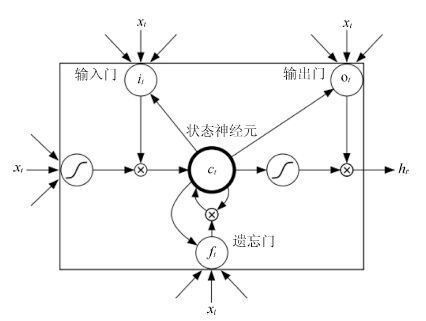
-
摘要: 人体行为识别和深度学习理论是智能视频分析领域的研究热点, 近年来得到了学术界及工程界的广泛重视, 是智能视频分析与理解、视频监控、人机交互等诸多领域的理论基础. 近年来, 被广泛关注的深度学习算法已经被成功运用于语音识别、图形识别等各个领域.深度学习理论在静态图像特征提取上取得了卓著成就, 并逐步推广至具有时间序列的视频行为识别研究中. 本文在回顾了基于时空兴趣点等传统行为识别方法的基础上, 对近年来提出的基于不同深度学习框架的人体行为识别新进展进行了逐一介绍和总结分析; 包括卷积神经网络(Convolution neural network, CNN)、独立子空间分析(Independent subspace analysis, ISA)、限制玻尔兹曼机(Restricted Boltzmann machine, RBM)以及递归神经网络(Recurrent neural network, RNN)及其在行为识别中的模型建立, 对模型性能、成果进展及各类方法的优缺点进行了分析和总结.Abstract: Human action recognition is an active research topic in intelligent video analysis and is gaining extensive attention in academic and engineering communities. This technology is an important basis of intelligent video analysis, video tagging, human computer interaction and many other fields. The deep learning theory has been made remarkable achievements on still image feature extraction and gradually extends to the time sequences of human action videos. This paper reviews the traditional design of action recognition methods, such as spatial-temporal interest point, introduces and analyzes different human action recognition framework based on deep learning, including convolution neural network (CNN), independent subspace analysis (ISA) model, restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM), and recurrent neural network (RNN). Finally, this paper summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of these methods.
-
表 1 基于几何形状或基于运动信息的识别结果(%)
Table 1 The results of recognition methods based on geometric shapes or motion information (%)
表 2 基于时空兴趣点的特征提取方法在KTH、UCF Sports 及Hollywood 数据库上的结果(%)
Table 2 The results of methods based on the interest of time and space on the KTH, UCF Sports and Hollywood databases (%)
表 3 基于CNN 的行为识别算法结果(%)
Table 3 The results of action recognition based on CNN (%)
表 4 ISA 在三个数据库上的结果统计(%)
Table 4 The results of ISA on three databases (%)
KTH UCF Sports Hollyword 2 Le 等[36] 93.9 86.5 53.3 -
[1] Fujiyoshi H, Lipton A J, Kanade T. Real-time human motion analysis by image skeletonization. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2004, 87-D(1) : 113-120 [2] Chaudhry R, Ravichandran A, Hager G, Vidal R. Histograms of oriented optical flow and Binet-Cauchy kernels on nonlinear dynamical systems for the recognition of human actions. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, FL: IEEE, 2009. 1932-1939 [3] Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2005. 886-893 [4] Lowe D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kerkyra: IEEE, 1999. 1150-1157 [5] Schuldt C, Laptev I, Caputo B. Recognizing human actions: a local SVM approach. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Cambridge: IEEE, 2004. 32-36 [6] Dollar P, Rabaud V, Cottrell G, Belongie S. Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005. 65-72 [7] Rapantzikos K, Avrithis Y, Kollias S. Dense saliency-based spatiotemporal feature points for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, FL: IEEE, 2009. 1454-1461 [8] Knopp J, Prasad M, Willems G, Timofte R, Van Gool L. Hough transform and 3D SURF for robust three dimensional classification. In: Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2010) . Berlin Heidelberg: Springer. 2010. 589-602 [9] Kláser A, Marszaéek M, Schmid C. A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3D-gradients. In: Proceedings of the 19th British Machine Vision Conference. Leeds: BMVA Press, 2008. 99.1-99.10 [10] Wang H, Ullah M M, Klaser A, Laptev I, Schmid C. Evaluation of local spatio-temporal features for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2009 British Machine Vision Conference. London, UK: BMVA Press, 2009. 124.1-124.11 [11] Wang H, Kláser A, Schmid C, Liu C L. Action recognition by dense trajectories. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, RI: IEEE, 2011. 3169-3176 [12] Hinton G E. Learning multiple layers of representation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2007, 11(10) : 428-434 [13] Deng L, Yu D. Deep learning: methods and applications. Foundations and Trends® in Signal Processing, 2014, 7(3-4) : 197-387 [14] Schmidhuber J. Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 85-117 [15] Gorelick L, Blank M, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R. Actions as space-time shapes. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005. 1395-1402 [16] Soomro K, Zamir A R. Action recognition in realistic sports videos. Computer Vision in Sports. Switzerland: Springer. 2014. 181-208 [17] Rodriguez M D, Ahmed J, Shah M. Action mach a spatio-temporal maximum average correlation height filter for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, AK: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 [18] Marszalek M, Laptev I, Schmid C. Actions in context. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, FL: IEEE, 2009. 2929-2936 [19] Yang X D, Tian Y L. Effective 3D action recognition using EigenJoints. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2014, 25(1) : 2-11 [20] Bobick A, Davis J. An appearance-based representation of action. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Vienna: IEEE, 1996. 307-312 [21] Weinland D, Ronfard R, Boyer E. Free viewpoint action recognition using motion history volumes. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2006, 104(2-3) : 249-257 [22] Bobick A F, Davis J W. The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2001, 23(3) : 257-267 [23] Sarikaya R, Hinton G E, Deoras A. Application of deep belief networks for natural language understanding. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(4) : 778-784 [24] Ren Y F, Wu Y. Convolutional deep belief networks for feature extraction of EEG signal. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2014. 2850-2853 [25] Bengio Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1) : 1-127 [26] LeCun Y, Ranzato M. Deep learning tutorial. In: Tutorials in International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML13) . Atlanta, USA: Citeseer, 2013. [27] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, Nevada, United States, 2012. 1097-1105 [28] Bouvrie J. Notes on Convolutional Neural Networks. MIT CBCL Technical Report, 2006, 38-44 [29] Ji S W, Xu W, Yang M, Yu K. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1) : 221-231 [30] Chéron G, Laptev I, Schmid C. P-CNN: pose-based CNN features for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago: IEEE, 2015. 3218-3226 [31] Varol G, Laptev I, Schmid C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. arXiV: 1604.04494, 2015. [32] Karpathy A, Toderici G, Shetty S, Leung T, Sukthankar R, Li F F. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, OH: IEEE, 2014. 1725-1732 [33] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook, NY: Curran Associates, Inc., 2014. 568-576 [34] Poultney C, Chopra S, Cun Y L. Efficient learning of sparse representations with an energy-based model. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2006. 1137-1144 [35] Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2006. [36] Le Q V, Zou W Y, Yeung S Y, Ng A Y. Learning hierarchical invariant spatio-temporal features for action recognition with independent subspace analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, RI: IEEE, 2011. 3361-3368 [37] Hyvárinen A, Hurri J, Hoyer P O. Natural Image Statistics: A Probabilistic Approach to Early Computational Vision. London: Springer-Verlag, 2009. [38] Hinton G. A practical guide to training restricted Boltzmann machines. Momentum, 2010, 9(1) : 926 [39] Fischer A, Igel C. An introduction to restricted Boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 17th Iberoamerican Congress on Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Springer. 2012. 14-36 [40] Larochelle H, Bengio Y. Classification using discriminative restricted Boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2008. 536-543 [41] Chen H, Murray A F. Continuous restricted Boltzmann machine with an implementable training algorithm. IEE Proceedings-Vision, Image and Signal Processing, 2003, 150(3) : 153-158 [42] Taylor G W, Hinton G E. Factored conditional restricted Boltzmann machines for modeling motion style. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2009. 1025-1032 [43] Chen B, Ting J A, Marlin B, de Freitas N. Deep learning of invariant spatio-temporal features from video. In: Proceedings of Conferrence on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) Workshop on Deep Learning and Unsupervised Feature Learning. Whistler BC Canada, 2010. [44] Pineda F J. Generalization of back-propagation to recurrent neural networks. Physical Review Letters, 1987, 59(19) : 2229-2232 [45] Chung J, Gulcehre C, Cho K, Bengio Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv: 1412.3555, 2014. [46] Omlin C W, Giles C L. Training second-order recurrent neural networks using hints. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop Machine Learning. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1992. 361-366 [47] Sak H, Senior A, Beaufays F. Long short-term memory based recurrent neural network architectures for large vocabulary speech recognition. arXiv: 1402.1128, 2014. [48] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8) : 1735-1780 [49] Sak H, Senior A, Beaufays F. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network architectures for large scale acoustic modeling. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Annual Conference of International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH). Singapore: ISCA, 2014. 338-342 [50] Ng J Y H, Hausknecht M, Vijayanarasimhan S, Vinyals O, Monga R, Toderici G. Beyond short snippets: deep networks for video classification. arXiv: 1503.08909, 2015. [51] Donahue J, Hendricks L A, Guadarrama S, Rohrbach M, Venugopalan S, Saenko K, Darrell T. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. arXiv: 1411.4389, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: