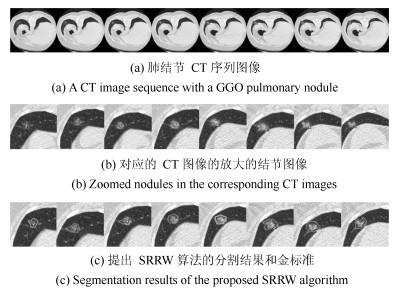
Segmentation of Ground Glass Opacity Pulmonary Nodules With Sparse Representation and Random Walk
-
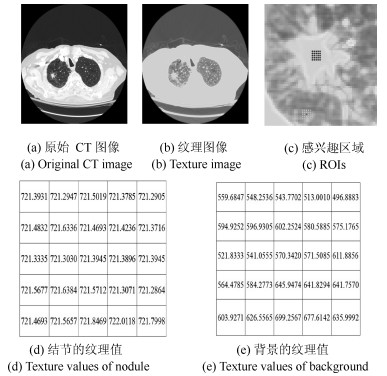
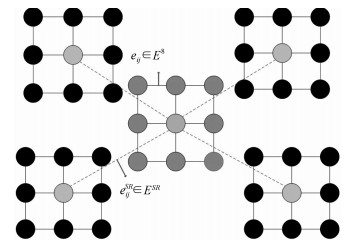
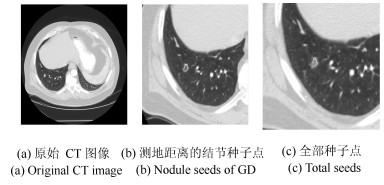
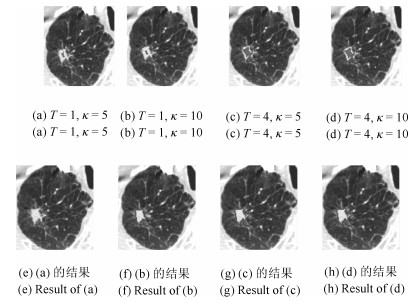
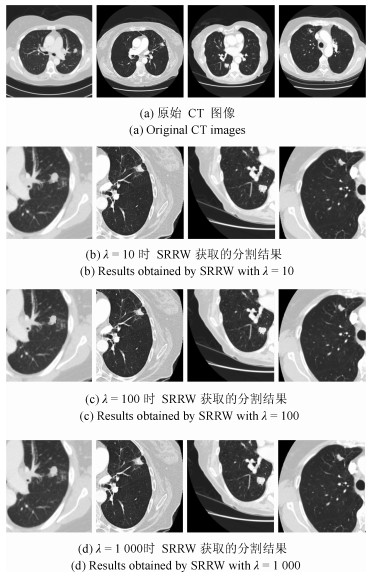
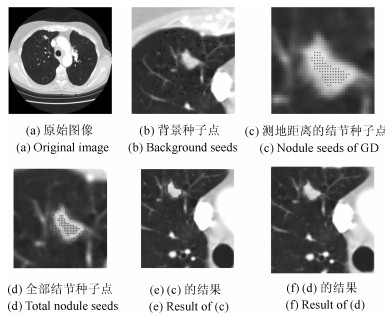
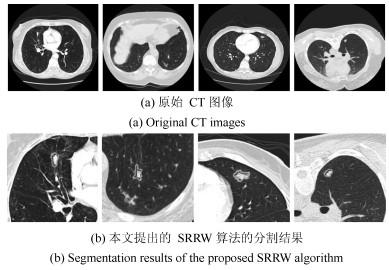
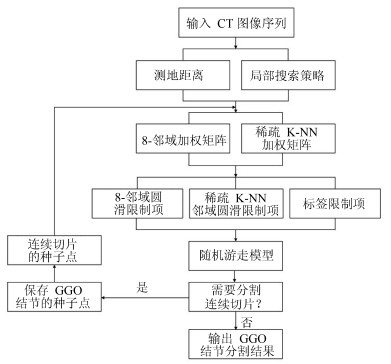
摘要: 肺结节是早期肺癌在影像学上的表现形式.磨玻璃型(Ground glass opacity,GGO)肺结节被认为是恶变可能性最大的一类结节之一.针对GGO结节边缘模糊、大小各异、形状不规则和灰度不均匀等造成分割准确率低问题,本文提出了一种基于稀疏表示和随机游走模型的分割算法.首先,利用测地距离和局部搜索策略,自动地选取了种子点.其次,联合8-!邻域和稀疏表示的K-!最近邻算法建立了新的图,避免了噪声的干扰.结合灰度、纹理、空间距离和稀疏系数构建了新的加权矩阵.最后,将标签限制项引入到随机游走的能量函数中.该算法分割准确性较高,鲁棒性较强.Abstract: Pulmonary nodules are the radiographic manifestation of lung cancer in early stages. Ground glass opacity (GGO) pulmonary nodules are considered to be one of the most likely nodules of malignancy. To address the low accuracy segmentation problem caused by blurred boundaries, different sizes, irregular shapes and inhomogeneous intensities of GGO nodules, a segmentation algorithm with the sparse representation and random walk model is proposed. Firstly, the geodesic distance and local search strategy are introduced to automatically select seeds. Secondly, 8-neighbor and sparse representation K-nearest neighbor algorithm are combined to build a new graph which avoids the interference of image noise. To construct a new weighted matrix, intensity, texture, spatial distance and sparse coefficients are incorporated. Finally, a label constraint term is added to the energy function of random walker. The proposed algorithm can obtain a high accuracy and strong robustness.1) 本文责任编委 张道强
-
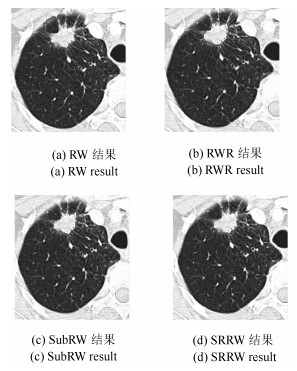
表 1 SRRW、RW和SubRW算法的Overlap值对比
Table 1 Comparison results of Overlap values among SRRW、RW and SubRW algorithms
CT图像 SRRW算法 RW算法 SubRW算法 LIDC-000498 0.9145 0.8534 0.8942 LIDC-000058 0.9324 0.9164 0.9632 LIDC-000125 0.8652 0.8432 0.8223 LIDC-000043 0.8942 0.9473 0.9024 LIDC-000074 0.9724 0.9636 0.9475 LIDC-000119 0.8148 0.7647 0.8086 LIDC-000063 0.9025 0.8437 0.8946 LIDC-000054 0.9438 0.9421 0.9676 LIDC-000106 0.8142 0.7642 0.8247 LIDC-000116 0.9798 0.9075 0.9248 Mean 0.9034 0.8746 0.8950 Std. 0.0583 0.0725 0.0590 表 2 本文的种子点选择策略的执行时间
Table 2 Execution times of seed selection strategy
序列号 执行时间(s) 序列号 执行时间(s) 1 0.2554 6 0.2054 2 0.2087 7 0.2081 3 0.2122 8 0.2225 4 0.2069 9 0.2041 5 0.2067 10 0.2060 -
[1] Aberle D R, Adams A M, Berg C D, Black W C, Clapp J D, Fagerstrom R M, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. New England Journal of Medicine, 2011, 365 (5):395-409 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102873 [2] Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout R G P M, Granton P, et al. Radiomics:extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. European Journal of Cancer, 2012, 48 (4):441-446 doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036 [3] Henschke C I, Yankelevitz D F, Mirtcheva R, McGuinness G, McCauley D, Miettinen O S. CT screening for lung cancer:frequency and significance of part-solid and nonsolid nodules. American Journal of Roentgenology, 2002, 178 (4):1053-1057 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=13640586 [4] 韩光辉, 刘峡壁, 郑光远.肺部CT图像病变区域检测方法.自动化学报, 2017, 43 (12):2071-2090 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19182.shtmlHan Guang-Hui, Liu Xia-Bi, Zheng Guang-Yuan. Automated detection of lesion regions in lung computed tomography images:a review. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43 (12):2071-2090 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19182.shtml [5] Reeves A P, Chan A B, Yankelevitz D F, Henschke C I, Kressler B, Kostis W J. On measuring the change in size of pulmonary nodules. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2006, 25 (4):435-450 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2006.871548 [6] Dehmeshki J, Amin H, Valdivieso M, Ye X J. Segmentation of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT scans:a region growing approach. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2008, 27 (4):467-480 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2007.907555 [7] Kubota T, Jerebko A K, Dewan M, Salganicoff M, Krishnan A. Segmentation of pulmonary nodules of various densities with morphological approaches and convexity models. Medical Image Analysis, 2011, 15 (1):133-154 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2010.08.005 [8] Nithila E E, Kumar S S. Segmentation of lung nodule in CT data using active contour model and Fuzzy C-mean clustering. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2016, 55 (3):2583-2588 doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2016.06.002 [9] Kuhnigk J M, Dicken V, Bornemann L, Bakai A, Wormanns D, Krass S, et al. Morphological segmentation and partial volume analysis for volumetry of solid pulmonary lesions in thoracic CT scans. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2006, 25 (4):417-434 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2006.871547 [10] Aoyama M, Li Q, Katsuragawa S, Li F, Sone S, DoiK. Computerized scheme for determination of the likelihood measure of malignancy for pulmonary nodules on low-dose CT images. Medical Physics, 2003, 30 (3):387-394 doi: 10.1118/1.1543575 [11] Diciotti S, Lombardo S, Falchini M, Picozzi G, Mascalchi M. Automated segmentation refinement of small lung nodules in CT scans by local shape analysis. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 58 (12):3418-3428 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2167621 [12] Ye X J, Lin X Y, Dehmeshki J, Slabaugh G, Beddoe G. Shape-based computer-aided detection of lung nodules in thoracic CT images. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 56 (7):1810-1820 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2009.2017027 [13] 孙文燕, 董恩清, 曹祝楼, 郑强.一种基于模糊主动轮廓的鲁棒局部分割方法.自动化学报, 2017, 43(4):611-621 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19039.shtmlSun Wen-Yan, Dong En-Qing, Cao Zhu-Lou, Zheng Qiang. A robust local segmentation method based on fuzzy-energy based active contour. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43 (4):611-621 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19039.shtml [14] 陈侃, 李彬, 田联房.基于模糊速度函数的活动轮廓模型的肺结节分割.自动化学报, 2013, 39 (8):1257-1264 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18157.shtmlChen Kan, Li Bin, Tian Lian-Fang. A segmentation algorithm of pulmonary nodules using active contour model based on fuzzy speed function. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39 (8):1257-1264 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18157.shtml [15] Keshani M, Azimifar Z, Tajeripour F, Boostani R. Lung nodule segmentation and recognition using SVM classifier and active contour modeling:a complete intelligent system. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2013, 43 (4):287-300 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2012.12.004 [16] Zhu Y J, Tan Y Q, Hua Y Q, Zhang G Z, Zhang J G. Automatic segmentation of ground-glass opacities in lung CT images by using Markov random field-based algorithms. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2012, 25 (3):409-422 doi: 10.1007/s10278-011-9435-5 [17] Li C F, Nie S D, Wang Y J, Sun X W, Zhang B. Segmentation of sub-solid pulmonary nodules based on improved fuzzy C-means clustering. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2013, 18 (8):1019-1030 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC0213326314 [18] Li B, Chen K, Peng G M, Guo Y X, Tian L F, Ou S X, et al. Segmentation of ground glass opacity pulmonary nodules using an integrated active contour model with wavelet energy-based adaptive local energy and posterior probability-based speed function. Materials Express, 2016, 6 (4):317-327 doi: 10.1166/mex.2016.1311 [19] Li B, Chen Q L, Peng G M, Guo Y X, Chen K, Tian L F, et al. Segmentation of pulmonary nodules using adaptive local region energy with probability density function-based similarity distance and multi-features clustering. Biomedical Engineering Online, 2016, 15 (1):49-77 doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0164-3 [20] Cheng J Z, Ni D, Chou Y H, Qin J, Tiu C M, Chang Y C, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture:applications to breast lesions in US images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:24454 doi: 10.1038/srep24454 [21] Wang S, Zhou M, Liu Z Y, Liu Z Y, Gu D S, Zang Y L, et al. Central focused convolutional neural networks:developing a data-driven model for lung nodule segmentation. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 40:172-183 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.06.014 [22] Grady L. Random walks for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28 (11):1768-1783 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2006.233 [23] Eslami A, Karamalis A, Katouzian A, Navab N. Segmentation by retrieval with guided random walks:application to left ventricle segmentation in MRI. Medical Image Analysis, 2013, 17 (2):236-253 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2012.10.005 [24] Onoma D P, Ruan S, Thureau S, Nkhali L, Modzelewski R, Monnehan G A, et al. Segmentation of heterogeneous or small FDG PET positive tissue based on a 3D-locally adaptive random walk algorithm. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2014, 38 (8):753-763 doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2014.09.007 [25] Wang Q, Lu L, Wu D J, El-Zehiry N, Zheng Y F, Shen D G, et al. Automatic segmentation of spinal canals in CT images via iterative topology refinement. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34 (8):1694-1704 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2436693 [26] Mi H M, Petitjean C, Vera P, Ruan S. Joint tumor growth prediction and tumor segmentation on therapeutic follow-up PET images. Medical Image Analysis, 2015, 23 (1):84-91 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.04.016 [27] Fan M Y, Gu N N, Qiao H, Zhang B. Sparse regularization for semi-supervised classification. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44 (8):1777-1784 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.02.013 [28] Liu G C, Lin Z C, Yan S C, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y. Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35 (1):171-184 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.88 [29] Li S, Fu Y. Learning balanced and unbalanced graphs via low-rank coding. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 27 (5):1274-1287 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2014.2365793 [30] Fu Y F, Gao J B, Tien D, Lin Z C, Hong X. Tensor LRR and sparse coding-based subspace clustering. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27 (10):2120-2133 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2553155 [31] Zhuang L S, Zhou Z H, Gao S H, Yin J W, Lin Z C, Ma Y. Label information guided graph construction for semi-supervised learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26 (9):4182-4192 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2703120 [32] Liao Y Y, Wang Y, Liu Y. Graph regularized auto-encoders for image representation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26 (2):2839-2852 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_1312.0786 [33] Yuan H X, Wu S Q, Cheng P H, An P, Bao S D. Nonlocal random walks algorithm for semi-automatic 2D-to-3D image conversion. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22 (3):371-374 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2359643 [34] Armato S G, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray M F, Meyer C R, Reeves A P, et al. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI):a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Medical Physics, 2011, 38 (2):915-931 doi: 10.1118/1.3528204 [35] Kim T H, Lee K M, Lee S U. Generative image segmentation using random walks with restart. In: Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision. Marseille, France: Springer-Verlag, 2008. 264-275 [36] Dong X P, Shen J B, Shao L, van Gool L. Sub-Markov random walk for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25 (2):516-527 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2505184 [37] Okada K, Comaniciu D, Krishnan A. Robust anisotropic Gaussian fitting for volumetric characterization of Pulmonary nodules in multislice CT. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2005, 24 (3):409-423 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2004.843172 [38] Kostis W J, Reeves A P, Yankelevitz D F, Henschke C I. Three-dimensional segmentation and growth-rate estimation of small pulmonary nodules in helical CT images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2003, 22 (10):1259-1274 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2003.817785 [39] Messay T, Hardie R C, Tuinstra T R. Segmentation of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography using a regression neural network approach and its application to the Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative dataset. Medical Image Analysis, 2015, 22 (1):48-62 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.02.002 -




 下载:
下载: