-
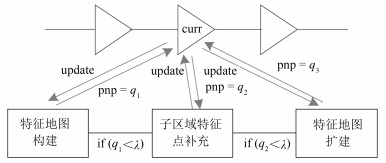
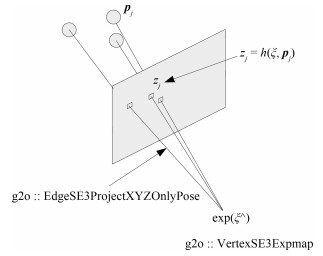
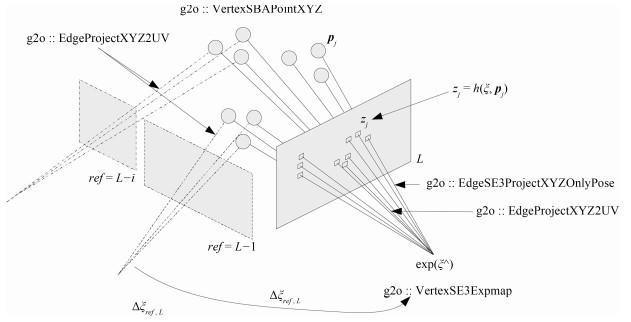
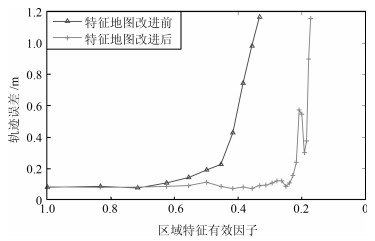
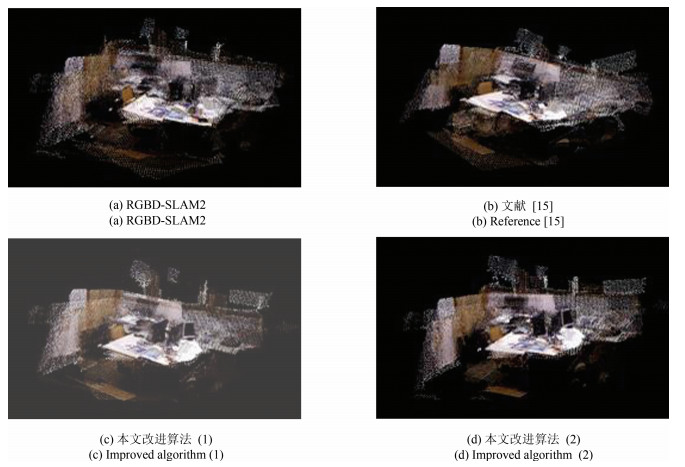
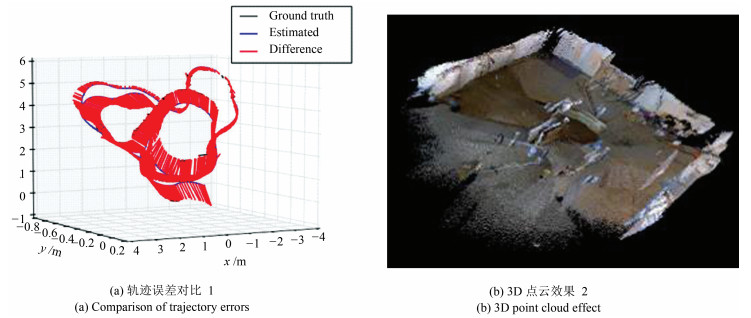
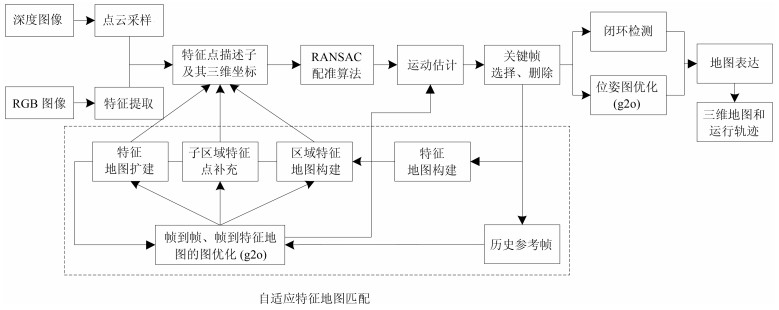
摘要: 从提高机器人视觉同时定位与地图构建(Visual simultaneous localization and mapping,VSLAM)算法的实时性出发,在VSLAM的视觉里程计中提出一种自适应特征地图配准的算法.首先,针对视觉里程计中特征地图信息冗余、耗费计算资源的问题,划分特征地图子区域并作为结构单元,再根据角点响应强度指标大小提取子区域中少数高效的特征点,以较小规模的特征地图配准各帧:针对自适应地图配准时匹配个数不满足的情况,提出一种区域特征点补充和特征地图扩建的方法,快速实现该情形下当前帧的再次匹配:为了提高视觉里程计中位姿估计的精度,提出一种帧到帧、帧到模型的g2o(General graph optimization)特征地图优化模型,更加有效地更新特征地图的内点和外点.通用数据集的实验表明,所提方法的定位精度误差在厘米级,生成的点云地图清晰、漂移少,相比于其他算法,具有更好的实时性、定位精度以及建图能力.Abstract: An improved visual simultaneous localization and mapping (VSLAM) algorithm based on the adaptive feature map is proposed in order to enhance real-time performance. The feature map is divided into sub-regions and structural units are employed to reduce computation cost. After that the most effective feature points, sorted by corner response intensity, are extracted and matched with the current frame. In the case that the adaptive map features are not enough for registration, a method of adding more region feature point supplements and extending the feature map is also proposed, which enables re-matching ability for the visual odometry system. A frame-to-frame and frame-to-map graph optimization method is also implemented to effectively update the internal and external points in the feature map. The results in public dataset show that the location accuracy error of the proposed method is centimeter and that the point cloud map is clear and has less drift. Compared with the original one, the proposed method has better real-time performance, positioning accuracy and the ability to build maps.1) 本文责任编委 黄庆明
-
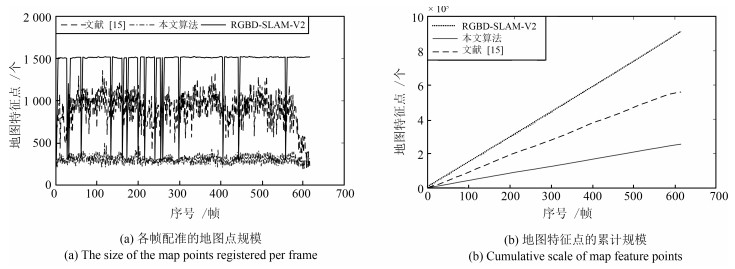
表 1 不同算法的实时性、特征地图累计规模比较
Table 1 Comparison of real time and feature map cumulative size of each algorithm
$T$(ms), $k$(个) RGBD-SLAM-V2 FVO 文献[15] 本文算法(1) 本文算法(2) fr1-xyz $52.31/11.88 \times {10^5}$ $44.11/6.12 \times {10^5}$ $46.07/6.13 \times {10^5}$ ${\bf{43.54}}/{\bf{3.03{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ $43.81/{\bf{3.03{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ fr1-360 $59.86/11.09 \times {10^5}$ $51.90/6.37 \times {10^5}$ $55.54/6.37 \times {10^5}$ ${\bf{49.14}}/{\bf{3.08{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ $49.71/{\bf{3.08{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ fr1-room $48.07/9.14 \times {10^5}$ $40.17/5.59 \times {10^5}$ $46.70/5.59 \times {10^5}$ ${\bf{39.24}}/{\bf{2.55{\rm{ \times }}1{0^5}}}$ $40.26/{\bf{2.55{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ fr1-desk $50.69/9.37 \times {10^5}$ ${\bf{43.86}}/5.65 \times {10^5}$ $47.32/5.63 \times {10^5}$ $43.95/{\bf{2.73{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ $44.32/{\bf{2.73{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ fr1-desk2 $56.32/10.36 \times {10^5}$ $47.80/6.22 \times {10^5}$ $53.92/6.22 \times {10^5}$ ${\bf{46.51}}/{\bf{2.95{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ $47.95/{\bf{2.95{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ flfh $240.45/38.74 \times {10^5}$ $186.43/17.86 \times {10^5}$ $197.80/17.86 \times {10^5}$ ${\bf{181.89}}/{\bf{8.72{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ $183.14/{\bf{8.72{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ flnp $301.11/43.47 \times {10^5}$ $255.96/21.55 \times {10^5}$ $269.35/21.55 \times {10^5}$ ${\bf{248.07}}/{\bf{11.66{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ $249.51/{\bf{11.66{\rm{ \times }}{10^5}}}$ 表 2 不同算法的轨迹误差对比
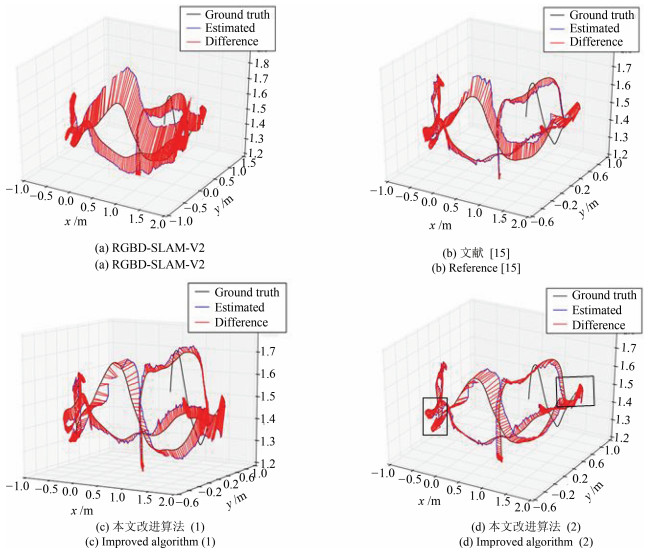
Table 2 Comparison of trajectory errors of different algorithms
$E$ (m) RGBD-SLAM2 FVO 文献[15] 本文算法(1) 本文算法(2) fr1-xyz 0.019 0.024 0.017 0.016 ${\bf{0.013}}$ fr1-360 0.018 0.022 ${\bf{0.017}}$ 0.018 ${\bf{0.017}}$ fr1-room 0.239 0.286 0.073 0.082 ${\bf{0.072}}$ fr1-desk 0.038 0.084 0.026 0.028 ${\bf{0.025}}$ fr1-desk2 0.092 0.157 0.039 0.042 ${\bf{0.032}}$ flfh 0.466 0.764 0.228 0.241 ${\bf{0.151}}$ flnp 0.836 0.988 0.381 0.411 ${\bf{0.188}}$ -
[1] Garcia-Fidalgo E, Ortiz A. Vision-based topological mapping and localization methods:a survey. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2015, 64:1-20 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2014.11.009 [2] Carlone L, Tron R, Daniilidis K, Dellaert F. Initialization techniques for 3D SLAM: a survey on rotation estimation and its use in pose graph optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2015. 4597-4604 [3] Merriaux P, Dupuis Y, Vasseur P, Savatier X. Wheel odometry-based car localization and tracking on vectorial map. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Qingdao, China: IEEE, 2014. 1890-1891 [4] Shen J L, Tick D, Gans N. Localization through fusion of discrete and continuous epipolar geometry with wheel and IMU odometry. In: Proceedings of the 2011 American Control Conference. San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2011. 1292-1298 [5] Ohno K, Tsubouchi T, Shigematsu B, Yuta S. Differential GPS and odometry-based outdoor navigation of a mobile robot. Advanced Robotics, 2004, 18(6):611-635 doi: 10.1163/1568553041257431 [6] Fuentes-Pacheco J, Ruiz-Ascencio J, Rendón-Mancha J M. Visual simultaneous localization and mapping:a survey. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2015, 43(1):55-81 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0229524923/ [7] Endres F, Hess J, Sturm J, Cremers D, Burgard W. 3-D mapping with an RGB-D camera. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2014, 30(1):177-187 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3a3af2654b557b27453ea4c4dfb2e7ab&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [8] Scaramuzza D, Fraundorfer F. Visual odometry. IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine, 2011, 18(4):80-92 doi: 10.1109/MRA.2011.943233 [9] Nister D, Naroditsky O, Bergen J. Visual odometry. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC, USA: IEEE, 2004. I-652-I-659 [10] Kerl C, Sturm J, Cremers D. Robust odometry estimation for RGB-D cameras. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 2013. 3748-3754 [11] Huang A S, Bachrach A, Henry P, Krainin M, Maturana D, Fox D, et al. Visual odometry and mapping for autonomous flight using an RGB-D camera. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on Robotics Research. Cham, Germany: Springer, 2017. 235-252 [12] Henry P, Krainin M, Herbst E, Ren X, Fox D. RGB-D mapping: using depth cameras for dense 3D modeling of indoor environments. In: Proceedings of Experimental Robotics. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2014. 477-491 [13] Endres F, Hess J, Engelhard N, Sturm J, Cremers D, Burgard W. An evaluation of the RGB-D SLAM system. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Saint Paul, MN, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1691-1696 [14] Dryanovski I, Valenti R G, Xiao J Z. Fast visual odometry and mapping from RGB-D data. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 2013. 2305-2310 [15] 高翔, 张涛, 刘毅, 颜沁睿.视觉SLAM十四讲:从理论到实践.北京:电子工业出版社, 2017. 140-150Gao Xiang, Zhang Tao, Liu Yi, Yan Qin-Rui. Fourteen the Visual SLAM from Theory to Practice. Beijing:Electronic Industry Press, 2017. 140-150 [16] Cao T Y, Cai H Y, Fang D M, Huang H, Liu C. Keyframes global map establishing method for robot localization through content-based image matching. Journal of Robotics, 2017, 2017: Article ID 1646095 [17] Martins R, Fernandez-Moral E, Rives P. Adaptive direct RGB-D registration and mapping for large motions. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Asian Conference on Computer Vision ACCV 2016: Computer Vision - ACCV 2016. Cham, Germany: Springer, 2017. 191-206 [18] Wadenbäck M, Aström K, Heyden A. Recovering planar motion from homographies obtained using a 2.5-point solver for a polynomial system. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Phoenix, AZ, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2966-2970 [19] Steinbrücker F, Sturm J, Cremers D. Real-time visual odometry from dense RGB-D images. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 719-722 [20] 李弋星, 刘士荣, 仲朝亮, 王坚.基于改进关键帧选择的RGB-D SLAM算法.大连理工大学学报, 2017, 57(4):411-417 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dllgdxxb201704012Li Yi-Xing, Liu Shi-Rong, Zhong Chao-Liang, Wang Jian. RGB-D SLAM algorithm based on improved key-frame selection. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2017, 57(4):411-417 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dllgdxxb201704012 [21] Rublee E, Rabaud V, Konolige K, Bradski G. ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 2564-2571 [22] Kümmerle R, Grisetti G, Strasdat H, Konolige K, Burgard W. g2o: a general framework for graph optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2011. 3607-3613 [23] Hornung A, Wurm K M, Bennewitz M, Stachniss C, Burgard W. OctoMap:an efficient probabilistic 3D mapping framework based on octrees. Autonomous Robots, 2013, 34(3):189-206 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyy201705042 [24] Sturm J, Engelhard N, Endres F, Burgard W, Cremers D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vilamoura, Portugal: IEEE, 2012. 573-580 -




 下载:
下载: