Classifier-designing Algorithm on a Small Dataset Based on Margin Fisher Criterion and Transfer Learning
-
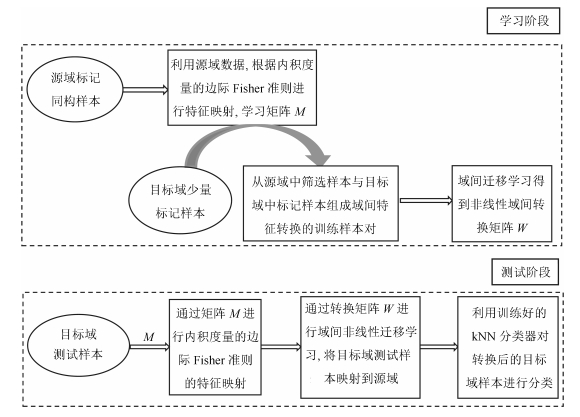
摘要: 如何利用大量已有的同构标记数据(源域)设计小样本训练数据(目标域)的分类器是一个具有很强应用意义的研究问题. 由于不同域的数据特征分布有差异,直接使用源域数据对目标域样本进行分类的效果并不理想. 针对上述问题,本文提出了一种基于迁移学习的分类器设计算法. 首先,本文利用内积度量的边际Fisher准则对源域进行特征映射,提高源域中类内紧凑性和类间区分性. 其次,为了筛选合理的训练样本对,本文提出一种去除边界奇异点的算法来选择源域密集区域样本点,与目标域中的标记样本点组成训练样本对. 在核化空间上,本文学习了目标域特征到源域特征的非线性转换,将目标域映射到源域. 最后,利用邻近算法(k-nearest neighbor,kNN)分类器对映射后的目标域样本进行分类. 本文不仅改进了边际Fisher准则方法,并且将基于自适应样本对 筛选的迁移学习应用到小样本数据的分类器设计中,提高域间适应性. 在通用数据集上的实验结果表明,本文提出的方法能够有效提高小样本训练域的分类器性能.
-
关键词:
- 小样本集分类器 /
- 迁移学习 /
- 边际Fisher准则 /
- kNN分类器 /
- 域间转换
Abstract: It has great practical significance to design a classifier on a small dataset (target domain) with the help of a large dataset (source domain). Since feature distribution varies on different datasets, the classifiers trained on the source domain cannot perform well on a target domain. To solve the problem, we propose a novel classifier-designing algorithm based on transfer learning theory. Firstly, to improve the compass of the same category and separateness of different categories in the source domain, this paper utilizes the extended margin Fisher criterion where the distance is measured by the inner product between data. Secondly, to select good sample pairs for transfer learning, this paper presents an algorithm to get rid of marginal singular points by selecting high-density samples in the source domain. The non-linear feature transformation mapping the target domain to the source domain is learned in the kernel space. Finally, k-nearest neighbor (kNN) classifiers are trained for classification. Compared with the existing works, this paper not only extends the margin Fisher criterion, but also applies the transfer learning theory based on the algorithm of selecting training sample pairs to design classifiers of a small dataset. We experimentally demonstrate the superiority of our method to effectively improve the performance of classifiers on the general datasets. -
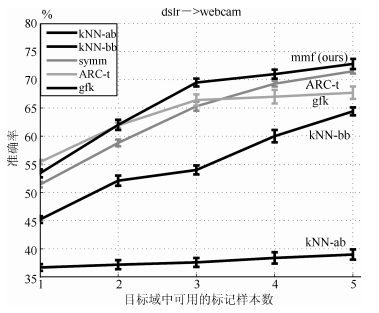
图 7 在目标域上的分类准确率随目标域中可用标记样本数量的变化曲线(其中源域中选择了20个标记样本, 源域为dslr, 目标域为webcam)
Fig. 7 The accuracy rate curves in the target domain varying with the number of labeled samples in the target domain (Where 20 labeled samples in source domain is selected, the source domain here is dslr, while the target domain is webcam.
表 1 本文算法的实验参数设置
Table 1 The experiment parameters set of our method
A→B k1 k2 kA kB σ a→w 22 1700 20 3 1 a→d 22 1700 20 3 1 w→a 20 680 15 3 1 w→d 20 680 15 3 1 d→a 17 420 15 3 1 d→w 17 420 15 3 1 表 2 在三个数据域上的分类准确率(%)(加粗字体表示最佳性能, 缩写: a: amazom, w: webcam, d: dslr)
Table 2 Accuracy rates in the three domains (%)(The bold font represents the best performance, abbreviation: a: amazom, w: webcam, d: dslr.
A→B kNN-ab kNN-bb symm[3] ARCt[16] gfk[20] svm-s hfa[28] mmf-Euclid mmf a→w 9.6±1.0 51.0±0.8 51.0±1.4 55.7±0.9 57.8±1.0 34.5±0.8 61.5±0.9 49.3±0.8 55.5±0.7 a→d 4.9±1.1 47.9±0.9 47.9±1.4 50.2±0.7 50.5±0.8 35.3±0.6 52.4±1.0 50.6±0.9 57.6±0.9 w→a 10.5±0.6 40.1±0.5 43.7±0.7 43.4±0.5 44.1±0.4 34.9±0.4 44.5±0.7 42.9±0.6 44.6±0.8 w→d 23.2±0.8 54.1±0.9 69.8±1.0 71.3±0.8 68.5±0.5 65.8±0.8 52.7±1.1 70.1±0.7 71.5±0.6 d→a 11.3±0.5 35.6±0.7 42.7±0.5 42.5±0.5 45.7±0.8 33.8±0.4 45.4±0.9 41.4±0.7 42.6±0.6 d→w 37.6±0.8 54.0±0.7 63.4±0.9 65.3±0.5 66.4±0.5 68.1±0.6 62.4±0.8 68.5±1.0 69.5±0.7 平均准确率 12.2±0.8 37.8±0.8 55.6±1.0 56.9±0.7 57.7±0.7 45.4±0.6 53.2±0.9 55.4±0.8 58.6±0.8 -
[1] Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J, Kandola J S. Spectral kernel methods for clustering. In: Proceedings of the 2001 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 14 (NIPS01). London: MIT, 2002. 649-655 [2] Bosch A, Zisserman A, Munoz X. Representing shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Image & Video Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2007. 401-408 [3] Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M, Darrell T. Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Heraklion, Crete, Greece: Springer, 2010. 213-226 [4] Patel V M, Gopalan R, Li R, Chellappa R. Visual domain adaptation: a survey of recent advances. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2015, 32(3): 53-69 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2347059 [5] Hoffman J, Rodner E, Donahue J, Darrell T, Saenko K. Efficient learning of domain-invariant image representations. arXiv: 1301.3224, 2013. [6] Shao L, Zhu F, Li X. Transfer learning for visual categorization: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2015, 26(5): 1019-1034 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2163345210&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [7] 顾鑫, 王士同, 许敏. 基于多源的跨领域数据分类快速新算法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(3): 531-547 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18319.shtmlGu Xin, Wang Shi-Tong, Xu Min. A new cross-multidomain classification algorithm and its fast version for large datasets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(3): 531-547 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18319.shtml [8] 张倩, 李明, 王雪松, 程玉虎, 朱美强. 一种面向多源领域的实例迁移学习. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(6): 1176-1183 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18387.shtmlZhang Qian, Li Ming, Wang Xue-Song, Cheng Yu-Hu, Zhu Mei-Qiang. Instance-based transfer learning for multi-source domains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(6): 1176-1183 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18387.shtml [9] Yang J, Yan R, Hauptmann A G. Cross-domain video concept detection using adaptive SVMS. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2007. 188-197 [10] 王雪松, 潘杰, 程玉虎, 曹戈. 基于相似度衡量的决策树自适应迁移. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(12): 2186-2192 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18260.shtmlWang Xue-Song, Pan Jie, Cheng Yu-Hu, Cao Ge. Self-adaptive transfer for decision trees based on similarity metric. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(12): 2186-2192 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18260.shtml [11] Bergamo A, Torresani L. Exploiting weakly-labeled web images to improve object classification: a domain adaptation approach. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 23. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2010. 181-189 [12] Li X. Regularized Adaptation: Theory, Algorithms and Applications [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Washington, USA, 2007 [13] 董爱美, 王士同. 共享隐空间迁移SVM. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(10): 2276-2287 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18502.shtmlDong Ai-Mei, Wang Shi-Tong. A shared latent subspace transfer learning algorithm using SVM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(10): 2276-2287 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18502.shtml [14] Oquab M, Bottou L, Laptev I, Sivic J. Learning and transferring mid-level image representations using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, OH: IEEE, 2014. 1717-1724 [15] Razavian A S, Azizpour H, Sullivan J, Carlsson S. CNN features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition. Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2014. 512-519 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2062118960&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [16] Kulis B, Saenko K, Darrell T. What you saw is not what you get: domain adaptation using asymmetric kernel transforms. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, RI: IEEE, 2011. 1785-1792 [17] Farhadi A, Tabrizi M K. Learning to recognize activities from the wrong view point. In: Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision——ECCV 2008. Marseille, France: Springer, 2008. 154-166 [18] Chopra S, Balakrishnan S, Gopalan R. DLID: deep learning for domain adaptation by interpolating between domains. In: Proceedings of the ICML Workshop on Representation Learning. Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 2013. [19] Wang H, Nie F P, Huang H, Ding C. Dyadic transfer learning for cross-domain image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona: IEEE, 2011. 551-556 [20] Gong B, Shi Y, Sha F, Grauman, K. Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, RI: IEEE, 2012. 2066-2073 [21] Long M, Wang J, Sun J, Yu P S. Domain invariant transfer kernel learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering, 2015, 27(6): 1519-1532 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2087977130&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [22] Shao L, Liu L, Li X L. Feature learning for image classification via multiobjective genetic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(7): 1359-1371 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2293418 [23] Davis J V, Kulis B, Jain P, Sra S, Dhillon I S. Information-theoretic metric learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning. Corvallis, Oregon, USA: ACM, 2007. 209-216 [24] Yan S C, Xu D, Zhang B Y, Zhang H J, Yang Q, Lin S. Graph embedding and extensions: a general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(1): 40-51 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.250598 [25] Li Y L, Liu P, Du H S, Li Z, Liu J H, Yu D Y, Li M Q. Marginal fisher analysis-based feature extraction for identification of drug and explosive concealed by body packing. Analytical Methods, 2013, 5(22): 6331-6337 doi: 10.1039/c3ay40998h [26] Wang Z Q, Sun X. Optimal kernel marginal fisher analysis for face recognition. Journal of Computers, 2012, 7(9): 2298-2305 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2171475570&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [27] Al Censor Y, Zenios S A. Parallel optimization: theory, algorithms and applications. Scalable Computing: Practice & Experience. New York: Oxford University Press, 1997. [28] Duan L X, Xu D, Tsang I W. Learning with augmented features for heterogeneous domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Machine Learning. Edinburgh, Scotland, UK: Omnipress, 2012. 711-718 -





 下载:
下载: