-
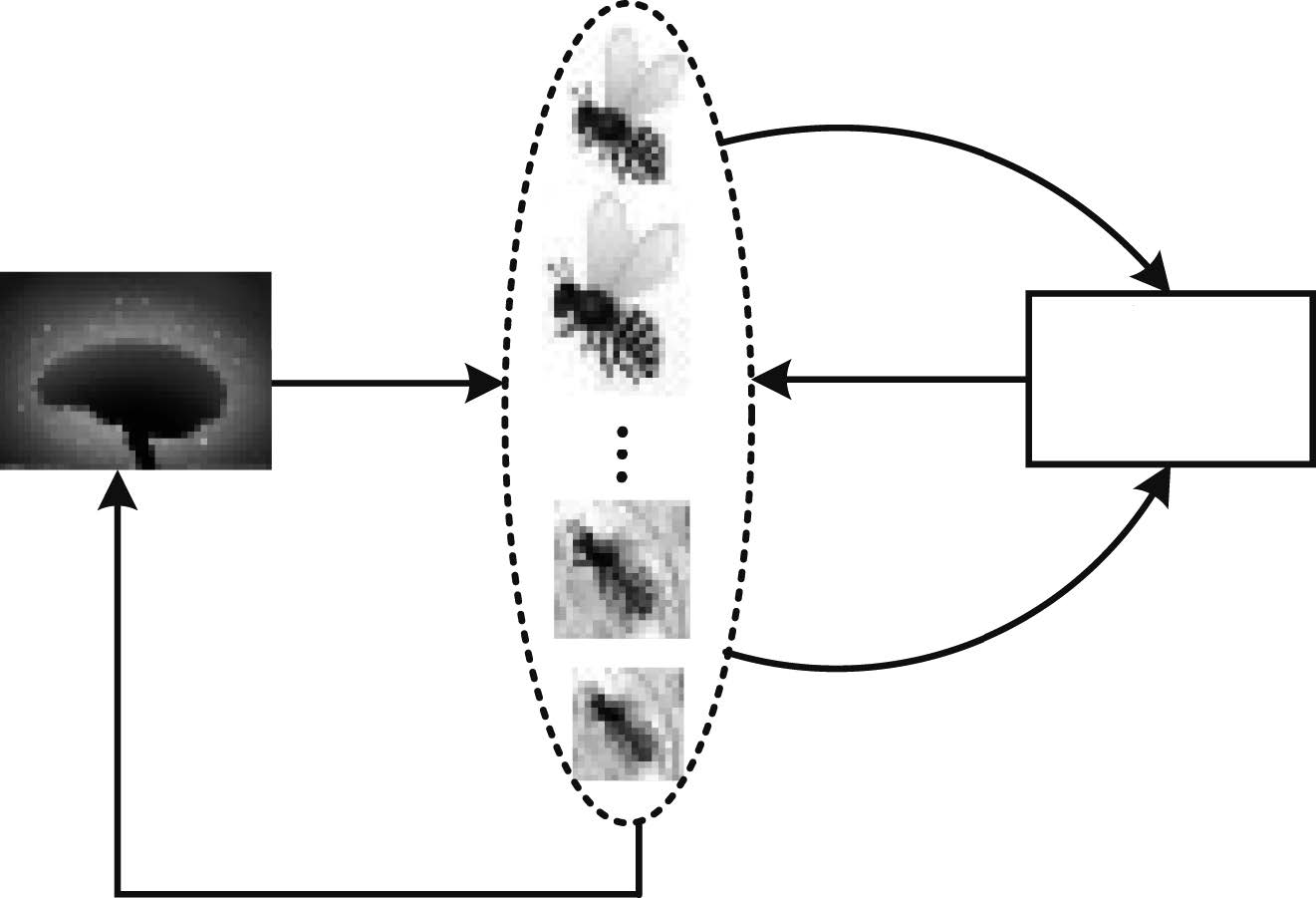
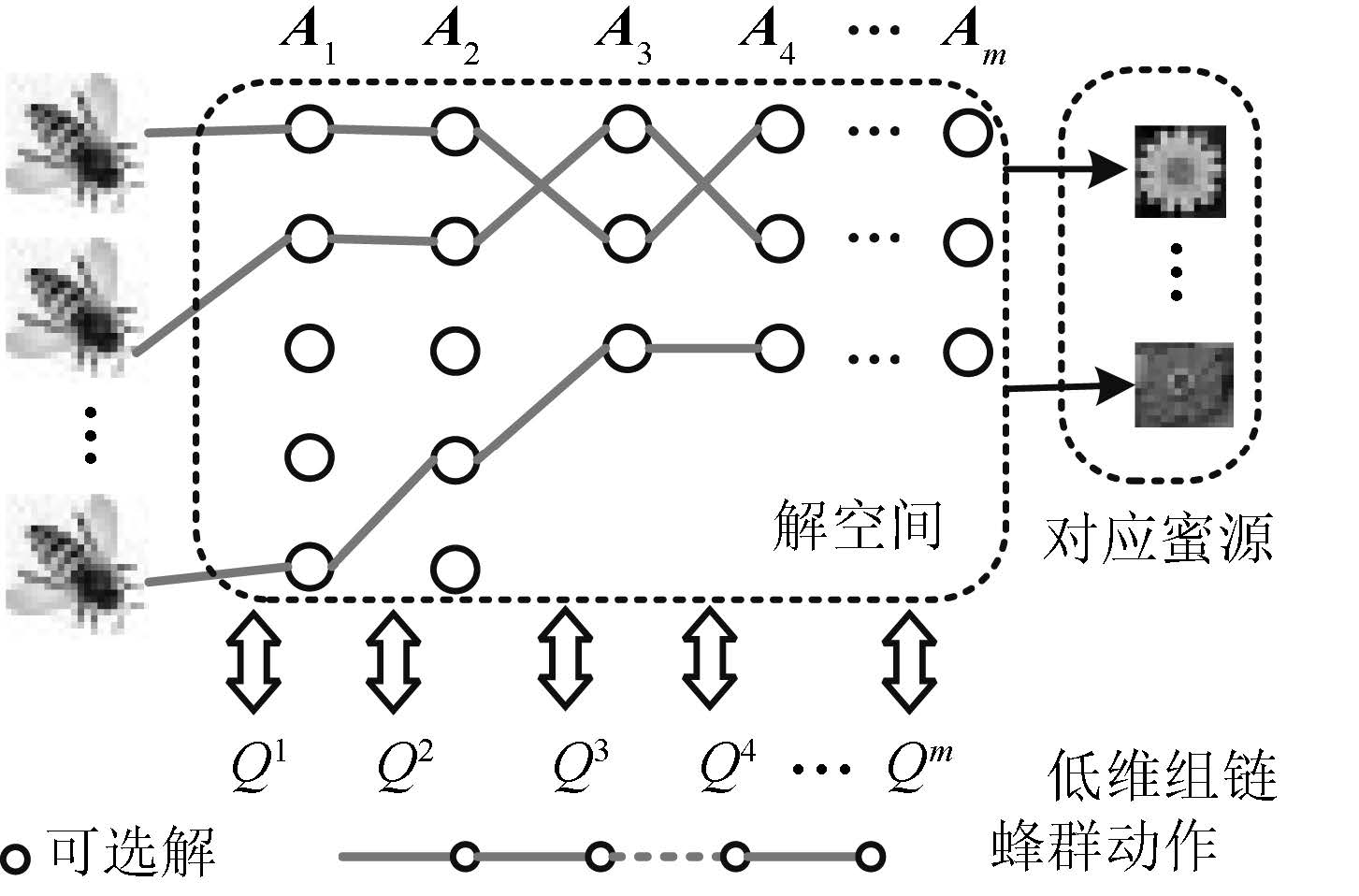
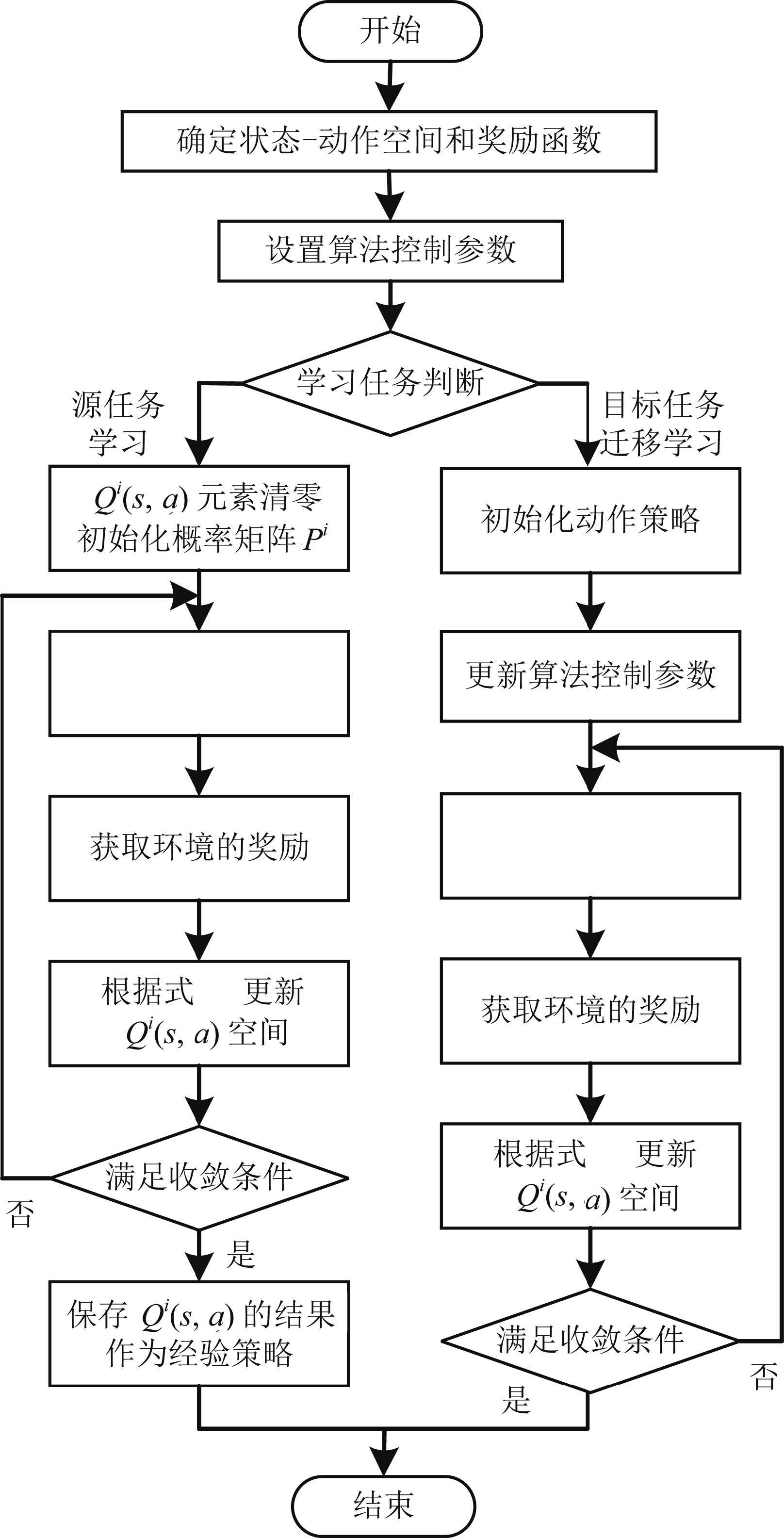
摘要: 提出了一种全新的迁移蜂群优化算法,并应用到电力系统无功优化问题.利用Q学习的试错与奖励机制构造蜂群的学习模式,并采用强化学习的行为迁移技术实现蜂群的迁移学习.为解决算法求解多变量优化问题遇到的维数灾难,提出了状态-组合动作链的方式将状态-动作空间分解成若干低维空间,明显降低算法的计算难度.仿真结果表明:本文所提算法可以保证最优解质量的同时,寻优速度能提高到传统启发式智能算法的4~67倍左右,非常适用于大规模复杂系统非线性规划问题的快速求解.Abstract: This paper proposes a novel transfer bees optimizer (TBO), which is implemented to solve the reactive power optimization of power systems. The trial-and-error and the reward mechanism of Q-learning is adopted to construct the learning mode of the bees, and the technology of behavior transfer from reinforcement learning is used for transfer learning. Moreover, a space-action chain is proposed to decompose the solution space into several lower-dimensional spaces, thus it can solve the curse of dimension resulted from the multiple variables optimization problem. Simulation results show that TBO can obtain a high-quality optimal solution, while its convergence speed can be accelerated as many as 4 to 67 times faster than that of the conventional heuristic artificial algorithm (AI) algorithm, which is very suitable for fast optimization of nonlinear programming in a large-scale complex system.
-
表 1 算例控制变量规模
Table 1 Control variable scale of the simulation case
仿真系统 控制变量个数 总计 无功补偿 变压器分接头 发电机端电压 IEEE 118 节点 3 5 17 25 IEEE 300 节点 11 44 56 111 表 2 TBO 算法参数设置
Table 2 TBO parameter setting
参数 取值范围 IEEE 118 节点 IEEE 300 节点 样本学习 迁移学习 样本学习 迁移学习 $n$ - 14 6 30 10 $\alpha $ 0<$\alpha$<1 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 $\gamma $ 0<$\gamma$<1 0.9 0.9 0.9 0.9 $\varepsilon $ 0<$\varepsilon$ <1 0.9 0.98 0.95 0.98 $\beta $ 0<$\beta$<1 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 表 3 对比算法主要参数设置
Table 3 Parameter setting of comparative algorithms
算法 参数 取值 IEEE 118 节点 IEEE 300 节点 ABC 蜂群总数 14 40 采蜜蜂 7 20 侦查蜂 2 5 观察蜂 5 15 限制次数 5 5 GSO 群体规模 100 500 游荡者比例 20% 20% 最大搜索角 $\pi/4$ $\pi/4$ 最大搜索转角 $\pi/8$ $\pi/8$ ACO 蚁群总数 50 100 信息素挥发系数 0.8 0.8 启发式值权重 1 1 搜索权重 0.8 0.8 PSO 粒子群总数 50 100 最小旋转速度 -5 -5 最大旋转速度 5 5 加速系数~$c1$/$c2$ 0.5/0.5 1/1 最小惯性系数 0.4 0.4 最大惯性系数 0.9 0.9 GA 种群规模 50 100 变异概率 0.05 0.10 交叉概率 0.80 0.80 遗传代沟 0.8 0.8 进化代数 50 100 CCGA 种群个体数 5 5 种群数 3 10 变异概率 0.90 0.90 交叉概率 0.95 0.95 最大进化代数 80 80 QGA 种群规模 50 100 量子旋转门 0.01$\pi $ 0.01$\pi $ 进化代数 50 100 Ant-Q 蚁群总数 50 80 折扣系数 0.05 0.1 学习因子 0.5 0.1 搜索权重因子 0.8 0.8 表 4 典型日96 个断面各算法运行10次平均结果统计表
Table 4 Average results of 96 load sections by each algorithm in 10 runs
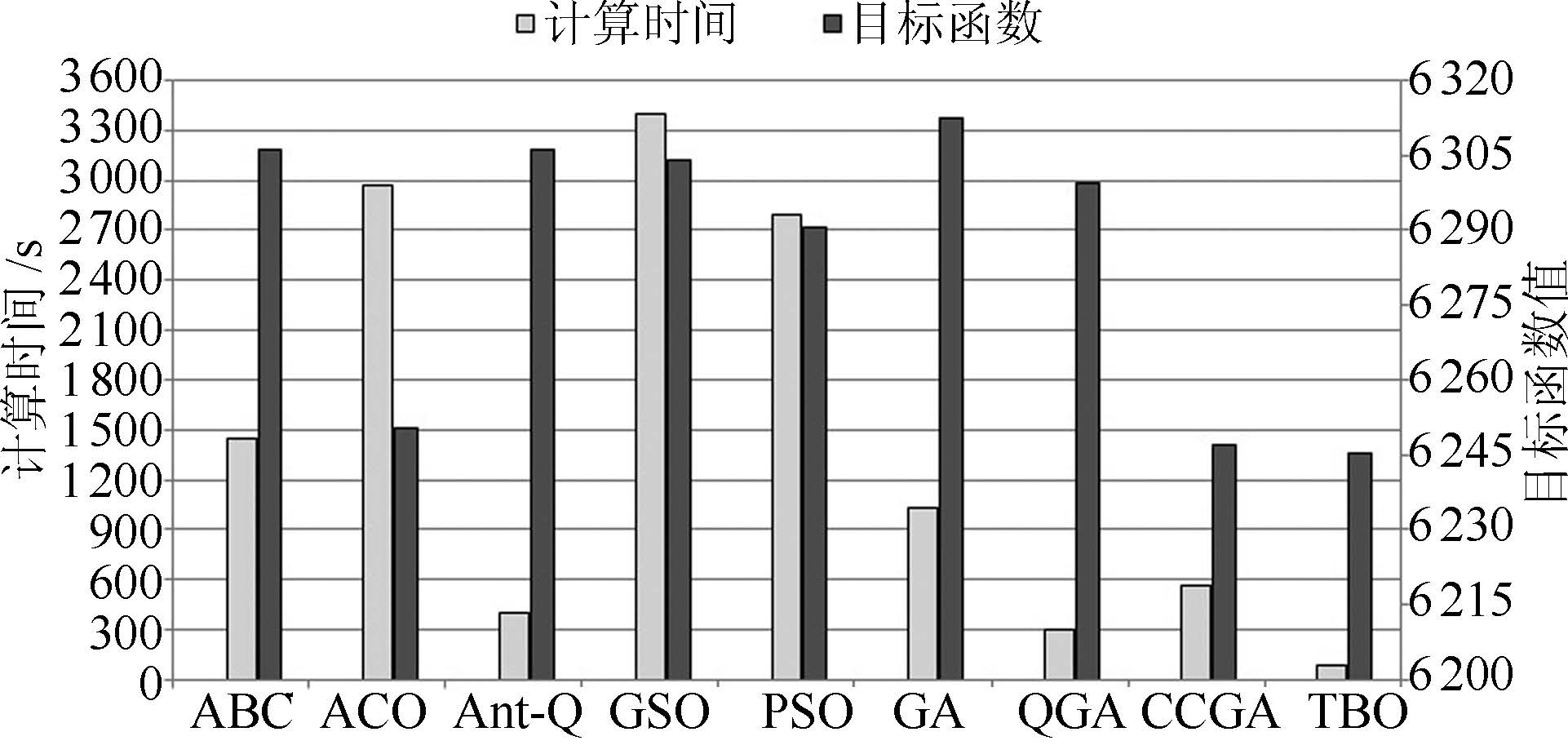
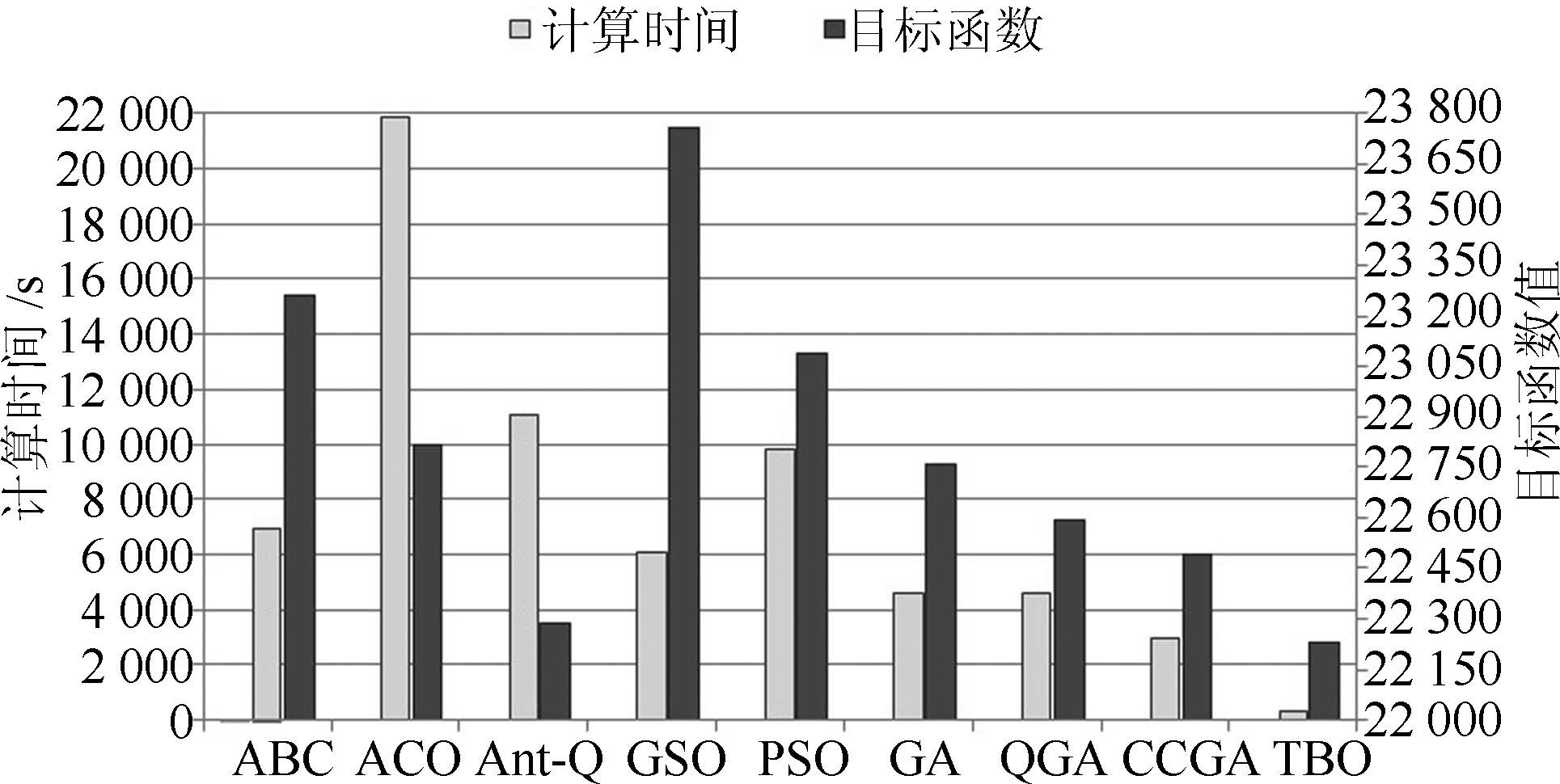
算法 IEEE 118 节点算例 IEEE 300 节点算例 计算时间(s) 收敛时间(s) $P_{\rm loss}$ (MW) $U_{\rm d}$ (%) 目标函数值 计算时间(s) 收敛时间(s) $P_{\rm loss}$ (MW) $U_{\rm d}$ (%) 目标函数值 ABC 1440 15.00 11105.12 1507.13 6306.13 6941.98 72.31 38182.69 8340.91 23261.80 ACO 2968.27 30.92 11062.35 1437.88 6250.12 21896.02 228.08 38265.31 7359.69 22812.50 Ant-Q 399.61 4.16 11110.67 1501.25 6305.96 11055.19 115.16 37427.55 7143.07 22285.31 GSO 3404.48 35.46 11121.77 1486.45 6304.11 6087.55 63.41 38644.40 8867.76 23756.08 PSO 2792.88 29.09 11103.69 1477.86 6290.77 9822.03 102.31 38098.85 8074.54 23086.70 GA 1032.95 10.76 11120.38 1504.56 6312.47 4631.66 48.25 37735.38 7779.54 22757.46 QGA 301.91 3.99 11093.48 1505.05 6299.27 4588.92 47.80 37631.03 7557.90 22594.46 CCGA 559.20 5.83 11011.74 1482.24 6246.99 2939.77 30.62 37474.88 7507.44 22491.16 TBO 89.91 0.94 11007.69 1482.84 6245.27 323.35 3.37 37513.53 6942.86 22228.19 表 5 典型日96个断面各算法运行10次目标函数值收敛性能统计表
Table 5 Convergence performance of 96 load sections by each algorithm in 10 runs
算法 IEEE 118 节点算例 IEEE 300 节点算例 最小值 最大值 方差 标准差 相对标准偏差 最小值 最大值 方差 标准差 相对标准偏差 ABC 6308.20 6302.70 3.62 1.90 3.02E-04 23286.90 23230.48 380.55 19.51 8.39E-04 ACO 6253.35 6244.85 5.79 2.41 3.85E-04 22824.96 22784.28 227.72 15.09 6.61E-04 Ant-Q 6310.36 6301.19 7.71 2.78 4.40E-04 22310.62 22263.10 220.97 14.86 6.67E-04 GSO 6312.36 6298.30 17.35 4.17 6.61E-04 23810.08 23711.90 1293.47 35.96 1.51E-03 PSO 6296.83 6284.23 14.64 3.83 6.08E-04 23193.06 23020.09 2371.10 48.69 2.11E-03 GA 6318.80 6308.79 10.80 3.29 5.21E-04 22777.53 22742.54 178.17 13.35 5.87E-04 QGA 6303.66 6295.88 5.73 2.39 3.80E-04 22613.61 22575.91 193.87 13.92 6.16E-04 CCGA 6242.94 6254.14 9.56 3.09 4.95E-04 22460.90 22509.55 286.29 16.92 7.52E-04 TBO 6241.93 6247.39 3.15 1.77 2.84E-04 22217.39 22244.14 84.56 9.20 4.06E-04 -
[1] Pozo D, Contreras J, Sauma E E. Unit commitment with ideal and generic energy storage units. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2014, 29(6):2974-2984 doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2014.2313513 [2] Shaw B, Mukherjee V, Ghoshal S P. Solution of reactive power dispatch of power systems by an opposition-based gravitational search algorithm. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2014, 55(2):29-40 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a00193bf967a199c20b3d4769a5bf89f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] Flueck A J, Chiang H D. Solving the nonlinear power flow equations with an inexact Newton method using GMRES. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 1998, 13(2):267-273 doi: 10.1109/59.667330 [4] Graville S. Optimal reactive dispatch through interior point methods. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 1994, 9(1):136-146 doi: 10.1109/59.317548 [5] Secui D C. A new modified artificial bee colony algorithm for the economic dispatch problem. Energy Conversion and Management, 2015, 89(1):43-62 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4d908f8af9eefc08ac53edc655528ab3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [6] Mohandas N, Balamurugan R, Lakshminarasimman L. Optimal location and sizing of real power DG units to improve the voltage stability in the distribution system using ABC algorithm united with chaos. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2015, 66:41-52 doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.10.033 [7] Iba K. Reactive power optimization by genetic algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 1994, 9(2):685-692 doi: 10.1109/59.317674 [8] Gómez J F, Khodr H M, De Oliveira P M, Ocque L, Yusta J M, Villasana R, Urdaneta A J. Ant colony system algorithm for the planning of primary distribution circuits. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2004, 19(2):996-1004 doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2004.825867 [9] Basu M. Modified particle swarm optimization for nonconvex economic dispatch problems. International Journal of Electrical Power Energy Systems, 2015, 69:304-312 doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.01.015 [10] Karaboga D. An Idea Based on Honey Bee Swarm for Numerical Optimization, Technical Report-TRO6, Erciyes University, Kasyeri, 2005. [11] Karaboga D, Basturk B. On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Applied Soft Computing, 2008, 8(1):687-697 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2007.05.007 [12] Dorigo M, Gambardella L M. A study of some properties of Ant-Q. In:Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature. Berlin, Germany:Springer, 1996. 656-665 [13] He S, Wu Q H, Saunders J R. Group search optimizer:an optimization algorithm inspired by animal searching behavior. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(5):973-990 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2011992 [14] Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10):1345-1359 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 [15] 张景祥, 王士同, 邓赵红, 蒋亦樟, 李奕. 融合异构特征的子空间迁移学习算法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(2):236-246 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201402008.htmZhang Jing-Xiang, Wang Shi-Tong, Deng Zhao-Hong, Jiang Yi-Zhang, Li Yi. A subspace transfer learning algorithm integrating heterogeneous features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(2):236-246 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201402008.htm [16] 王皓, 高阳, 陈兴国. 强化学习中的迁移:方法和进展. 电子学报, 2008, 36(12A):39-43 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU2008S1006.htmWang Hao, Gao Yang, Chen Xing-Guo. Transfer of reinforcement learning:the state of the art. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2008, 36(12A):39-43 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU2008S1006.htm [17] 张倩, 李明, 王雪松, 程玉虎, 朱美强. 一种面向多源领域的实例迁移学习. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(6):1176-1183 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201406015.htmZhang Qian, Li Ming, Wang Xue-Song, Cheng Yu-Hu, Zhu Mei-Qiang. Instance-based transfer learning for multi-source domains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(6):1176-1183 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201406015.htm [18] Watkins C J C H, Dayan P. Q-learning. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3-4):279-292 doi: 10.1007/BF00992698 [19] 张孝顺, 郑理民, 余涛. 基于多步回溯Q(λ)学习的电网多目标最优碳流算法. 电力系统自动化, 2014, 38(17):118-123 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXT201417022.htmZhang Xiao-Shun, Zheng Li-Min, Yu Tao. Multi-objective optimal carbon emission flow calculation of power grid based on multi-step Q(λ) learning algorithm. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38(17):118-123 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXT201417022.htm [20] Malossini A, Blanzieri E, Calarco T. Quantum genetic optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2008, 12(2):231-241 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2007.905006 [21] 王建学, 王锡凡, 陈皓勇, 王秀丽. 基于协同进化法的电力系统无功优化. 中国电机工程学报, 2004, 24(9):124-129 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC200409021.htmWang Jian-Xue, Wang Xi-Fan, Chen Hao-Yong, Wang Xiu-Li. Reactive power optimization based on cooperative coevolutionary approach. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2004, 24(9):124-129 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC200409021.htm [22] Sutton R S, Precup D, Singh S. Between MDPs and semi-MDPs:a framework for temporal abstraction in reinforcement learning. Artificial Intelligence, 1999, 112(1-2):181-211 doi: 10.1016/S0004-3702(99)00052-1 [23] 张孝顺, 余涛, 唐捷. 基于分层相关均衡强化学习的CPS指令优化分配算法. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39(8):80-86 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXT201508013.htmZhang Xiao-Shun, Yu Tao, Tang Jie. Optimal CPS command dispatch based on hierarchically correlated equilibrium reinforcement learning. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39(8):80-86 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXT201508013.htm [24] Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning:an Introduction. Cambridge:MIT Press, 1998. 87-160 [25] 李宝磊, 施心陵, 苟常兴, 吕丹桔, 安镇宙, 张榆锋. 多元优化算法及其收敛性分析. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(5):949-959Li Bao-Lei, Shi Xin-Ling, Gou Chang-Xing, Lv Dan-Ju, An Zhen-Zhou, Zhang Yu-Feng. Multivariant optimization algorithm and its convergence analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5):949-959 -





 下载:
下载: