A Kind of Deep Belief Networks Based on Nonlinear Features Extraction with Application to PM2.5 Concentration Prediction and Diagnosis
-
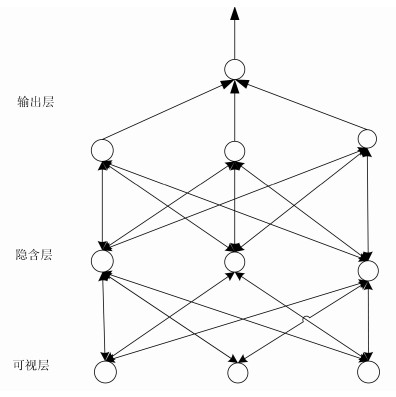
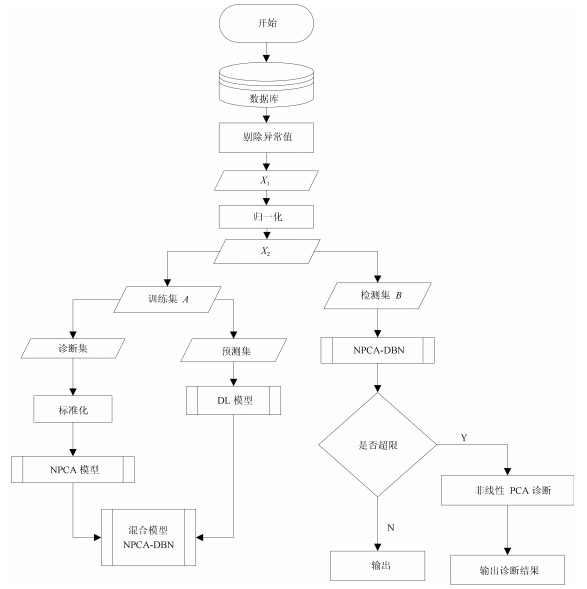
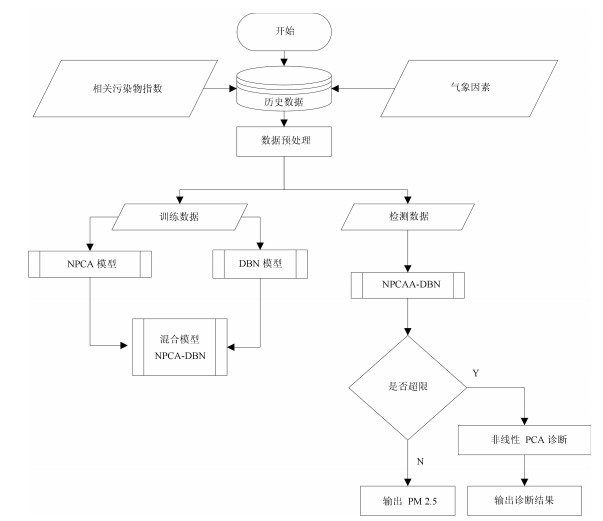
摘要: 传统的深度置信网络(Deep brief networks,DBN)在建立高维数据分类模型时,往往存在网络负荷大,运算复杂度高等问题.本文首先基于非线性PCA(NPCA)对高维样本数据进行降维,然后以提取到的非线性特征作为DBN的网络输入,构建了一类含非线性特征提取预处理机制的DBN分类器.并从信息熵理论的角度出发,证明了所提改进DBN分类器在网络结构和算法复杂度方面的优势.通过一个PM2.5浓度预测与影响因素诊断实例,验证了所提改进DBN在一类分类和影响因素诊断问题中的应用,并与传统的分类器进行对比,显示了所提方法在建模精度及收敛速度上的优势.Abstract: To build a classifier model of high dimensional data, the traditional deep brief networks (DBN) modeling method suffers from large network load and high algorithm complexity. In this work, the data dimension is reduced based on the nonlinear PCA (NPCA), then a new DBN classifier with nonlinear feature extraction pre-processing mechanism is proposed where the nonlinear feature is extracted as the network input to the DBN. With the entropy theory, the advantage of the improved DBN is proved in terms of network structure and algorithm complexity. A PM2.5 concentration prediction and diagnosis problem is employed to exemplify applications of the proposed methods. Compared with the traditional classifier, it shows the advantage of the proposed method in modeling accuracy and convergence speed.
-
Key words:
- Deep brief networks (DBN) /
- nonlinear-PCA (NPCA) /
- PM2.5 /
- entropy
1) 本文责任编委 刘艳军 -
表 1 网络结构对比
Table 1 The comparison of the network structure
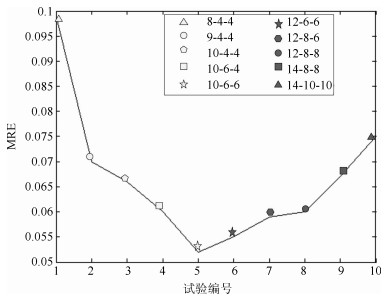
模型 结构 隐含层节点数 总节点数 算法总空间复杂度 NPCA-DBN (6-10-10) + (6-10-6-6-1) 32 55 $6\times 10\times 10+6\times 10\times 6\times 6\times 1$ DBN 10-12-10-10-1 32 43 $10\times 12\times 10\times 10$ 表 2 建模精度与收敛速度对比
Table 2 The comparison of the network structure
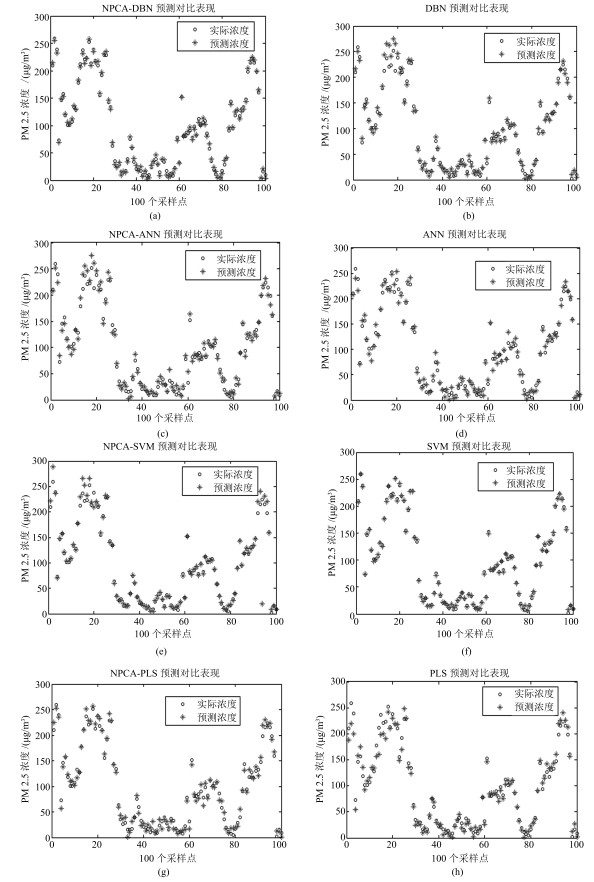
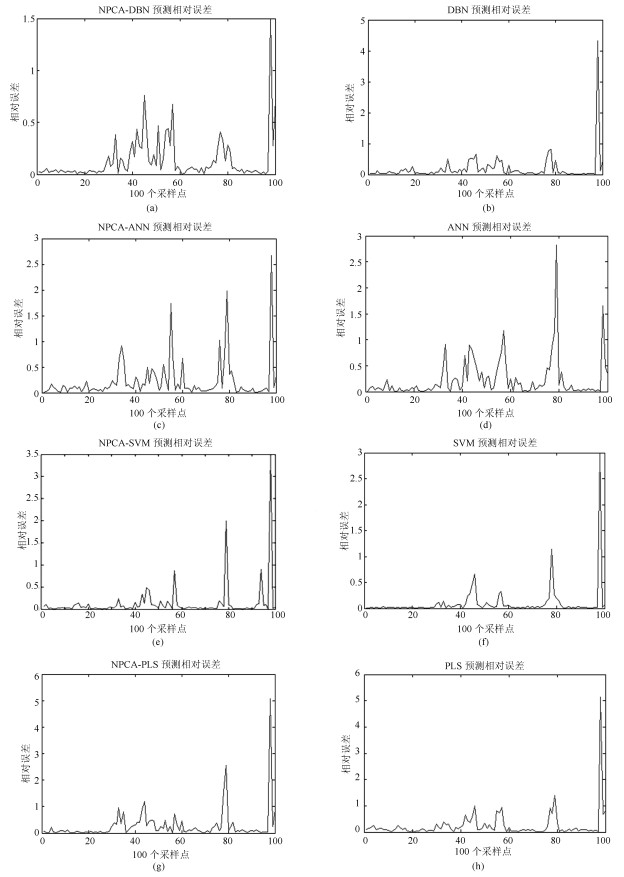
监测点 指标 NPCA-DBN NPCA-ANN NPCA-SVM NPCA-PLS DBN ANN SVM PLS 地表 MRE ($\times10^{-2}$) 13.32 22.21 13.14 26.82 17.92 23.40 12.19 24.54 水厂 训练时间(s) 44 16 180 46 89 33 349 94 华电 MRE ($\times10^{-2}$) 14.57 25.15 13.04 29.48 17.01 24.16 10.22 27.16 二区 训练时间(s) 37 12 211 49 90 38 401 103 胶片 MRE ($\times10^{-2}$) 10.51 26.49 11.09 33.16 12.77 23.32 12.73 30.06 厂 训练时间(s) 42 16 198 57 108 42 399 108 表 3 PM2.5浓度级别
Table 3 The PM2.5 concentration level
浓度范围(${\rm \mu g/m^3}$) 级别 优良级别 0$\, \sim\, $50 1级 优 50$\, \sim\, $100 2级 良 101$\, \sim\, $150 3级 轻度污染 151$\, \sim\, $200 4级 中度污染 201$\, \sim\, $ 5级 重度污染 -
[1] Saki F, Kehtarnavaz N. Online frame-based clustering with unknown number of clusters. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 57:70-83 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.03.010 [2] Li H, Chung F L, Wang S T. A SVM based classification method for homogeneous data. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 36:228-235 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.07.027 [3] Embrechts M J, Rossi F, Schleif F M, Lee J A. Advances in artificial neural networks, machine learning, and computational intelligence (ESANN 2013). Neurocomputing, 2014, 141:1-2 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.03.002 [4] Zhang Y P, Li X, Zhang Z F, Wu F, Zhao L M. Deep learning driven blockwise moving object detection with binary scene modeling. Neurocomputing, 2015, 168:454-463 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.082 [5] Shang C, Yang F, Huang D X, Lyu W X. Data-driven soft sensor development based on deep learning technique. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24 (3):223-233 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.01.012 [6] 高莹莹, 朱维彬.深层神经网络中间层可见化建模.自动化学报, 2015, 41 (9):1627-1637 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18736.shtmlGao Ying-Ying, Zhu Wei-Bin. Deep neural networks with visible intermediate layers. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41 (9):1627-1637 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18736.shtml [7] 丁科, 谭营. GPU通用计算及其在计算智能领域的应用.智能系统学报, 2015, 10 (1):1-11 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=znxt201501001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQDing Ke, Tan Ying. A review on general purpose computing on GPUs and its applications in computational intelligence. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2015, 10 (1):1-11 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=znxt201501001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [8] Shen F R, Chao J, Zhao J X. Forecasting exchange rate using deep belief networks and conjugate gradient method. Neurocomputing, 2015, 167:243-253 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.071 [9] Huang S, Yang D, Ge Y X, Zhang X H. Combined supervised information with PCA via discriminative component selection. Information Processing Letters, 2015, 115 (11):812-816 doi: 10.1016/j.ipl.2015.06.010 [10] 甘俊英, 李春芝.基于小波变换、二维主元分析与独立元分析的人脸识别方法.模式识别与人工智能, 2007, 20 (3):377-381 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=mssb200703013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQGan Jun-Ying, Li Chun-Zhi. Face Recognition based on wavelet transform, two-dimensional principal component analysis and independent component analysis. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2007, 20 (3):377-381 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=mssb200703013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [11] 汤健, 柴天佑, 余文, 赵立杰.在线KPLS建模方法及在磨机负荷参数集成建模中的应用.自动化学报, 2013, 39 (5):471-486 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17934.shtmlTang Jian, Chai Tian-You, Yu Wen, Zhao Li-Jie. On-line KPLS algorithm with application to ensemble modeling parameters of mill load. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39 (5):471-486 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17934.shtml [12] Cobourn W G. An enhanced PM2.5 air quality forecast model based on nonlinear regression and back-trajectory concentrations. Atmospheric Environment, 2010, 44 (25):3015-3023 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.05.009 [13] Voukantsis D, Karatzas K, Kukkonen J, Räsänen T, Karppinen A, Kolehmainen M. Intercomparison of air quality data using principal component analysis, and forecasting of PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations using artificial neural networks, in Thessaloniki and Helsinki. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409 (7):1266-1276 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.12.039 [14] Xia D H, Jiang B F, Xie Y L. Modeling and analysis of PM2.5 generation for key factors identification in China. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 134:208-216 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.03.055 [15] De Ridder K, Kumar U, Lauwaet D, Blyth L, Lefebvre W. Kalman filter-based air quality forecast adjustment. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 50:381-384 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.01.032 [16] de Gennaro G, Trizio L, Gilio A D, Pey J, Pérez N, Cusack M, Alastuey A, Querol X. Neural network model for the prediction of PM10 daily concentrations in two sites in the Western Mediterranean. Science of The Total Environment, 2013, 463-464:875-883 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.093 [17] Feng X, Li Q, Zhu Y J, Hou J X, Jin L Y, Wang J J. Artificial neural networks forecasting of PM2.5 pollution using air mass trajectory based geographic model and wavelet transformation. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 107:118-128 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.030 [18] Tan S F, Mayrovouniotis M L. Reducing data dimensionality through optimizing neural network inputs. AIChE Journal, 1995, 41 (6):1471-1480 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905 [19] Hinton G E, Osindero S, The Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18 (7):1527-1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [20] 乔俊飞, 潘广源, 韩红桂.一种连续型深度信念网的设计与应用.自动化学报, 2015, 41 (12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtmlQiao Jun-Fei, Pan Guang-Yuan, Han Hong-Gui. Design and application of continuous deep belief network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41 (12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtml [21] 李尔国, 俞金寿.一种基于输入训练神经网络的非线性PCA故障诊断方法.控制与决策, 2003, 18 (2):229-232 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kzyc200302023&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLi Er-Guo, Yu Jin-Shou. An input-training neural network based nonlinear principal component analysis approach for fault diagnosis. Control and Decision, 2003, 18 (2):229-232 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kzyc200302023&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [22] He R, Hu B G, Yuan X T, Zheng W S. Principal component analysis based on non-parametric maximum entropy. Neurocomputing, 2010, 73 (10-12):1840-1852 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2009.12.032 [23] 武妍, 张立明.神经网络的泛化能力与结构优化算法研究.计算机应用研究, 2002, 19 (6):21-25, 84 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsyj200206006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWu Yan, Zhang Li-Ming. A survey of research work on neural network generalization and structure optimization algorithms. Application Research of Computers, 2002, 19 (6):21-25, 84 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsyj200206006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [24] Deco G, Finnoff W, Zimmermann H G. Unsupervised mutual information criterion for elimination of overtraining in supervised multilayer networks. Neural Computation, 1995, 7 (1):86-107 doi: 10.1162/neco.1995.7.1.86 [25] 吴新根, 吕维雪.一种基于信息熵的神经网络规则表示.计算机工程, 1996, 22 (5):46-51 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsjc605.010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWu Xin-Gen, Lv Wei-Xue. A neural network rule expression based on information entropy. Computer Engineering, 1996, 22 (5):46-51 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsjc605.010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [26] Sánchez D, Melin P, Castillo O. Optimization of modular granular neural networks using a hierarchical genetic algorithm based on the database complexity applied to human recognition. Information Sciences, 2015, 309:73-101 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.02.020 [27] Wang L T, Wei Z, Yang J, Zhang Y, Zhang F F, Su J, et al. The 2013 severe haze over southern Hebei, China:model evaluation, source apportionment, and policy implications. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, 2013, 13 (11):28395-28451 doi: 10.5194/acpd-13-28395-2013 [28] Peng K X, Zhang K, Li G. Online contribution rate based fault diagnosis for nonlinear industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40 (3):423-430 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(14)60005-7 [29] Yao L, Yang L X, Yuan Q, Yan C, Dong C, Meng C P, et al. Sources apportionment of PM2.5 in a background site in the North China Plain. Science of The Total Environment, 2016, 541:590-598 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.123 -




 下载:
下载: