-
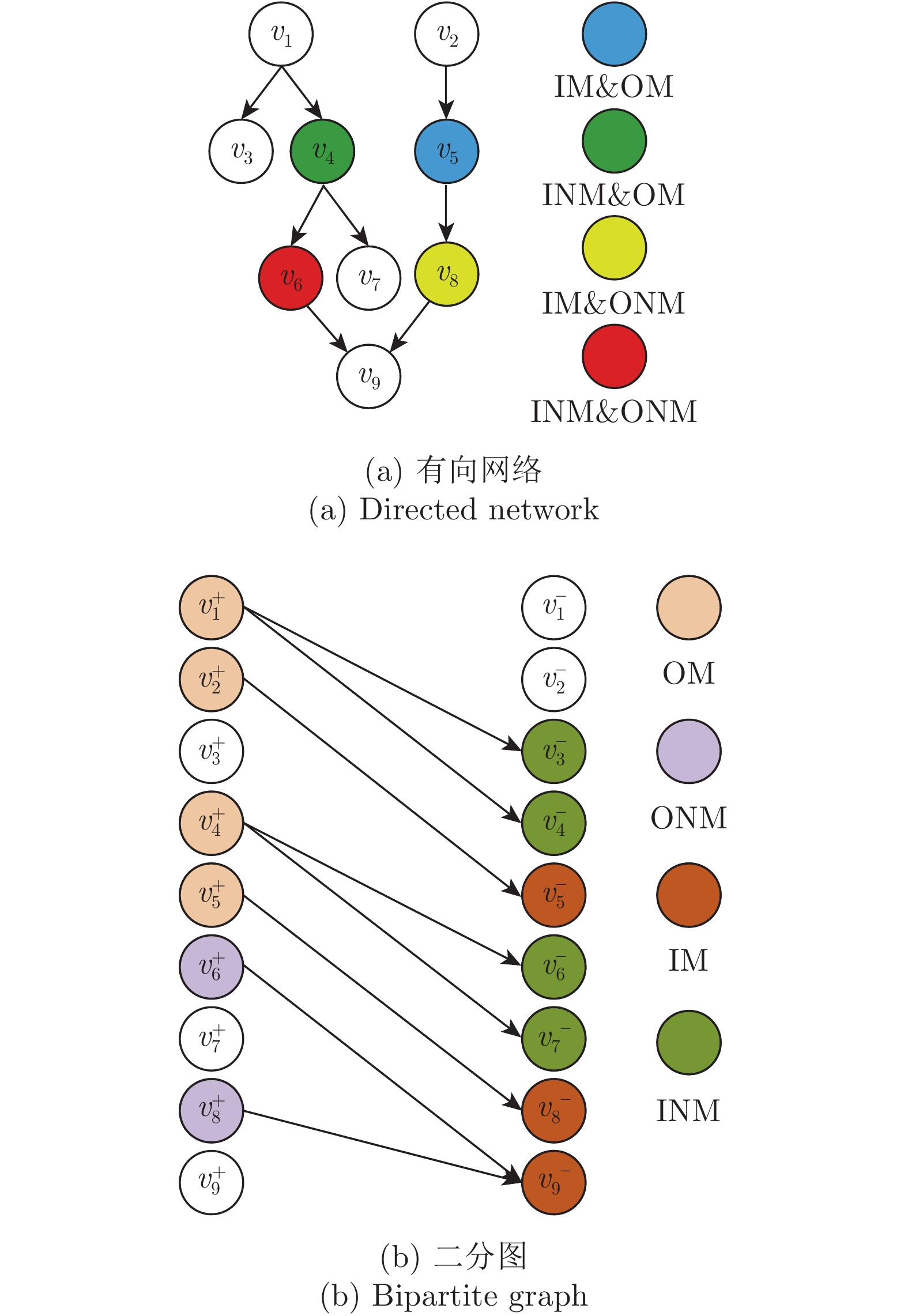
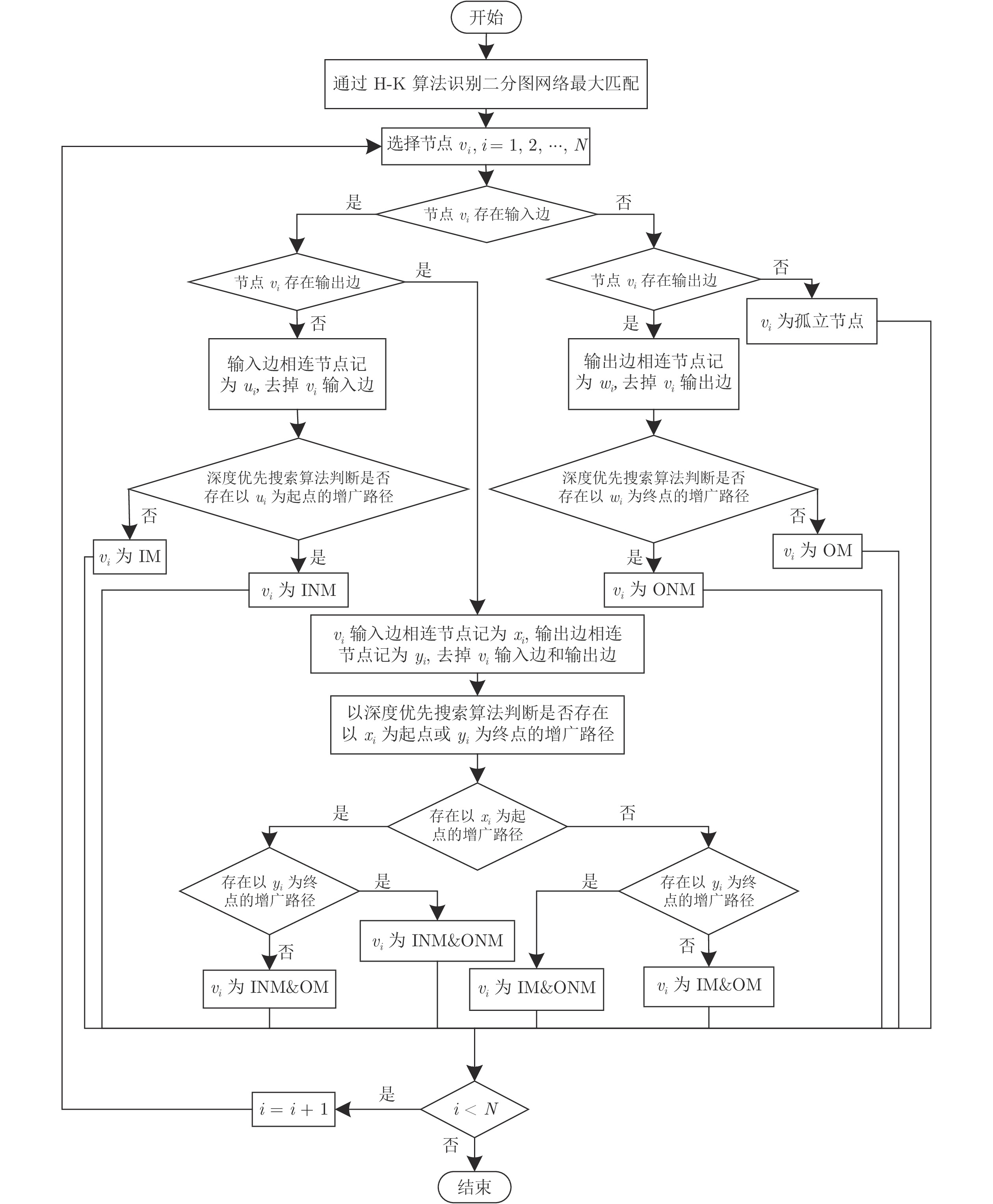
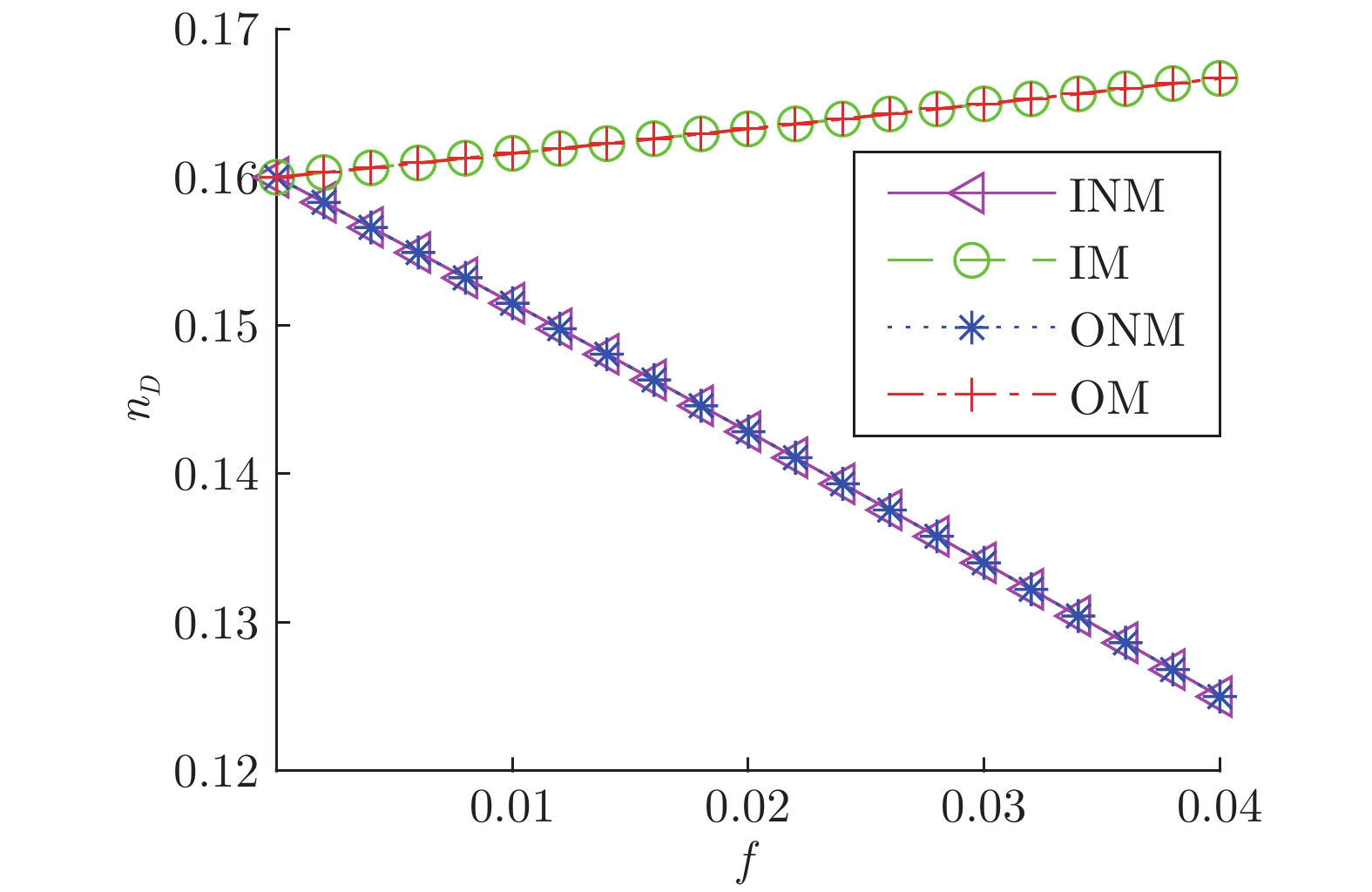
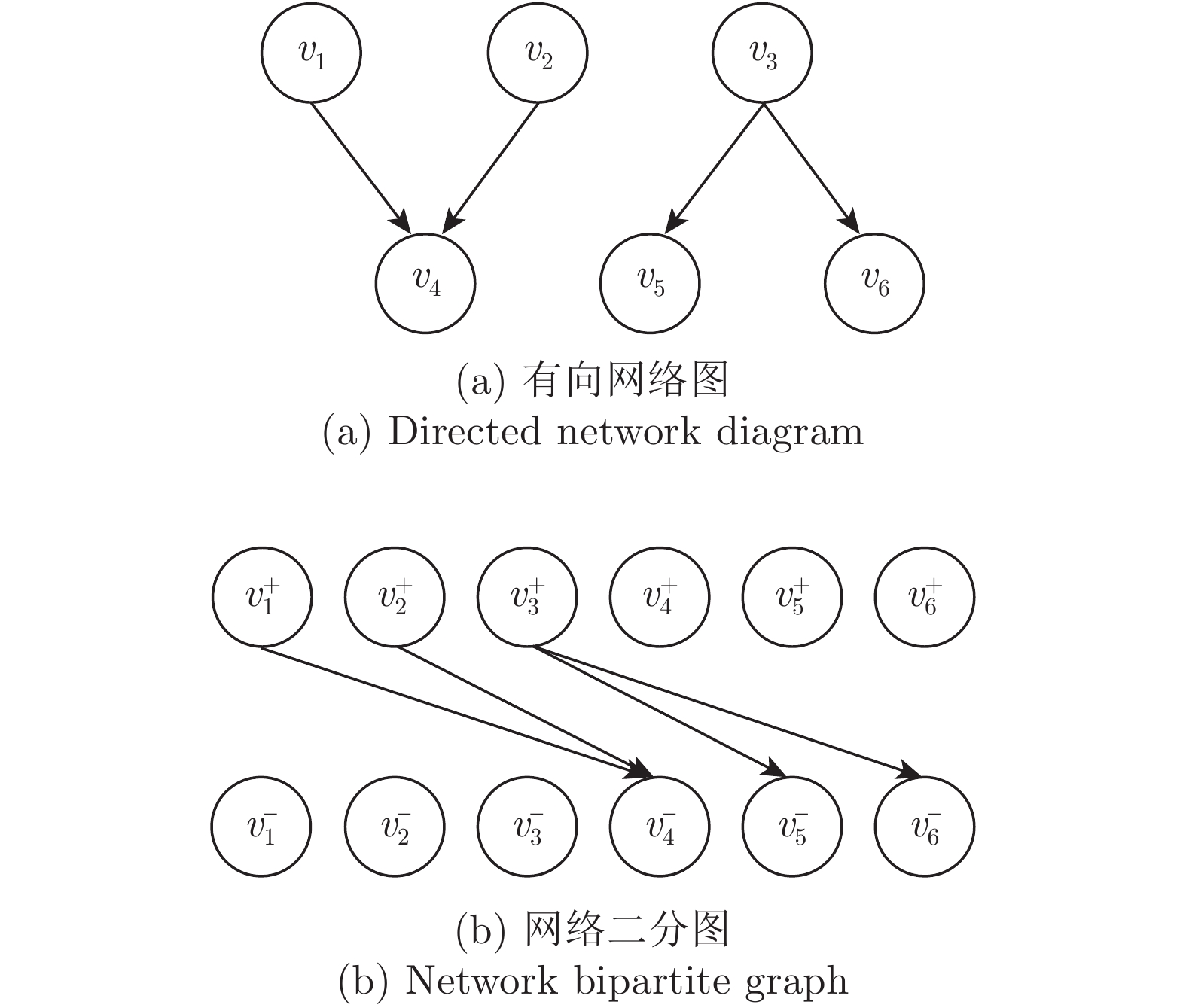
摘要: 复杂系统间的相互作用能够用复杂网络描述. 复杂网络中某些节点遭受攻击或破坏会造成网络故障, 导致整个网络能控性变化. 不同节点失效会对网络能控性有不同的影响. 本文提出一种网络节点的分类方式, 将网络中的节点根据边的方向和匹配关系分成九种类型, 并给出了辨识节点类型的算法. 另外, 本文给出了基于此分类方式下复杂网络中某类节点失效时, 网络中驱动节点数量(用来衡量网络能控性大小的指标)的变化规律. 并通过模型网络进行仿真实验, 验证了当节点失效时本文给出的驱动节点数量变化情况, 同时还分析社交网络中不同类型节点的占比与实际中人际交往的对应关系.Abstract: The interaction between complex systems can be described by complex networks. In complex network, some nodes are attacked or destroyed, which may cause network failure and lead to the change of the whole network controllability. Different node failures have different effects on network controllability. In this paper, a classification method of network nodes is proposed, which divides the nodes into nine types according to the direction of the edge and the matching relationship, and the algorithm for identifying the type of nodes is given. In addition, the change rule of the number of driving nodes is given when a certain type of node fails in the complex network based on this classification method, which is used to measure the controllability of the network. And simulation experiments are carried out through the model network to demonstrate the change of the number of driving nodes given in this paper when the node fails. At the same time, the corresponding relationship between the proportion of different types of nodes in social networks and actual interpersonal communication is also analyzed.
-
Key words:
- Complex networks /
- network controllability /
- nodes failure /
- driver node
-
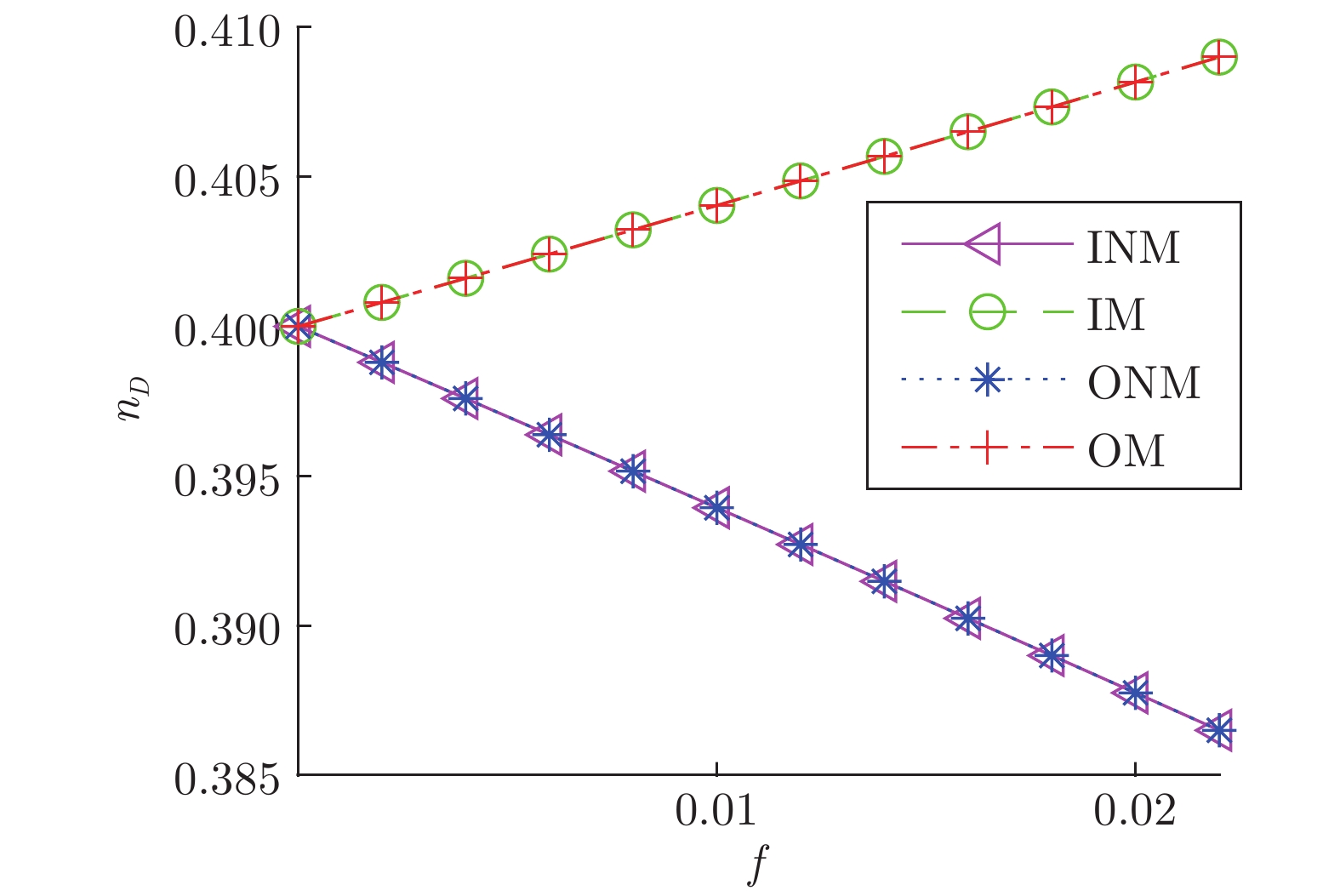
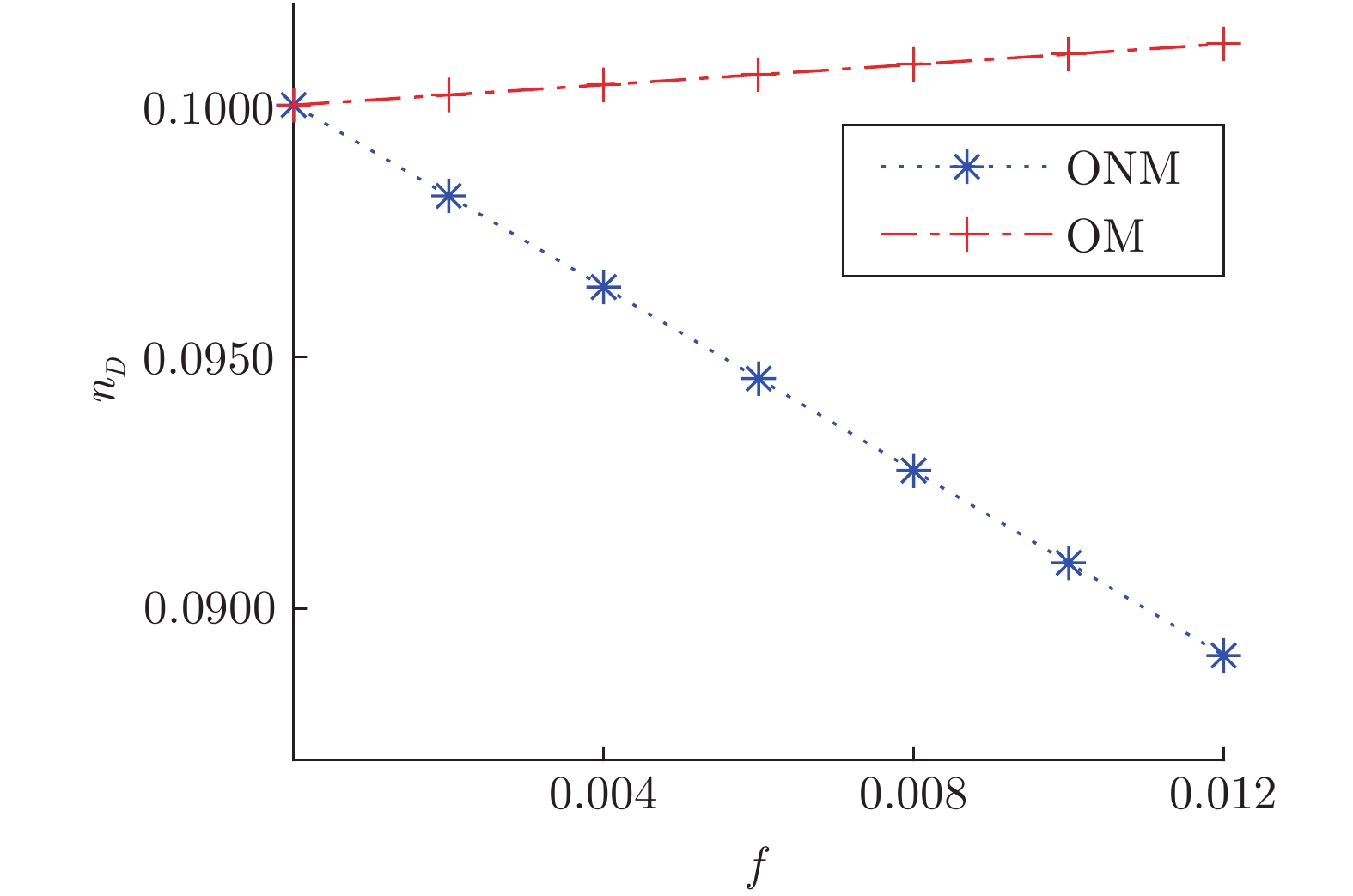
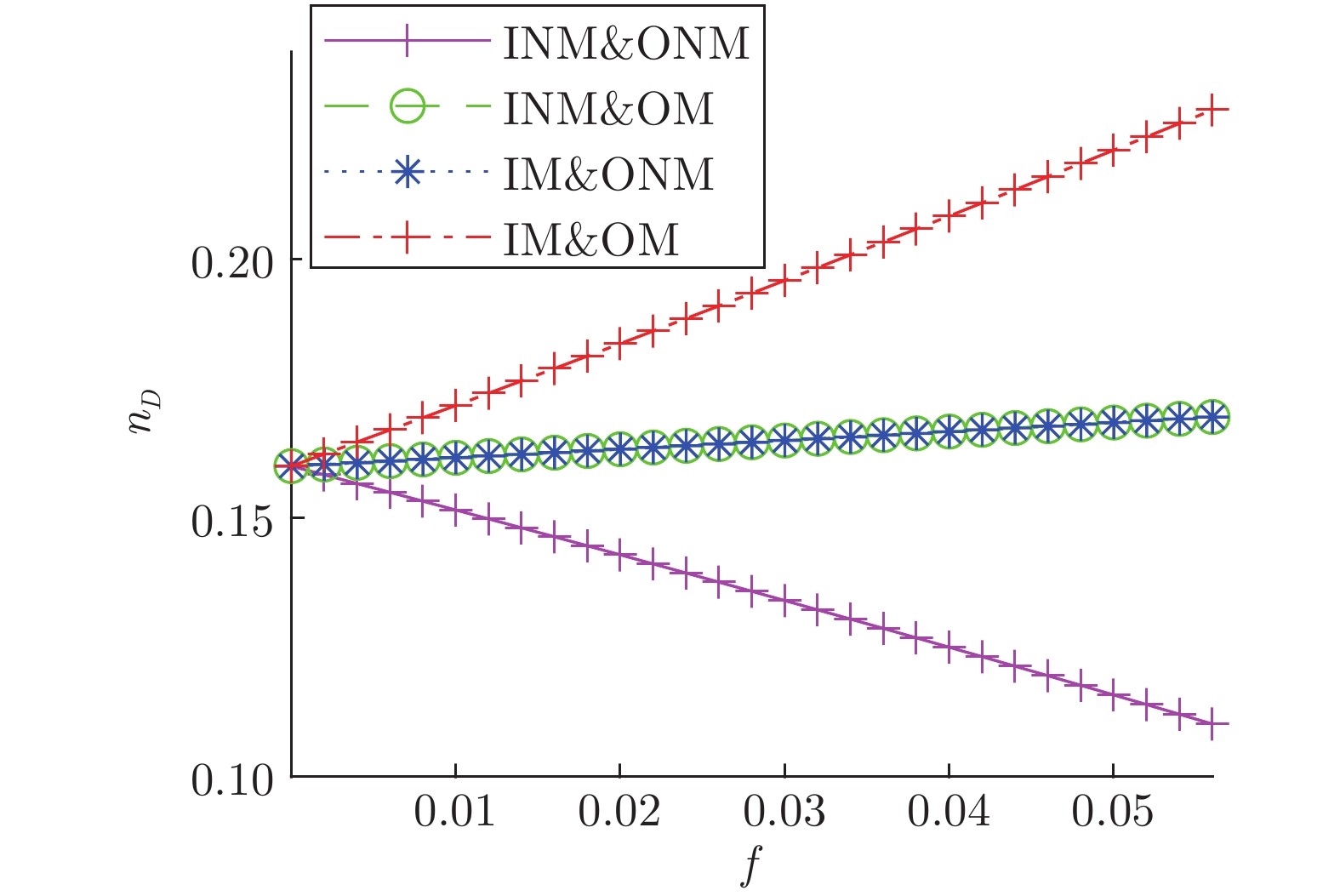
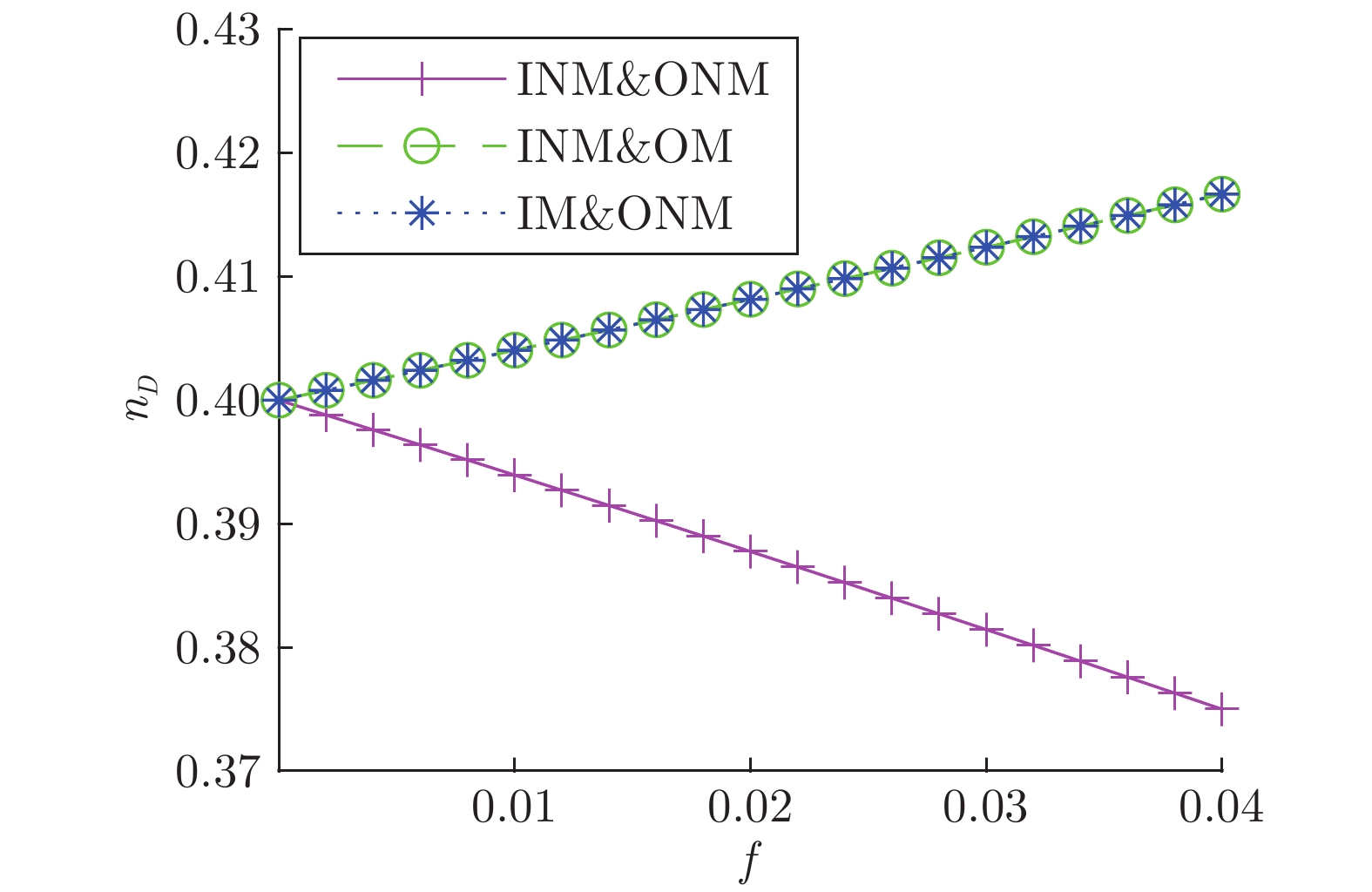
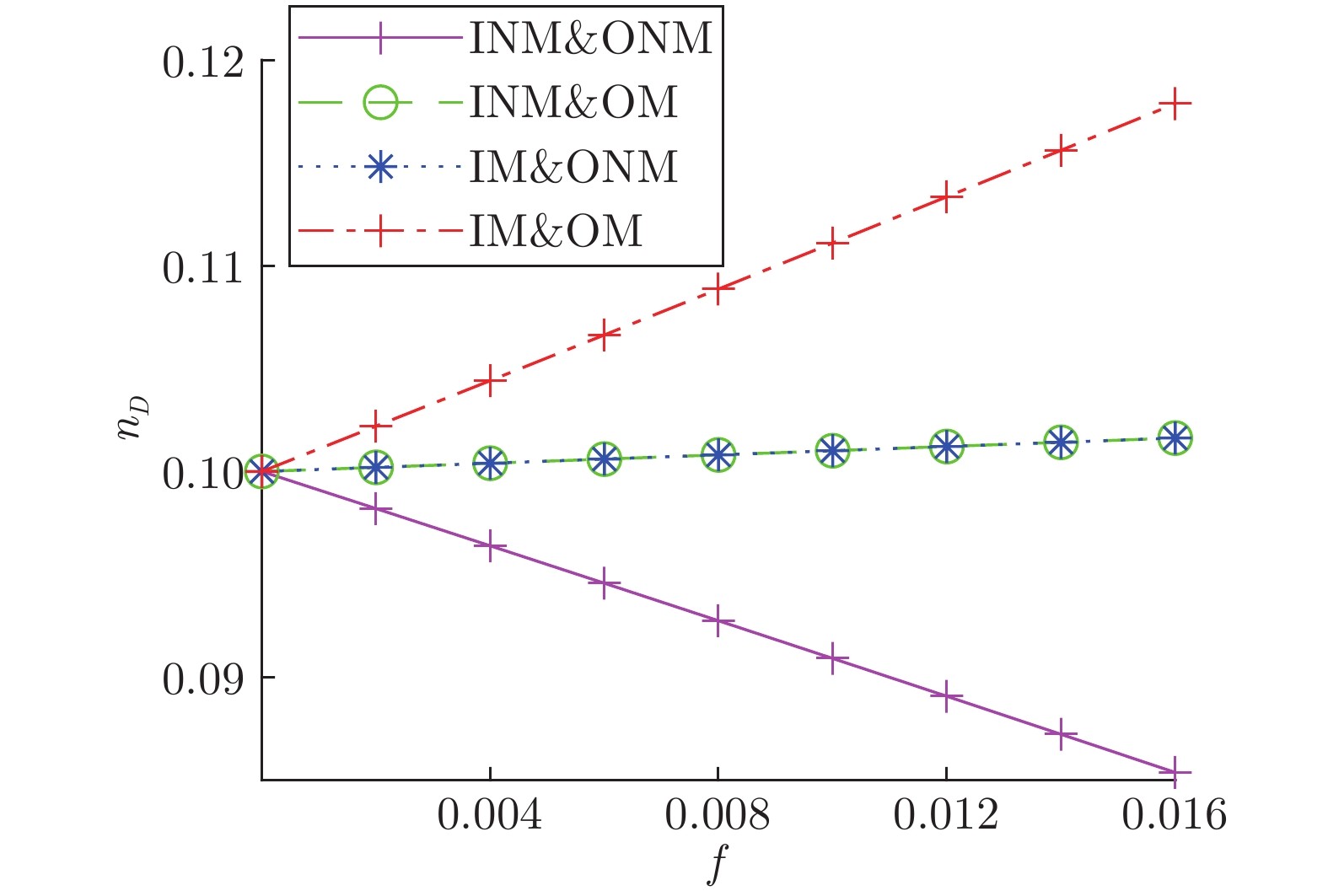
表 1 模型网络不同类型节点占比表
Table 1 Proportion of different types of nodes in the model network
ER网络 BA网络 WS网络 节点数 500 500 500 边数 2485 1968 1000 INM 27 25 0 IM 24 43 0 ONM 24 46 10 OM 31 39 2 INM&ONM 272 266 358 INM&OM 51 48 105 IM&ONM 42 33 20 IM&OM 32 0 5 $ V_{D}$ 0 0 0 表 2 实际网络不同类型节点占比表
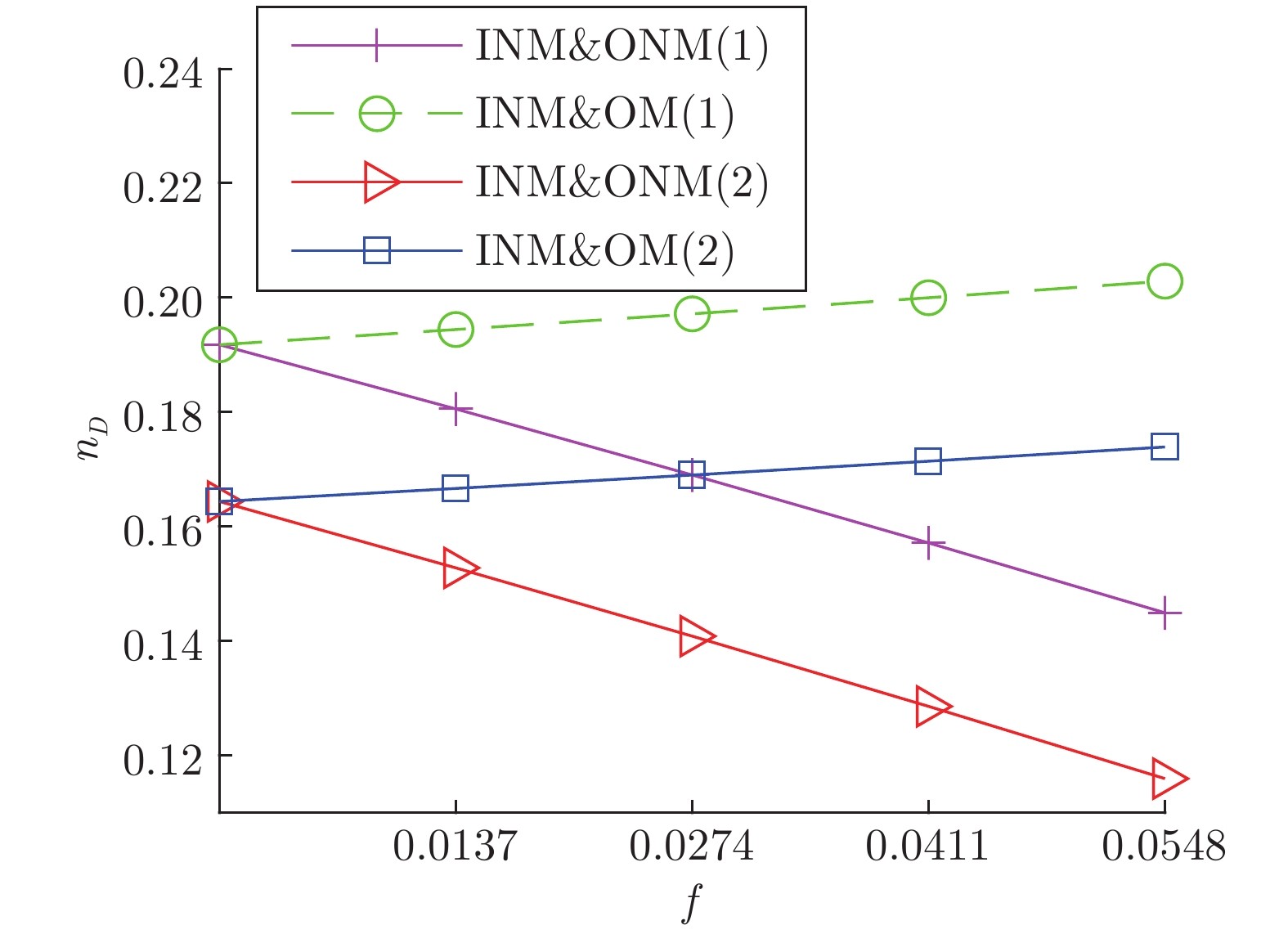
Table 2 Proportion of different types of nodes in the actual network
经理社交网络 律师社交网络 银行员工社交网络 (1) 银行员工社交网络 (2) 银行员工社交网络 (3) 学生社交网络 (1) 学生社交网络 (2) 节点 21 71 11 11 11 73 73 边 190 892 30 51 27 243 263 $\langle k \rangle$ 9.05 12.56 2.73 4.64 2.54 3.33 3.60 INM 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 IM 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 ONM 0 1 2 0 0 4 4 OM 0 0 1 0 1 2 2 INM&ONM 18 67 3 8 3 44 47 INM&OM 0 2 1 0 3 13 10 IM&ONM 0 0 3 0 2 3 5 IM&OM 0 0 0 0 1 3 0 $V_{D} $ 0 0 0 0 0 3 4 -
[1] Watts D J. The “new” science of networks. Annual Review of Sociology, 2004, 30(1): 243-270 doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.30.020404.104342 [2] Yan G, Vértes P E, Towlson E K, Chew Y L, Walker D s, Schafer W R. Network control principles predict neuron function in the caenorhabditis elegans connectome. Nature, 2017, 550(7677): 519-523 doi: 10.1038/nature24056 [3] Zhang Z K, Liu C, Zhan X X, Lu X, Zhang C X, Zhang Y C. Dynamics of information diffusion and its applications on complex networks. Physics Reports, 2016, 651(1): 1-34 [4] Urena R, Kou G, Dong Y C, Chiclana F, Herrera-Viedma E. A review on trust propagation and opinion dynamics in social networks and group decision making frameworks. Information Sciences, 2019, 478(1): 461-475 [5] 任卓明. 动态复杂网络节点影响力的研究进展. 物理学报, 2020, 69(4): 048901 doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20190830Ren Zhuo-Ming. Research progress of node influence in dynamic complex networks. Acta Physica Sinica, 2020, 69(4): 048901 doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20190830 [6] Li A, Cornelius S P, Liu Y Y, Wang L, Barabási A L. The fundamental advantages of temporal networks. Science, 2017, 358(6366): 1042-1046 doi: 10.1126/science.aai7488 [7] Gao J X, Liu Y Y, D'Souza R M, Barabási A L. Target control of complex networks. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 5415-5422 doi: 10.1038/ncomms6415 [8] Wang X F, Chen G R. Pinning control of scale-free dynamical networks. Physica A, 2002, 310(3): 521-531 [9] Li X, Wang X F, Chen G R. Pinning a complex dynamical network to its equilibrium. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2004, 51(10): 2074-2087 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2004.835655 [10] Liu X W, Chen T P. Cluster synchronization in directed networks via intermittent pinning control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(7): 1009-1020 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2139224 [11] Liu X W, Chen T P. Finite-time and fixed-time cluster synchronization with or without pinning control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(1): 240-252 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2630703 [12] Yu W W, DeLellis P, Chen G R. Distributed adaptive control of synchronization in complex networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(8): 2153-2158 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2012.2183190 [13] Su H S, Rong Z H, Chen M Z. Decentralized adaptive pinning control for cluster synchronization of complex dynamical networks. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2013, 43(1): 394-399 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2202647 [14] 杨青林, 王立夫, 李欢, 余牧舟. 基于相对距离的复杂网络谱粗粒化方法. 物理学报, 2019, 68(10): 100501 doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181848Yang Qing-Lin, Wang Li-Fu, Li Huan, Yu Mu-Zhou. A spectral coarse-graining algorithm based on relative distance. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(10): 100501 doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181848 [15] 王振华, 刘宗华. 复杂网络上的部分同步化: 奇异态、遥同步与集团同步. 物理学报, 2020, 69(8): 088902 doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20191973Wang Zhen-Hua, Liu Zong-Hua. Partial synchronization on complex networks: singular state, remote synchronization and group synchronization. Acta Physica Sinica, 2020, 69(8): 088902 doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20191973 [16] Ren H R, Karimi H R, Lu R Q, Wu Y Q. Synchronization of network systems via aperiodic sampled-data control with constant delay and application to unmanned ground vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(6): 4980-4990 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2928241 [17] 张檬, 韩敏. 基于单向耦合法的不确定复杂网络间有限时间同步. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(x): 1-9Zhang Meng, Han Min. Finite-time synchronization between uncertain complex networks based on unidirectional coupling method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(x): 1-9 [18] 潘永昊, 于洪涛. 基于网络同步的链路预测连边机理分析研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(12): 2607-2616Pan Yong-Hao, Yu Hong-Tao. Analysis of linkage mechanism of link prediction based on network synchronization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 2607-2616 [19] 郭天姣, 涂俐兰. 噪声下相互依存网络的自适应 $ H_{\infty}$ 异质同步. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1229-1239GUO Tian-Jiao, TU Li-Lan. Adaptive$ H_{\infty}$ Heterogeneous Synchronization for 0.3 nterdependent Networks With Noise. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1229-1239[20] Ren H R, Lu R Q, Xiong J L, Wu Y Q, Shi P. Optimal filtered and smoothed estimators for discrete-time linear systems with multiple packet dropouts under markovian communication constraints. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(9): 4169-4180 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2924485 [21] Liu Y Y, Slotine J J, Barabási A L. Controllability of complex networks. Nature, 2011, 473(7346): 167-173 doi: 10.1038/nature10011 [22] Yuan Z, Zhao C, Di Z, Wang W X, Lai Y C. Exact controllability of complex networks. Nature Communications, 2013, 4(1): 2447-2455 doi: 10.1038/ncomms3447 [23] Posfai M, Hovel P. Structural controllability of temporal networks. New Journal of Physics, 2014, 16(12): 123055 doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/16/12/123055 [24] Wu J N, Li X, Chen G R. Controllability of deep-coupling dynamical networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(12): 1-12 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3033927 [25] Tommaso M, Danielle S. Bassett, Fabio P. Structural controllability of symmetric networks IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(9): 3740-3747 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2881112 [26] Sun C, Hu G Q, Xie L H. Controllability of multi-agent networks with antagonistic interactions. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(10): 5457-5462 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2697202 [27] Posfai M, Gao J, Cornelius S P, Barabási A L. Controllability of multiplex multi-time-scale networks. Physical Review E, 2016, 94(3): 032316 [28] Pu C L, Pei W J, Michaelson A. Robustness analysis of network controllability. Physica A, 2012, 391(18): 4420-4425 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2012.04.019 [29] Liu Y Y, Slotine J J, Barabási A L. Control centrality and hierarchical structure in complex networks. PloS One, 2012, 7(9): e44459 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044459 [30] Lu Z M, Li X F. Attack vulnerability of network controllability. PloS One, 2016, 11(9): e0162289 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162289 [31] Pu C L, Cui W. Vulnerability of complex networks under path-based attacks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2015, 419(1): 622-629 [32] Hopcroft J E, Karp R M. An $ n.{5/2}$ algorithm for maximum matchings in bipartite graphs. SIAM Journal on Computing, 1971, 2(4): 122-125[33] Erdos P, Renyi A. On random graphs. Publicationes Mathematicae, 1959, 6(1): 290-297 [34] Barabási A L, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science, 1999, 286(5439): 509-512 doi: 10.1126/science.286.5439.509 [35] Watts D J, Strogatz S H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature, 1998, 393(6684): 440-442 doi: 10.1038/30918 [36] Coleman J S. Introduction to mathermatical sociology[Online], available: http://moreno.ss.uci.edu/data.html, September 10, 2020 -




 下载:
下载: