Multi-objective Layer-wise Optimization and Multi-level Probability Fusion for Image Description Generation Using LSTM
-
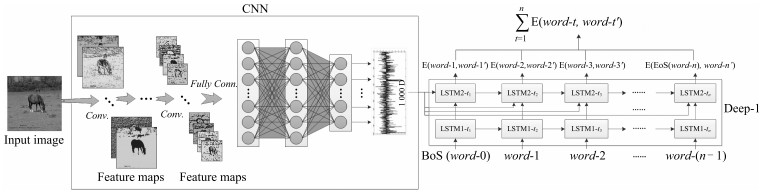
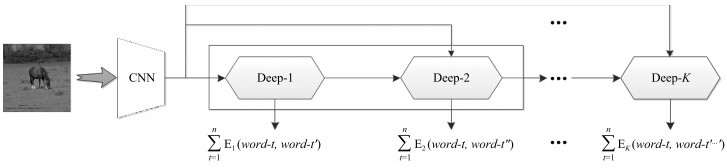
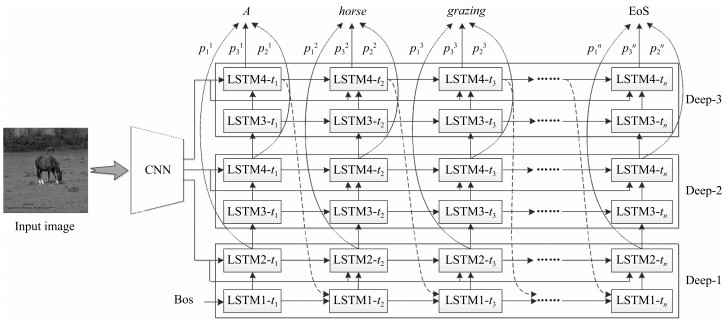
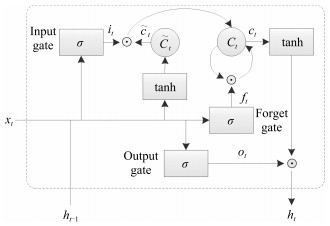
摘要: 使用计算模型对图像进行自动描述属于视觉高层理解,要求模型不仅能够对图像中的目标及场景进行描述,而且能够对目标与目标之间、目标与场景之间的关系进行表达,同时能够生成符合一定语法和结构的自然语言句子.目前基于深度卷积神经网络(Convolutional neural network,CNN)和长短时记忆网络(Long-short term memory,LSTM)的方法已成为解决该问题的主流,虽然已取得巨大进展,但存在LSTM层次不深,难以优化的问题,导致模型性能难以提升,生成的描述句子质量不高.针对这一问题,受深度学习思想的启发,本文设计了基于逐层优化的多目标优化及多层概率融合的LSTM(Multi-objective layer-wise optimization/multi-layer probability fusion LSTM,MLO/MLPF-LSTM)模型.模型中首先使用浅层LSTM进行训练,收敛之后,保留原LSTM模型中的分类层及目标函数,并添加新的LSTM层及目标函数重新对模型进行训练,对模型原有参数进行微调;在测试时,将多个分类层使用Softmax函数进行变换,得到每层对单词的预测概率分值,然后将多层的概率分值进行加权融合,得到单词的最终预测概率.在MSCOCO和Flickr30K两个数据集上实验结果显示,该模型性能显著,在多个统计指标上均超过了同类其他方法.Abstract: The task of image automatic description by computer belongs to high-level visual understanding. Unlike image classification, object detection, etc., it usually requires that the model should not only have abilities of describing scene and objects, but also have capacities of expressing the relations between different objects and between objects and background in the image. In addition, it is required that the model should generate natural sentences which accord with correct grammars and appropriate structures. Nowadays, the approaches based on convolutional neural network (CNN) and long-short term memory network (LSTM) have been the popular solutions to this task, and a series of successes have been obtained. However, there are still several sticky problems, for instance, the LSTM network is not deep enough and the model is difficult to optimize, and as a result, performances cannot be improved and the sentences generated are of low quantity. To address these difficulties, inspired by the idea of deep learning, a model named MLO/MLPF-LSTM is proposed, in which the method of layer-wise optimization, multi-objective optimization and multi-layer probability fusion are employed. In details, an LSTM network with shallow depth is trained firstly, then, new LSTM layers and related objective functions are added to the optimized LSTM network. Meanwhile, the classification layers and objective functions in the original LSTM model are reserved and fine-tuned with the new layers. During the test, the probabilities of all the Softmax functions which are fed with the corresponding classification layers are fused for the final predicted probabilities by a weighted average method. Experimental results on MSCOCO and Flickr30K datasets demonstrate that our model is effective and outperforms other methods of same kinds on a number of evaluation metrics.1) 本文责任编委 王立威
-
表 1 MSCOCO数据集上不同层次及多层融合之后的性能对比(非联调方式) ($\%$)
Table 1 Performance comparison under different fusion conditions on MSCOCO (non-jointly optimizing) ($\%$)
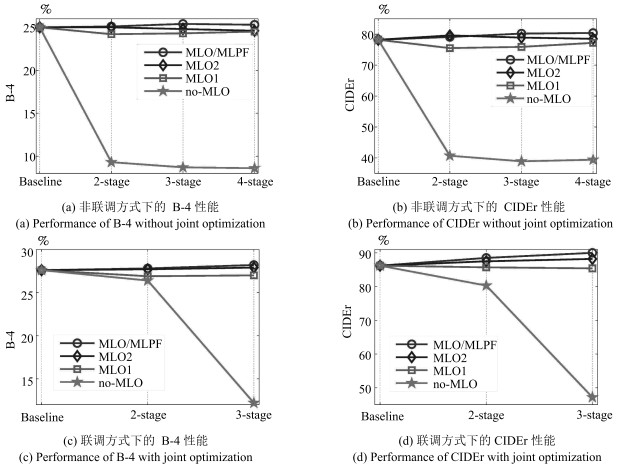
Models B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 C Baseline 67.7 49.4 35.2 25.0 78.2 2-stage P1 67.8 49.7 35.3 25.0 78.5 P2 67.5 49.6 35.3 25.0 79.6 Fusion 68.0 50.0 35.5 25.1 79.1 3-stage P1 67.9 49.8 35.5 25.2 79.0 P2 67.5 49.6 35.3 25.0 79.6 P3 67.3 49.4 35.1 24.8 78.9 Fusion 68.0 50.0 35.8 25.4 80.2 4-stage P1 67.6 49.5 35.3 25.1 78.7 P2 67.0 49.1 34.9 24.8 79.7 P3 66.8 49.0 34.8 24.7 79.5 P4 66.9 49.0 34.8 24.6 78.9 Fusion 67.7 49.8 35.6 25.3 80.4 C表示CIDEr 表 2 MSCOCO数据集上不同层次及多层融合之后的性能对比(联调方式) ($\%$)
Table 2 Performance comparison under different fusion conditions on MSCOCO (jointly optimizing) ($\%$)
Models B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 C Baseline$^+$ 70.2 52.7 38.3 27.6 86.2 2-stage P1 70.2 52.7 38.4 27.8 88.4 P2 69.9 52.6 38.3 27.7 87.5 Fusion 70.2 52.8 38.4 27.8 88.5 3-stage P1 70.5 52.8 38.4 27.8 89.3 P2 70.1 52.5 38.2 27.8 88.9 P3 70.1 52.8 38.5 27.9 88.2 Fusion 70.6 53.2 38.8 28.2 90.0 C表示CIDEr 表 3 Flickr30K数据集上不同层次及多层融合之后的性能对比(联调方式) ($\%$)
Table 3 Performance comparison under different fusion conditions on Flickr30K (jointly optimizing) ($\%$)
Models B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 M Baseline$^+$ 60.2 41.8 28.5 19.2 19.2 2-stage P1 61.5 42.9 29.2 19.7 19.4 P2 60.7 42.2 29.0 19.8 19.2 Fusion 61.4 42.8 29.2 19.8 19.6 M表示METEOR 表 4 MSCOCO数据集上不同层次及多层融合之后的性能对比(使用联调方式和集束搜索算法) ($\%$)
Table 4 Performance comparison under different fusion conditions on MSCOCO (jointly optimizing and Beam search algorithm are employed) ($\%$)
Models B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 C Baseline$^+$ 71.3 54.4 40.8 30.5 92.0 2-stage P1 71.4 54.3 40.7 30.6 93.8 P2 71.6 54.8 41.1 31.0 93.7 Fusion 71.5 54.5 41.0 31.0 94.2 C表示CIDEr 表 5 Flickr30K数据集上不同层次及多层融合之后的性能对比(使用联调方式和集束搜索算法) ($\%$)
Table 5 Performance comparison under different fusion conditions on Flickr30K (jointly optimizing and Beam search algorithm are employed) ($\%$)
Models B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 M Baseline$^+$ 63.4 44.5 30.9 21.1 19.0 2-stage P1 65.1 45.8 31.8 21.9 19.2 P2 65.0 46.0 32.0 21.9 19.3 Fusion 66.2 47.2 33.1 23.0 19.6 M表示METEOR 表 6 不同方法在MSCOCO数据集上的性能对比($\%$)
Table 6 Performance comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on MSCOCO ($\%$)
Methods B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 C multimodal RNN[14] 62.5 45.0 32.1 23.0 66.0 Google NIC[2] 66.6 46.1 32.9 24.6 -- LRCN-AlexNet[13] 62.8 44.2 30.4 21.0 -- m-RNN[1] 67.0 49.0 35.0 25.0 -- Soft-attention[15] 70.7 49.2 34.4 24.3 -- Hard-attention[15] 71.8 50.4 35.7 25.0 -- emb-gLSTM, Gaussian[28] 67.0 49.1 35.8 26.4 81.3 MLO/MLPF-LSTM 67.7 49.8 35.6 25.3 80.4 MLO/MLPF-LSTM$^+$ 70.6 53.2 38.8 28.2 90.0 MLO/MLPF-LSTM$^+$(BS) 71.5 54.5 41.0 31.0 94.2 BS表示Beam search, C表示CIDEr 表 7 不同方法在Flickr30K数据集上的性能对比($\%$)
Table 7 Performances comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on Flickr30K ($\%$)
Methods B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 M multimodal RNN[14] 57.3 36.9 24.0 15.7 15.3 Google NIC[2] 66.3 42.3 27.7 18.3 -- LRCN-AlexNet[13] 58.7 39.1 25.1 16.5 -- m-RNN[1] 60.0 41.0 28.0 19.0 -- Soft-attention[15] 66.7 43.4 28.8 19.1 18.5 Hard-attention[15] 66.9 43.9 29.6 19.9 18.5 emb-gLSTM, Gaussian[28] 64.6 44.6 30.5 20.6 17.9 MLO/MLPF-LSTM$^+$ 61.4 42.8 29.2 19.8 19.6 MLO/MLPF-LSTM$^+$(BS) 66.2 47.2 33.1 23.0 19.6 M表示METEOR, BS表示Beam search -
[1] Mao J H, Xu W, Yang Y, Wang J, Huang Z H, Yuille A. Deep captioning with multimodal recurrent neural networks (m-RNN). In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA, 2015. [2] Vinyals O, Toshev A, Bengio S, Erhan D. Show and tell: a neural image caption generator. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3156-3164 [3] Kulkarni G, Premraj V, Ordonez V, Dhar S, Li S M, Choi Y, Berg A C, Berg T L. BabyTalk:understanding and generating simple image descriptions. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(12):2891-2903 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.162 [4] Mitchell M, Han X F, Dodge J, Mensch A, Goyal A, Berg A, Yamaguchi K, Berg T, Stratos K, Daumé H Ⅲ. Midge: generating image descriptions from computer vision detections. In: Proceedings of the 13th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Avignon, France: ACL, 2012. 747-756 http://tamaraberg.com/papers/EACL12.pdf [5] Elliott D, Keller F. Image description using visual dependency representations. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Seattle, USA: ACL, 2013. 1292-1302 http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/D/D13/D13-1128.pdf [6] Farhadi A, Hejrati M, Sadeghi M A, Young P, Rashtchian C, Hockenmaieret J, Forsyth D. Every picture tells a story: generating sentences from images. In: Proceedings of the 2010 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2010. 15-29 https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~afarhadi/papers/sentence.pdf [7] 张红斌, 姬东鸿, 尹兰, 任亚峰.基于梯度核特征及N-gram模型的商品图像句子标注.计算机科学, 2016, 43(5):269-273, 287 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsja201605053&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQZhang Hong-Bin, Ji Dong-Hong, Yin Lan, Ren Ya-Feng. Product image sentence annotation based on gradient kernel feature and N-gram model. Computer Science, 2016, 43(5):269-273, 287 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsja201605053&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [8] Socher R, Karpathy A, Le Q V, Manning C D, Ng A Y. Grounded compositional semantics for finding and describing images with sentences. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014, 2:207-218 https://nlp.stanford.edu/~socherr/SocherKarpathyLeManningNg_TACL2013.pdf [9] Kuznetsova P, Ordonez V, Berg T L, Choi Y. TreeTalk:composition and compression of trees for image descriptions. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014, 2:351-362 [10] Kuznetsova P, Ordonez V, Berg A, Berg T, Choi Y. Generalizing image captions for image-text parallel corpus. In: Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Sofia, Bulgaria: ACL, 2013. 790-796 http://www.cs.unc.edu/~vicente/files/acl13_generalization.pdf [11] Mason R, Charniak E. Nonparametric method for data-driven image captioning. In: Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Baltimore, USA: ACL, 2014. 592-598 http://aclweb.org/anthology/P/P14/P14-2097.pdf [12] 蒋树强, 闵巍庆, 王树徽.面向智能交互的图像识别技术综述与展望.计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(1):113-122 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20150689Jiang Shu-Qiang, Min Wei-Qing, Wang Shu-Hui. Survey and prospect of intelligent interaction-oriented image recognition techniques. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(1):113-122 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20150689 [13] Donahue J, Hendricks L A, Guadarrama S, Rohrbach M, Venugopalan S, Darrell T, Saenko K. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2625-2634 http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Donahue_Long-Term_Recurrent_Convolutional_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf [14] Karpathy A, Li F F. Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3128-3137 [15] Xu K, Ba J L, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhutdinov R, Zemel R S, Bengio Y. Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France, 2015. 2048-2057 [16] Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786):504-507 doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [17] Hermans M, Schrauwen B. Training and analyzing deep recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2013. 190-198 https://papers.nips.cc/paper/5166-training-and-analysing-deep-recurrent-neural-networks.pdf [18] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1-9 https://www.cs.unc.edu/~wliu/papers/GoogLeNet.pdf [19] Lee C Y, Xie S N, Gallagher P W, Zhang Z Y, Tu Z W. Deeply-supervised nets. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. San Diego, USA, 2015. 562-570 [20] Gerber R, Nagel H H. Knowledge representation for the generation of quantified natural language descriptions of vehicle traffic in image sequences. In: Proceedings of the 1996 International Conference on Image Processing. Lausanne, Switzerland: IEEE, 1996. 805-808 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/561027/ [21] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: MIT Press, 2012. 1097-1105 https://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf [22] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA, 2015. [23] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770-778 [24] 石俊飞, 刘芳, 林耀海, 刘璐.基于深度学习和层次语义模型的极化SAR分类.自动化学报, 2017, 43(2):215-226 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19010.shtmlShi Jun-Fei, Liu Fang, Lin Yao-Hai, Liu Lu. Polarimetric SAR image classification based on deep learning and hierarchical semantic model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(2):215-226 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19010.shtml [25] 王伟凝, 王励, 赵明权, 蔡成加, 师婷婷, 徐向民.基于并行深度卷积神经网络的图像美感分类.自动化学报, 2016, 42(6):905-914 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18881.shtmlWang Wei-Ning, Wang Li, Zhao Ming-Quan, Cai Cheng-Jia, Shi Ting-Ting, Xu Xiang-Min. Image aesthetic classification using parallel deep convolutional neural networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6):905-914 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18881.shtml [26] 段艳杰, 吕宜生, 张杰, 赵学亮, 王飞跃.深度学习在控制领域的研究现状与展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):643-654 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18852.shtmlDuan Yan-Jie, Lv Yi-Sheng, Zhang Jie, Zhao Xue-Liang, Wang Fei-Yue. Deep learning for control:the state of the art and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):643-654 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18852.shtml [27] 郭潇逍, 李程, 梅俏竹.深度学习在游戏中的应用.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):676-684 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18857.shtmlGuo Xiao-Xiao, Li Cheng, Mei Qiao-Zhu. Deep learning applied to games. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):676-684 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18857.shtml [28] Jia X, Gavves E, Fernando B, Tuytelaars T. Guiding the long-short term memory model for image caption generation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2407-2415 https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_iccv_2015/papers/Jia_Guiding_the_Long-Short_ICCV_2015_paper.pdf [29] 奚雪峰, 周国栋.面向自然语言处理的深度学习研究.自动化学报, 2016, 42(10):1445-1465 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18934.shtmlXi Xue-Feng, Zhou Guo-Dong. A survey on deep learning for natural language processing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10):1445-1465 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18934.shtml [30] Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11):2278-2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [31] Chatfield K, Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A. Return of the devil in the details: delving deep into convolutional nets. In: Proceedings of the 2014 British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham, England: British Machine Vision Association, 2014. [32] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z H, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg A C, Li F F. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3):211-252 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [33] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8):1735-1780 doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [34] Graves A. Generating sequences with recurrent neural networks[Online], available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1308.0850v5.pdf, June 5, 2014 [35] Bengio Y, Simard P, Frasconi P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1994, 5(2):157-166 doi: 10.1109/72.279181 [36] Gers F A, Schmidhuber J. Recurrent nets that time and count. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE-INNS-ENNS International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Como, Italy: IEEE, 2000. 189-194 [37] Cho K, Van Merrienboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[Online], available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1406.1078v3.pdf, September 3, 2014 [38] Greff K, Srivastava R K, Koutník J, Steunebrink B R, Schmidhuber J. LSTM:a search space odyssey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(10):2222-2232 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2582924 [39] Zhou B L, Lapedriza A, Xiao J X, Torralaba A, Oliva A. Learning deep features for scene recognition using places database. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 487-495 http://places.csail.mit.edu/places_NIPS14.pdf [40] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick C L. Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 740-755 [41] Young P, Lai A, Hodosh M, Hockenmaier J. From image descriptions to visual denotations:new similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014, 2:67-78 http://nlp.cs.illinois.edu/HockenmaierGroup/Papers/TACL2014/TACLDenotationGraph.pdf [42] Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W J. BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics. Philadelphia, USA: ACL, 2002. 311-318 http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P02-1040.pdf [43] Banerjee S, Lavie A. METEOR: an automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for MT and/or Summarization. Ann Arbor, USA: ACL, 2005. 65-72 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~alavie/METEOR/pdf/Banerjee-Lavie-2005-METEOR.pdf [44] Vedantam R, Zitnick C L, Parikh D. CIDEr: consensus-based image description evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 4566-4575 [45] Jia Y Q, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, Karayev S, Long J, Girshick R, Guadarrama S, Darrell T. Caffe: convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Orlando, Florida, USA: ACM, 2014. 675-678 [46] Krishna R, Zhu Y K, Groth O, Johnson J, Hata K, Kravitz J, Chen S, Kalantidis Y, Li L J, Shamma D A, Bernstein M S, Li F F. Visual Genome: connecting language and vision using crowd sourced dense image annotations[Online], available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1602.07332.pdf, February 23, 2016 -




 下载:
下载: