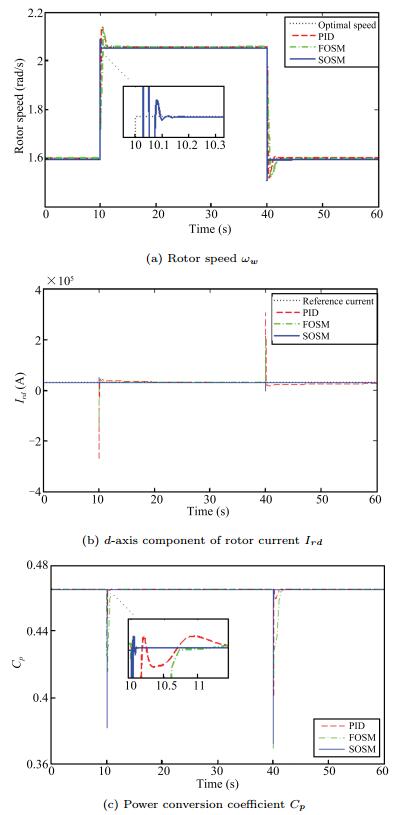
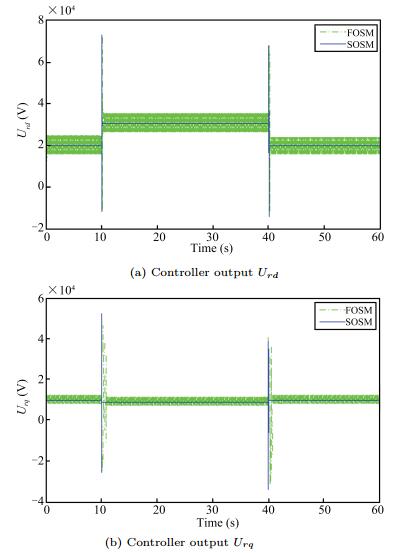
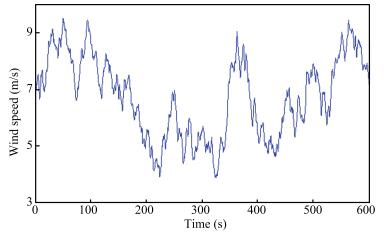
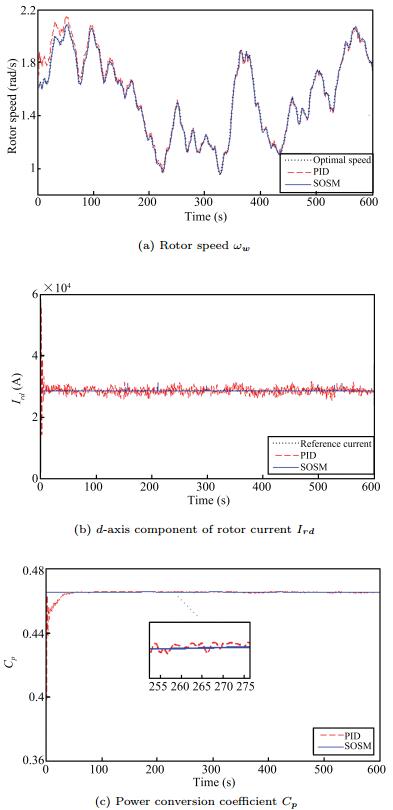
Second-order Sliding Mode Control of DFIG Based Variable Speed Wind Turbine for Maximum Power Point Tracking
-
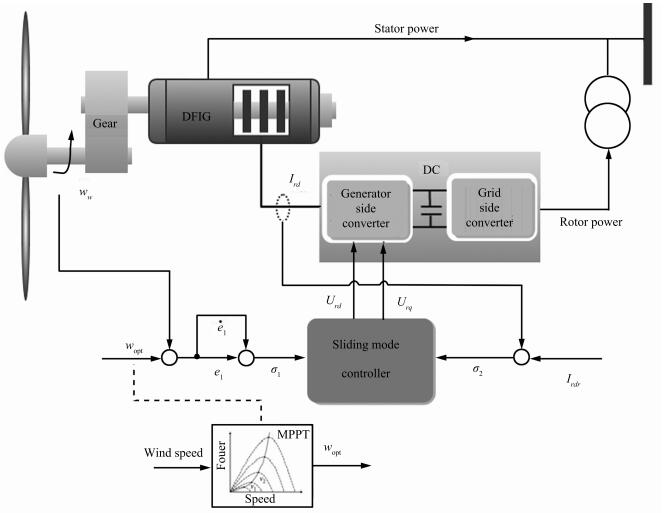
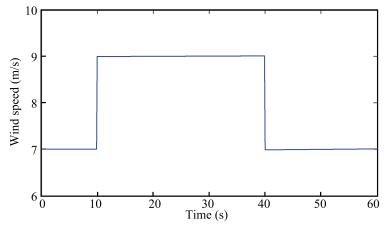
摘要: 本文提出一种超螺旋二阶滑模控制方案同时实现双馈变速风力发电系统最大风能捕获和无功功率调节.通过设计两个二阶滑模控制器,实现控制目标,降低机械磨损,提高控制精度,通过调节发电机转子电压,跟踪风机最优转速和转子电流设定值,实现额定风速以下的最大风能捕获和无功功率调节.采用二次型李雅普诺夫函数确定控制参数范围、确保系统有限时间稳定性.1.5 MW风机系统仿真实验验证所提方案有效性.Abstract: This paper proposes a super-twisting second order sliding mode control scheme to maximize the wind energy capture of a doubly fed induction generator based variable speed wind turbine (VSWT) system, and minimize the reactive power simultaneously. Two second order sliding mode controllers are designed to achieve the control objectives, reduce mechanical stress and improve control accuracy. By regulating the generator rotor voltage, one controller makes the wind turbine rotor speed track the optimal speed, which can maximize power generation. The other maintains the rotor current at rated value to minimize the reactive power. A quadratic form Lyapunov function is adopted to determine the range of controller parameters and guarantee the finite time stability. Simulation results on a 1.5MW doubly fed induction generator (DFIG)-based variable speed wind turbine demonstrate the validity of the proposed control strategy.
-
Key words:
- Doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) /
- maximum power point tracking (MPPT) /
- second order sliding mode (SOSM) control /
- variable speed wind turbine (VSWT)
-
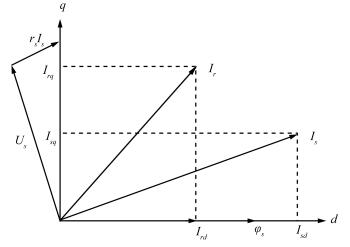
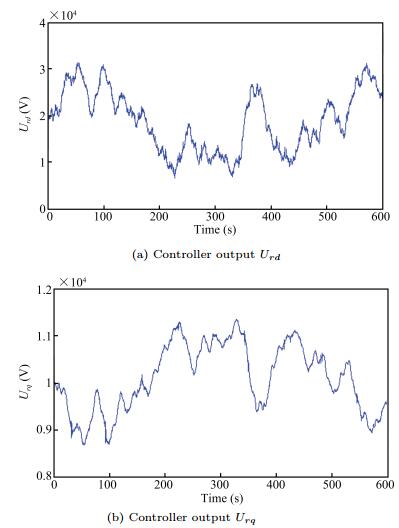
$ \omega _w $ wind turbine rotor speed; $ I_{rd} $ the $d$ -axis component of rotor current; $ I_{rq} $ the $q$ -axis component of rotor current; $ U_{rd} $ the $d$ -axis component of the rotor voltage; $ U_{rq} $ the $q$ -axis component of the rotor voltage; $ J $ the inertia of the combined rotating parts; $ K $ turbine total external damping; $ n_g $ gearbox ratio; $ \phi _s $ stator flux; $ L_m $ mutual inductance; $ L_s $ stator leakage inductance; $ L_r $ rotor leakage inductance; $ R_r $ rotor resistance; $ \omega _1 $ synchronous speed; $ n_p $ pole pair number. Table Ⅰ Characteristic of the Simulated Wind Turbine System
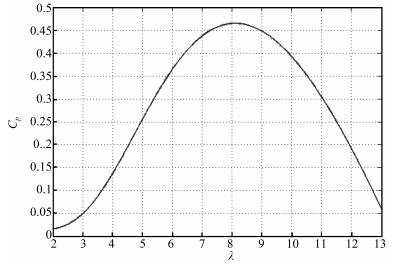
Wind turbine parameters Value Number of blades 3 Rotor radius 35 m Hub height 84.3 m Rated power 1.5 MW $ J$ $4.4532\times 10^5 {\rm kg\cdot m^2}$ $K$ $200 {\rm N\cdot m\cdot s/rad}$ $n_g$ $83.531$ $\lambda_{\rm opt} $ 8 $n_p$ $2$ $\rho$ $1.2 {\rm g/m^3}$ $U_s$ $690 {\rm V}$ $R_r$ $0.0089 {\rm \Omega}$ $\omega _1$ $1500 {\rm r/\min}$ $L_m $ $0.016 {\rm mH}$ $L_r$ $0.299 {\rm mH}$ $L_s$ $0.407 {\rm mH}$ $ \Delta K$ $40\sin (\pi / {300})t $ $ \Delta R_r$ $0.00178\sin (\pi / {300})t $ -
[1] C. Ming and Z. Ying, "The state of the art of wind energy conversion systems and technologies: A review, " Energy Convers. Manage. , vol. 88, pp. 332-347, Dec. 2014. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890414007614 [2] M. L. Corradini, G. Ippoliti, and G. Orlando, "Fully sensorless robust control of variable-speed wind turbines for efficiency maximization, " Automatica, vol. 49, no. 10, pp. 3023 -3031, Oct. 2013. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005109813003762 [3] F. Poitiers, T. Bouaouiche, and M. Machmoum, "Advanced control of a doubly-fed induction generator for wind energy conversion, " Electric Power Syst. Res. , vol. 79, no. 7, pp. 1085-1096, Jul. 2009. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378779609000352 [4] J. S. Wang, N. Tse, and Z. W. Gao, "Synthesis on PI-based pitch controller of large wind turbines generator, " Energy Convers. Manage. , vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 1288-1294, Feb. 2011. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890410004280 [5] I. Munteanu, N. A. Cutululis, A. I. Bratcu, and E. Ceangǎ, "Optimization of variable speed wind power systems based on a LQG approach, " Control Eng. Pract. , vol. 13, no. 7, pp. 903-912, Jul. 2005. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0967066104002254 [6] H. Chitsaz, N. Amjady, and H. Zareipour, "Wind power forecast using wavelet neural network trained by improved Clonal selection algorithm, " Energy Convers. Manage. , vol. 89, pp. 588-598, Jan. 2015. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890414008814 [7] S. Abdeddaim, A. Betka, S. Drid, and M. Becherif, "Implementation of MRAC controller of a DFIG based variable speed grid connected wind turbine, " Energy Convers. Manage. , vol. 79, pp. 281-288, Mar. 2014. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890413007796 [8] B. Boukhezzar and H. Siguerdidjane, "Nonlinear control with wind estimation of a DFIG variable speed wind turbine for power capture optimization, " Energy Convers. Manage. , vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 885-892, Apr. 2009. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890409000065 [9] X. B. Kong and X. J. Liu, "Nonlinear model predictive control for DFIG-based wind power generation, " Acta Automat. Sin. , vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 636-643, May 2013. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201305023.htm [10] Z. Y. Chen, M. H. Yin, C. X. Cai, B. Y. Zhang, and Y. Zou, "An accelerated optimal torque control of wind turbines for maximum power point tracking, " Acta Automat. Sin. , vol. 41, no. 12, pp. 2047-2057, Dec. 2015. http://www.aas.net.cn/EN/Y2015/V41/I12/2047 [11] B. Beltran, T. Ahmed-Ali, and M. El Hachemi Benbouzid, "Sliding mode power control of variable-speed wind energy conversion systems, " IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. , vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 551-558, Jun. 2008. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4270775/ [12] G. Bartolini, A. Ferrara, and E. Usai, "Chattering avoidance by second-order sliding mode control, " IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 241-246, Feb. 1998. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=661074 [13] F. Valenciaga and C. A. Evangelista, "2-Sliding active and reactive power control of a wind energy conversion system, " IET Control Theory Appl. , vol. 4, no. 11, pp. 2479-2490, Nov. 2010. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=5645800 [14] B Beltran, M El Hachemi Benbouzid, and T Ahmed-Ali, "Second-order sliding mode control of a doubly fed induction generator driven wind turbine, " IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. , vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 261-269, Jun. 2012. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6130597/ [15] C. Evangelista, F. Valenciaga, and P. Puleston, "Active and reactive power control for wind turbine based on a MIMO 2-sliding mode algorithm with variable gains, " IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. , vol. 28, no. 3, 682-689, Sep. 2013. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6582571/ [16] J. A. Moreno and M. Osorio, "Strict Lyapunov functions for the super-twisting algorithm, " IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 1035-1040, Apr. 2012. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6144710 [17] J. Zaragoza, J. Pou, A. Arias, C. Spiteri, E. Robles, and S. Ceballos, "Study and experimental verification of control tuning strategies in a variable speed wind energy conversion system, " Renew. Energy, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 1421-1430, May 2011. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960148110005045 [18] W. B. Gao, Variable Structure Control Theory. Beijing, China:China Science and Technology Press, 1990. [19] A. Levant, "Sliding order and sliding accuracy in sliding mode control, " Int. J. Control, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 1247-1263, Dec. 1993. -




 下载:
下载: