-
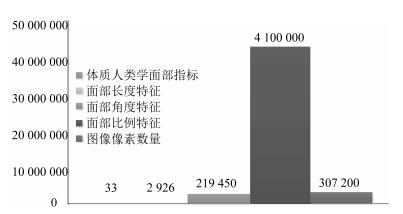
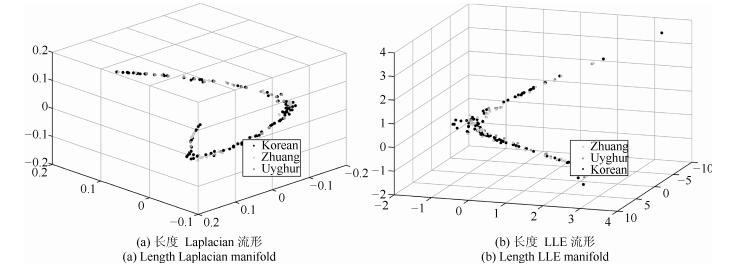
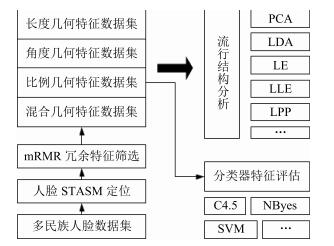
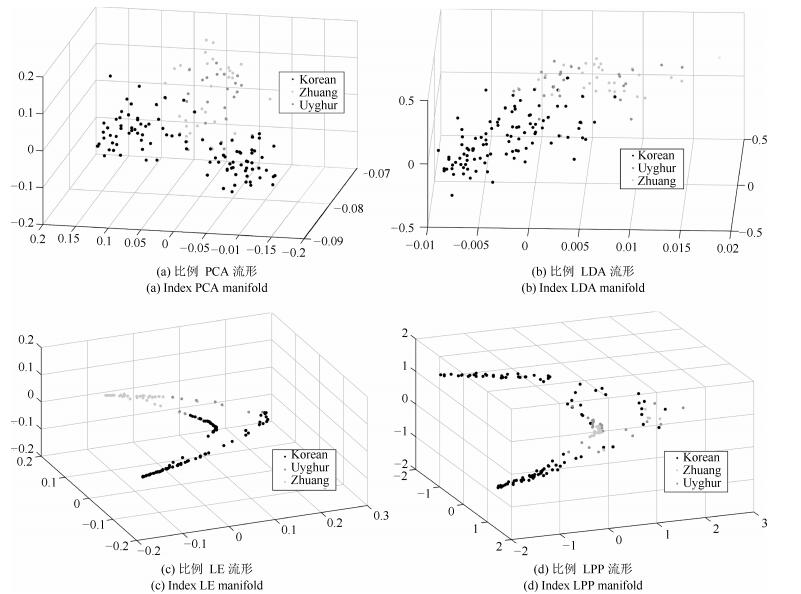
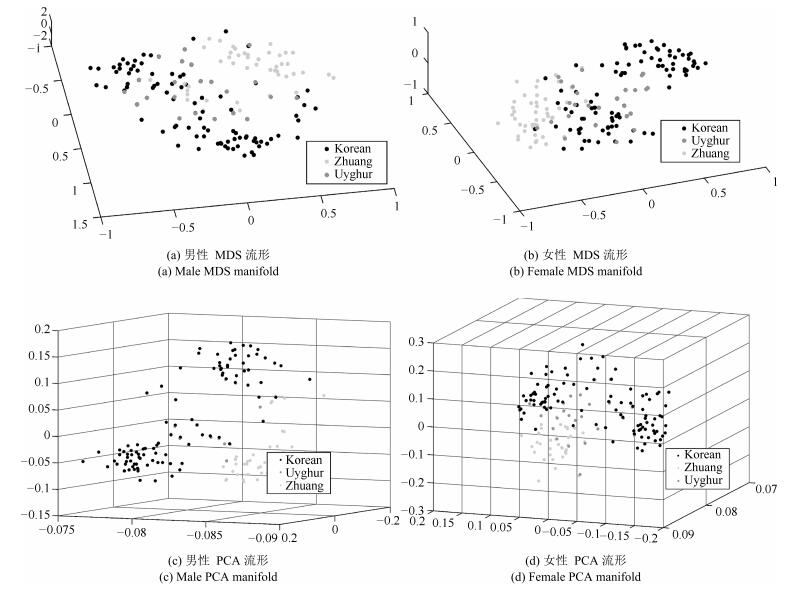
摘要: 人脸民族特征选取与分析是人脸识别与人类学重要研究方向之一.本文建立了中国三个民族人脸数据库,通过流形结构来研究和分析人脸的民族特征.首先,在体质人类学定义的人脸几何特征指标进行流形分析,未形成按语义分布的子流形.因此本文将人脸特征扩至全部组合的长度、角度和比例特征进行分析,利用mRMR算法对2926个长度特征、21万余个角度特征、427万个比例特征中冗余特征进行筛选,加上人类学指标及混合筛选的数据集共形成5个数据集.利用LPP、Isomap、LE、PCA和LDA等流形方法分析5数据集,其中的4个数据集都形成了民族语义的子流形分布.为验证筛选特征指标的有效性,本文利用分类算法J48、SVM、RBF network、Naive Bayes、Bayes network在Weka平台对数据集以族群语义作为类别进行交叉验证实验,实验结果表明混合特征的人脸数据集族群分类平均准确率最高,且比例特征分类指标优于其他特征数据集.本文通过大量实验揭示了民族人脸数据可在子空间内形成按民族语义分布的子流形结构.中国三个民族人脸特征在低维空间存在不同民族语义的子流形,通过流形分析和特征筛选构建的人脸测量指标不仅可为人脸族群分析提供方法,同时也将丰富和补充体质人类学的相关研究工作.Abstract: Facial ethnic feature selection and analysis is one of the most significant research focuses in face recognition and anthropology. In this paper, we build a Chinese ethnic face database including three ethnic groups. Manifold learning is used to analyze facial ethnic features. Firstly, we conduct manifold analysis on the basis of facial geometric indicators proposed by anthropologist, which, however, does not formulate sub-manifold distributed by semantics. Therefore, we intend to expand the scope of facial features by calculating the complete distances, angles and indexes with landmarks. Then, we adopt mRMR to filter 2926 distance indicators, more than 219450 angle indicators and more than 4279275 index indicators. Finally, we can obtain 5 datasets with features of distance, angle, index, anthropology and mixing. Several popular manifold learning methods including LPP, ISOMAP, LE, PCA and LDA are utilized to study the above mentioned datasets, and we get the distinguishable manifold structure of facial ethic feature and clusters in 4 of the 5 datasets. To evaluate the validity of filtered features, we make use of classification algorithms including J48, SVM, RBF network, Naive Bayes, and Bayes network implemented in Weka for cross validation experiments by ethnic semantics. Experimental results indicate that the average of classification accuracy on the dataset with mixing features is higher than that of other datasets, and that the index is more salient than other geometric features. Moreover, by full experimental investigation, we find that ethnic facial data can generate sub-manifold structure distributed by semantics. Facial features of three Chinese ethnic groups exhibit different ethnic semantic sub-manifolds in the low-dimensional space. Facial measurement indicators obtained by manifold analysis and feature selection not only provide a method for facial ethnic groups analysis, but also enrich and improve the related research work in anthropology.
-
Key words:
- Facial ethnic features /
- biometrics recognition /
- face recognition /
- manifold learning
1) 本文责任编委 杨健 -
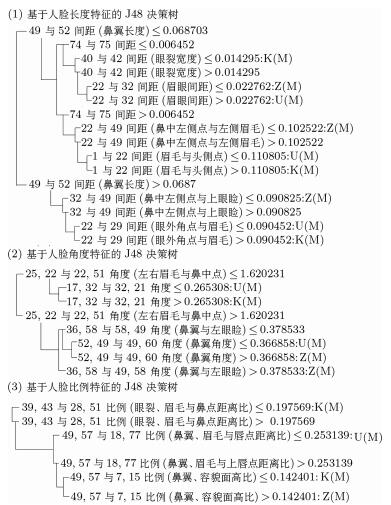
民族 人口数量 人口比例(%) 地理位置 壮族 16 926 381 1.27 广西 维吾尔族 10 069 346 0.76 新疆 朝鲜族 1 830 929 0.14 吉林 表 2 筛选的几何特征
Table 2 The selected geometric features
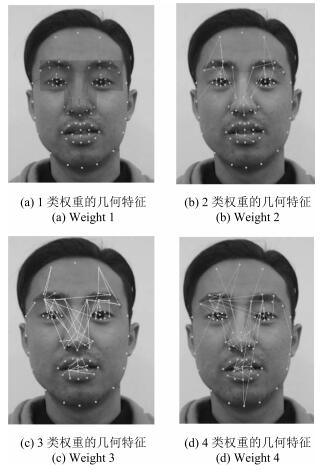
长度几何特征 角度几何特征 比例几何特征 特征维度 2 926 219 450 4 279 275 筛选后特征维度 195 250 500 表 3 mRMR筛选的4个权重范围的长度特征
Table 3 The selected distance-based features by mRMR
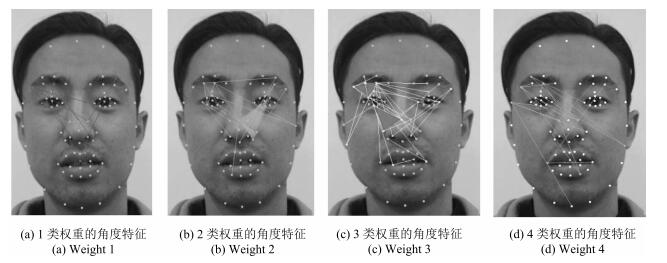
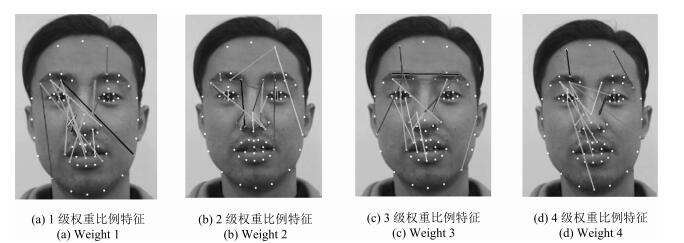
权重 权重区域特点 1 眼裂宽度、眉眼距离、眉与鼻翼距离、鼻翼长度特征 2 眉毛各长度特征、额头宽度、鼻翼与眼内角距离、下唇厚度 3 更为精细的鼻部和嘴部几何长度特征 4 嘴部与眉尖距离, 嘴部与下颚距离, 眉与耳朵距离 人类学常用指标体系 头长、头宽、面宽、鼻宽、鼻高、唇厚、口裂宽、内眼角宽、外眼角间距、内眼角间距、颧间宽、下颌长度、下颌角间距 表 4 mRMR筛选的4个权重范围的角度特征
Table 4 The selected angle features by mRMR
权重 角点 权重区域特点 1 眉尖点 眉毛与内眼角点和鼻根部形成的角度关系 2 鼻根点, 眉尖点, 形成鼻翼与鼻眼角度关系热区, 耳位置点 通过角度度量眉眼距离关系 3 眉、眼角点 眼裂角度, 眉眼之间角度关系, 鼻翼角度关系 4 眉和嘴部 更为精细的眼鼻嘴之间定位关系 表 5 体质人类学定义的15个正脸指数
Table 5 The 15 Physical anthropological definition of 15 frontal face index
序号 指数特征名称 1 头宽高指数 2 额顶宽指数 3 头面宽指数 4 形态面指数 5 形态上面指数 6 容貌面指数 7 颧下颌宽度指数 8 颧额宽指数 9 容貌上面指数 10 额面指数 11 容貌上面高 12 头面高指数 13 鼻指数 14 鼻宽深指数 15 唇指数 表 6 不同权重的比例特征
Table 6 The index features with different weight
序号 权重区域特点 权重值 (眼裂高度) / (眉眼距离) 0.329 1 (眼裂高度) / (鼻翼与眉毛距离) 0.362 (鼻翼与眉毛距离)/ (嘴部与眉尖) 0.312 (鼻翼与眼内角点距离) / (额头高度) 0.35 (眼裂高度) / (鼻翼与眉毛距离) 0.302 2 (鼻翼长度) / (眉眼距离) 0.302 (眉眼距离) / (眉毛与鼻翼距离) 0.301 (鼻翼长度) / (眉毛与嘴部距离) 0.302 (眼裂高度) / (鼻翼与眉毛距离) 0.30 3 (鼻翼与眼内角点距离) / (额头高度) 0.294 (鼻翼距离) / (嘴巴与眼外角点距离) 0.297 (眉间距) / (鼻翼与眼内角距离) 0.297 (眼裂高度) / (鼻翼与眼内角点距离) 0.274 4 (眉毛与上唇距离) / (眉毛与下唇距离) 0.283 (鼻翼长度) / (眼睛与下颌距离) 0.281 表 7 长度、角度筛选出的51个人脸几何特征
Table 7 The selected 51 geometric features from distance-based and angular attributes
ID 类型 详细 权重 ID 类型 详细 权重 1 I (49, 57)/(22, 7) 0.669 27 I (39, 43)/(7, 22) 0.299 2 I (35, 47)/(23, 51) 0.362 28 I (49, 69)/(34, 72) 0.296 3 I (37, 51)/(16, 24) 0.35 29 I (22, 73)/(21, 64) 0.298 4 I (39, 43)/(22, 36) 0.329 30 I (49, 52)/(15, 7) 0.296 5 I (50, 71)/(33, 60) 0.33 31 I (35, 47)/(28, 51) 0.298 6 I (49, 52)/(5, 17) 0.312 32 I (25, 50)/(21, 27) 0.292 7 I (22, 76)/(21, 54) 0.312 33 I (37, 51)/(14, 19) 0.294 8 I (51, 59)/(22, 45) 0.302 34 A ∠(21, 55, 26) 0.289 9 I (31, 35)/(37, 51) 0.305 35 I (39, 43)/(28, 51) 0.287 10 A ∠(51, 59, 27) 0.311 36 I (49, 52)/(22, 38) 0.289 11 I (39, 43)/(20, 58) 0.302 37 I (49, 76)/(35, 72) 0.289 12 I (37, 59)/(14, 22) 0.302 38 I (50, 52)/(22, 60) 0.286 13 I (17, 36)/(23, 50) 0.302 39 I (35, 47)/(23, 50) 0.287 14 I ∠(31, 22, 33) 0.297 40 I (49, 52)/(7, 35) 0.287 15 I (49, 52)/(60, 74) 0.304 41 I (22, 53)/(21, 50) 0.284 16 I (50, 55)/(17, 55) 0.301 42 I (50, 70)/(33, 60) 0.285 17 I (18, 21)/(33, 49) 0.302 43 A ∠(17, 49, 21) 0.285 18 I (35, 60)/(21, 54) 0.305 44 I (37, 51)/(16, 24) 0.285 19 I (39, 43)/(23, 51) 0.303 45 I (37, 51)/(16, 24) 0.282 20 I (37, 51)/(18, 25) 0.301 46 A ∠(51, 25, 59) 0.283 21 I (22, 73)/(21, 76) 0.347 47 A ∠(35, 29, 49) 0.284 22 I (49, 52)/(24, 66) 0.303 48 I (49, 57)/(22, 43) 0.282 23 I (49, 57)/(14, 22) 0.302 49 I (39, 43)/(19, 49) 0.282 24 I (50, 57)/(29, 61) 0.296 50 A ∠(21, 49, 25) 0.281 25 A ∠(21, 36, 22) 0.299 51 I (31, 35)/(24, 51) 0.279 26 A ∠(22, 60, 50) 0.298 注: I代表长度, A代表角度 表 8 混合指标中的特征边与点的频繁项集
Table 8 The frequent itemsets of the characteristic edge and point in the mixed attributes
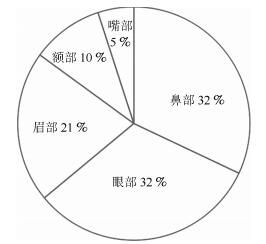
ID 边 支持度 说明 ID 点 支持度 部位 1 39 ~ 43 6 眼裂 1 22 16 眉 2 49 ~ 52 6 鼻翼长度 2 49 16 鼻 3 37 ~ 51 4 鼻眼距离 3 51 14 鼻 4 35 ~ 47 3 眼裂 4 21 11 眉 5 49 ~ 57 3 鼻翼宽度 5 50 10 鼻 6 22 ~ 73 2 眉嘴距离 6 35 9 眼 7 31 ~ 35 2 眼裂 7 37 7 眼 8 14 ~ 22 2 额头高度1 8 43 7 眼 9 16 ~ 24 2 额头高度2 9 52 7 鼻 10 21 ~ 54 2 眉鼻距离1 10 39 6 眼 11 23 ~ 50 2 眉鼻距离2 11 24 5 眉 12 23 ~ 51 2 眉鼻距离3 12 57 4 鼻 13 23 4 眉 14 31 3 眼 15 46 3 眼 16 14 3 额头 17 16 3 额头 18 73 2 嘴 19 54 2 鼻 表 9 J48交叉验证学习后结果指标
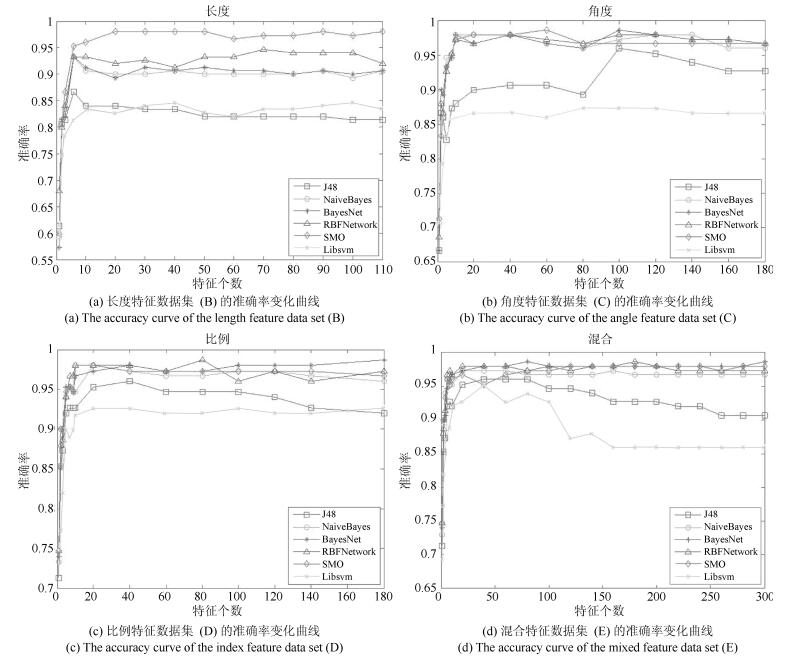
Table 9 J48 cross validation results after feature learning
DataSet Sex TP Rate FP Rate Precision Recall F-Measure AUC A M 0.753 0.123 0.753 0.753 0.753 0.814 B M 0.833 0.083 0.834 0.833 0.833 0.879 C M 0.92 0.04 0.921 0.921 0.921 0.935 D M 0.90 0.05 0.902 0.9 0.90 0.935 E M 0.96 0.02 0.96 0.96 0.96 0.975 A F 0.727 0.137 0.725 0.727 0.724 0.775 B F 0.773 0.113 0.776 0.773 0.773 0.863 C F 0.813 0.093 0.814 0.813 0.812 0.853 D F 0.767 0.117 0.765 0.767 0.764 0.844 E F 0.813 0.093 0.818 0.813 0.814 0.888 表 10 Naive Bayes实验结果
Table 10 Naive Bayes experimental results
DataSet Sex TP Rate FP Rate Precision Recall F-Measure AUC A M 0.82 0.09 0.821 0.82 0.82 0.927 B M 0.90 0.05 0.903 0.90 0.901 0.96 C M 0.96 0.02 0.96 0.96 0.96 0.993 D M 0.967 0.017 0.968 0.967 0.967 0.992 E M 0.973 0.013 0.974 0.973 0.973 0.999 A F 0.773 0.113 0.779 0.773 0.772 0.882 B F 0.753 0.123 0.755 0.753 0.750 0.902 C F 0.893 0.053 0.894 0.893 0.893 0.947 D F 0.887 0.057 0.889 0.887 0.887 0.956 E F 0.92 0.04 0.921 0.92 0.92 0.979 表 11 Bayes network实验结果
Table 11 Bayes network experimental results
DataSet Sex TP Rate FP Rate Precision Recall F-Measure AUC A M 0.793 0.103 0.793 0.793 0.793 0.923 B M 0.893 0.053 0.897 0.893 0.894 0.962 C M 0.967 0.017 0.967 0.967 0.967 0.995 D M 0.967 0.017 0.967 0.967 0.967 0.992 E M 0.967 0.017 0.967 0.987 0.987 1.0 A F 0.733 0.133 0.735 0.733 0.734 0.883 B F 0.767 0.117 0.766 0.767 0.766 0.898 C F 0.887 0.057 0.888 0.887 0.887 0.951 D F 0.900 0.05 0.901 0.9 0.9 0.964 E F 0.913 0.043 0.914 0.913 0.913 0.983 表 12 RBF network实验结果
Table 12 RBF network experimental results
DataSet Sex TP Rate FP Rate Precision Recall F-Measure AUC A M 0.773 0.113 0.775 0.773 0.773 0.871 B M 0.913 0.043 0.915 0.913 0.914 0.947 C M 0.967 0.017 0.967 0.967 0.967 0.978 D M 0.973 0.013 0.974 0.973 0.973 0.976 E M 0.993 0.003 0.993 0.993 0.993 0.994 A F 0.753 0.123 0.753 0.753 0.753 0.866 B F 0.807 0.097 0.805 0.807 0.805 0.904 C F 0.900 0.050 0.900 0.900 0.900 0.937 D F 0.893 0.053 0.893 0.893 0.893 0.943 E F 0.907 0.047 0.909 0.907 0.907 0.94 表 13 SVM中LibSVM实验结果
Table 13 SVM in LibSVM experimental results
DataSet Sex TP Rate FP Rate Precision Recall F-Measure AUC A M 0.773 0.113 0.775 0.773 0.772 0.83 B M 0.82 0.09 0.823 0.82 0.823 0.865 C M 0.86 0.07 0.858 0.86 0.857 0.895 D M 0.933 0.033 0.934 0.933 0.933 0.95 E M 0.953 0.023 0.953 0.953 0.953 0.965 A F 0.733 0.133 0.752 0.733 0.734 0.8 B F 0.720 0.14 0.758 0.72 0.713 0.79 C F 0.667 0.167 0.715 0.667 0.608 0.75 D F 0.860 0.07 0.862 0.86 0.859 0.895 E F 0.92 0.04 0.922 0.92 0.92 0.94 表 14 SVM中SMO实验结果
Table 14 SVM in SMO experimental results
DataSet Sex TP Rate FP Rate Precision Recall F-Measure AUC A M 0.893 0.053 0.895 0.893 0.893 0.944 B M 0.967 0.017 0.967 0.967 0.967 0.982 C M 0.967 0.017 0.967 0.967 0.967 0.983 D M 0.973 0.013 0.974 0.973 0.973 0.985 E M 0.973 0.013 0.973 0.973 0.973 0.985 A F 0.867 0.067 0.868 0.867 0.867 0.922 B F 0.907 0.047 0.907 0.907 0.907 0.947 C F 0.907 0.047 0.907 0.907 0.907 0.943 D F 0.933 0.033 0.934 0.933 0.934 0.965 E F 0.953 0.023 0.954 0.953 0.953 0.97 表 15 SVM中SMO实验结果
Table 15 SVM in SMO experimental results
性别 J48 Naive Bayes BayesNet M(20长度特征) 80.00±1.83 89.33±1.04 79.30±1.62 M(195长度特征) 83.33±2.21 90.00±1.06 89.33±0.69 M(250角度特征) 92.00±1.05 96.00±0.55 96.70±0.85 M(400角度特征) 90.00±1.11 96.70±0.47 96.70±0.28 M(51混合特征) 96.00±0.55 97.33±0.21 98.67±0.53 F(20长度特征) 72.67±2.31 77.33±1.44 73.33±1.94 F(195长度特征) 77.33±1.51 75.33±1.21 76.67±1.20 F(250角度特征) 81.33±2.78 89.33±0.95 88.67±0.47 F(400角度特征) 76.67±2.51 88.67±0.55 90.00±0.38 F(51混合特征) 81.33±2.10 92.00±0.35 91.33±0.32 M(20长度特征) 77.33±2.17 89.33±1.65 77.33±1.03 M(195长度特征) 91.33±0.95 96.67±0.54 82.00±0.99 M(250角度特征) 96.70±0.85 96.70±0.56 86.00±0.32 M(400角度特征) 97.30±0.35 97.30±0.61 93.30±0.52 M(51混合特征) 99.33±1.25 97.33±0.49 95.33±0.49 F(20长度特征) 75.33±2.87 86.67±1.19 73.33±1.67 F(195长度特征) 80.67±1.14 90.67±1.29 72.00±1.43 F(250角度特征) 90.00±1.10 90.67±0.88 66.67±1.08 F(400角度特征) 89.33±0.85 93.33±1.30 86.00±0.73 F(51混合特征) 90.67±0.94 95.33±0.76 92.00±0.89 -
[1] Calder A J, Rhodes G, Johnson M, Haxby J. The Oxford Handbook of Face Perception. Oxford:Oxford University Press, 2011. [2] Bruce V, Young A. Understanding face recognition. British Journal of Psychology, 1986, 77(3):305-327 doi: 10.1111/bjop.1986.77.issue-3 [3] 苏连成, 朱枫.一种新的全向立体视觉系统的设计.自动化学报, 2006, 32(1):67-72 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract15769.shtmlSu Lian-Cheng, Zhu Feng. Design of a novel omnidirectional stereo vision system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 32(1):67-72 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract15769.shtml [4] O'Toole A J, Roark D A, Abdi H. Recognizing moving faces:a psychological and neural synthesis. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2002, 6(6):261-266 doi: 10.1016/S1364-6613(02)01908-3 [5] Eberhardt J L, Dasgupta N, Banaszynski T L. Believing is seeing:the effects of racial labels and implicit beliefs on face perception. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 2003, 29(3):360-370 doi: 10.1177/0146167202250215 [6] Kumar N, Berg A, Belhumeur P N, Nayar S. Describable visual attributes for face verification and image search. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(10):1962-1977 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.48 [7] Demirkus M, Garg K, Guler S. Automated person categorization for video surveillance using soft biometrics. In: Proceedings of the 2010 SPIE 7667, biometric technology for human identification Ⅶ. Orlando, Florida, USA: SPIE, 2010. Article No. 76670P doi: 10.1117/12.851424 [8] Senior A, Pankanti S, Hampapur A, Brown L, Tian Y L, Ekin A, Connell J, Shu C F, Lu M. Enabling video privacy through computer vision. IEEE Security and Privacy, 2005, 3(3):50-57 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2005.65 [9] Ito T A, Bartholow B D. The neural correlates of race. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2009, 13(12):524-531 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2009.10.002 [10] 张继宗.中国体质人类学研究.北京:科学出版社, 2010.Zhang Ji-Zong. The Research of Chinese Physical Anthropology. Beijing:Science Press, 2010. [11] 席焕久.体质人类学.北京:知识产权出版社, 2012.Xi Huan-Jiu. Physical Anthropology. Beijing:Intellectual Property Publish House, 2012. [12] Bledsoe W W. Man-Machine Facial Recognition. Panoramic Research Inc. Palo Alto, CA, Report PRI: 22, 1966. [13] Kanade T. Picture Processing System by Computer Complex and Recognition of Human Faces[Ph. D. dissertation]. Kyoto University, Japan, 1973 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/239021259_Picture_Processing_by_Computer_Complex_and_Recognition_of_Human_Faces [14] Brunelli R, Poggio T. Face recognition:features versus templates. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1993, 15(10):1042-1052 doi: 10.1109/34.254061 [15] Malpass R S, Kravitz J. Recognition for faces of own and other race. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1969, 13(4):330-334 doi: 10.1037/h0028434 [16] Lindsay D S, Jack P C, Christian M A. Other-race face perception. Journal of Applied Psychology, 1991, 76(4):587-589 doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.76.4.587 [17] Li Z, Duan X, Zhang Q, Wang C R, Wang Y G, Liu W Q. Multi-ethnic facial features extraction based on axiomatic fuzzy set theory. Neurocomputing, 2017, 242:161-177 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.070 [18] Hadid A, Pietikäinen M. Demographic classification from face videos using manifold learning. Neurocomputing, 2013, 100:197-205 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2011.10.040 [19] Seung H S, Lee D D. The manifold ways of perception. Science, 2000, 290(5500):2268-2269 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2268 [20] Fu S Y, He H B, Hou Z G. Learning race from face:a survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(12):2483-2509 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2321570 [21] Duan X D, Wang C R, Liu X D, Li Z J, Wu J, Zhang H L. Ethnic features extraction and recognition of human faces. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computer Control (ICACC). Shenyang, China: IEEE, 2010. 125-130 [22] 段晓东, 王存睿, 刘向东, 刘慧.人脸的民族特征抽取及其识别.计算机科学, 2010, 37(8):276-279, 301 http://www.docin.com/p-1301615906.htmlDuan Xiao-Dong, Wang Cun-Rui, Liu Xiang-Dong, Liu Hui. Minorities features extraction and recognition of human faces. Computer Science, 2010, 37(8):276-279, 301 http://www.docin.com/p-1301615906.html [23] Li Z D, Duan X D, Zhang Q L. A novel survey based on multiethnic facial semantic web. TELKOMNIKA, 2013, 11(9):5076-5083 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Qingling_Zhang4/publication/275415292_A_Novel_Survey_Based_on_Multiethnic_Facial_Semantic_Web/links/5675798408aebcdda0e46b5e.pdf?inViewer=0&pdfJsDownload=0&origin=publication_detail [24] 段晓东, 李泽东, 王存睿, 张庆灵, 刘晓东.基于AFS的多民族人脸语义描述与挖掘方法研究.计算机学报, 2016, 39(7):1435-1449 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2016.01435Duan Xiao-Dong, Li Ze-Dong, Wang Cun-Rui, Zhang Qing-Ling, Liu Xiao-Dong. Multi-ethnic face semantic description and mining method based on AFS. Chinese Journal of Computer, 2016, 39(7):1435-1449 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2016.01435 [25] Turk M, Pentland A. Eigenfaces for recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 1991, 3(1):71-86 doi: 10.1162/jocn.1991.3.1.71 [26] Belhumeur P N, Hespanha J P, Kriegman D J. Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces:recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1997, 19(7):711-720 doi: 10.1109/34.598228 [27] Bartlett M S, Movellan J R, Sejnowski T J. Face recognition by independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2002, 13(6):1450-1464 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2002.804287 [28] Yang J, Zhang D, Frangi A F, Yang J Y. Two-dimensional PCA:a new approach to appearance-based face representation and recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(1):131-137 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.1261097 [29] Li M, Yuan B Z. 2D-LDA:a statistical linear discriminant analysis for image matrix. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2005, 26(5):527-532 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2004.09.007 [30] Tenenbaum J B, de Silva V, Langford J C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science, 2000, 290(5500):2319-2323 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2319 [31] Belkin M, Niyogi P. Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation. Neural Computation, 2003, 15(6):1373-1396 doi: 10.1162/089976603321780317 [32] He X F, Niyogi X. Locality preserving projections. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2004, 16(4):153-160 [33] He X F, Yan S C, Hu Y X, Niyogi P, Zhang H J. Face recognition using Laplacianfaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(3):328-340 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.55 [34] He X F, Cai D, Yan S C, Zhang H J. Neighborhood preserving embedding. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005, 2: 1208-1213 [35] 詹德川, 周志华.基于集成的流形学习可视化.计算机研究与发展, 2005, 42(9):1533-1537 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXJY201508008.htmZhan De-Chuan, Zhou Zhi-Hua. Ensemble-based manifold learning for visualization. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2005, 42(9):1533-1537 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXJY201508008.htm [36] 何力, 张军平, 周志华.基于放大因子和延伸方向研究流形学习算法.计算机学报, 2005, 28(12):2000-2009 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2005.12.007He Li, Zhang Jun-Ping, Zhou Zhi-Hua. Investigating manifold learning algorithms based on magnification factors and principal spread directions. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2005, 28(12):2000-2009 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2005.12.007 [37] 曾宪华, 罗四维.动态增殖流形学习算法.计算机研究与发展, 2007, 44(9):1462-1468 https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/d9249222a32d7375a417801c.htmlZeng Xian-Hua, Luo Si-Wei. A dynamically incremental manifold learning algorithm. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2007, 44(9):1462-1468 https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/d9249222a32d7375a417801c.html [38] Chen S B, Zhao H F, Kong M, Luo B. 2D-LPP:a two-dimensional extension of locality preserving projections. Neurocomputing, 2007, 70(4-6):912-921 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2006.10.032 [39] 张大明, 符茂胜, 罗斌.基于二维近邻保持嵌入的图像识别.模式识别与人工智能, 2011, 24(6):810-815 http://www.oalib.com/paper/4238112Zhang Da-Ming, Fu Mao-Sheng, Luo Bin. Image recognition with two-dimensional neighbourhood preserving embedding. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2011, 24(6):810-815 http://www.oalib.com/paper/4238112 [40] Li Z D, Zhang Q L, Duan X D, Wang C R, Shi Y. New semantic descriptor construction for facial expression recognition based on axiomatic fuzzy set. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 1:1-31 doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-4818-3 [41] Roweis S T, Saul L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science, 2000, 290(5500):2323-2326 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2323 [42] Li Z D, Zhang Q L, Duan X D, Wei W. Semantic knowledge based on fuzzy system for describing facial expression. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Control Conference. 2017: 9865-9870 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/320114803_Semantic_knowledge_based_on_fuzzy_system_for_describing_facial_expression [43] Guo G D, Fu Y, Dyer C R, Huang T S. Image-based human age estimation by manifold learning and locally adjusted robust regression. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(7):1178-1188 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.924280 [44] Yan S C, Xu D, Zhang B Y, Zhang H J. Graph embedding: a general framework for dimensionality reduction. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2005, 2: 830-837 [45] 续爽, 贾云得.基于表情相似性的人脸表情流形.软件学报, 2009, 20(8):2191-2198 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/JSJF201702007.htmXu Shuang, Jia Yun-De. Facial expression manifold based on expression similarity. Journal of Software, 2009, 20(8):2191-2198 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/JSJF201702007.htm [46] 李小林. 中国南方五个少数民族人群面部五官形态特征研究[硕士学位论文], 重庆医科大学, 中国, 2008 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1353533Li Xiao-Lin. Analysis of Morphous Characteristics of Facial Reconstruction and the Five Organs in Chinese South Five National Minorities Crowd[Master dissertation], Chongqing Medical University, China, 2008 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1353533 [47] 赵明, 文建军, 赵霞, 孙嬿嬿.藏、蒙、土、回、汉五民族青年面部测量数据分析.青海医学院学报, 1995, 16(3):7-8 http://paper.usc.cuhk.edu.hk/Details.aspx?id=5247Zhao Ming, Wen Jian-Jun, Zhao Xia, Sun Yan-Yan. An analysis on measuring data of face in 169 young students of Tibetan, Mongolian, Tu, Huis, and Han nationality. Journal of Qinghai Medical College, 1995, 16(3):7-8 http://paper.usc.cuhk.edu.hk/Details.aspx?id=5247 [48] 席焕久, 陈昭.人体测量方法.第2版.北京:科学出版社, 2010.Xi Huan-Jiu, Chen Zhao. Anthropometric Methods (Second edition). Beijing:Science Press, 2010. [49] Wang X, Liu X, Zhang L. A rapid fuzzy rule clustering method based on granular computing. Applied Soft Computing, 2014, 24(C):534-542 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S156849461400369X [50] Heo J, Savvides M. Gender and ethnicity specific generic elastic models from a single 2D image for novel 2D pose face synthesis and recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(12):2341-2350 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.275 [51] Feng Ding-Cheng, Chen Feng, Xu Wen-Li. Detecting local manifold structure for unsupervised feature selection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(10):2253-2261 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(14)60362-1 [52] 王朝云, 蒋刚毅, 郁梅, 陈芬.基于流形特征相似度的感知图像质量评价.自动化学报, 2016, 42(7):1113-1124 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2016/V42/I7/1113Wang Chao-Yun, Jiang Gang-Yi, Yu Mei, Chen Fen. Manifold feature similarity based perceptual image quality assessment. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(7):1113-1124 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2016/V42/I7/1113 [53] Huang D, Shan C, Ardabilian M, Wang Y, Chen L. Local binary patterns and its application to facial image analysis:a survey. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C:Applications and Reviews. 2011, 41:765-781 doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2011.2118750 [54] Wang Y G, Duan X D, Liu X D, Wang C R, Li Z D. Semantic description method for face features of larger Chinese ethnic groups based on improved WM method. Neurocomputing, 2016, 175:515-528 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.089 [55] Milborrow S, Nicolls F. Active shape models with SIFT descriptors and MARS. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP). Lisbon, Portugal: IEEE, 2014. 380-387 [56] Ding C, Peng H C. Minimum redundancy feature selection from microarray gene expression data. Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 2005, 3(2):185-205 doi: 10.1142/S0219720005001004 [57] Peng H C, Long F H, Ding C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(8):1226-1238 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159 [58] 洪泉, 陈松灿, 倪雪蕾.子模式典型相关分析及其在人脸识别中的应用.自动化学报, 2008, 34(1):21-30 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16043.shtmlHong Quan, Chen Song-Can, Ni Xue-Lei. Sub-pattern canonical correlation analysis with application in face recognition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(1):21-30 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16043.shtml [59] 高全学, 潘泉, 梁彦, 张洪才, 程咏梅.基于描述特征的人脸识别研究.自动化学报, 2006, 32(3):386-392 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract15824.shtmlGao Quan-Xue, Pan Quan, Liang Yan, Zhang Hong-Cai, Cheng Yong-Mei. Face recognition based on expressive features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 32(3):386-392 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract15824.shtml [60] Bouckaert R R, Frank E, Hall M A, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten I H. WEKA-experiences with a java open-source project. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11:2533-2541 https://researchcommons.waikato.ac.nz/handle/10289/4766 [61] Han J W, Kamber M, Pei J. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques (Third edition). Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2011. [62] Quinlan J R. C4. 5: Programs for Machine Learning. San Mateo, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 1993. [63] Zhang M L, Peña J M, Robles V. Feature selection for multi-label naive Bayes classification. Information Sciences, 2009, 179(19):3218-3229 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2009.06.010 [64] Gopnik A, Glymour C, Sobel D M, Schulz L E, Kushnir T, Danks D. A theory of causal learning in children:causal maps and Bayes nets. Psychological Review, 2004, 111(1):3-32 doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.111.1.3 [65] Kokshenev I, Braga A P. A multi-objective approach to RBF network learning. Neurocomputing, 2008, 71(7-9):1203-1209 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2007.11.021 [66] Joachims T. Making Large Scale SVM Learning Practical[Ph. D. dissertation]. Universität Dortmund, Germany, 1999 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/28355923_Making_Large-Scale_SVM_Learning_Practical [67] Keerthi S S, Shevade S K, Bhattacharyya C, Murthy K R K. Improvements to Platt's SMO algorithm for SVM classifier design. Neural Computation, 2001, 13(3):637-649 doi: 10.1162/089976601300014493 -




 下载:
下载: