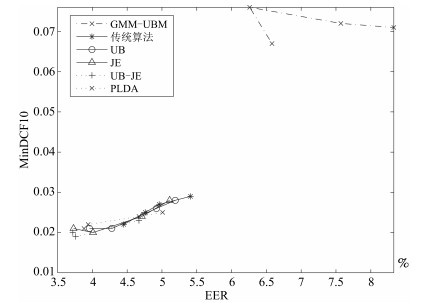
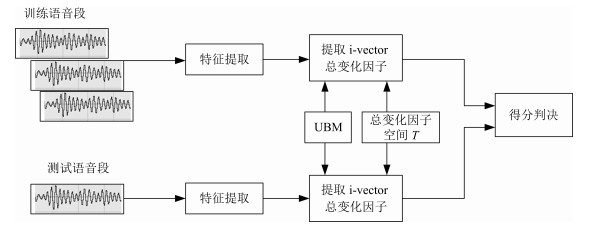
摘要: 在说话人识别中,有效的识别方法是核心.近年来,基于总变化因子分析(i-vector)方法成为了说话人识别领域的主流,其中总变化因子空间的估计是整个算法的关键.本文结合常规的因子分析方法提出一种新的总变化因子空间估计算法,即通用背景—联合估计(Universal background-joint estimation algorithm,UB-JE)算法.首先,根据高斯混合—通用背景模型(Gaussian mixture model-universal background model,GMM-UBM)思想提出总变化矩阵通用背景(UB)算法;其次,根据因子分析理论结合相关文献提出了一种总变化矩阵联合估计(JE)算法;最后,将两种算法相结合得到通用背景—联合估计(UB-JE)算法.采用TIMIT和MDSVC语音数据库,结合i-vector方法将所提的算法与传统算法进行对比实验.结果显示,等错误率(Equal error rate,EER)和最小检测代价函数(Minimum detection cost function,MinDCF)分别提升了8.3%与6.9%,所提方法能够提升i-vector方法的性能.
-
关键词:
- 总变化因子分析 /
- 总变化因子空间 /
- 通用背景—联合估计算法 /
- 说话人识别
Abstract: In the speaker recognition, the effective identification method is the core. In recent years, i-vector method has become the mainstream in the field of speaker recognition, and estimation of the total variation factor space is the key of whole algorithm. In this paper, we propose a new algorithm for total variation factor space estimation named UB-JE, which is combined with conventional factor analysis method. Firstly, the universal background algorithm of total variation matrix is proposed according to Gaussian mixture model-universal background model (GMM-UBM). Secondly, the joint estimation algorithm of total variation matrix is proposed according to the factor analysis theory and related works. Finally, the two algorithms are combined to get the universal background-joint estimation algorithm (UB-JE). TIMIT and MDSVC corpus are adopted in the experiment to compare the proposed algorithm with the traditional algorithm. Experimental results show that the equal error rate (EER) and the minimum detection cost function (MinDCF) are improved by 8.3% and 6.9%, respectively. The proposed method can improve the performance of i-vector method.1) 本文责任编委 吴玺宏 -
表 1 实验所用语音库
Table 1 The corpus used in the experiment
类型 TIMIT MDSVC MDSVC长句 male female male female UBM 3 860 1 620 2 808 2376 136 T 3 860 1 620 2 808 2 376 136 训练GSV 630 270 1 150 850 1 500 1 500 测试 70 30 92 68 120 120 表 2 MinDCF10参数设定
Table 2 MinDCF10 parameter setting
$C_{\rm Miss} $ $C_{\rm FalseAlarm} $ $P_{\rm Target} $ 1 1 0.001 表 3 GMM-UBM、传统算法估计$T$、本文所提出算法估计$T$以及PLDA在TIMIT语音库上的性能对比
Table 3 Performance comparison of GMM-UBM, the traditional algorithm to estimate $T$, the proposed algorithms to estimate $T$, and the PLDA on TIMIT corpora
算法 EER (%) MinDCF10 GMM-UBM 6.26 0.076 传统算法估计$T$ 4.76 0.025 通用背景估计$T$ 4.28 0.021 联合估计$T$ 4.01 0.020 通用背景-联合估计$T$ 3.76 (21 %) 0.019 (24 %) PLDA 3.94 0.022 表 4 GMM-UBM、传统算法估计$T$、本文所提出算法估计$T$以及PLDA在MDSVC语音库上的性能对比
Table 4 Performance comparison of GMM-UBM, the traditional algorithm to estimate $T$, the proposed algorithms to estimate $T$, and the PLDA on MDSVC corpora
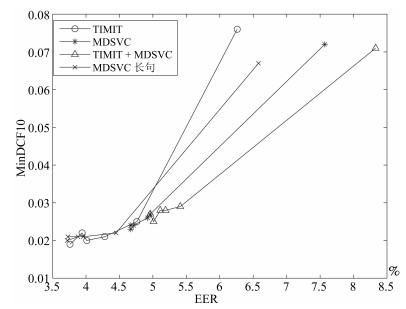
算法 EER (%) MinDCF10 GMM-UBM 7.57 0.072 传统算法估计$T$ 4.96 0.027 通用背景估计$T$ 4.92 0.026 联合估计$T$ 4.71 0.024 通用背景-联合估计$T$ 4.67 (5.8 %) 0.023 (14.8 %) PLDA 4.67 0.024 表 5 GMM-UBM、传统算法估计$T$、本文所提出算法估计$T$以及PLDA在TIMIT + MDSVC语音库上的性能对比
Table 5 Performance comparison of GMM-UBM, the traditional algorithm to estimate $T$, the proposed algorithms to estimate $T$, and the PLDA on TIMIT mixed MDSVC corpora
算法 EER (%) MinDCF10 GMM-UBM 8.33 0.071 传统算法估计$T$ 5.41 0.029 通用背景估计$T$ 5.19 0.028 联合估计$T$ 5.11 0.028 通用背景-联合估计$T$ 4.96 (8.3 %) 0.027 (6.9 %) PLDA 5.01 0.025 表 6 GMM-UBM、传统算法估计$T$、本文所提出算法估计$T$以及PLDA在MDSVC长句语音库上的性能对比
Table 6 Performance comparison of GMM-UBM, the traditional algorithm to estimate $T$, the proposed algorithms to estimate $T$, and the PLDA on MDSVC long sentence corpora
算法 EER (%) MinDCF10 GMM-UBM 6.58 0.067 传统算法估计$T$ 4.45 0.022 通用背景估计$T$ 3.96 0.021 联合估计$T$ 3.73 0.021 通用背景-联合估计$T$ 3.72 (16.40 %) 0.020 (9.09 %) PLDA 3.88 0.021 表 7 通用背景-联合估计算法在不同语音库中的性能对比
Table 7 Performance comparison of universal background-joint estimation algorithm on different speech corpus
语音库 EER (%) MinDCF10 TIMIT 3.76 0.019 MDSVC 4.67 0.023 TIMIT + MDSVC 4.96 0.027 MDSVC长句 3.72 0.020 -
[1] Reynolds D A. An overview of automatic speaker recognition technology. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Orlando, FL, USA: IEEE, 2002. IV-4072-IV-4075 [2] Kinnunen T, Li H Z. An overview of text-independent speaker recognition:from features to supervectors. Speech Communication, 2010, 52(1):12-40 doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2009.08.009 [3] Reynolds D A, Quatieri T F, Dunn R B. Speaker verification using adapted Gaussian mixture models. Digital Signal Processing, 2000, 10(1-3):19-41 doi: 10.1006/dspr.1999.0361 [4] Cumani S, Laface P. Large-scale training of pairwise support vector machines for speaker recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(11):1590-1600 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2014.2341914 [5] Yessad D, Amrouche A. SVM based GMM supervector speaker recognition using LP residual signal. In: Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Image and Signal Processing. Agadir, Morocco: Springer, 2012. 579-586 [6] Kenny P, Boulianne G, Ouellet P, Dumouchel P. Speaker and session variability in gmm-based speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2007, 15(4):1448-1460 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2007.894527 [7] Kenny P, Boulianne G, Ouellet P, Dumouchel P. Joint factor analysis versus eigenchannels in speaker recognition. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2007, 15(4):1435-1447 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2006.881693 [8] Dehak N. Discriminative and Generative Approaches for Long-and Short-Term Speaker Characteristics Modeling: Application to Speaker Verification[Ph. D. dissertation], École de Technologie Supérieure, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2009. [9] Dehak N, Kenny P J, Dehak R, Dumouchel P, Ouellet P. Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2011, 19(4):788-798 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2010.2064307 [10] Dehak N, Dehak R, Kenny P, Brummer N, Ouellet P, Dumouchel P. Support vector machines versus fast scoring in the low-dimensional total variability space for speaker verification. In: Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Brighton, UK: DBLP, 2009. 1559-1562 [11] Cumani S, Laface P. I-vector transformation and scaling for PLDA based speaker recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Odyssey Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop. Bilbao, Spain: IEEE, 2016. 39-46 [12] Rouvier M, Bousquet P M, Ajili M, Kheder W B, Matrouf D, Bonastre J F. LIA system description for NIST SRE 2016. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Speech Communication Association. San Francisco, USA: Elsevier, 2016. [13] Xu Y, McLoughlin I, Song Y, Wu K. Improved i-vector representation for speaker diarization. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2016, 35(9):3393-3404 doi: 10.1007/s00034-015-0206-2 [14] Fine S, Navratil J, Gopinath R A. Enhancing GMM scores using SVM "hints". In: Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology. Aalborg, Denmark: DBLP, 2001. 1757-1760 [15] Campbell W M, Sturim D E, Reynolds D A. Support vector machines using GMM supervectors for speaker verification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2006, 13(5):308-311 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2006.870086 [16] 何亮, 史永哲, 刘加.联合因子分析中的本征信道空间拼接方法.自动化学报, 2011, 37(7):849-856 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17496.shtmlHe Liang, Shi Yong-Zhe, Liu Jia. Eigenchannel space combination method of joint factor analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(7):849-856 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17496.shtml [17] 郭武, 李轶杰, 戴礼荣, 王仁华.说话人识别中的因子分析以及空间拼接.自动化学报, 2009, 35(9):1193-1198 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13565.shtmlGuo Wu, Li Yi-Jie, Dai Li-Rong, Wang Ren-Hua. Factor analysis and space assembling in speaker recognition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(9):1193-1198 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13565.shtml [18] Jankowski C, Kalyanswamy A, Basson S, Spitz J. NTIMIT: a phonetically balanced, continuous speech, telephone bandwidth speech database. In: Proceedings of the 1990 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Albuquerque, NM, USA: IEEE, 1990, 1: 109-122 [19] Woo R H, Park A, Hazen T J. The MIT mobile device speaker verification corpus: data collection and preliminary experiments. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Odyssey: the Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop. San Juan, Puerto Rico: IEEE, 2006. 1-6 [20] Young S, Evermann G, Gales M, Hain T, Liu X Y, Moore G, Odell J, Ollason D, Povey D, Valtchev V, Woodland P. The HTK Book (for HTK Version 3. 4). Cambridge: Cambridge University Engineering Department, 2006. [21] NIST Speaker Recognition Evaluation[Online], available: http://www.itl.nist.gov/iad/mig/tests/sre/2010/index.html, April 21, 2010 [22] Chen L P, Lee K A, Ma B, Li H Z, Dai L R. Adaptation of PLDA for multi-source text-independent speaker verification. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5380-5384 -




 下载:
下载: