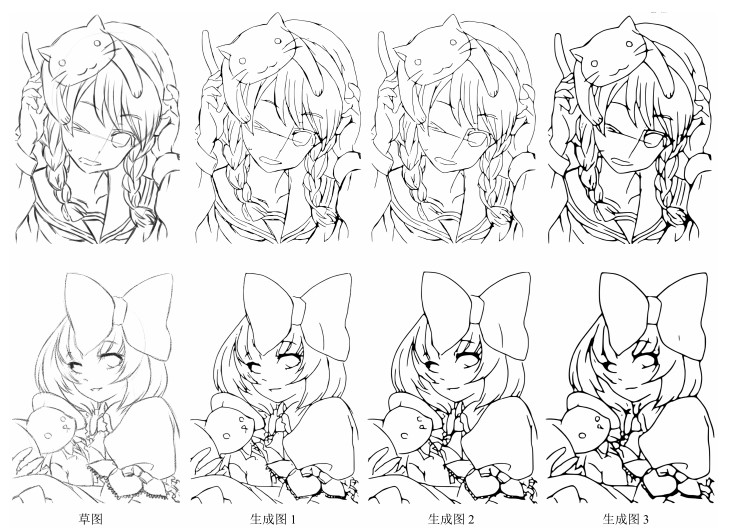
-
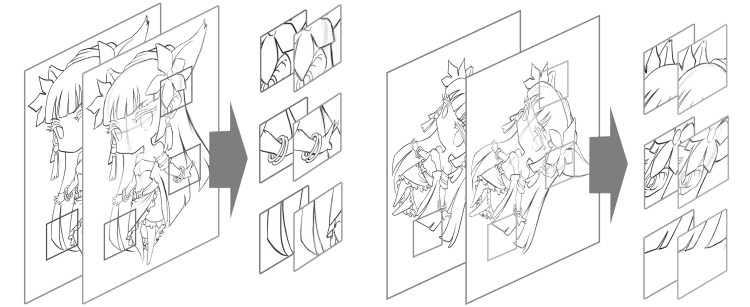
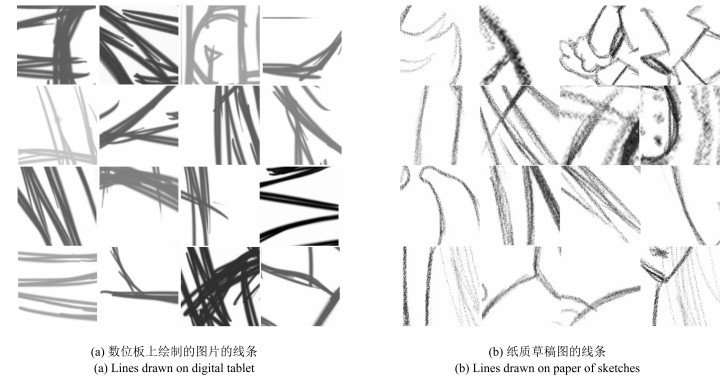
摘要: 在漫画绘制的过程中,按草稿绘制出线条干净的线稿是很重要的一环.现有的草图简化方法已经具有一定的线条简化能力,然而由于草图的绘制方式的多样性以及画面复杂程度的不同,这些方法适用范围有限且效果不理想.本文提出了一种新颖的草图简化方法,利用条件随机场(Conditional random field,CRF)和最小二乘生成式对抗网络(Least squares generative adversarial networks,LSGAN)理论搭建了深度卷积神经网络的草图简化模型,通过该网络生成器与判别器之间的零和博弈与条件约束,得到更加接近真实的简化线稿图.同时,为了训练对抗模型的草图简化能力,本文建立了包含更多绘制方式与不同内容的草图与简化线稿图对的训练数据集.实验表明,本文算法对于复杂情况下的草图,相比于目前的方法,具有更好的简化效果.
-
关键词:
- 草图简化 /
- 最小二乘生成式对抗网络 /
- 深度学习 /
- 条件随机场
Abstract: Sketch simplification is a critical part of cartoon drawing. To some extent, the existing approaches already have basic ability of sketch cleanup, but still have limitation in some situations because of the diversity of sketch drawing methods and complexity of sketch contents. In this paper, we present a novel approach of building a model for sketch simplification, which is based on the conditional random field (CRF) and least squares generative adversarial networks (LSGAN). Through the zero-sum game of generator and discriminator in the model and the learning restriction of conditional random field, we can obtain simplified images more similar to standard clean images. At the same time, we build a dataset containing a large number of pairs of sketches and clean images in different painting ways and contents. Finally, experiments show that our approach can obtain better results than the state of the art approach for sketch simplification.1) 本文责任编委 王坤峰 -
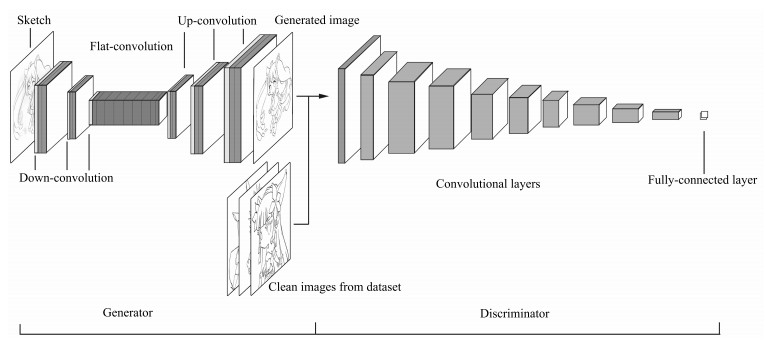
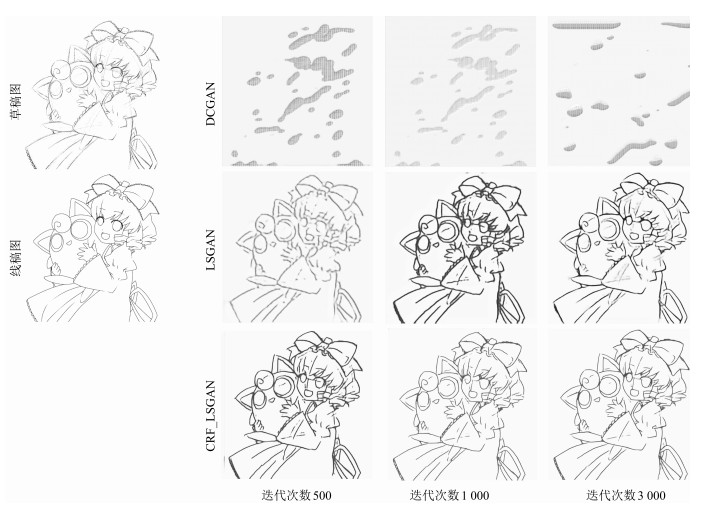
表 1 基于条件随机场和最小二乘生成式对抗网络的草图简化模型
Table 1 Sketch simplification model based on the conditional random field and least squares generative adversarial networks
序号 层类型 卷积核 步长 深度 序号 层类型 卷积核 步长 深度 0 Input - - 1 20 Up-convolution 4×4 1/2×1/2 128 1 Down-convolution 5×5 2×2 48 21 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 128 2 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 128 22 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 48 3 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 128 23 Up-convolution 4×4 1/2×1/2 48 4 Down-convolution 3×3 2×2 256 24 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 24 5 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 256 25 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 1 6 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 256 26 Convolution 5×5 1×1 20 7 Down-convolution 3×3 2×2 256 27 Convolution 5×5 1×1 50 8 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 512 28 Convolution 4×4 1×1 500 9 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 1 024 29 Convolution 5×5 2×2 500 10 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 1 024 30 Convolution 5×5 2×2 500 11 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 1 024 31 Convolution 5×5 2×2 500 12 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 1 024 32 Convolution 5×5 2×2 500 13 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 1 024 33 Convolution 5×5 2×2 1 000 14 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 1 024 34 Convolution 5×5 2×2 1 000 15 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 512 35 Convolution 4×4 2×2 1 000 16 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 256 36 Fully-connected 1×1 1×1 2 17 Up-convolution 4×4 1/2×1/2 256 37 Dloss - - - 18 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 256 38 Gloss - - - 19 Flat-convolution 3×3 1×1 128 表 2 生成器网络生成简化图所需时间
Table 2 Time needed for generating a simplified image by the generator
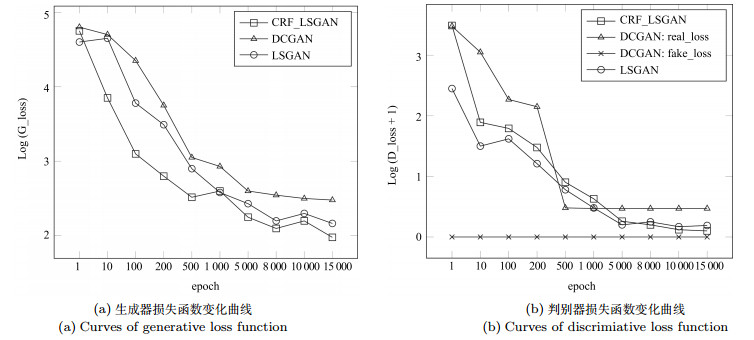
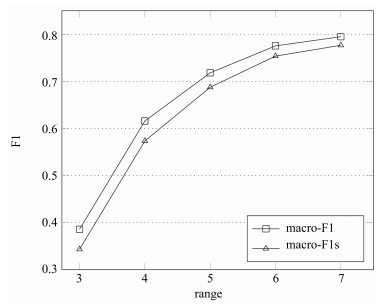
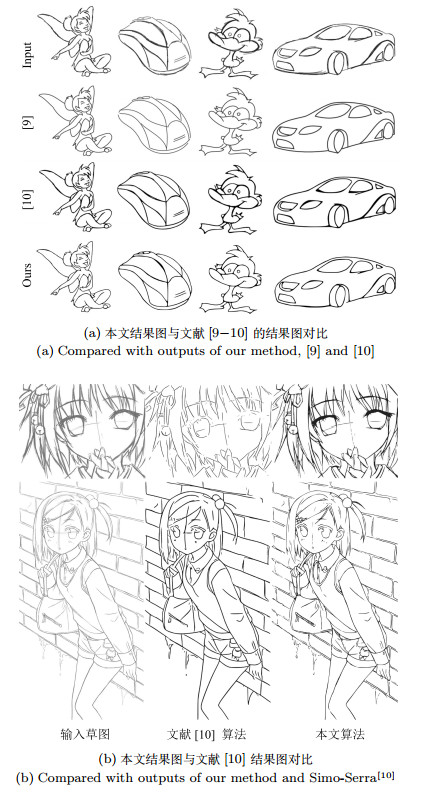
图片大小(像素) 像素个数 GPU (Nvidia gtx980ti) (s) 500×500 250 000 1.377 1 500×1 500 2 250 000 11.632 2 000×2 000 4 000 000 21.431 表 3 利用测试集获得的Simo-Serra[10]简化模型输出图和本文简化模型输出图的宏查全率、宏查准率和宏F1的测试结果
Table 3 Test results of macro-$R$, macro-$P$ and macro-F1 of output images of Simo-Serra[10] simplification model and output images of our model using test dataset
测试项目 Simo-Serra模型结果图 本文模型结果图 宏查全率(范围为5像素×5像素) 0.6660 0.7278 宏查准率(范围为5像素×5像素) 0.7105 0.7078 宏F1 (范围为5像素×5像素) 0.6875 0.7181 -
[1] 孙旭, 李晓光, 李嘉锋, 卓力.基于深度学习的图像超分辨率复原研究进展.自动化学报, 2017, 43(5):697-709 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19048.shtmlSun Xu, Li Xiao-Guang, Li Jia-Feng, Zhuo Li. Review on deep learning based image super-resolution restoration algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5):697-709 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19048.shtml [2] 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃.深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望.自动化学报, 2017, 43(8):1289-1305 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19104.shtmlZhang Hui, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Advances and perspectives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8):1289-1305 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19104.shtml [3] Wilson B, Ma K L. Rendering complexity in computer-generated pen-and-ink illustrations. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2004. 129-137 [4] Grabli S, Durand F, Sillion F X. Density measure for line-drawing simplification. In: Proceedings of the 12th Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2004. 309-318 [5] Cole F, DeCarlo D, Finkelstein A, Kin K, Morley K, Santella A. Directing gaze in 3D models with stylized focus. In: Proceedings of the 17th Eurographics Conference on Rendering Techniques. Nicosia, Cyprus: ACM, 2006. 377-387 [6] Grimm C, Joshi P. Just Drawit: a 3D sketching system. In: Proceedings of the 2012 International Symposium on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling. Annecy, France: ACM, 2012. 121-130 [7] Fišer J, Asente P, Sýkora D. ShipShape: a drawing beautification assistant. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Workshop on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling. Istanbul, Turkey: ACM, 2015. 49-57 [8] Orbay G, Kara L B. Beautification of design sketches using trainable stroke clustering and curve fitting. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2011, 17(5):694-708 doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2010.105 [9] Liu X T, Wong T T, Heng P A. Closure-aware sketch simplification. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2015, 34(6):Article No. 168 https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2818067 [10] Simo-Serra E, Iizuka S, Sasaki K, Ishikawa H. Learning to simplify:fully convolutional networks for rough sketch cleanup ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2016, 35(4):Article No. 121 https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2925972 [11] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Montreal, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2014. 2672-2680 [12] 王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 林懿伦, 郑心湖, 王飞跃.生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望.自动化学报, 2017, 43(3):321-332 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19012.shtmlWang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Duan Yan-Jie, Lin Yi-Lun, Zheng Xin-Hu, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative adversarial networks:the state of the art and beyond. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3):321-332 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19012.shtml [13] Qi G J. Loss-sensitive generative adversarial networks on Lipschitz densities. ArXiv: 1701. 06264, 2017. [14] Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein GAN. ArXiv: 1701. 07875, 2017. [15] Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Diego, CA, USA: ICLR, 2015. [16] Mao X D, Li Q, Xie H R, Lau R Y K, Wang Z, Smolley S P. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2813-2821 [17] Huang Q X, Han M, Wu B, Ioffe S. A hierarchical conditional random field model for labeling and segmenting images of street scenes. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Colorado Springs, CO, USA: IEEE, 2011. 1953-1960 [18] Yang M Y, Förstner W. A hierarchical conditional random field model for labeling and classifying images of man-made scenes. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 196-203 [19] Chen L C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille A L. DeepLab:semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4):834-848 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [20] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: PMLR, 2015. [21] Selinger P. Potrace: a polygon-based tracing algorithm[Online], available: http://potrace.sourceforge.net/potrace.pdf, May 10, 2017 -





 下载:
下载: