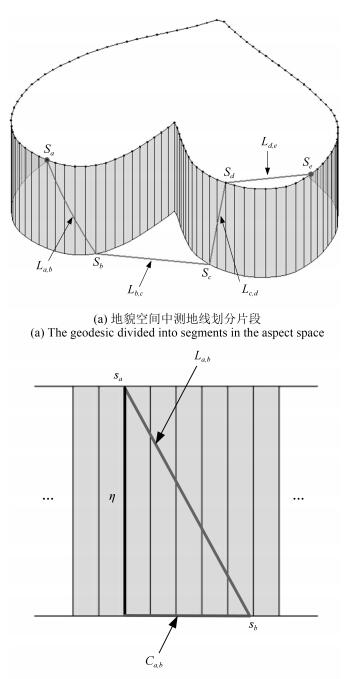
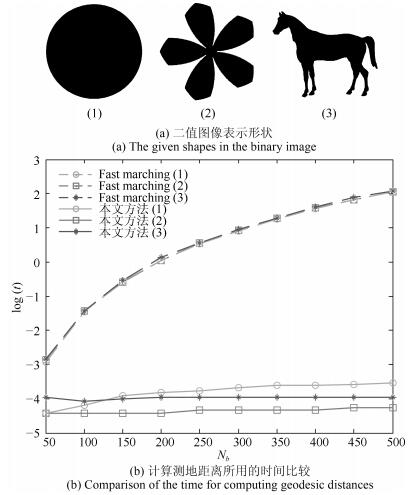
-
摘要: 在基于地貌形状上下文的形状匹配方法中,计算地貌空间测地距离消耗时间较高,对应形状特征提取过程的效率较低.针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于地貌模糊形状上下文的快速形状匹配方法.在形状特征提取过程中,通过引入最短路径算法对轮廓采样点间的测地距离进行快速计算.在此基础上结合对数极坐标模糊直方图构造地貌模糊形状上下文,其能够更好地描述轮廓点分布情况进而有效提升形状描述符的表达能力.考虑到轮廓点集顺序已知,进一步引入动态规划分析不同地貌空间下形状片段间的对应关系,以获取准确的形状匹配结果.通过对不同的数据集进行实验仿真分析,验证了本文方法能够有效地提升运算效率并取得较好形状检索精度.Abstract: In shape matching method based on aspect shape context, it is time consuming to calculate the geodesic distances on the aspect spaces, and the process of shape feature extraction is inefficient. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a fast shape method based on aspect fuzzy shape context. During the process of shape feature extraction, the geodesic distances between sample points on the shape contour can be effectively obtained by using the shortest path algorithm, and log-polar fuzzy histogram is further introduced to construct aspect fuzzy shape context, and the description ability is improved with the sample point distributions represented precisely. With the orders of sample points, the dynamic programming method is employed to analyze the correspondence between shape segments in different aspect spaces, and the shape matching result can be obtained accurately. With the proposed method tested on different shape databases, the computation efficiency can be effectively improved and desirable shape retrieval results can be achieved.
-
Key words:
- Shape matching /
- aspect space /
- shortest path /
- fuzzy histogram /
- aspect fuzzy shape context(AFSC)
1) 本文责任编委 胡清华 -
表 1 Kimia-99数据形状特征提取时间比较(s)
Table 1 Comparison of the time used for shape feature extraction on Kimia-99 database (s)
方法 特征提取时间(s) Fast marching[11] 208.56 本文方法 11.77 表 2 Kimia-99数据在不同方法下检索结果比较
Table 2 Comparison of retrieval rates for different algorithms tested on Kimia-99 database
方法 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 9th 10th 全部 SC[6] 97 91 88 85 84 77 75 66 56 37 756 Hierarchical parts[16] 99 99 98 98 98 97 96 94 93 82 954 IDSC + DP[10] 99 99 99 98 98 97 97 98 94 79 958 MDS + SC + DP[10] 99 98 98 98 97 99 97 96 97 85 964 GM + SC[17] 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 97 93 86 969 Height functions[18] 99 99 99 99 98 99 99 96 95 88 971 FSC + SCS[13] 99 99 99 99 98 99 98 95 94 91 972 Symbolic representation[19] 99 99 99 98 99 98 98 95 96 94 975 AFSC 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 98 92 982 表 3 Kimia-216数据在不同方法下检索结果比较
Table 3 Comparison of retrieval rates for different algorithms tested on Kimia-216 database
方法 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 9th 10th 全部 Generative model[20] 216 216 214 212 212 207 203 190 179 175 2024 Shock edit[21] 216 216 216 215 210 210 207 204 200 187 2081 SC + DP[10] 216 216 215 210 210 209 208 204 200 191 2079 FSC + SCS[13] 216 216 215 214 213 214 210 201 193 188 2080 Path similarity[22] 216 216 215 216 213 210 210 207 205 191 2099 IDSC + DP[10] 216 216 215 211 211 210 211 207 203 198 2098 AFSC 216 216 216 214 214 215 209 207 209 199 2115 表 4 Tari-1000数据在不同方法下的结果比较
Table 4 Comparison of results for different algorithms tested on Tari-1000 database
-
[1] Kendall D G. Shape manifolds, procrustean metrics, and complex projective spaces. Bulletin of the London Mathematical Society, 1984, 16(2):81-121 doi: 10.1112/blms.1984.16.issue-2 [2] Su Y Q, Liu Y H, Cuan B N, Zheng N N. Contour guided hierarchical model for shape matching. In:Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile:IEEE, 2015. 1609-1617 [3] Janan F, Brady M. Shape description and matching using integral invariants on eccentricity transformed images. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 113(2):92-112 doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0773-x [4] Roman-Rangel E, Pallan C, Odobez J M, Gatica-Perez D. Analyzing ancient maya glyph collections with contextual shape descriptors. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2011, 94(1):101-117 doi: 10.1007/s11263-010-0387-x [5] 周瑜, 刘俊涛, 白翔.形状匹配方法研究与展望.自动化学报, 2012, 38(6):889-910 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201206002.htmZhou Yu, Liu Jun-Tao, Bai Xiang. Research and perspective on shape matching. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(6):889-910 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201206002.htm [6] Belongie S, Malik J, Puzicha J. Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(4):509-522 doi: 10.1109/34.993558 [7] Mori G, Belongie S, Malik J. Efficient shape matching using shape contexts. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(11):1832-1837 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.220 [8] Xie J, Heng P A, Shah M. Shape matching and modeling using skeletal context. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(5):1756-1767 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.11.005 [9] Premachandran V, Kakarala R. Perceptually motivated shape context which uses shape interiors. Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(8):2092-2102 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2013.01.030 [10] Ling H B, Jacobs D W. Shape classification using the innerdistance. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(2):286-299 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.41 [11] Ling H B, Yang X W, Latecki L J. Balancing deformability and discriminability for shape matching. In:Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision. Crete, Greece:Springer, 2010. 411-424 [12] Ling H B, Jacobs D W. Deformation invariant image matching. In:Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Beijing, China:IEEE, 2005. 1466-1473 [13] 韩敏, 郑丹晨.基于模糊形状上下文特征的形状识别算法.自动化学报, 2012, 38(1):68-75 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17656.shtmlHan Min, Zheng Dan-Chen. Shape recognition based on fuzzy shape context. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(1):68-75 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17656.shtml [14] Sebastian T B, Klein P N, Kimia B B. Recognition of shapes by editing their shock graphs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(5):550-571 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.1273924 [15] Sebastian T B, Klein P N, Kimia B B. On aligning curves. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(1):116-125 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1159951 [16] Donoser M, Riemenschneider H, Bischof H. Efficient partial shape matching of outer contours. In:Proceedings of the 9th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Xi'an China:Springer, 2010. 281-292 [17] Egozi A, Keller Y, Guterman H. Improving shape retrieval by spectral matching and meta similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(5):1319-1327 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2040448 [18] Wang J W, Bai X, You X G, Liu W Y, Latecki L J. Shape matching and classification using height functions. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2012, 33(2):134-143 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.09.042 [19] Daliri M R, Torre V. Robust symbolic representation for shape recognition and retrieval. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(5):1782-1798 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.10.020 [20] Tu Z W, Yuille A L. Shape matching and recognition-using generative models and informative features. In:Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Computer Vision. Prague, Czech Republic:Springer, 2004. 195-209 [21] Siddiqi K, Shokoufandeh A, Dickinson S J, Zucker S W. Shock graphs and shape matching. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1999, 35(1):13-32 doi: 10.1023/A:1008102926703 [22] Bai X, Latecki L J. Path similarity skeleton graph matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(7):1282-1292 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70769 [23] Baseski E, Erdem A, Tari S. Dissimilarity between two skeletal trees in a context. Pattern Recognition, 2009, 42(3):370-385 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2008.05.022 [24] Wang Z, Ouyang J. Shape classes registration and retrieval based on shape parts matching. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 2013, 9(4):1493-1499 http://or.nsfc.gov.cn/handle/00001903-5/326740 [25] Zhou Y, Wang J W, Zhou Q, Bai X, Liu W Y. Shape matching using points co-occurrence pattern. In:Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Image and Graphics. Hefei, China:IEEE, 2011. 344-349 [26] Wang J W, Zhou Y, Bai X, Liu W Y. Shape matching and recognition using group-wised points. In:Proceedings of the 5th Pacific Rim Symposium on Image and Video Technology. Gwangju, Korea:Springer, 2012. 393-404 -




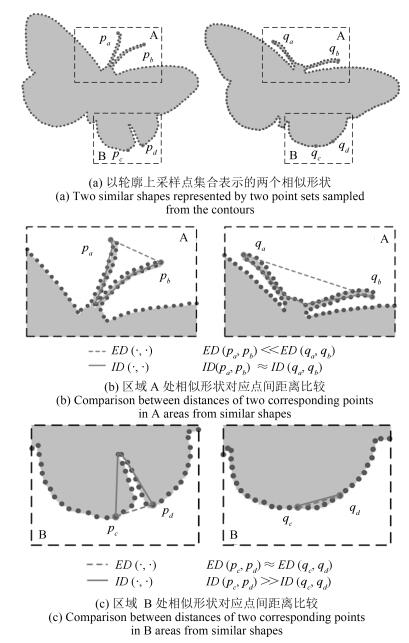
 下载:
下载: