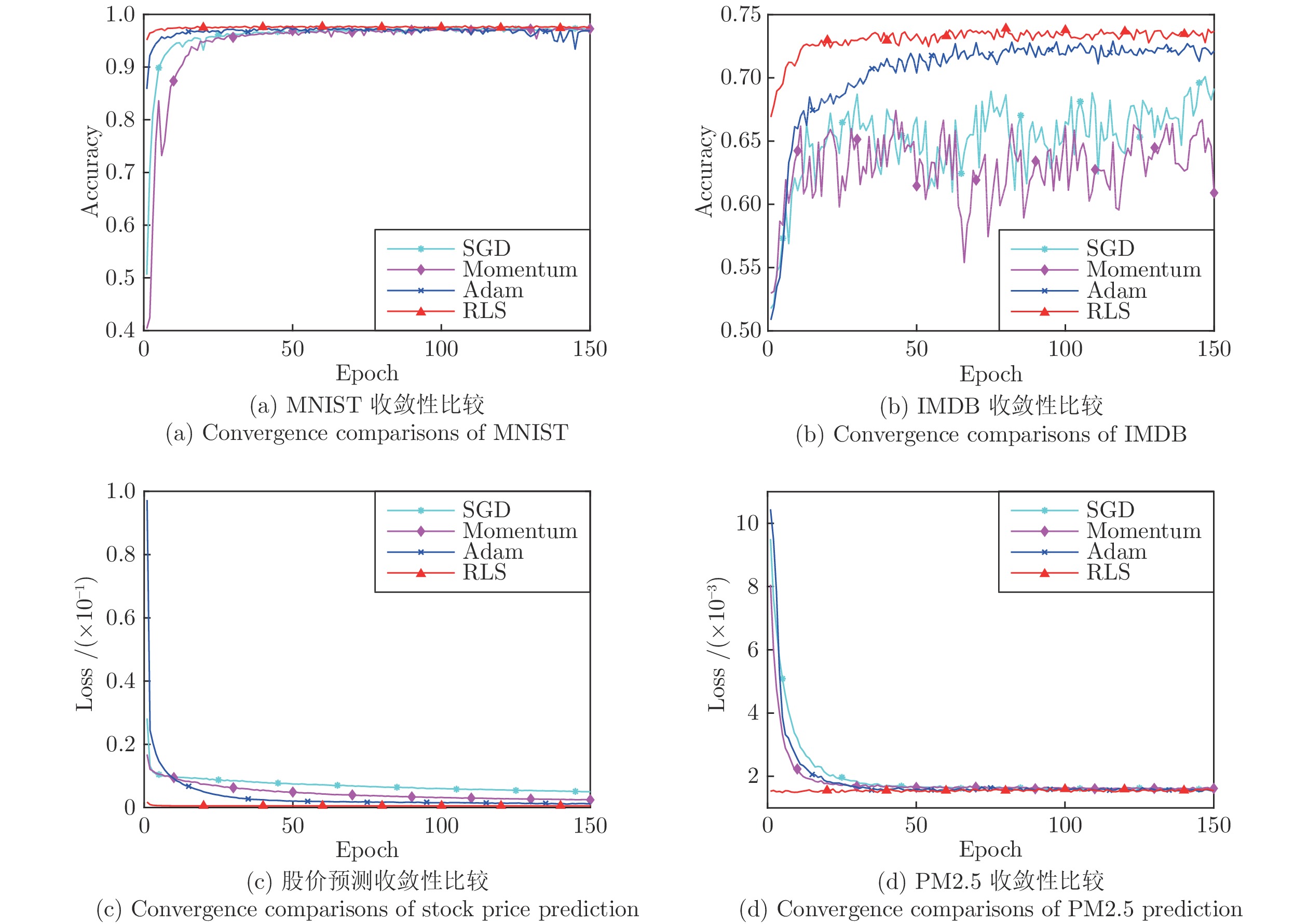
-
摘要: 针对循环神经网络(Recurrent neural networks, RNNs)一阶优化算法学习效率不高和二阶优化算法时空开销过大, 提出一种新的迷你批递归最小二乘优化算法. 所提算法采用非激活线性输出误差替代传统的激活输出误差反向传播, 并结合加权线性最小二乘目标函数关于隐藏层线性输出的等效梯度, 逐层导出RNNs参数的迷你批递归最小二乘解. 相较随机梯度下降算法, 所提算法只在RNNs的隐藏层和输出层分别增加了一个协方差矩阵, 其时间复杂度和空间复杂度仅为随机梯度下降算法的3倍左右. 此外, 本文还就所提算法的遗忘因子自适应问题和过拟合问题分别给出一种解决办法. 仿真结果表明, 无论是对序列数据的分类问题还是预测问题, 所提算法的收敛速度要优于现有主流一阶优化算法, 而且在超参数的设置上具有较好的鲁棒性.Abstract: In recurrent neural networks (RNNs), the first-order optimization algorithms usually converge slowly, and the second-order optimization algorithms commonly have high time and space complexities. In order to solve these problems, a new minibatch recursive least squares (RLS) optimization algorithm is proposed. Using the inactive linear output error to replace the conventional activation output error for backpropagation, together with the equivalent gradients of the weighted linear least squares objective function with respect to linear outputs of the hidden layer, the proposed algorithm derives the minibatch recursive least squares solutions of RNNs parameters layer by layer. Compared with the stochastic gradient descent algorithm, the proposed algorithm only adds one covariance matrix into each layer of RNNs, and its time and space complexities are almost three times as much. Furthermore, in order to address the adaptive problem of the forgetting factor and the overfitting problem of the proposed algorithm, two approaches are also presented, respectively, in this paper. The simulation results, on the classification and prediction problems of sequential data, show that the proposed algorithm has faster convergence speed than popular first-order optimization algorithms. In addition, the proposed algorithm also has good robustness in the selection of hyperparameters.
-
表 1 SGD-RNN与RLS-RNN复杂度分析
Table 1 Complexity analysis of SGD-RNN and RLS-RNN
SGD-RNN RLS-RNN 时间复杂度 $O_{s}$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mdh)$ — $Z_{s}$ — ${\rm{O}}(\tau mdh)$ $H_{s}$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mh(h+a))$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mh(h+a))$ ${\Delta}^O_{s}$ ${\rm{O}}(4\tau md)$ ${\rm{O}}(3\tau md)$ ${\Delta}^H_{s}$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mh(h+d))$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mh(h+d))$ ${P}_{s}^O$ — ${\rm{O}}(2\tau mh^2)$ ${P}_{s}^H$ — ${\rm{O}}(2\tau m(h+a)^2)$ ${\Theta}_{s}^O$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mdh)$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mdh)$ ${\Theta}_{s}^H$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mh(h+a))$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau mh(h+a))$ 合计 ${\rm{O}}(\tau m(3dh+3h^2+2ha))$ ${\rm{O}}(\tau m(7h^2+2a^2+3dh+6ha))$ 空间复杂度 $\Theta_{s}^O$ ${\rm{O}}(hd)$ ${\rm{O}}(hd)$ $\Theta_{s}^H$ ${\rm{O}}(h(h+a))$ ${\rm{O}}(h(h+a))$ ${P}_{s}^H$ — ${\rm{O}}((h+a)^2)$ ${P}_{s}^O$ — ${\rm{O}}(h^2)$ 合计 ${\rm{O}}(h^2+hd+ha)$ ${\rm{O}}(hd+3ha+a^2+3h^2)$ 表 2 初始化因子
$\alpha$ 鲁棒性分析Table 2 Robustness analysis of the initializing factor
$\alpha$ $\alpha$ 0.01 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 MNIST分类准确率 (%) 97.10 97.36 97.38 97.35 97.57 97.70 97.19 97.27 97.42 97.25 97.60 IMDB分类准确率 (%) 72.21 73.50 73.24 73.32 74.02 73.01 73.68 73.25 73.20 73.42 73.12 股价预测MSE ($\times 10^{-4}$) 5.32 5.19 5.04 5.43 5.42 5.30 4.87 4.85 5.32 5.54 5.27 PM2.5预测MSE ($\times 10^{-3}$) 1.58 1.55 1.53 1.55 1.61 1.55 1.55 1.54 1.57 1.58 1.57 表 3 比例因子
$\eta$ 鲁棒性分析Table 3 Robustness analysis of the scaling factor
$\eta$ $\eta$ 0.1 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 MNIST分类准确率 (%) 97.80 97.59 97.48 97.61 97.04 97.62 97.44 97.33 97.38 97.37 97.45 IMDB分类准确率 (%) 73.58 73.46 73.62 73.76 73.44 73.82 73.71 72.97 72.86 73.12 73.69 股价预测MSE ($\times 10^{-4}$) 5.70 5.32 5.04 5.06 5.61 4.73 5.04 5.14 4.85 4.97 5.19 PM2.5预测MSE ($\times 10^{-3}$) 1.53 1.55 1.56 1.59 1.56 1.53 1.58 1.55 1.54 1.50 1.52 -
[1] Mikolov T, Karafiát M, Burget L, Cernockỳ J, Khudanpur S. Recurrent neural network based language model. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Chiba, Japan: ISCA, 2010. 1045−1048 [2] Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: Proceeding of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada: MIT Press, 2014. 3104−3112 [3] Graves A, Mohamed A R, Hinton G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2013. 6645−6649 [4] Pascanu R, Mikolov T, Bengio Y. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. Atlanta, USA: JMLR.org, 2013. 1310−1318 [5] Bengio Y, Simard P, Frasconi P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1994, 5(2): 157−166 doi: 10.1109/72.279181 [6] Bottou L. On-line learning and stochastic approximations. On-Line Learning in Neural Networks. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1999. 9−42 [7] Polyak B T. Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods. USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics, 1964, 4(5): 1−17 doi: 10.1016/0041-5553(64)90137-5 [8] Sutskever I, Martens J, Dahl G, Hinton G. On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Atlanta, USA: JMLR.org, 2013. 1139−1147 [9] Duchi J, Hazan E, Singer Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2121−2159 [10] Tieleman T, Hinton G. Lecture 6.5-rmsprop: Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude [Online], available: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~tijmen/csc321/slides/lecture_slides_lec6.pdf, February 19, 2020 [11] Zeiler M D. ADADELTA: An adaptive learning rate method [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1212.5701\newblock, February 19, 2020 [12] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. [13] Keskar N S, Socher R. Improving generalization performance by switching from adam to SGD [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07628, February 19, 2020 [14] Reddi S J, Kale S, Kumar S. On the convergence of Adam and beyond. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: OpenReview.net, 2018. [15] Martens J. Deep learning via hessian-free optimization. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning. Haifa, Israel: Omnipress, 2010. 735−742 [16] Keskar N S, Berahas A S. adaQN: An adaptive quasi-newton algorithm for training RNNs. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Riva del Garda, Italy: Springer, 2016. 1−16. [17] Martens J, Grosse R. Optimizing neural networks with kronecker-factored approximate curvature. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: JMLR.org, 2015. 2408−2417 [18] Shanno D F. Conditioning of quasi-newton methods for function minimization. Mathematics of Computation, 1970, 24(111): 647−656 doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1970-0274029-X [19] Liu D C, Nocedal J. On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Mathematical Programming, 1989, 45(1−3): 503−528 doi: 10.1007/BF01589116 [20] Le Q V, Ngiam J, Coates A, Lahiri A, Prochnow B, Ng A Y. On optimization methods for deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning. Bellevue, USA: Omnipress, 2011. 265−272 [21] Azimi-Sadjadi M R, Liou R J. Fast learning process of multilayer neural networks using recursive least squares method. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1992, 40(2): 446−450 doi: 10.1109/78.124956 [22] 谭永红. 多层前向神经网络的RLS训练算法及其在辨识中的应用. 控制理论与应用, 1994, 11(5): 594−599Tan Yong-Hong. RLS training algorithm for multilayer feedforward neural networks and its application to identification. Control Theory and Applications, 1994, 11(5): 594−599 [23] Xu Q, Krishnamurthy K, McMillin B, Lu W. A recursive least squares training algorithm for multilayer recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 1994 American Control Conference-ACC’94. Baltimore, USA: IEEE, 1994. 1712−1716 [24] Peter T, Pospíchal J. Neural network training with extended Kalman filter Using graphics processing unit. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2008. 198−207 [25] Jaeger H. Adaptive nonlinear system identification with echo state networks. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2002. 609−616 [26] Werbos P J. Backpropagation through time: What it does and how to do it. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1990, 78(10): 1550−1560 doi: 10.1109/5.58337 [27] Sherman J, Morrison W J. Adjustment of an inverse matrix corresponding to a change in one element of a given matrix. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1950, 21(1): 124−127 doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177729893 [28] Paleologu C, Benesty J, Ciochina S. A robust variable forgetting factor recursive least-squares algorithm for system identification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2008, 15: 597−600 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2008.2001559 [29] Albu F. Improved variable forgetting factor recursive least square algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics and Vision (ICARCV). Guangzhou, China: IEEE, 2012. 1789−1793 [30] Ekșioğlu E M. RLS adaptive filtering with sparsity regularization. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and Their Applications (ISSPA 2010). Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IEEE, 2010. 550−553 [31] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278−2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [32] Gawlik D. New York stock exchange [Online], available: https://www.kaggle.com/dgawlik/nyse, February 19, 2020 [33] Liang X, Zou T, Guo B, Li S, Zhang H Z, Zhang S Y, et al. Assessing Beijing's PM2.5 pollution: Severity, weather impact, APEC and winter heating. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2015, 471(2182): Article No. 20150257 [34] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1026−1034 [35] Pennington J, Socher R, Manning C. GloVe: Global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). Doha, Qatar: ACL, 2014. 1532−1543 -




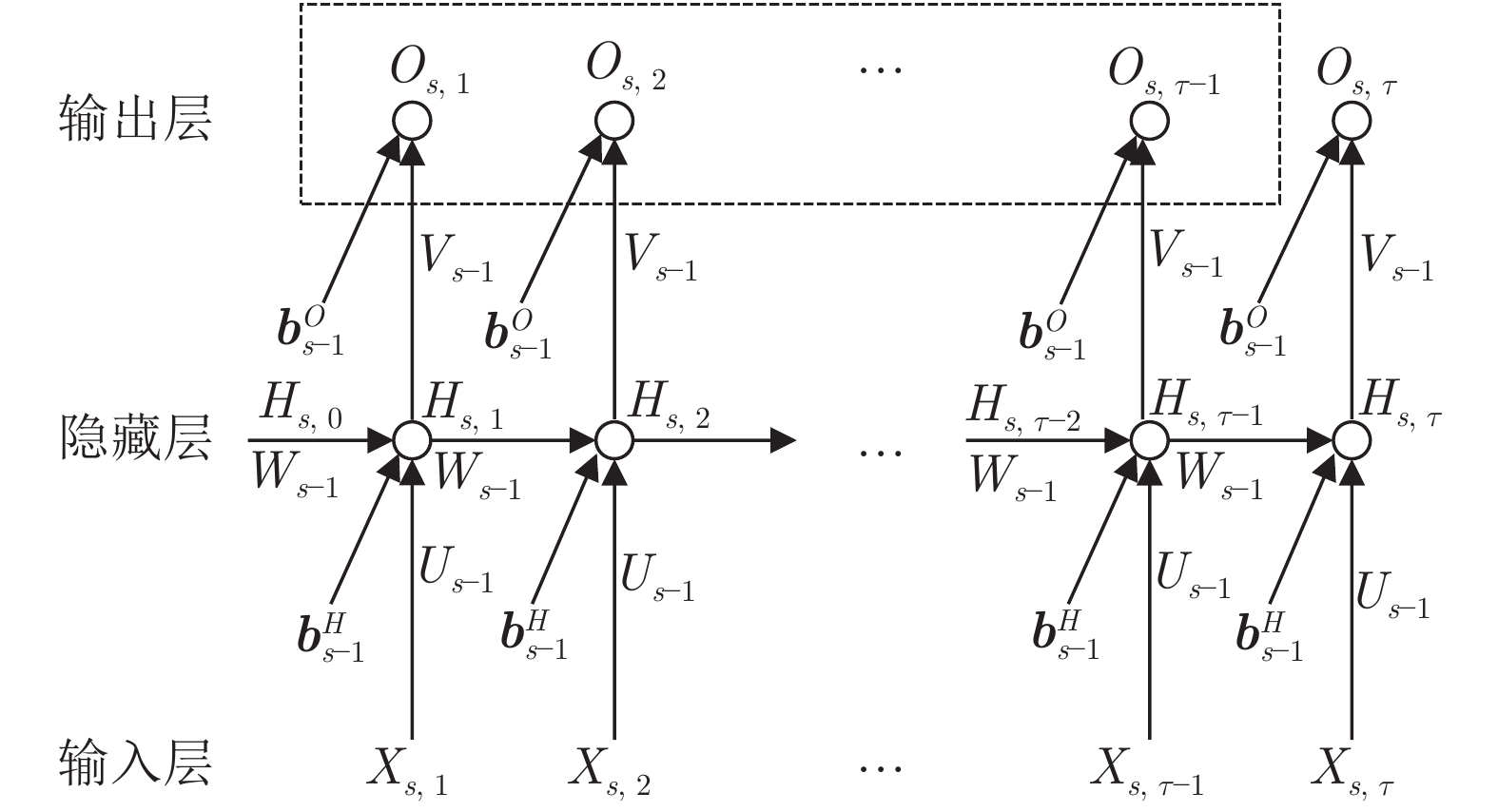
 下载:
下载: