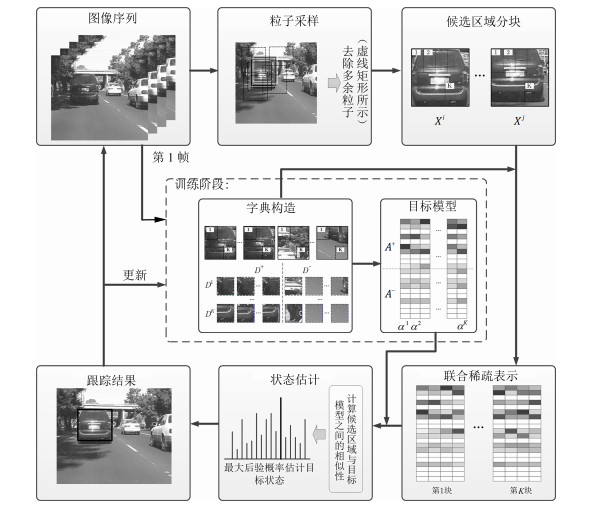
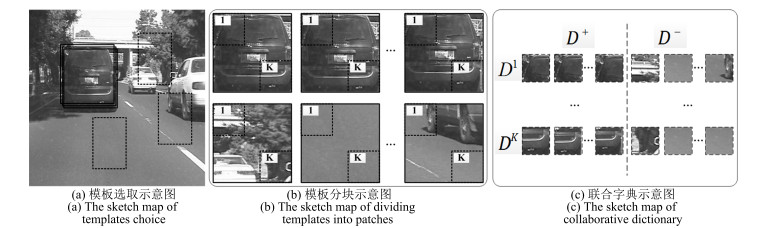
-
摘要: 目标表观建模是基于稀疏表示的跟踪方法的研究重点, 针对这一问题, 提出一种基于判别性局部联合稀疏表示的目标表观模型, 并在粒子滤波框架下提出一种基于该模型的多任务跟踪方法(Discriminative local joint sparse appearance model based multitask tracking method, DLJSM).该模型为目标区域内的局部图像分别构建具有判别性的字典, 从而将判别信息引入到局部稀疏模型中, 并对所有局部图像进行联合稀疏编码以增强结构性.在跟踪过程中, 首先对目标表观建立上述模型; 其次根据目标表观变化的连续性对采样粒子进行初始筛选以提高算法的效率; 然后求解剩余候选目标状态的联合稀疏编码, 并定义相似性函数衡量候选状态与目标模型之间的相似性; 最后根据最大后验概率估计目标当前的状态.此外, 为了避免模型频繁更新而引入累积误差, 本文采用每5帧判断一次的方法, 并在更新时保留首帧信息以减少模型漂移.实验测试结果表明DLJSM方法在目标表观发生巨大变化的情况下仍然能够稳定准确地跟踪目标, 与当前最流行的13种跟踪方法的对比结果验证了DLJSM方法的高效性.Abstract: Appearance modeling is the research focus in tracking method based on sparse representation. In this paper, a discriminative local joint sparse appearance model based multitask tracking method (DLJSM) is proposed within particle filter framework. The proposed model builds a discriminative dictionary for each image patch within the object-region in order to introduce the discriminative information into the local sparse model, and enhances the structure feature via joint sparse representation. During tracking, the target appearance is modeled firstly. Then the sampling particles are pre-selected according to the target appearance's consecutive changes characteristic to improve efficiency of the algorithm. Next, joint sparse representations of all the candidates are solved jointly. Furthermore, a function is defined to measure the similarities between candidates and the target model. Lastly, the target state is estimated by the maximum posterior probability. Besides, update is judged every five frames to avoid the accumulative error caused by frequent update and the target information in the first frame is reserved to alleviate drifting. Test results show that the proposed DLJSM tracker can maintain a stable and accurate tracking when the target appearance undergoes huge variations. Comparison results on challenging benchmark image sequences show that the DLJSM method out performs 13 other state-of-the-art algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Object tracking /
- appearance modeling /
- sparse representation /
- multitask tracking /
- particle filter
-
表 1 DLJSM算法与非稀疏跟踪方法的结果对比
Table 1 Comparison of the results between DLJSM algorithm and the methods not based on sparse representation
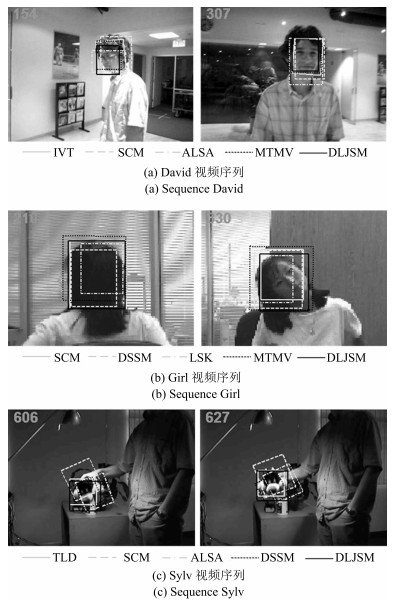
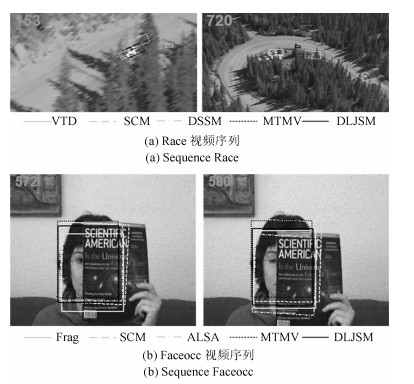
中心误差(pixel) F -参数 IVT VTD Frag MIL TLD DLJSM IVT VTD Frag MIL TLD DLJSM Girl 29.6 23.8 81.6 31.3 - 14.4 0.703 0.740 0.134 0.681 - 0.836 Singerl 9.1 3.7 42.1 241.0 27.5 3.2 0.642 0.898 0.394 0.021 0.444 0.904 Faceocc ll.2 9.5 89.5 18.6 16.0 6.3 0.891 0.903 0.940 0.838 0.786 0.938 Car4 4.0 144.8 180.5 142.1 - 4.5 0.937 0.341 0.263 0.262 - 0.939 Sylv 5.9 21.5 45.1 6.9 5.6 5.1 0.837 0.672 0.809 0.837 0.835 0.867 Race 176.4 82.2 221.4 310.6 - 2.7 0.025 0.372 0.053 0.013 - 0.721 Jumping 34.8 111.9 21.2 41.8 - 5.2 0.273 0.175 0.429 0.255 - 0.787 Animal 10.5 11.8 45.7 252.6 - 9.7 0.736 0.765 0.120 0.014 - 0.748 表 2 DLJSM算法与基于单个稀疏跟踪方法的结果对比
Table 2 Comparison of the results between DLJSM algorithm and the methods based on single sparse representation
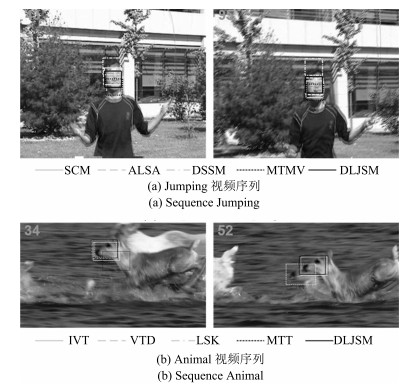
中心误差(pixel) F -参数 l1 APG-l1 SCM ALSA LSK DLJSM l1 APG-l1 SCM ALSA LSK DLJSM Animal 23.1 23.9 20.2 289.5 10.2 9.7 0.583 0.619 0.652 0.046 0.732 0.748 David 20.1 13.7 9.8 11.4 11.8 9.3 0.605 0.652 0.759 0.707 0.713 0.772 Car11 33.7 2.9 2.1 2.3 73.3 2.0 0.501 0.857 0.895 0.897 0.09 0.897 Singer1 5.6 3.8 3.7 5.1 7.7 3.2 0.780 0.870 0.910 0.887 0.742 0.904 Race 214.7 203.9 28.7 245.5 217.2 2.7 0.049 0.059 0.628 0.062 0.017 0.721 Jumping 38.0 16.4 6.1 12.3 63.5 5.2 0.256 0.582 0.767 0.748 0.214 0.787 Skatingl 137.5 60.5 37.0 64.5 106.4 8.1 0.221 0.475 0.628 0.580 0.335 0.789 表 3 DLJSM算法与基于联合稀疏表示跟踪方法的结果对比
Table 3 Comparison of the results between DLJSM algorithm and the methods based on joint sparse representation
中心误差(pixel) F -参数 MTT MTMV DSSM DLJSM MTT MTMV DSSM DLJSM Car11 17.4 27.7 2.0 2.0 0.612 0.514 0.896 0.897 David 21.4 10.2 10.4 9.3 0.565 0.745 0.663 0.772 Race - 41.2 4.3 2.7 - 0.163 0.695 0.721 Skatingl - 81.9 73.8 8.1 - 0.451 0.569 0.789 Animal 19.4 19.5 23.7 9.7 0.630 0.635 0.574 0.748 Stone 3.3 12.5 43.9 2.8 0.746 0.50 0.166 0.720 -
[1] Yilmaz A, Javed O, Shah M. Object tracking:a survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2006, 38(4):Article No. 13 [2] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Online object tracking:a benchmark. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA:IEEE, 2013. 2411-2418 [3] Smeulders A W M, Chu D M, Cucchiara R, Calderara S, Dehghan A, Shah M. Visual tracking:an experimental survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(7):1442-1468 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.230 [4] Adam A, Rivlin E, Shimshoni I. Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram. In:Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York, USA:IEEE, 2006. 798-805 [5] Kwon J, Lee K M. Visual tracking decomposition. In:Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA:IEEE, 2010. 1269-1276 [6] Ross D A, Lim J, Lin R S, Yang M H. Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 77(1-3):125-141 doi: 10.1007/s11263-007-0075-7 [7] Babenko B, Yang M H, Belongie S. Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning. In:Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami FL, USA:IEEE, 2009. 983-990 [8] Kalal Z, Matas J, Mikolajczyk K. P-N learning:bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints. In:Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA:IEEE, 2010. 49-56 [9] Mei X, Ling H B. Robust visual tracking using L1 minimization. In:Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kyoto, Japan:IEEE, 2009. 1436-1443 [10] Bao C L, Wu Y, Ling H B, Ji H. Real time robust L1 tracker using accelerated proximal gradient approach. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA:IEEE, 2012. 1830-1837 [11] Zhang S P, Yao H X, Zhou H Y, Sun X, Liu S H. Robust visual tracking based on online learning sparse representation. Neurocomputing, 2013, 100:31-40 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2011.11.031 [12] Wang D, Lu H C, Yang M H. Online object tracking with sparse prototypes. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(1):314-325 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2202677 [13] Wang L F, Yan H P, Lv K, Pan C H. Visual tracking via kernel sparse representation with multikernel fusion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2014, 24(7):1132-1141 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2014.2302496 [14] Liu B Y, Huang J Z, Yang L, Kulikowsk C. Robust tracking using local sparse appearance model and k-selection. In:Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA:IEEE, 2011. 1313-1320 [15] Jia X, Lu H C, Yang M H. Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA:IEEE, 2012. 1822-1829 [16] Xie Y, Zhang W S, Li C H, Lin S Y, Qu Y Y, Zhang Y H. Discriminative object tracking via sparse representation and online dictionary learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(4):539-553 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2013.2259230 [17] Zhong W, Lu H C, Yang M H. Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA:IEEE, 2012. 1838-1845 [18] Zhang T Z, Ghanem B, Liu S, Ahuja N. Robust visual tracking via multi-task sparse learning. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA:IEEE, 2012. 2042-2049 [19] Hong Z B, Mei X, Prokhorov D, Tao D C. Tracking via robust multi-task multi-view joint sparse representation. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, NSW:IEEE, 2013. 649-656 [20] Dong W H, Chang F L, Zhao Z J. Visual tracking with multifeature joint sparse representation. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2015, 24(1):013006 doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.24.1.013006 [21] Zhuang B H, Lu H C, Xiao Z Y, Wang D. Visual tracking via discriminative sparse similarity map. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(4):1872-1881 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2308414 [22] Zhang T Z, Liu S, Xu C S, Yan S C, Ghanem B, Ahuja N, Yang M H. Structural sparse tracking. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, USA:IEEE, 2015. 150-158 [23] 王梦.基于复合稀疏模型的多任务视频跟踪算法研究[硕士学位论文], 上海交通大学, 中国, 2014.Wang Meng. Multi-Task Visual Tracking Using Composite Sparse Model[Master dissertation], Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China, 2014. [24] Yuan X T, Liu X B, Yan S C. Visual classification with multitask joint sparse representation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(10):4349-4360 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2205006 [25] Doucet A, de Freitas N, Gordon N. Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Practice. New York:Springer-Verlag, 2001. [26] Zhang T Z, Liu S, Ahuja N, Yang M H, Ghanem B. Robust visual tracking via consistent low-rank sparse learning. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111(2):171-190 doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0738-0 -




 下载:
下载: