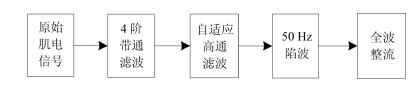
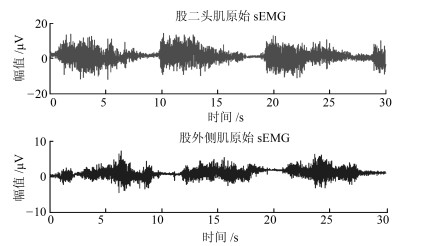
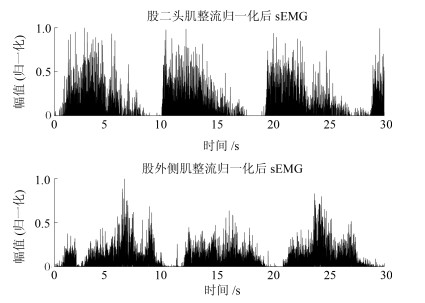
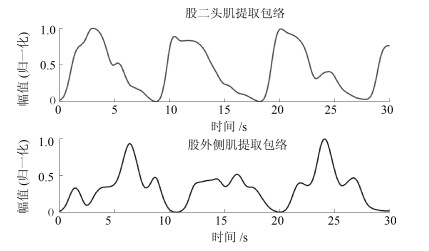
-
摘要: 针对康复机器人运动过程中的人机交互性问题,提出一种下肢康复机器人自适应人机交互控制策略.提取伸屈运动中下肢表面肌电信号(Surface electromyography,sEMG)和足底压力特征,分别用于表征下肢运动意图和人机交互力(Interaction force,IF)信息,建立基于sEMG-IF的人机交互信息融合模型,实现下肢康复机器人运动轨迹的在线规划;考虑主动康复运动过程中的人机交互作用,建立具有时变动态特性的人机系统动力学模型,设计间接模糊自适应控制器对期望轨迹进行跟踪控制,实现下肢康复机器人自适应人机交互控制.通过对5名被试者进行下肢康复机器人运动控制实验研究,验证所提方法的可行性和有效性.Abstract: Aiming at the problem of human-machine interaction in rehabilitation robot's movement, we propose an adaptive control strategy for lower limb rehabilitation robots. During flexion and extension, the surface electromyography (sEMG) of lower limbs and plantar pressure features are extracted respectively to represent lower limbs' motion intention and interaction force (IF). An sEMG-IF based human-machine interaction and information fusion model is established to program the motion trails of the rehabilitation robot online. Considering the human-machine interaction in active rehabilitation, a man-machine system dynamic model with time-varying dynamic characteristics is established. An indirect fuzzy adaptive controller is designed to trace and control the desired trajectory, and achieve adaptive interactive control of the lower limb rehabilitation robot. Validity and feasibility of the proposed strategy are verified by analysis of the data from 5 subjects under limb movement with the rehabilitation robot.1) 本文责任编委 王卫群
-
表 1 人体运动意图识别结果
Table 1 Results of human motion intent recognition
被试者 识别总数(个) 识别正确数(个) 识别率(%) A 348 332 95.40 B 315 301 95.55 C 296 285 96.28 D 308 291 94.48 E 286 277 96.85 -
[1] Lo A C, Guarino P D, Richards L G, Haselkorn J K, Wittenberg G F, Federman D G, Ringer R J, Wagner T H, Krebs H I, Volpe B T, Bever C T, Bravata D M, Duncan P W, Corn B H, Maffucci A D, Nadeau S E, Conroy S S, Powell J M, Huang G D, Peduzzi P. Robot-assisted therapy for long-term upper-limb impairment after stroke. New England Journal of Medicine, 2010, 362(19):1772-1783 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0911341 [2] Klamroth-Marganska V, Blanco J, Campen K, Curt A, Dietz V, Ettlin T, Felder M, Fellinghauer B, Guidali M, Kollmar A, Luft A, Nef T, Schuster-Amft C, Stahel W, Riener R. Three-dimensional, task-specific robot therapy of the arm after stroke:a multicentre, parallel-group randomised trial. The Lancet Neurology, 2014, 13(2):159-166 doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70305-3 [3] Meng W, Liu Q, Zhou Z D, Ai Q S, Sheng B, Xie S Q. Recent development of mechanisms and control strategies for robot-assisted lower limb rehabilitation. Mechatronics, 2015, 31:132-145 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2015.04.005 [4] 彭亮, 侯增广, 王卫群.康复机器人的同步主动交互控制与实现.自动化学报, 2015, 41(11):1837-1846 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18759.shtmlPeng Liang, Hou Zeng-Guang, Wang Wei-Qun. Synchronous active interaction control and its implementation for a rehabilitation robot. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(11):1837-1846 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18759.shtml [5] 佟丽娜, 侯增广, 彭亮, 王卫群, 陈翼雄, 谭民.基于多路sEMG时序分析的人体运动模式识别方法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(5):810-821 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18349.shtmlTong Li-Na, Hou Zeng-Guang, Peng Liang, Wang Wei-Qun, Chen Yi-Xiong, Tan Min. Multi-channel sEMG time series analysis based human motion recognition method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(5):810-821 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18349.shtml [6] Pittaccio S, Viscuso S. An EMG-controlled SMA device for the rehabilitation of the ankle joint in post-acute stroke. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2011, 20(4-5):666-670 doi: 10.1007/s11665-010-9826-7 [7] Song R, Tong K Y, Hu X L, Zhou W. Myoelectrically controlled wrist robot for stroke rehabilitation. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation, 2013, 10(1):Article No.52 doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-10-52 [8] 胡进, 侯增广, 陈翼雄, 张峰, 王卫群.下肢康复机器人及其交互控制方法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(11):2377-2390 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18514.shtmlHu Jin, Hou Zeng-Guang, Chen Yi-Xiong, Zhang Feng, Wang Wei-Qun. Lower limb rehabilitation robots and interactive control methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(11):2377-2390 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18514.shtml [9] Saglia J A, Tsagarakis N G, Dai J S, Caldwell D G. Control strategies for patient-assisted training using the ankle rehabilitation robot (ARBOT). IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2013, 18(6):1799-1808 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2012.2214228 [10] Duschau-Wicke A, Von Zitzewitz J, Caprez A, Lunenburger L, Riener R. Path control:a method for patient-cooperative robot-aided gait rehabilitation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2010, 18(1):38-48 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2009.2033061 [11] Koopman B, van Asseldonk E H F, van der Kooij H. Selective control of gait subtasks in robotic gait training:foot clearance support in stroke survivors with a powered exoskeleton. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation, 2013, 10(1):Article No.3 doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-10-3 [12] 刘金琨.机器人控制系统的设计与MATLAB仿真.北京:清华大学出版社, 2008. 169-172Liu Jin-Kun. Design and Simulation of Robot Control System Based on MATLAB. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 2008. 169-172 [13] 谢平, 宋妍, 郭子晖, 陈晓玲, 吴晓光, 苏玉萍, 杜义浩.中风康复运动中肌肉异常耦合分析.生物医学工程学杂志, 2016, 33(2):244-254 doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160043Xie Ping, Song Yan, Guo Zi-Hui, Chen Xiao-Ling, Wu Xiao-Guang, Su Yu-Ping, Du Yi-Hao. Analysis of abnormal muscular coupling during rehabilitation after stroke. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(2):244-254 doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160043 [14] Hu J, Hou Z G, Peng L, Peng L, Gu N. sEMG-Based single-joint active training with iLeg-a horizontal exoskeleton for lower limb rehabilitation. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference. Kuching, Malaysia: Springer, 2014. 535-542 -




 下载:
下载: