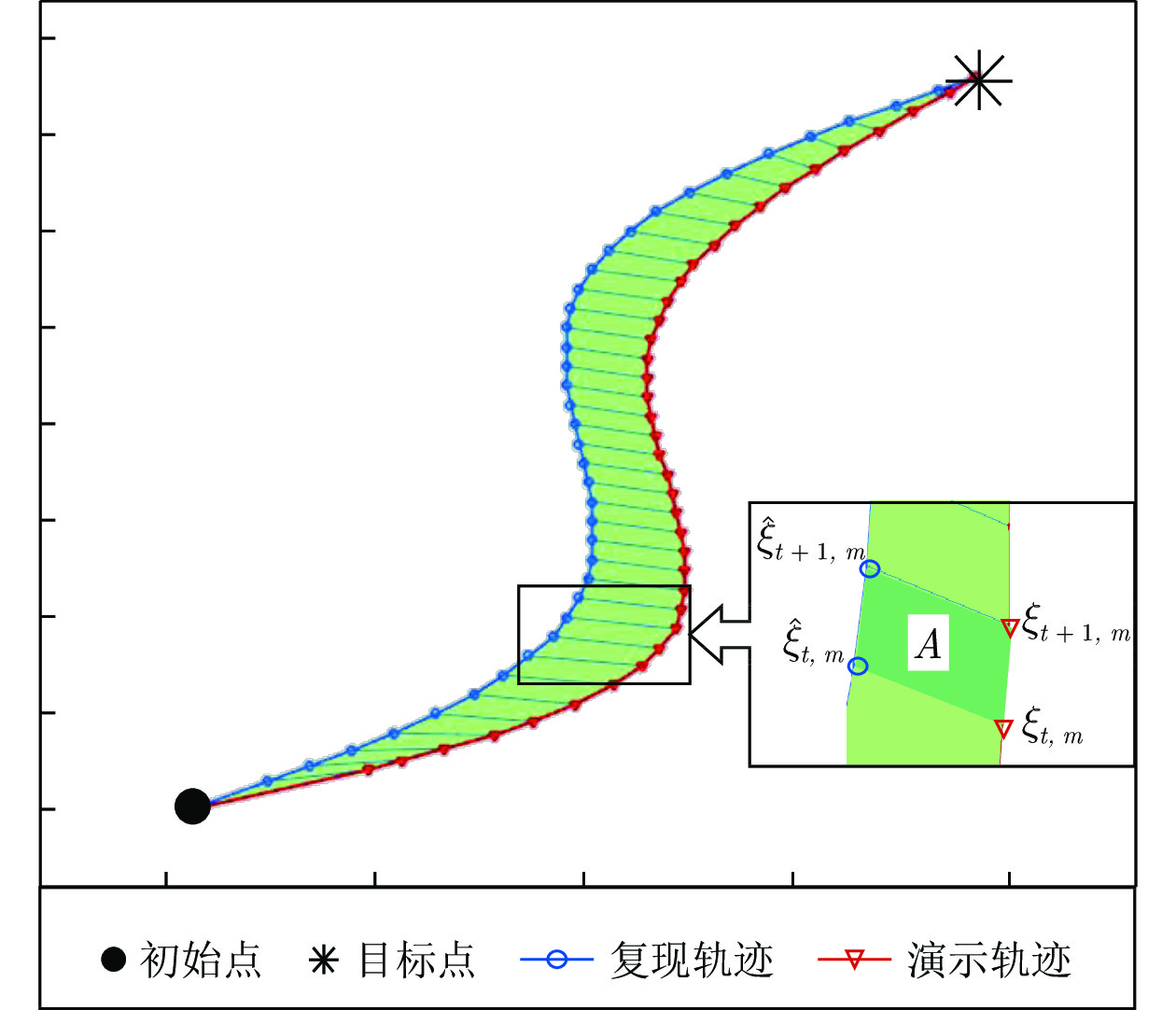
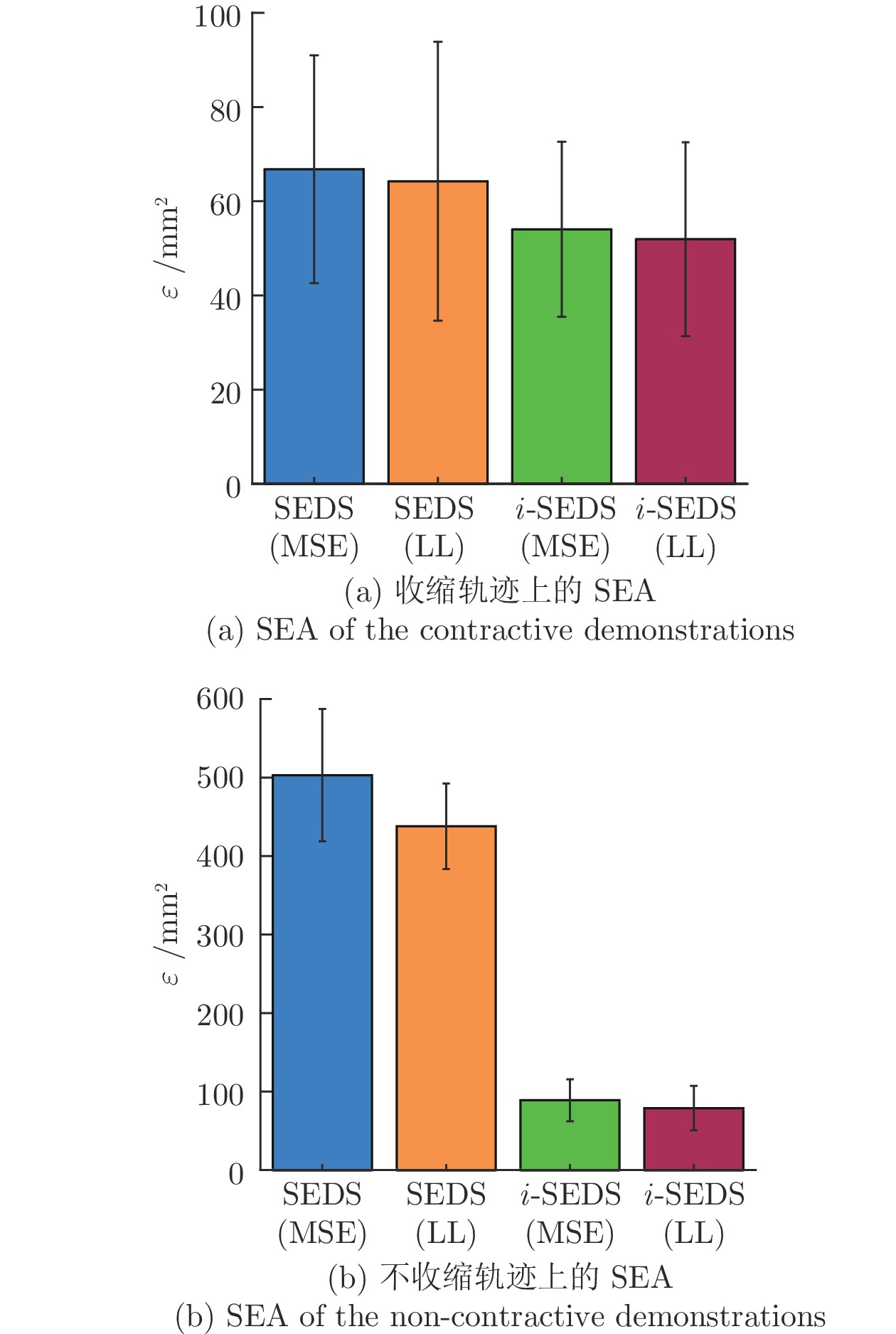
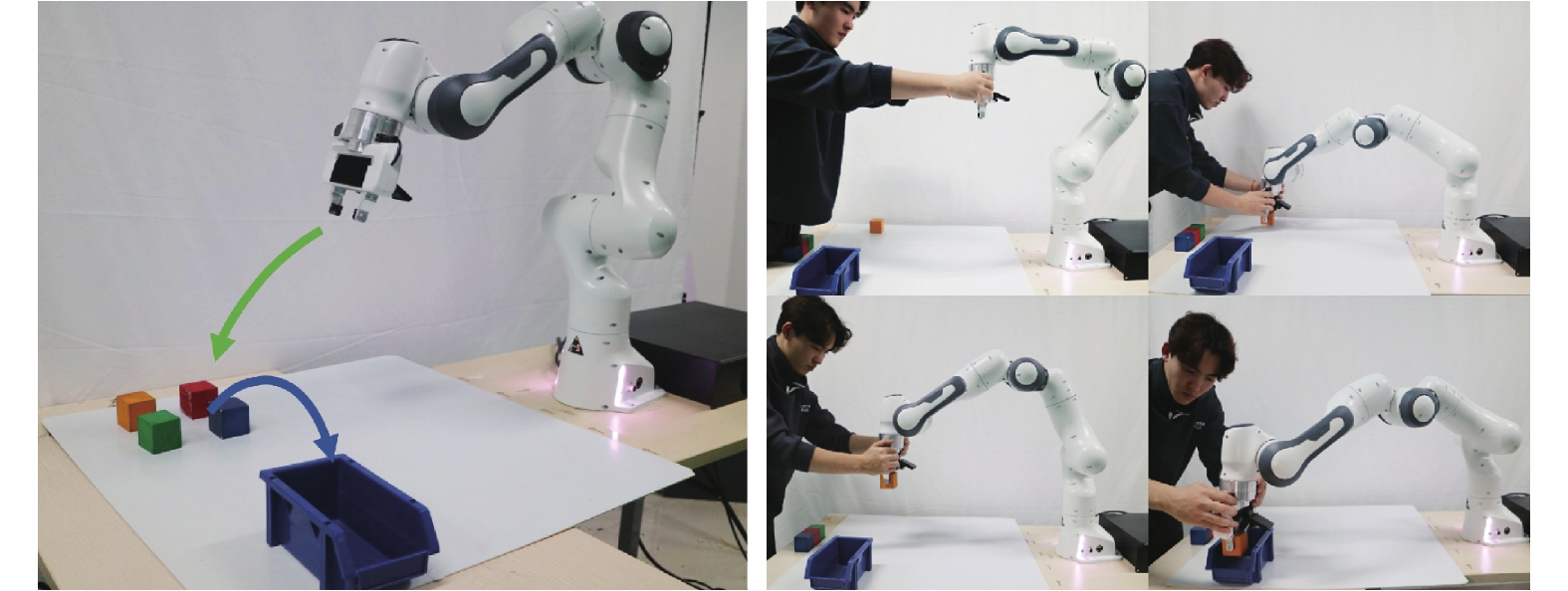
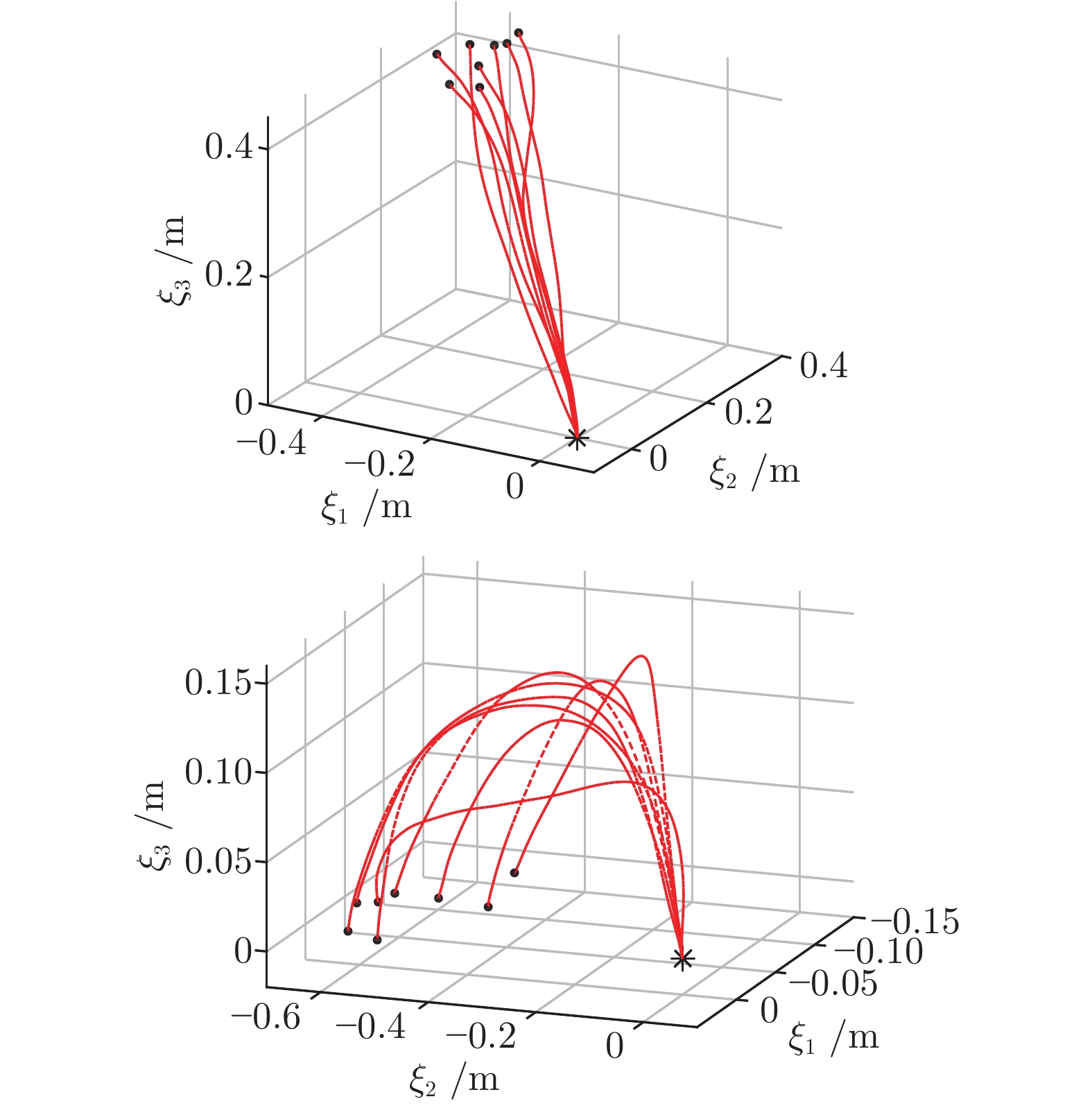
A Robot Skill Learning Method Based on Improved Stable Estimator of Dynamical Systems
-
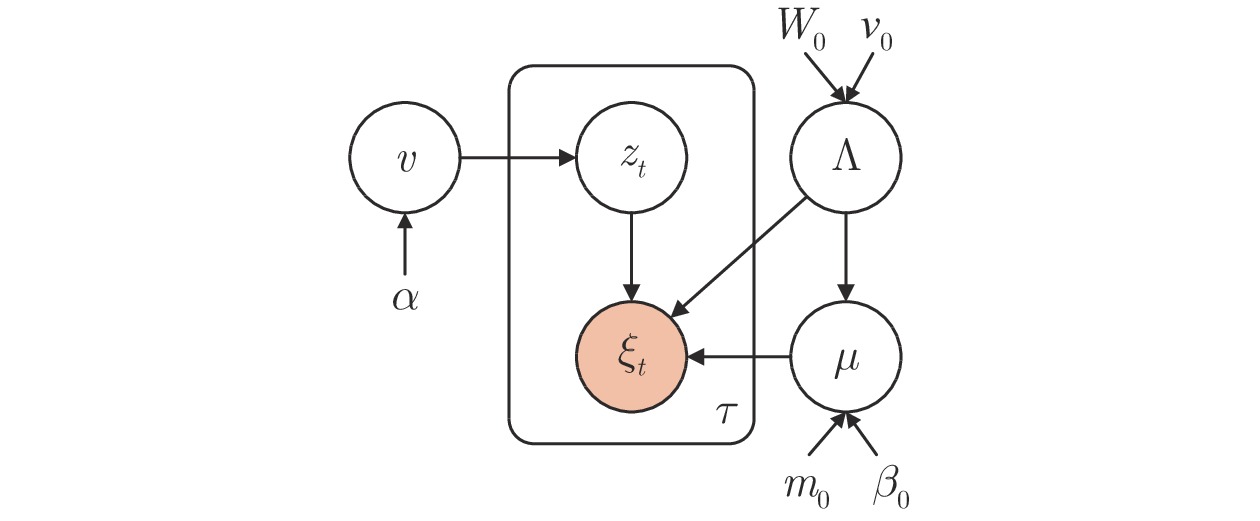
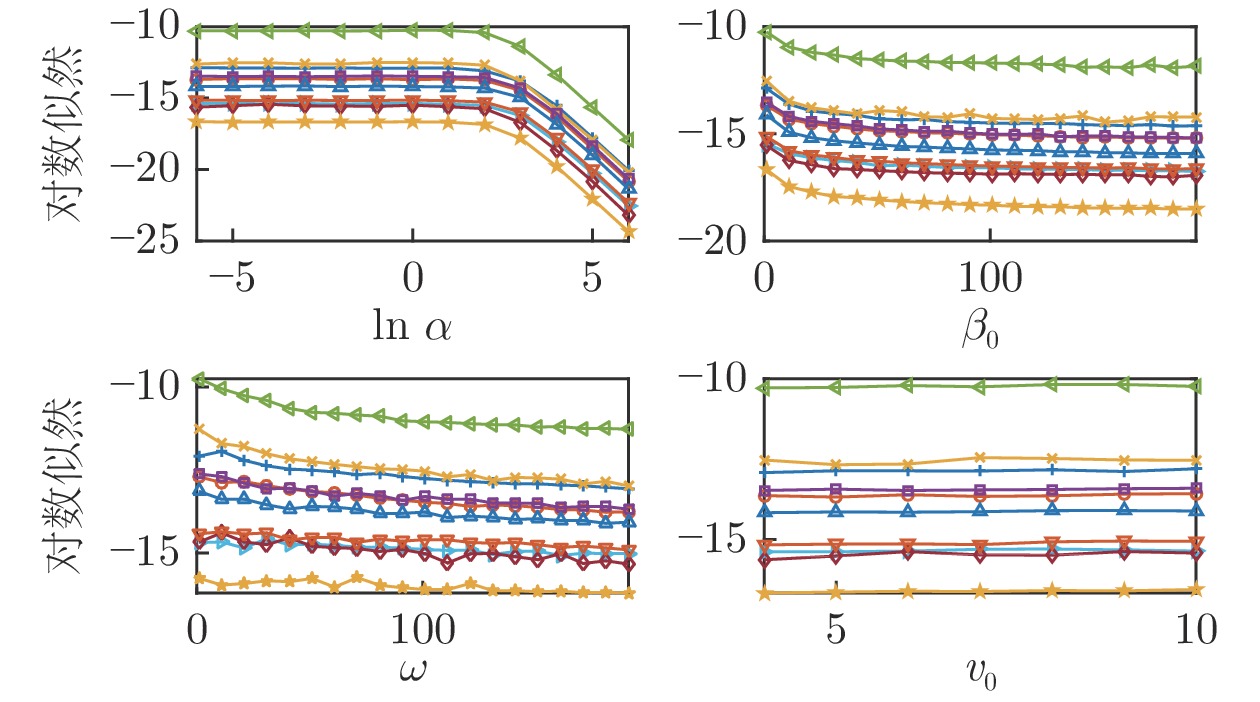
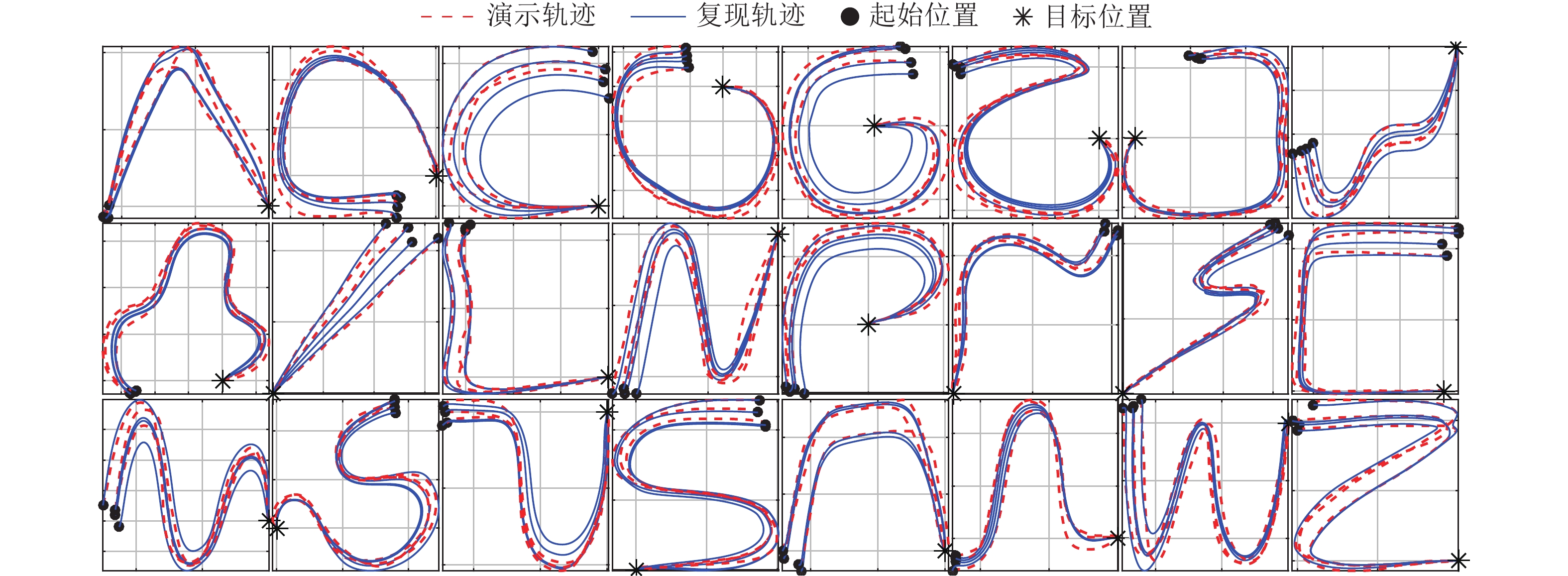
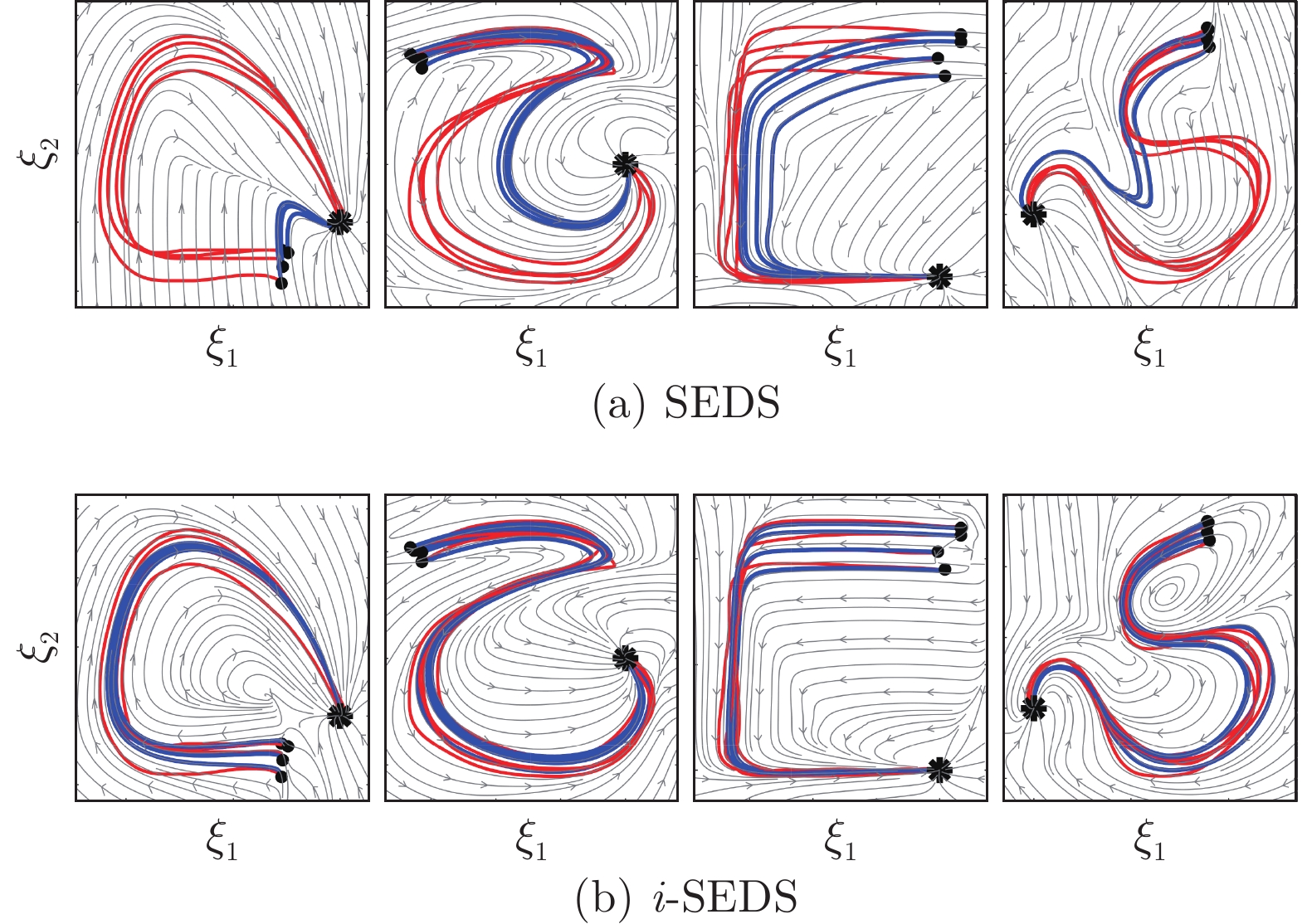
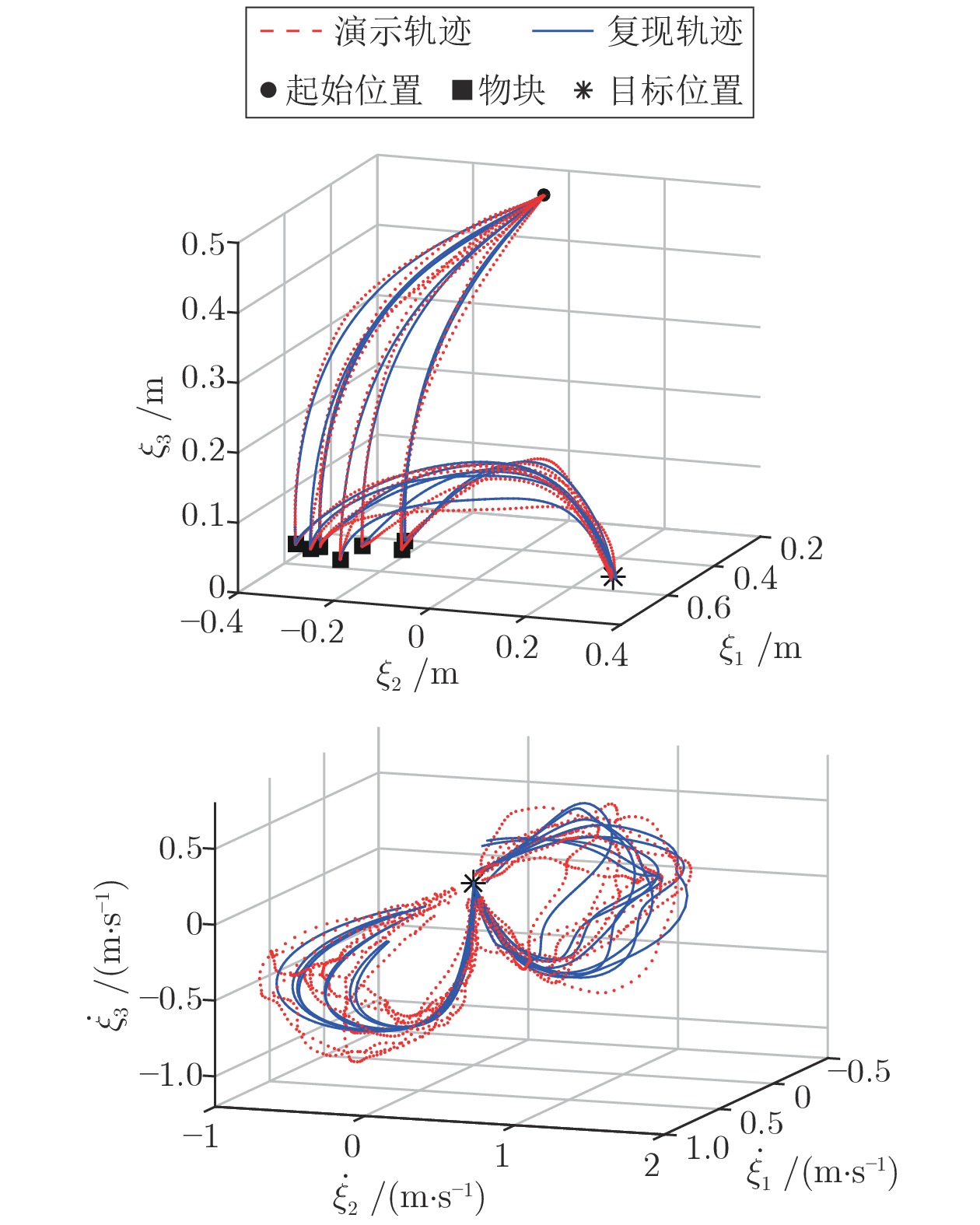
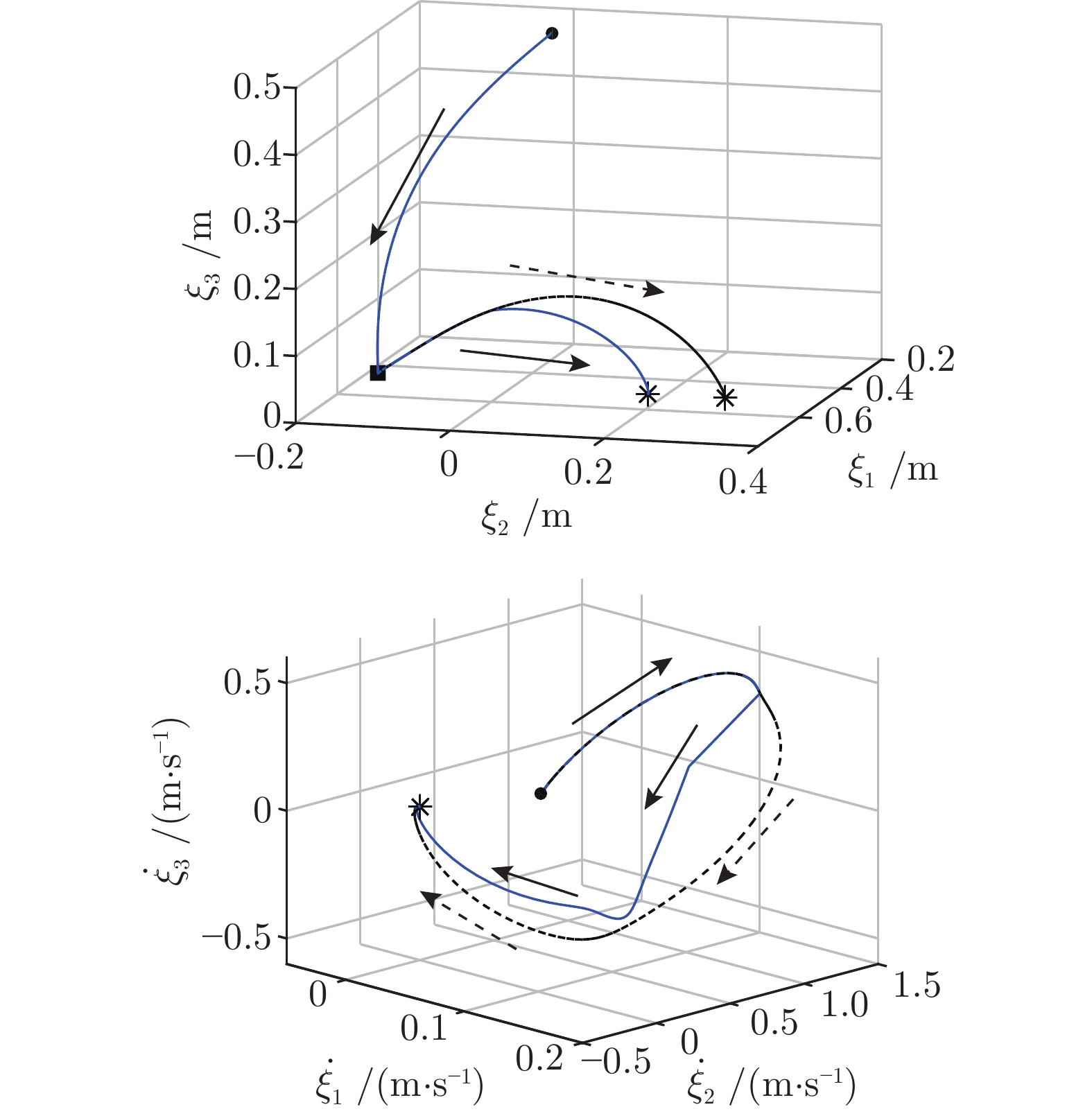
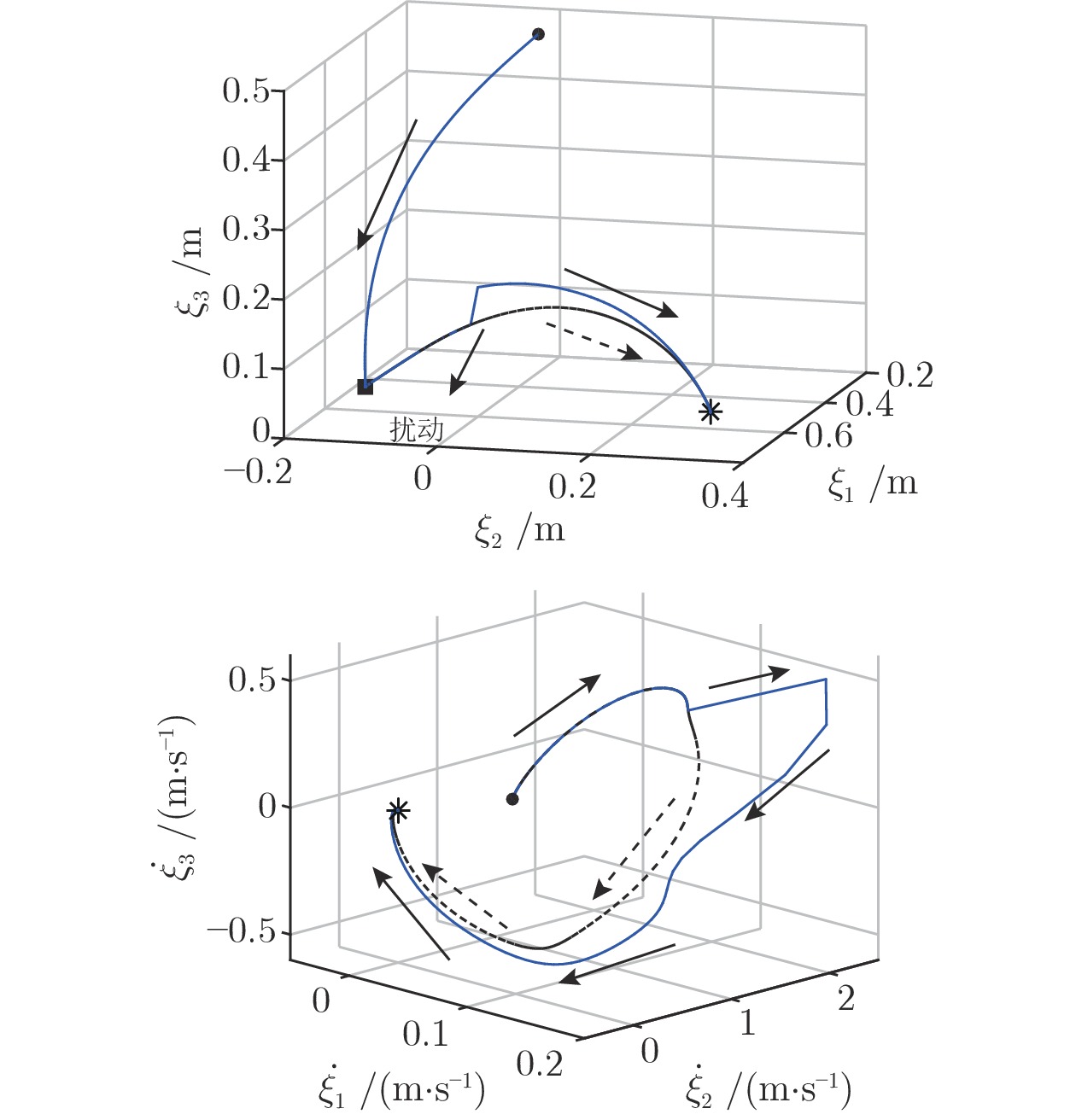
摘要: 提出一种基于改进动态系统稳定估计器的机器人技能学习方法. 现有的动态系统稳定估计器方法可以通过非线性优化来确保学习系统的全局稳定性, 但是存在确定高斯混合分量个数困难以及稳定性和精度无法兼顾的问题. 因此, 根据贝叶斯非参数模型可以自动确定合适分量个数的特性, 采用狄利克雷过程高斯混合模型对演示进行初始拟合. 随后利用参数化二次李雅普诺夫函数重新推导新的稳定性约束, 有效地解决了动态系统稳定估计器方法中稳定性和精度难以兼顾的问题. 最后, 在LASA数据库和Franka-panda机器人上的实验验证了新方法的有效性和优越性.Abstract: This paper presents a novel robot skill learning method based on improved stable estimator of dynamical systems (SEDS). The original SEDS method can ensure the global stability of the learning system through nonlinear optimization. However, it cannot automatically determine the optimal number of Gaussian components and is difficult to make a trade-off between reconcile the stability and accuracy. Therefore, note that the Bayesian non-parametric model can be used to determine the appropriate number of components, the Dirichlet process Gaussian mixture model is applied to perform the initial fitting of the demonstrations in this paper. Then, the stability constraints are reformulated by using the parameterized Lyapunov function. The problems of stability and accuracy in the SEDS method are solved effectively. Finally, experiments on a LASA dataset and a Franka-panda cooperative robot validate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.
-
表 1 4种GMR算法在数据库LASA上的性能比较
Table 1 Performance comparison of four GMR algorithmson database LASA
方法 总RMSE 总训练时间 (${\rm s}$) BIC-GMM (EM) 269.43 75.26 DdGMM (VI) 206.15 49.39 DPGMM (Gibbs) 118.58 157.48 DPGMM (VI) 130.79 39.79 -
[1] 曾超, 杨辰光, 李强, 戴诗陆. 人-机器人技能传递研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1813-1828.Zeng Chao, Yang Chen-Guang, Li Qiang, Dai Shi-Lu. Research progress on human-robot skill transfer. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1813–1828. [2] 刘乃军, 鲁涛, 蔡莹皓, 王硕. 机器人操作技能学习方法综述. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(3): 458-470.Liu Nai-Jun1, Lu Tao, Cai Ying-Hao, Wang Shuo. A review of robot manipulation skills learning methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 458-470. [3] 秦方博, 徐德. 机器人操作技能模型综述. 自动化学报, 2019; 45(8): 1401-1418.Qing Fang-Bo; Xu De. Review of robot manipulation skill models. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1401–1418. [4] Ravichandar H, Polydoros A S, Chernova S, Billard A. Recent advances in robot learning from demonstration. Annual Review of Control, Robotics, and Autonomous Systems, 2020, 3(1): 297-330. doi: 10.1146/annurev-control-100819-063206 [5] Brock O, Khatib O. Elastic Strips: A Framework for Integrated Planning and Execution. London: Experimental Robotics VI, 2000. 329−338 [6] Billard A, Hayes G. DRAMA, A connectionist architecture for control and learning in autonomous robots. Adaptive Behavior, 1999, 7(1): 35-63. doi: 10.1177/105971239900700103 [7] Ijspeert A J, Nakanishi J, Hoffmann H, Pastor P, Schaal Stefan. Dynamical movement primitives: learning attractor models for motor behaviors. Neural Computation, 2012, 25(2): 328-373. [8] Gribovskaya E, Khansari-Zadeh S M, Billard A. Learning non-linear multivariate dynamics of motion in robotic manipulators. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(1): 80-117. doi: 10.1177/0278364910376251 [9] Khansari-Zadeh S M, Billard A. Learning stable nonlinear dynamical systems with Gaussian mixture models. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2011, 27(5): 943-957. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2011.2159412 [10] Yang C G, Chen C Z, He W, Cui R X, Li Z J. Robot learning system based on adaptive neural control and dynamic movement primitives. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2019, 30(3): 777-787. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2852711 [11] Neumann K, Steil J J. Learning robot motions with stable dynamical systems under diffeomorphic transformations. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2015, 70: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2015.04.006 [12] Duan J H, Ou Y S, Hu J B, Wang Z Y, Jin S K, Xu C. Fast and stable learning of dynamical systems based on extreme learning machine. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(6): 1175-1185. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2705279 [13] Jin S K, Wang Z Y, Ou Y S, Feng W. Learning accurate and stable dynamical system under manifold immersion and submersion. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(12): 3598-3610. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2892207 [14] Schwarz G. Estimating the Dimension of a model. The annals of statistics, 1978, 6(2): 461–464. doi: 10.1214/aos/1176344136 [15] Chatzis S P., Korkinof D, Demiris Y. A nonparametric Bayesian approach toward robot learning by demonstration. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2012, 60(6): 789-802. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2012.02.005 [16] Blei D M, Jordan M I. Variational methods for the Dirichlet process. In: Proceedings of the twenty-first international conference on Machine learning. New York, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2004. 12 [17] Müller P, Quintana F A. Nonparametric Bayesian data analysis. Statistical Science, 2004, 19(1): 95-110. doi: 10.1214/088342304000000017 [18] Blei D M., Kucukelbir A, McAuliffe J D. Variational inference: A review for statisticians. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2017, 112(518): 859-877. doi: 10.1080/01621459.2017.1285773 [19] Figueroa N, Billard A. A physically-consistent Bayesian non-parametric mixture model for dynamical system learning. In: Proceedings of the Machine Learning Research. Zurich, Switzerland: CoRL, 2018. 927−946 [20] Deisenroth M P, Rasmussen C E, Peters J. Gaussian process dynamic programming. Neurocomputing, 2009, 72(7): 1508-1524. [21] Vijayakumar S, D’Souza A, Schaal S. Incremental online learning in high dimensions. Neural Computation, 2005, 17(12): 2602-2634. doi: 10.1162/089976605774320557 [22] Ferguson T S. A Bayesian Analysis of Some Nonparametric Problems. The Annals of Statistics, 1973, 1(2): 209-230. doi: 10.1214/aos/1176342360 [23] Ahmed A, Xing E P. Dynamic non-parametric mixture models and the recurrent Chinese restaurant process: With applications to evolutionary clustering. In: Proceedings of the 2008 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining. Atlanta, USA: 2008. 219−230 [24] Blei D M., Jordan M I. Variational inference for Dirichlet process mixtures. Bayesian Anal, 2006, 1(1): 121-143. doi: 10.1214/06-BA104 [25] Chatzis S P., Kosmopoulos D I., Varvarigou T A. signal modeling and classification using a robust latent space model based on t distributions. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(3): 949-963. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.907912 [26] Bishop C M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. New York: Springer, 2006. 461−522 [27] Zhu J L, Ge Z Q, Song Z H. Variational Bayesian Gaussian mixture regression for soft sensing key variables in non-Gaussian industrial processes. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(3): 1092-1099. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2016.2576999 [28] Khansari-Zadeh S M, Billard A. Learning control Lyapunov function to ensure stability of dynamical system-based robot reaching motions. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2014, 62(6): 752-765. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2014.03.001 -





 下载:
下载: